Deck 14: Firms in Competitive Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/381
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Firms in Competitive Markets
1
For a firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry,marginal revenue and average revenue are equal.
True
2
In a competitive market,firms are unable to differentiate their product from that of other producers.
True
3
Because there are many buyers and sellers in a perfectly competitive market,no one seller can influence the market price.
True
4
If a firm notices that its average revenue equals the current market price,that firm must be participating in a competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A dairy farmer must be able to calculate sunk costs in order to determine how much revenue the farm receives for the typical gallon of milk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A firm's incentive to compare marginal revenue and marginal cost is an application of the principle that rational people think at the margin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A firm is currently producing 100 units of output per day.The manager reports to the owner that producing the 100th unit costs the firm $5.The firm can sell the 100th unit for $5.The firm should continue to produce 100 units in order to maximize its profits (or minimize its losses).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When an individual firm in a competitive market increases its production,it is likely that the market price will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Firms operating in perfectly competitive markets produce an output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Because nothing can be done about sunk costs,they are irrelevant to decisions about business strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A firm is currently producing 100 units of output per day.The manager reports to the owner that producing the 100th unit costs the firm $5.The firm can sell the 100th unit for $4.75.The firm should continue to produce 100 units in order to maximize its profits (or minimize its losses).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market will increase production when average revenue exceeds marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A miniature golf course is a good example of where fixed costs become relevant to the decision of when to open and when to close for the season.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A popular resort restaurant will maximize profits if it chooses to stay open during the less-crowded "off season" when its total revenues exceed its variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Firms operating in perfectly competitive markets try to maximize profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Firms in a competitive market are said to be price takers because there are many sellers in the market and the goods offered by the firms are very similar if not identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For a firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry,total revenue,marginal revenue,and average revenue are all equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In competitive markets,firms that raise their prices are typically rewarded with larger profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
By comparing the marginal revenue and marginal cost from each unit produced,a firm in a competitive market can determine the profit-maximizing level of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A firm is currently producing 100 units of output per day.The manager reports to the owner that producing the 100th unit costs the firm $5.The firm can sell the unit for $6.The firm should produce more than 100 units in order to maximize its profits (or minimize its losses).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When a resource used in the production of a good sold in a competitive market is available in only limited quantities,the long-run supply curve is likely to be upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose a firm is considering producing zero units of output.We call this shutting down in the short run and exiting an industry in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The supply curve of a firm in a competitive market is the average variable cost curve above the minimum of marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market will earn zero accounting profits in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market experiences rising prices,it will respond with an increase in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In making a short-run profit-maximizing production decision,the firm must consider both fixed and variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the short run,a firm should exit the industry if its marginal cost exceeds its marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry will continue to operate in the short run but earn losses if the market price is less than that firm's average total cost but greater than the firm's average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry will shut down in the short run but earn losses if the market price is less than that firm's average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the long run,when price is less than average total cost for all possible levels of production,a firm in a competitive market will choose to exit (or not enter)the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry will continue to operate in the short run but earn losses if the market price is less than that firm's average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry will continue to operate if it earns zero economic profits because it is likely to be earning positive accounting profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
All firms maximize profits by producing an output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost;for firms operating in perfectly competitive industries,maximizing profits also means producing an output level where price equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry will shut down in the short run if its economic profits fall to zero because it is likely to be earning negative accounting profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the long run,a firm should exit the industry if its total costs exceed its total revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the long run,when price is greater than average total cost,some firms in a competitive market will choose to enter the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose a firm is considering producing zero units of output.We call this exiting an industry in the short run and shutting down in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A firm will shut down in the short run if revenue is not sufficient to cover its variable costs of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A firm will shut down in the short run if revenue is not sufficient to cover all of its fixed costs of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The marginal firm in a competitive market will earn zero economic profit in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The short-run supply curve in a competitive market must be more elastic than the long-run supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive market may earn positive,negative,or zero economic profit in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive market earns zero economic profit in the long run but remains in business because the firm's revenues cover the business owners' opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The long-run equilibrium in a competitive market characterized by firms with identical costs is generally characterized by firms operating at efficient scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a long-run equilibrium where firms have identical costs,it is possible that some firms in a competitive market are making a positive economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Describe the difference between average revenue and marginal revenue.Why are both of these revenue measures important to a profit-maximizing firm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
At its current level of production a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market receives $12.50 for each unit it produces and faces an average total cost of $10.At the market price of $12.50 per unit,the firm's marginal cost curve crosses the marginal revenue curve at an output level of 1,000 units.What is the firm's current profit? What is likely to occur in this market and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
List and describe the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Explain how a firm in a competitive market identifies the profit-maximizing level of production.When should the firm raise production,and when should the firm lower production?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When economic profits are zero in equilibrium,the firm's revenue must be sufficient to cover all opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Give two reasons why the long-run industry supply curve may slope upward.Use an example to demonstrate your reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A competitive market will typically experience entry and exit until accounting profits are zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Why would a firm in a perfectly competitive market always choose to set its price equal to the current market price? If a firm set its price below the current market price,what effect would this have on the market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
News reports from the western United States occasionally report incidents of cattle ranchers slaughtering a large number of newborn calves and burying them in mass graves rather than transporting them to markets.Assuming that this is rational behavior by profit-maximizing "firms," explain what economic factors may influence such behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use a graph to demonstrate the circumstances that would prevail in a competitive market where firms are earning economic profits.Can this scenario be maintained in the long run? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use a graph to demonstrate the circumstances that would prevail in a perfectly competitive market where firms are experiencing economic losses.Identify costs,revenue,and the economic losses on your graph.Using your graph,determine whether an individual firm will shut down in the short run,or choose to remain in the market.Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the long run,a competitive market with 1,000 identical firms will experience an equilibrium price equal to the minimum of each firm's average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The long-run supply curve in a competitive market is more elastic than the short-run supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If identical firms that remain in a competitive market over the long run make zero economic profit,why do these firms choose to remain in the market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A firm operating in a perfectly competitive market may earn positive,negative,or zero economic profit in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose that firms in each of the two markets listed below were to increase their prices by 20 percent.Which pair represents the example where customers would decrease their quantity purchased dramatically in one market and only slightly in the other market due to differences in market structure?
A) corn and soybeans
B) gasoline and restaurants
C) water and cable television
D) spiral notebooks and college textbooks
A) corn and soybeans
B) gasoline and restaurants
C) water and cable television
D) spiral notebooks and college textbooks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When firms are said to be price takers,it implies that if a firm raises its price,
A) buyers will go elsewhere.
B) buyers will pay the higher price in the short run.
C) competitors will also raise their prices.
D) firms in the industry will exercise market power.
A) buyers will go elsewhere.
B) buyers will pay the higher price in the short run.
C) competitors will also raise their prices.
D) firms in the industry will exercise market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
For any competitive market,the supply curve is closely related to the
A) preferences of consumers who purchase products in that market.
B) income tax rates of consumers in that market.
C) firms' costs of production in that market.
D) interest rates on government bonds.
A) preferences of consumers who purchase products in that market.
B) income tax rates of consumers in that market.
C) firms' costs of production in that market.
D) interest rates on government bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When buyers in a competitive market take the selling price as given,they are said to be
A) market entrants.
B) monopolists.
C) free riders.
D) price takers.
A) market entrants.
B) monopolists.
C) free riders.
D) price takers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When a firm has little ability to influence market prices it is said to be in a
A) competitive market.
B) strategic market.
C) thin market.
D) power market.
A) competitive market.
B) strategic market.
C) thin market.
D) power market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A) Firms are price takers.
B) Firms can freely enter the market.
C) Many firms have market power.
D) Goods offered for sale are largely the same.
A) Firms are price takers.
B) Firms can freely enter the market.
C) Many firms have market power.
D) Goods offered for sale are largely the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following industries is most likely to exhibit the characteristic of free entry?
A) nuclear power
B) municipal water and sewer
C) dairy farming
D) airport security
A) nuclear power
B) municipal water and sewer
C) dairy farming
D) airport security

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Who is a price taker in a competitive market?
A) buyers only
B) sellers only
C) both buyers and sellers
D) neither buyers nor sellers
A) buyers only
B) sellers only
C) both buyers and sellers
D) neither buyers nor sellers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A firm has market power if it can
A) maximize profits.
B) minimize costs.
C) influence the market price of the good it sells.
D) hire as many workers as it needs at the prevailing wage rate.
A) maximize profits.
B) minimize costs.
C) influence the market price of the good it sells.
D) hire as many workers as it needs at the prevailing wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Because the goods offered for sale in a competitive market are largely the same,
A) there will be few sellers in the market.
B) there will be few buyers in the market.
C) only a few buyers will have market power.
D) sellers will have little reason to charge less than the going market price.
A) there will be few sellers in the market.
B) there will be few buyers in the market.
C) only a few buyers will have market power.
D) sellers will have little reason to charge less than the going market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Competitive markets are characterized by
A) a small number of buyers and sellers.
B) unique products.
C) the interdependence of firms.
D) free entry and exit by firms.
A) a small number of buyers and sellers.
B) unique products.
C) the interdependence of firms.
D) free entry and exit by firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A market is competitive if
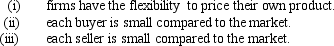
A) (i)and (ii)only
B) (i)and (iii)only
C) (ii)and (iii)only
D) (i),(ii),and (iii)
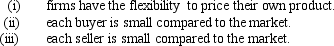
A) (i)and (ii)only
B) (i)and (iii)only
C) (ii)and (iii)only
D) (i),(ii),and (iii)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Free entry means that
A) the government pays any entry costs for individual firms.
B) no legal barriers prevent a firm from entering an industry.
C) a firm's marginal cost is zero.
D) a firm has no fixed costs in the short run.
A) the government pays any entry costs for individual firms.
B) no legal barriers prevent a firm from entering an industry.
C) a firm's marginal cost is zero.
D) a firm has no fixed costs in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In a competitive market,the actions of any single buyer or seller will
A) have a negligible impact on the market price.
B) have little effect on market equilibrium quantity but will affect market equilibrium price.
C) affect marginal revenue and average revenue but not price.
D) adversely affect the profitability of more than one firm in the market.
A) have a negligible impact on the market price.
B) have little effect on market equilibrium quantity but will affect market equilibrium price.
C) affect marginal revenue and average revenue but not price.
D) adversely affect the profitability of more than one firm in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a competitive market?
A) Buyers and sellers are price takers.
B) Each firm sells a virtually identical product.
C) Free entry is limited.
D) Each firm chooses an output level that maximizes profits.
A) Buyers and sellers are price takers.
B) Each firm sells a virtually identical product.
C) Free entry is limited.
D) Each firm chooses an output level that maximizes profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements best reflects a price-taking firm?
A) If the firm were to charge more than the going price,it would sell none of its goods.
B) The firm has an incentive to charge less than the market price to earn higher revenue.
C) The firm can sell only a limited amount of output at the market price before the market price will fall.
D) Price-taking firms maximize profits by charging a price above marginal cost.
A) If the firm were to charge more than the going price,it would sell none of its goods.
B) The firm has an incentive to charge less than the market price to earn higher revenue.
C) The firm can sell only a limited amount of output at the market price before the market price will fall.
D) Price-taking firms maximize profits by charging a price above marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A) Firms are price takers.
B) Firms have difficulty entering the market.
C) There are many sellers in the market.
D) Goods offered for sale are largely the same.
A) Firms are price takers.
B) Firms have difficulty entering the market.
C) There are many sellers in the market.
D) Goods offered for sale are largely the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A key characteristic of a competitive market is that
A) government antitrust laws regulate competition.
B) producers sell nearly identical products.
C) firms minimize total costs.
D) firms have price setting power.
A) government antitrust laws regulate competition.
B) producers sell nearly identical products.
C) firms minimize total costs.
D) firms have price setting power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The analysis of competitive firms sheds light on the decisions that lie behind the
A) demand curve.
B) supply curve.
C) way firms make pricing decisions in the not-for-profit sector of the economy.
D) way financial markets set interest rates.
A) demand curve.
B) supply curve.
C) way firms make pricing decisions in the not-for-profit sector of the economy.
D) way financial markets set interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In a perfectly competitive market,
A) no one seller can influence the price of the product.
B) price exceeds marginal revenue for each unit sold.
C) average revenue exceeds marginal revenue for each unit sold.
D) administrative barriers can make it difficult for firms to enter an industry.
A) no one seller can influence the price of the product.
B) price exceeds marginal revenue for each unit sold.
C) average revenue exceeds marginal revenue for each unit sold.
D) administrative barriers can make it difficult for firms to enter an industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 381 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



