Deck 20: Income Inequality and Poverty
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/312
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Income Inequality and Poverty
1
About half of black and Hispanic children in female-headed households live in poverty.
True
2
The top 5 percent of U.S.annual family income in 2005 was $184,500 or more.
True
3
The United States has more income inequality than Brazil and South Africa.
False
4
The poverty line is an absolute standard and is based on the cost of providing an adequate diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Although globalization has reduced income inequality,the number of people living in extreme poverty has remained unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The measured poverty rate may not reflect the true extent of economic deprivation because it does not include some forms of government assistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the United States in 2005,the bottom fifth of the income distribution had incomes below $19,250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The poverty rate is a measure of people unable to meet the government's poverty line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
One existing government program that works much like a negative income tax is the Earned Income Tax Credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Standard measurements of the degree of income inequality take both money income and in-kind transfers into account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
One existing government program that works much like a negative income tax is Medicaid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The poverty line is based on the percentage of people who cannot afford an adequate diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When the government enacts policies to make the distribution of income more equitable,it distorts incentives,alters behavior,and makes the allocation of resources less efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A U.S.family earning $80,000 would be in the top 20 percent of income distribution in 2005.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The elderly represent the largest demographic group in poverty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The poverty line is set by the government so that 10 percent of all families fall below that line and are thereby classified as "poor."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The invisible hand of the marketplace acts to allocate resources efficiently,but it does not necessarily ensure that resources are allocated fairly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Free trade and economic growth have reduced poverty worldwide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The United States has more income inequality than Japan,Germany,and Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
John Rawls,who developed the way of thinking called liberalism,argued that government policies should be aimed at maximizing the sum of utility of everyone in society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In 2005 the top fifth of income earners accounted for over 50% of all income received by United States' families.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The utilitarian justification for redistributing income is based on the assumption of diminishing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In 2005 the top 5 percent of income earners accounted for over 50% of all income received by United States' families.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When poor families in developing countries experience an increase in family income,their children supply fewer hours of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Fewer than three percent of families are poor for eight or more years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An income distribution may not give an accurate picture of families' standards of living because it does not include in-kind transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The economic life cycle describes how young people usually have higher savings rates than middle-aged people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Libertarians believe that the government should enforce individual rights to ensure that all people have the same opportunities to use their talents to achieve success.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Internet access is the most important factor explaining reductions in child labor in Vietnam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Many economists believe that a family bases its spending decisions on its permanent,or average,income rather than on transitory income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF)is an example of a negative income tax program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
About four out of five millionaires in the United States earned their money rather than inherited it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
According to libertarians,the government should redistribute income from rich individuals to poor individuals to achieve a more equal distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Utilitarians believe that the proper goal of the government is to maximize the sum of the utilities of everyone in society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Education is the most important factor explaining reductions in child labor in Vietnam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The poverty rate is an absolute level of income set by the federal government for each family size below which a family is deemed to be in poverty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A goal of libertarians is to provide citizens with equal opportunities rather than to ensure equal outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a government could successfully achieve the maximin criterion,each member of society would have an equal income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
From 1935 to 2005 the share of total income earned by the bottom fifth of income earners rose and then fell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Since 1959 the United States' income distribution has become more equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Explain the concept of diminishing marginal utility,and describe the role that it plays in the utilitarian argument for the redistribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Assume that the government proposes a negative income tax that calculates taxes owed by the formula,Taxes Owed = (a *Income)-
a.What is the value for "a"?
b.What is the value for "b"?
b.A family with an income of $40,000 pays $5,000 in taxes,and a family with an income of $12,000 receives an income subsidy of $2,000.
c.What is the tax liability of a family with an income of $50,000?
d.At what level of income will a family neither pay taxes,nor receive an income subsidy?
a.What is the value for "a"?
b.What is the value for "b"?
b.A family with an income of $40,000 pays $5,000 in taxes,and a family with an income of $12,000 receives an income subsidy of $2,000.
c.What is the tax liability of a family with an income of $50,000?
d.At what level of income will a family neither pay taxes,nor receive an income subsidy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The invisible hand of the marketplace acts to allocate resources
A) efficiently but does not necessarily ensure that resources are allocated fairly.
B) both fairly and efficiently.
C) fairly but does not necessarily ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
D) neither fairly nor efficiently.
A) efficiently but does not necessarily ensure that resources are allocated fairly.
B) both fairly and efficiently.
C) fairly but does not necessarily ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
D) neither fairly nor efficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A government's policy of redistributing income makes the income distribution
A) more equal,distorts incentives,alters behavior,and makes the allocation of resources more efficient.
B) more equal,distorts incentives,alters behavior,and makes the allocation of resources less efficient.
C) less equal,distorts incentives,alters behavior,and makes the allocation of resources more efficient.
D) less equal,distorts incentives,alters behavior,and makes the allocation of resources less efficient.
A) more equal,distorts incentives,alters behavior,and makes the allocation of resources more efficient.
B) more equal,distorts incentives,alters behavior,and makes the allocation of resources less efficient.
C) less equal,distorts incentives,alters behavior,and makes the allocation of resources more efficient.
D) less equal,distorts incentives,alters behavior,and makes the allocation of resources less efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is meant by a perfectly equal distribution of income? Use a graph to depict such a situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When the government redistributes income to achieve greater equality,it
A) distorts incentives.
B) improves efficiency.
C) focuses on middle income brackets.
D) relies on foreign aid to help balance the budget.
A) distorts incentives.
B) improves efficiency.
C) focuses on middle income brackets.
D) relies on foreign aid to help balance the budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Outline the possible work disincentives created by anti-poverty programs.Is there a way to solve this problem without causing other forms of inefficiency to arise? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Explain what is meant by "in-kind transfer" programs.Briefly outline the advantages and disadvantages of an in-kind transfer program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is most likely to occur when the government enacts policies to make the distribution of income more equal?
A) A more efficient allocation of resources.
B) A distortion of incentives.
C) Unchanged behavior.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) A more efficient allocation of resources.
B) A distortion of incentives.
C) Unchanged behavior.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Given the table shown,which country has a more equal income distribution? Explain your answer.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Assume that the government proposes a negative income tax that calculates taxes owed by the following formula, Taxes Owed = (1/3 * Income)- $10,000.
Compute the tax that would be owed given each level of income.
a.$120,000
b.$90,000
c.$60,000
d.$30,000
e.$0
Compute the tax that would be owed given each level of income.
a.$120,000
b.$90,000
c.$60,000
d.$30,000
e.$0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Assume you are a critic of welfare reforms that impose a time limit on the number of years a person is eligible for welfare benefits.What is the foundation of your critique?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the United States,labor earnings are what percent of total income?
A) 75 percent
B) 70 percent
C) 65 percent
D) 50 percent
A) 75 percent
B) 70 percent
C) 65 percent
D) 50 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The table below reflects the levels of total utility received from income for each of four members of a society.
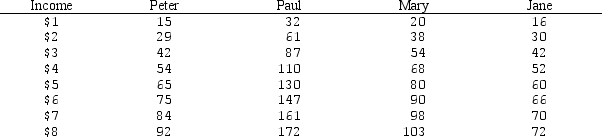
a.
Assume that the society has the following income distribution:
Peter $3
Paul $7
Mary $5
Jane $3
Is it possible for the government to increase total aggregate utility by redistributing income among members of society? Explain your answer.
b.
Assume that the government has $19 to allocate among the four members of society.(Assume that no one has any income to start with. )If the government is interested in distributing income in a way that maximizes aggregate total utility,how should it distribute the $19 of income?
c.
Does the table above describe a situation characterized by diminishing marginal utility? Explain your answer.

a.
Assume that the society has the following income distribution:
Peter $3
Paul $7
Mary $5
Jane $3
Is it possible for the government to increase total aggregate utility by redistributing income among members of society? Explain your answer.
b.
Assume that the government has $19 to allocate among the four members of society.(Assume that no one has any income to start with. )If the government is interested in distributing income in a way that maximizes aggregate total utility,how should it distribute the $19 of income?
c.
Does the table above describe a situation characterized by diminishing marginal utility? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Explain the relationship between labor earnings and the distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Explain what information is contained in the poverty rate statistic.Are there problems in using an absolute scale to measure poverty? If so,explain them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Compare and contrast the "life cycle" hypothesis and the "permanent income" hypothesis.What are their respective implications for inequality in the income distribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Briefly describe the three prominent schools of thought in political philosophy.Identify one of the most well-known philosophers in each school.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The marketplace allocates resources
A) fairly.
B) efficiently.
C) to those desiring them least.
D) both efficiently and equitably.
A) fairly.
B) efficiently.
C) to those desiring them least.
D) both efficiently and equitably.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Explain how a "leaky bucket" can be used to illustrate the utilitarian argument that governments should not attempt to completely equalize individual incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Governments enact policies to
A) make the distribution of income more efficient.
B) make the distribution of income more equal.
C) maximize the use of the welfare system.
D) minimize the use of in-kind transfers.
A) make the distribution of income more efficient.
B) make the distribution of income more equal.
C) maximize the use of the welfare system.
D) minimize the use of in-kind transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Based on data from 2005,the top fifth of all families received approximately what percent of all income in the United States?
A) 78 percent
B) 48 percent
C) 21 percent
D) 4 percent
A) 78 percent
B) 48 percent
C) 21 percent
D) 4 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Comparing the United States household income distribution to other countries is
A) easy,because data is available for all countries in the world.
B) easy,because some countries collect data on expenditures instead of incomes.
C) problematic,because international agreements require countries to standardize their income accounting procedures.
D) problematic,because countries collect data in different ways.
A) easy,because data is available for all countries in the world.
B) easy,because some countries collect data on expenditures instead of incomes.
C) problematic,because international agreements require countries to standardize their income accounting procedures.
D) problematic,because countries collect data in different ways.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In 2003,what percentage of U.S.families had income levels above $103,100?
A) 5 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 80 percent
D) 95 percent
A) 5 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 80 percent
D) 95 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the Ten Principles of Economics come into conflict with each other in this chapter?
A) A country's standard of living depends on its ability to produce goods & People face tradeoffs.
B) Prices rise when the government prints too much money & Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes.
C) Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes & People face tradeoffs.
D) People face tradeoffs & Prices rise when the government prints too much money .
A) A country's standard of living depends on its ability to produce goods & People face tradeoffs.
B) Prices rise when the government prints too much money & Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes.
C) Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes & People face tradeoffs.
D) People face tradeoffs & Prices rise when the government prints too much money .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In 2005,what percentage of U.S.families had income levels below $103,100?
A) 5 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 80 percent
D) 95 percent
A) 5 percent
B) 20 percent
C) 80 percent
D) 95 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Based on U.S.income data from 2005,the top fifth of all families received
A) the same share of income as the bottom fifth.
B) twice as much income as the bottom fifth.
C) approximately 5 times more income than the bottom fifth.
D) more than 10 times more income than the bottom fifth.
A) the same share of income as the bottom fifth.
B) twice as much income as the bottom fifth.
C) approximately 5 times more income than the bottom fifth.
D) more than 10 times more income than the bottom fifth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Government programs that take money from high-income people and give it to low-income people typically
A) improve economic efficiency by reducing poverty.
B) reduce economic efficiency because they distort incentives.
C) have no effect on economic efficiency because they both reduce poverty and distort incentives.
D) sometimes improve,sometimes reduce,and sometimes have no effect on economic efficiency.
A) improve economic efficiency by reducing poverty.
B) reduce economic efficiency because they distort incentives.
C) have no effect on economic efficiency because they both reduce poverty and distort incentives.
D) sometimes improve,sometimes reduce,and sometimes have no effect on economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When the government enacts policies to redistribute income,
A) the objective is to enhance efficiency and a side effect is that the allocation of resources becomes more equal.
B) the objective is to enhance efficiency and a side effect is that the allocation of resources becomes less equal.
C) the objective is to enhance equality and a side effect is that the allocation of resources becomes more efficient.
D) the objective is to enhance equality and a side effect is that the allocation of resources becomes less efficient.
A) the objective is to enhance efficiency and a side effect is that the allocation of resources becomes more equal.
B) the objective is to enhance efficiency and a side effect is that the allocation of resources becomes less equal.
C) the objective is to enhance equality and a side effect is that the allocation of resources becomes more efficient.
D) the objective is to enhance equality and a side effect is that the allocation of resources becomes less efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is not a question that economists try to answer when measuring the distribution of income?
A) How many people live in poverty?
B) How often and how large are people's raises?
C) How often do people move among income classes?
D) What problems arise in measuring the amount of inequality?
A) How many people live in poverty?
B) How often and how large are people's raises?
C) How often do people move among income classes?
D) What problems arise in measuring the amount of inequality?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the U.S.economy,labor earnings make up about
A) one-half of total income.
B) two-thirds of total income.
C) three-fourths of total income.
D) nine-tenths of total income.
A) one-half of total income.
B) two-thirds of total income.
C) three-fourths of total income.
D) nine-tenths of total income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is correct?
A) Governments can never improve market outcomes.
B) Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes.
C) Governments can always improve market outcomes.
D) Government can never make the income distribution more equal.
A) Governments can never improve market outcomes.
B) Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes.
C) Governments can always improve market outcomes.
D) Government can never make the income distribution more equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Based on U.S.income data from 2005,the bottom fifth of all families received approximately what percent of all income?
A) 48 percent
B) 21 percent
C) 10 percent
D) 4 percent
A) 48 percent
B) 21 percent
C) 10 percent
D) 4 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is not correct?
A) Poverty is long-term problem for relatively few families.
B) Measurements of income inequality usually do not include in-kind transfers.
C) Measurements of income inequality use lifetime incomes rather than annual incomes.
D) Measurements of income inequality would be more meaningful if they reflected permanent rather than current income.
A) Poverty is long-term problem for relatively few families.
B) Measurements of income inequality usually do not include in-kind transfers.
C) Measurements of income inequality use lifetime incomes rather than annual incomes.
D) Measurements of income inequality would be more meaningful if they reflected permanent rather than current income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following represents a problem in measuring inequality?
A) Measurements of income distributions typically include in-kind transfers,which distort the measure of inequality.
B) A normal life-cycle pattern causes inequality in the income distribution but may not reflect inequality in living standards.
C) Transitory income is a better measure of inequality than permanent income.
D) Both a and b are correct.
A) Measurements of income distributions typically include in-kind transfers,which distort the measure of inequality.
B) A normal life-cycle pattern causes inequality in the income distribution but may not reflect inequality in living standards.
C) Transitory income is a better measure of inequality than permanent income.
D) Both a and b are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
U.S.income data over the last seventy years suggests that the distribution of income
A) has gradually become more equal over the entire time period.
B) has gradually become less equal over the entire time period.
C) gradually became less equal until about 1970,then became more equal from 1970 to 2005.
D) gradually became more equal until about 1970,then became less equal from 1970 to 2005.
A) has gradually become more equal over the entire time period.
B) has gradually become less equal over the entire time period.
C) gradually became less equal until about 1970,then became more equal from 1970 to 2005.
D) gradually became more equal until about 1970,then became less equal from 1970 to 2005.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Economists study poverty and income inequality in order to answer which of the following questions?
A) What are people's wages?
B) How does labor-force experience affect wages?
C) How much inequality is there in society?
D) How do people adjust their behavior due to taxation?
A) What are people's wages?
B) How does labor-force experience affect wages?
C) How much inequality is there in society?
D) How do people adjust their behavior due to taxation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the Ten Principles of Economics do governments run into when they redistribute income to achieve greater equality?
A) Trade can make everyone better off.
B) The cost of something is what you give up to get it.
C) People face trade-offs.
D) Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity.
A) Trade can make everyone better off.
B) The cost of something is what you give up to get it.
C) People face trade-offs.
D) Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A family's ability to buy goods and services depends largely on its
A) permanent income,which is its normal,or average,income.
B) permanent income,which is the lowest annual income the family has received over a 10-year period.
C) transitory income,which is the measure of income used by the government to analyze the distribution of income and the poverty rate.
D) transitory income,which is its money income plus any in-kind transfers it receives.
A) permanent income,which is its normal,or average,income.
B) permanent income,which is the lowest annual income the family has received over a 10-year period.
C) transitory income,which is the measure of income used by the government to analyze the distribution of income and the poverty rate.
D) transitory income,which is its money income plus any in-kind transfers it receives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The income distribution in the United States shows that the income share of the top fifth of all families is
A) over 50 percent.
B) around 25 percent.
C) more than 10 times the income of the bottom fifth.
D) not much different from the income of the top 5 percent.
A) over 50 percent.
B) around 25 percent.
C) more than 10 times the income of the bottom fifth.
D) not much different from the income of the top 5 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



