Deck 30: Money Growth and Inflation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/312
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: Money Growth and Inflation
1
When the value of money is on the vertical axis,an increase in the price level shifts money demand to the right.
False
2
Hyperinflations are associated with governments printing money to finance expenditures.
True
3
As the price level falls,the value of money falls.
False
4
According to the Fisher effect,if inflation rises then the nominal interest rate rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The quantity equation is M x V = P x Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A rising price level eliminates an excess supply of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the quantity of money supplied is greater than the quantity demanded,then prices should fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The United States has never had deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
For a given level of money and real GDP,an increase in velocity would lead to an increase in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
U.S.prices rose at an average annual rate of about 4 percent over the last 70 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The quantity theory of money can explain hyperinflations but not moderate inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The money supply curve shifts to the left when the Fed buys government bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The inflation rate is measured as the percentage change in a price index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The price level is determined by the supply of,and demand for,money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the Fed increases the money supply,the equilibrium value of money decreases and the equilibrium price level increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An increase in money demand would create a surplus of money at the original value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If P represents the price of goods and services measured in money,then 1/P is the value of money measured in terms of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When the value of money is on the vertical axis,the money supply curve slopes upward because an increase in the value of money induces banks to create more money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the 1990s,U.S.prices rose at about the same rate as in the 1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Dollar prices and relative prices are both nominal variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The quantity theory of money implies that if output and velocity are constant,then a 50 percent increase in the money supply would lead to less than a 50 percent increase in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The classical dichotomy is useful for analyzing the economy because in the long run nominal variables are heavily influenced by developments in the monetary system,and real variables are not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the long run,an increase in the growth rate of the money supply leads to an increase in the real interest rate,but no change in the nominal interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Shoeleather costs and menu costs are both costs of anticipated inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If inflation is higher than expected,then borrowers make nominal interest payments that are less than they expected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose the nominal interest rate is 10 percent;the tax rate on interest income is 28 percent,and the inflation rate is 6 percent.Then the after-tax real interest rate is -3.2 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Inflation necessarily distorts saving when either real interest income or nominal interest income is taxed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the Fed were to unexpectedly increase the money supply,creditors would gain at the expense of debtors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Inflation is costly only if it is unanticipated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Explain the adjustment process in the money market that creates a change in the price level when the money supply increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For a given real interest rate,an increase in the inflation rate reduces the after-tax real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The source of all four classic hyperinflations was high rates of money growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose the nominal interest rate is 5 percent;the tax rate on interest income is 30 percent,and the after-tax real interest rate is 0.8 percent.Then the inflation rate is 2.7 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Even though monetary policy is neutral in the short run,it may have profound real effects in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The irrelevance of monetary changes for real variables is called monetary neutrality.Most economists accept monetary neutrality as a good description of the economy in the long run,but not the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A rising value of money eliminates an excess supply of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Inflation induces people to spend more resources maintaining lower money holdings.The costs of doing this are called shoeleather costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Inflation distorts savings when real interest income,rather than nominal interest income,is taxed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Nominal GDP measures output of final goods and services in physical terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Why did farmers in the late 1800s dislike deflation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Explain how inflation affects savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Over the last 70 years,the average annual U.S.inflation rate was about
A) 2 percent,implying that prices have increased 10-fold.
B) 4 percent,implying that prices have increased 10-fold.
C) 2 percent,implying that prices have increased 16-fold.
D) 4 percent,implying that prices increased about 16-fold.
A) 2 percent,implying that prices have increased 10-fold.
B) 4 percent,implying that prices have increased 10-fold.
C) 2 percent,implying that prices have increased 16-fold.
D) 4 percent,implying that prices increased about 16-fold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What assumptions are necessary to argue that the quantity equation implies that increases in the money supply lead to proportional changes in the price level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In recent years Venezuela and Russia have had much higher nominal interest rates than the United States while Japan has had lower nominal interest rates.What would you predict is true about money growth in these other countries? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Define each of the symbols and explain the meaning of M 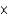
V = P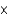
Y.
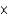
V = P
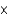
Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to the classical dichotomy,what changes nominal variables? What changes real variables?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Using separate graphs,demonstrate what happens to the money supply,money demand,the value of money,and the price level if:
a.
the Fed increases the money supply.
b.
people decide to demand less money at each value of money.
a.
the Fed increases the money supply.
b.
people decide to demand less money at each value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Wages and prices are many times higher today than they were 30 years ago,yet people do not work a lot more hours or buy fewer goods.How can this be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
List and define any two of the costs of high inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Inflation can be measured by the
A) change in the consumer price index.
B) percentage change in the consumer price index.
C) percentage change in the price of a specific commodity.
D) change in the price of a specific commodity.
A) change in the consumer price index.
B) percentage change in the consumer price index.
C) percentage change in the price of a specific commodity.
D) change in the price of a specific commodity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The U.S.Treasury Department began issuing inflation-indexed bonds in early 1997.Since these assets are virtually risk free,both in terms of default risk and inflation risk,will they quickly replace all other kinds of assets that still entail risk of one kind or another,such as ordinary government bonds or corporate bonds? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The U.S.Treasury Department issues inflation-indexed bonds.What are inflation-indexed bonds and why are they important?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose the Fed sells government bonds.Use a graph of the money market to show what this does to the value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the inflation tax,and how might it explain the creation of inflation by a central bank?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose that velocity and output are constant and that the quantity theory and the Fisher effect both hold.What happens to inflation,real interest rates,and nominal interest rates when the money supply growth rate increases from 5 percent to 10 percent?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Economists agree that increases in the money-supply growth rate increase inflation and that inflation is undesirable.So why have there been hyperinflations and how have they been ended?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is not correct?
A) The inflation rate is measured as the percentage change in a price index.
B) For the last 40 or so years,U.S.inflation hasn't shown much variation from its average rate of about 2 percent.
C) During the 19th century there were long periods of falling prices.
D) Some economists argue that the costs of moderate inflation are not nearly as large as the general public believes.
A) The inflation rate is measured as the percentage change in a price index.
B) For the last 40 or so years,U.S.inflation hasn't shown much variation from its average rate of about 2 percent.
C) During the 19th century there were long periods of falling prices.
D) Some economists argue that the costs of moderate inflation are not nearly as large as the general public believes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Inflation distorts relative prices.What does this mean and why does it impose a cost on society?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Over the past 70 years,prices in the U.S.have risen on average about
A) 2 percent per year.
B) 4 percent per year.
C) 6 percent per year.
D) 8 percent per year.
A) 2 percent per year.
B) 4 percent per year.
C) 6 percent per year.
D) 8 percent per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Over the past 70 years,the overall price level in the U.S.has experienced a(n)
A) 4-fold increase.
B) 8-fold increase.
C) 12-fold increase.
D) 16-fold increase.
A) 4-fold increase.
B) 8-fold increase.
C) 12-fold increase.
D) 16-fold increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the price level increased from 120 to 126,then what was the inflation rate?
A) 3 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 6 percent
D) None of the above is correct.
A) 3 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 6 percent
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In early 2008,the central bank of Zimbabwe announced the inflation rate in that country had reached
A) 60 percent.
B) 80 percent.
C) 220 percent.
D) 24,000 percent.
A) 60 percent.
B) 80 percent.
C) 220 percent.
D) 24,000 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Economists agree that
A) neither high inflation nor moderate inflation is very costly.
B) both high and moderate inflation are quite costly.
C) high inflation is costly,but they disagree about the costs of moderate inflation.
D) moderate inflation is as costly as high inflation.
A) neither high inflation nor moderate inflation is very costly.
B) both high and moderate inflation are quite costly.
C) high inflation is costly,but they disagree about the costs of moderate inflation.
D) moderate inflation is as costly as high inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is correct?
A) A period of hyperinflation is a period of extraordinarily high or extraordinarily low inflation.
B) A period of deflation is any period during which the inflation rate is decreasing.
C) During the 1990s,U.S.inflation averaged about 2 percent per year.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) A period of hyperinflation is a period of extraordinarily high or extraordinarily low inflation.
B) A period of deflation is any period during which the inflation rate is decreasing.
C) During the 1990s,U.S.inflation averaged about 2 percent per year.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If P denotes the price of goods and services measured in terms of money,then
A) 1/P represents the value of money measured in terms of goods and services.
B) P can be interpreted as the inflation rate.
C) the supply of money influences the value of P,but the demand for money does not.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) 1/P represents the value of money measured in terms of goods and services.
B) P can be interpreted as the inflation rate.
C) the supply of money influences the value of P,but the demand for money does not.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
There was hyperinflation during the
A) period 1880-1896 in the United States.
B) 1970s in the United States.
C) early part of the current century in Zimbabwe.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) period 1880-1896 in the United States.
B) 1970s in the United States.
C) early part of the current century in Zimbabwe.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When we assume that the supply of money is a variable that the central bank controls,we
A) must then assume as well that the demand for money is not influenced by the value of money.
B) must then assume as well that the price level is unrelated to the value of money.
C) are ignoring the fact that,in the real world,households are suppliers of money also.
D) are ignoring the complications introduced by the role of the banking system.
A) must then assume as well that the demand for money is not influenced by the value of money.
B) must then assume as well that the price level is unrelated to the value of money.
C) are ignoring the fact that,in the real world,households are suppliers of money also.
D) are ignoring the complications introduced by the role of the banking system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
With the value of money on the vertical axis,the money supply curve is
A) upward-sloping.
B) downward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.
A) upward-sloping.
B) downward-sloping.
C) horizontal.
D) vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Deflation
A) increases incomes and enhances the ability of debtors to pay off their debts.
B) increases incomes and reduces the ability of debtors to pay off their debts.
C) decreases incomes and enhances the ability of debtors to pay off their debts.
D) decreases incomes and reduces the ability of debtors to pay off their debts.
A) increases incomes and enhances the ability of debtors to pay off their debts.
B) increases incomes and reduces the ability of debtors to pay off their debts.
C) decreases incomes and enhances the ability of debtors to pay off their debts.
D) decreases incomes and reduces the ability of debtors to pay off their debts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When prices are falling,economists say that there is
A) disinflation.
B) deflation.
C) a contraction.
D) an inverted inflation.
A) disinflation.
B) deflation.
C) a contraction.
D) an inverted inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the price index in some country were falling over time,economists would say that country had
A) disinflation.
B) deflation.
C) a contraction.
D) an inverted inflation.
A) disinflation.
B) deflation.
C) a contraction.
D) an inverted inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements about U.S.inflation is not correct?
A) Low inflation was viewed as a triumph of President Carter's economic policy.
B) There were long periods in the nineteenth century during which prices fell.
C) The U.S.public has viewed inflation rates of even 7 percent as a major economic problem.
D) The U.S.inflation rate has varied over time,but international data show even more variation.
A) Low inflation was viewed as a triumph of President Carter's economic policy.
B) There were long periods in the nineteenth century during which prices fell.
C) The U.S.public has viewed inflation rates of even 7 percent as a major economic problem.
D) The U.S.inflation rate has varied over time,but international data show even more variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The term hyperinflation refers to
A) the spread of inflation from one country to others.
B) a decrease in the inflation rate.
C) a period of very high inflation.
D) inflation accompanied by a recession.
A) the spread of inflation from one country to others.
B) a decrease in the inflation rate.
C) a period of very high inflation.
D) inflation accompanied by a recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In which of the following cases was the inflation rate 10 percent over the last year?
A) One year ago the price index had a value of 110 and now it has a value of 120.
B) One year ago the price index had a value of 120 and now it has a value of 132.
C) One year ago the price index had a value of 126 and now it has a value of 140.
D) One year ago the price index had a value of 145 and now it has a value of 163.
A) One year ago the price index had a value of 110 and now it has a value of 120.
B) One year ago the price index had a value of 120 and now it has a value of 132.
C) One year ago the price index had a value of 126 and now it has a value of 140.
D) One year ago the price index had a value of 145 and now it has a value of 163.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When the money market is drawn with the value of money on the vertical axis,a decrease in the price level causes a
A) movement to the right along the money demand curve.
B) movement to the left along the money demand curve.
C) shift to the right of the money supply curve.
D) shift to the left of the money supply curve.
A) movement to the right along the money demand curve.
B) movement to the left along the money demand curve.
C) shift to the right of the money supply curve.
D) shift to the left of the money supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements concerning the history of U.S.inflation is not correct?
A) Prices rose at an average annual rate of about 4 percent over the last 70 years.
B) There was about a 16-fold increase in the price level over the last 70 years.
C) Inflation in the 1970s was below the average over the last 70 years.
D) During its history the United States has experienced periods of deflation.
A) Prices rose at an average annual rate of about 4 percent over the last 70 years.
B) There was about a 16-fold increase in the price level over the last 70 years.
C) Inflation in the 1970s was below the average over the last 70 years.
D) During its history the United States has experienced periods of deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The value of money falls as the price level
A) rises,because the number of dollars needed to buy a representative basket of goods rises.
B) rises,because the number of dollars needed to buy a representative basket of goods falls.
C) falls,because the number of dollars needed to buy a representative basket of goods rises.
D) falls,because the number of dollars needed to buy a representative basket of goods falls.
A) rises,because the number of dollars needed to buy a representative basket of goods rises.
B) rises,because the number of dollars needed to buy a representative basket of goods falls.
C) falls,because the number of dollars needed to buy a representative basket of goods rises.
D) falls,because the number of dollars needed to buy a representative basket of goods falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If the price level increased from 120 to 150,then what was the inflation rate?
A) 30 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 20 percent
D) None of the above is correct.
A) 30 percent
B) 25 percent
C) 20 percent
D) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If P denotes the price of goods and services measured in terms of money,then
A) 1/P represents the value of money measured in terms of goods and services.
B) P can be regarded as the "overall price level."
C) an increase in the value of money is associated with a decrease in P.
D) All of the above are correct.
A) 1/P represents the value of money measured in terms of goods and services.
B) P can be regarded as the "overall price level."
C) an increase in the value of money is associated with a decrease in P.
D) All of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Inflation is
A) more about the value of goods than about the value of money.
B) more about the value of money than about the value of goods.
C) best understood by looking at the individual prices that make up price indexes.
D) viewed by most economists today as a phenomenon that cannot be explained by the ideas of the "classical" economists.
A) more about the value of goods than about the value of money.
B) more about the value of money than about the value of goods.
C) best understood by looking at the individual prices that make up price indexes.
D) viewed by most economists today as a phenomenon that cannot be explained by the ideas of the "classical" economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 312 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



