Deck 10: Monoprotic Acid-Base Equilibria
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Monoprotic Acid-Base Equilibria
1
Which of the following is NOT true for weak acids and weak bases?
A)Kw = Ka.Kb
B)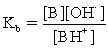
C)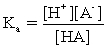
D)pKa = −log Ka
E)pKb = −log Kb
A)Kw = Ka.Kb
B)
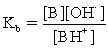
C)
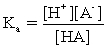
D)pKa = −log Ka
E)pKb = −log Kb
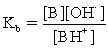
2
Calculate the percentage dissociation for a 0.010 M hypochlorous acid solution.The Ka for hypochlorous acid is 3.0 x 10−8.
A)0)35%
B)0)30%
C)0)17%
D)0)99%
E)0)65%
A)0)35%
B)0)30%
C)0)17%
D)0)99%
E)0)65%
0)17%
3
For a 0.0005 M HBr solution,the dissociation of water produces____________________ H3O+ and____________________ OH−.
A)1)00E-07 M;2.00E-11 M
B)5)00E-04 M;5.00E-04 M
C)2)00E-11 M;2.00E-11 M
D)1)00E-07 M;1.00E-07 M
E)5)00E-04 M;2.00E-11 M
A)1)00E-07 M;2.00E-11 M
B)5)00E-04 M;5.00E-04 M
C)2)00E-11 M;2.00E-11 M
D)1)00E-07 M;1.00E-07 M
E)5)00E-04 M;2.00E-11 M
2)00E-11 M;2.00E-11 M
4
Which is NOT a property of buffers?
A)Buffers resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added or when dilution occurs.
B)Buffers are a mixture of weak acid and conjugate base.
C)The pH of a buffer is independent of ionic strength.
D)The pH of a buffer is dependent on temperature.
E)Buffers are a mixture of weak bases and conjugate acid.
A)Buffers resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added or when dilution occurs.
B)Buffers are a mixture of weak acid and conjugate base.
C)The pH of a buffer is independent of ionic strength.
D)The pH of a buffer is dependent on temperature.
E)Buffers are a mixture of weak bases and conjugate acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The rule of thumb for neglecting the change in the formal concentration of a weak acid or a weak base,x,during an equilibrium problem is valid:
A)if the change in x is greater than 1% of the formal concentration.
B)if the change in x is less than 0.1% of the formal concentration.
C)if the change in x is equal to 0.1% of the formal concentration.
D)if the change in x is less than 10% of the formal concentration.
E)if the change in x is less than 1% of the formal concentration.
A)if the change in x is greater than 1% of the formal concentration.
B)if the change in x is less than 0.1% of the formal concentration.
C)if the change in x is equal to 0.1% of the formal concentration.
D)if the change in x is less than 10% of the formal concentration.
E)if the change in x is less than 1% of the formal concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is NOT true for weak acids?
A)Weak acids are partially ionized.
B)The conjugate base is A− and its strength is weak.
C)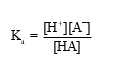
D)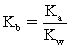
For the conjugate base.
E)HA + H2O ⇋ A− + H3O+
A)Weak acids are partially ionized.
B)The conjugate base is A− and its strength is weak.
C)
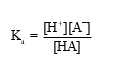
D)
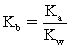
For the conjugate base.
E)HA + H2O ⇋ A− + H3O+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Calculate the pH for a 4.3 × 10−8 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of = 0.1. H+ = 0.83, OH− = 0.76 and Cl− = 0.755.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
There are seven common strong acids.Which of the following statements is NOT true for strong acids?
A)Dilute solutions are completely ionized.
B)HNO2 is a strong acid.
C)For strong acid solutions with a concentration between 10−6 and 10−8 M,the pH is determined using systematic equilibrium.
D)For strong acid solutions with concentrations 10−6 M,the pH is calculated from the concentration of the strong acid.
E)For strong acid solutions with concentrations 10−8 M,the pH is always 7.
A)Dilute solutions are completely ionized.
B)HNO2 is a strong acid.
C)For strong acid solutions with a concentration between 10−6 and 10−8 M,the pH is determined using systematic equilibrium.
D)For strong acid solutions with concentrations 10−6 M,the pH is calculated from the concentration of the strong acid.
E)For strong acid solutions with concentrations 10−8 M,the pH is always 7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The pH of a weak-base solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pOH?
A)![<strong>The pH of a weak-base solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pOH?</strong> A) B)F = [BH<sup>+</sup>] + [B] C)[OH<sup>−</sup>] = [BH<sup>+</sup>] + [H<sup>+</sup>] D) E)K<sub>w</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4000/11ea6952_25a6_4630_a4b1_a3392b2c35c8_TB4000_11.jpg)
B)F = [BH+] + [B]
C)[OH−] = [BH+] + [H+]
D)![<strong>The pH of a weak-base solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pOH?</strong> A) B)F = [BH<sup>+</sup>] + [B] C)[OH<sup>−</sup>] = [BH<sup>+</sup>] + [H<sup>+</sup>] D) E)K<sub>w</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4000/11ea6952_25a6_6d41_a4b1_ad3d3cc97096_TB4000_11.jpg)
E)Kw = [H+][OH−]
A)
![<strong>The pH of a weak-base solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pOH?</strong> A) B)F = [BH<sup>+</sup>] + [B] C)[OH<sup>−</sup>] = [BH<sup>+</sup>] + [H<sup>+</sup>] D) E)K<sub>w</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4000/11ea6952_25a6_4630_a4b1_a3392b2c35c8_TB4000_11.jpg)
B)F = [BH+] + [B]
C)[OH−] = [BH+] + [H+]
D)
![<strong>The pH of a weak-base solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pOH?</strong> A) B)F = [BH<sup>+</sup>] + [B] C)[OH<sup>−</sup>] = [BH<sup>+</sup>] + [H<sup>+</sup>] D) E)K<sub>w</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4000/11ea6952_25a6_6d41_a4b1_ad3d3cc97096_TB4000_11.jpg)
E)Kw = [H+][OH−]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A student calculates the pOH for a 0.01 M triethanolamine solution to be 4.12.To simplify the math she decided to neglect the change in the formal concentration.Was she justified in her decision? Kb = 5.78 × 10−7
A)She was justified,as the change in ×,7.59 × 10−5,is less than 1% of the formal concentration.
B)She was not justified,as the change in ×,9.92 × 10−3,is greater than 1% of the formal concentration.
C)She was justified,as the change in ×,1.32 × 10−10,is less than 1% of the formal concentration.
D)She was not justified,as the change in ×,1.00 × 10−2,is greater than 1% of the formal concentration.
E)She was justified,as the change in ×,5.78 × 10−5,is less than 1% of the formal concentration.
A)She was justified,as the change in ×,7.59 × 10−5,is less than 1% of the formal concentration.
B)She was not justified,as the change in ×,9.92 × 10−3,is greater than 1% of the formal concentration.
C)She was justified,as the change in ×,1.32 × 10−10,is less than 1% of the formal concentration.
D)She was not justified,as the change in ×,1.00 × 10−2,is greater than 1% of the formal concentration.
E)She was justified,as the change in ×,5.78 × 10−5,is less than 1% of the formal concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A buffer is prepared by mixing 200.0 mL of 0.1500 M NaOH with 200.0 mL of 0.200 M CH3CO2H in a 1-L volumetric flask and then diluted to volume with distilled deionized water.Calculate the pH of the buffer.Ka = 1.75 × 10−5
A)5)23
B)9)72
C)7)00
D)8)77
E)4)28
A)5)23
B)9)72
C)7)00
D)8)77
E)4)28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The pH of a weak-acid solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pH?
A)![<strong>The pH of a weak-acid solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pH?</strong> A) B)F = [HA] + [A<sup>−</sup>] C)[H<sup>+</sup>] = [A<sup>−</sup>] + [OH<sup>−</sup>] D) E)K<sub>w</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4000/11ea6952_25a6_1f1e_a4b1_cd85fec99523_TB4000_11.jpg)
B)F = [HA] + [A−]
C)[H+] = [A−] + [OH−]
D)![<strong>The pH of a weak-acid solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pH?</strong> A) B)F = [HA] + [A<sup>−</sup>] C)[H<sup>+</sup>] = [A<sup>−</sup>] + [OH<sup>−</sup>] D) E)K<sub>w</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4000/11ea6952_25a6_462f_a4b1_d7a16b738684_TB4000_11.jpg)
E)Kw = [H+][OH−]
A)
![<strong>The pH of a weak-acid solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pH?</strong> A) B)F = [HA] + [A<sup>−</sup>] C)[H<sup>+</sup>] = [A<sup>−</sup>] + [OH<sup>−</sup>] D) E)K<sub>w</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4000/11ea6952_25a6_1f1e_a4b1_cd85fec99523_TB4000_11.jpg)
B)F = [HA] + [A−]
C)[H+] = [A−] + [OH−]
D)
![<strong>The pH of a weak-acid solution is calculated using systematic treatment.Which of the following is NOT an equation needed to solve for pH?</strong> A) B)F = [HA] + [A<sup>−</sup>] C)[H<sup>+</sup>] = [A<sup>−</sup>] + [OH<sup>−</sup>] D) E)K<sub>w</sub> = [H<sup>+</sup>][OH<sup>−</sup>]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4000/11ea6952_25a6_462f_a4b1_d7a16b738684_TB4000_11.jpg)
E)Kw = [H+][OH−]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 0.01 M solution of a weak base has a percent association of 18.32%.Calculate the Kb for the weak base.
A)1)83 × 10−3
B)2)43 × 10 −11
C)5)46 × 10−12
D)4)11 × 10−4
E)1)22 × 10−12
A)1)83 × 10−3
B)2)43 × 10 −11
C)5)46 × 10−12
D)4)11 × 10−4
E)1)22 × 10−12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Calculate the pH of 0.01 M HCN ( = 0.10)using activity coefficients,neglecting activity coefficients,and the percent difference between the two.Ka = 6.2 x 10−10 for HCN. H+ = 0.83, OH− = 0.76 and CN− = 0.755.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Calculate the percent dissociation for a 0.01 M HCN solution,neglecting activity coefficients.Ka = 6.2 × 10−10 for HCN.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
There are two types of metal hydroxides,soluble metal hydroxides and insoluble hydroxides,both of which are strong bases.Which of the following statements is NOT true for strong bases?
A)Dilute solutions are completely dissociated.
B)Fe(OH)2 is a strong soluble base.
C)For strong base solutions with a concentration between 10−6 and 10−8 M,the pOH is determined using systematic equilibrium.
D)For strong base solutions with concentrations 10−6 M,the pOH is calculated from the concentration of the strong base.
E)For strong base solutions with concentrations 10−8 M,the pOH is always 7.
A)Dilute solutions are completely dissociated.
B)Fe(OH)2 is a strong soluble base.
C)For strong base solutions with a concentration between 10−6 and 10−8 M,the pOH is determined using systematic equilibrium.
D)For strong base solutions with concentrations 10−6 M,the pOH is calculated from the concentration of the strong base.
E)For strong base solutions with concentrations 10−8 M,the pOH is always 7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The buffer needed for a capillary electrophoresis experiment must have a pH of 10.0.Which weak acid is the best choice for the buffer? Assume = 0.
A)ammonium chloride____________________ pKa = 9.24
B)disodium phosphate____________________ pKa = 12.38
C)3-(Cyclohexylamino)propanesulfonic acid pKa = 10.40
D)sodium dihydrogen borate____________________ pKa = 12.74
E)cyclohexylaminoethanesulfonic acid____________________pKa = 9.39
A)ammonium chloride____________________ pKa = 9.24
B)disodium phosphate____________________ pKa = 12.38
C)3-(Cyclohexylamino)propanesulfonic acid pKa = 10.40
D)sodium dihydrogen borate____________________ pKa = 12.74
E)cyclohexylaminoethanesulfonic acid____________________pKa = 9.39

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Calculate the pH of a 0.2 M ethylamine solution.Kb = 5.0 × 10−4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
One liter of a pH 5.00 propionic acid buffer with a total concentration of 50 mM must be prepared.Calculate the mmols propionic acid and sodium propionate needed to prepare the buffer.Ka = 1.34 x 10-5 for propionic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is NOT true for weak bases?
A)Weak bases partially hydrolyze water.
B)The conjugate acid is BH+ and its strength is strong.
C)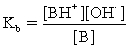
D)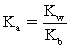
For the conjugate acid.
E)B + H2O ⇋ BH+ + OH−
A)Weak bases partially hydrolyze water.
B)The conjugate acid is BH+ and its strength is strong.
C)
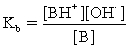
D)
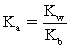
For the conjugate acid.
E)B + H2O ⇋ BH+ + OH−

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



