Deck 17: International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/143
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: International Trade
1
Voluntary exchanges:
A)generate surplus,leaving both participants better off than they were before.
B)generate deadweight loss,leaving both participants worse off than they were before.
C)generate deadweight loss,leaving at least one participant worse off than they were before.
D)create a transfer of surplus from one participant to another.
A)generate surplus,leaving both participants better off than they were before.
B)generate deadweight loss,leaving both participants worse off than they were before.
C)generate deadweight loss,leaving at least one participant worse off than they were before.
D)create a transfer of surplus from one participant to another.
generate surplus,leaving both participants better off than they were before.
2
When a country has the ability to produce more of a good than others with a given amount of resources,they:
A)have an absolute advantage.
B)have a comparative advantage.
C)are free-traders.
D)should remain self-sufficient.
A)have an absolute advantage.
B)have a comparative advantage.
C)are free-traders.
D)should remain self-sufficient.
have an absolute advantage.
3
Gains from trade are:
A)the increase in welfare in both countries that results from specialization and trade.
B)the transfer of surplus by the receiving country that results from trade.
C)the deadweight loss by the losing country that results from trade.
D)the increased skills and human capital that results from specialization and trade.
A)the increase in welfare in both countries that results from specialization and trade.
B)the transfer of surplus by the receiving country that results from trade.
C)the deadweight loss by the losing country that results from trade.
D)the increased skills and human capital that results from specialization and trade.
the increase in welfare in both countries that results from specialization and trade.
4
When trade is possible,each country can produce the goods that it has:
A)a comparative advantage at producing,rather than the exact combination of goods its consumers want.
B)an absolute advantage at producing,rather than the exact combination of goods its consumers want.
C)an absolute advantage at producing,rather than the goods it has a comparative advantage in.
D)None of these is true.
A)a comparative advantage at producing,rather than the exact combination of goods its consumers want.
B)an absolute advantage at producing,rather than the exact combination of goods its consumers want.
C)an absolute advantage at producing,rather than the goods it has a comparative advantage in.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Comparative advantage is the ability to produce:
A)more of a good than others with a given amount of resources.
B)relatively more than any other good with a given amount of resources.
C)a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than others can.
D)None of these is true.
A)more of a good than others with a given amount of resources.
B)relatively more than any other good with a given amount of resources.
C)a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than others can.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The increase in welfare in both countries that results from specialization and trade is called:
A)gains from trade.
B)surplus enhancement.
C)exportation surplus.
D)deadweight gain.
A)gains from trade.
B)surplus enhancement.
C)exportation surplus.
D)deadweight gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
For the most part,in the real world,trade between countries:
A)is free.
B)is regulated or restricted in some way.
C)is free,with the notable exception of China.
D)None of these is true.
A)is free.
B)is regulated or restricted in some way.
C)is free,with the notable exception of China.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Multifibre Arrangement and African Growth and Opportunity Act:
A)explains why a country not suitable for trade could become a major exporter.
B)altered trade patterns from those that would have occurred in the absence of these agreements.
C)was a group of restrictive trade treaties between individual countries,and agreements exempting others from the restrictions.
D)All of these are true.
A)explains why a country not suitable for trade could become a major exporter.
B)altered trade patterns from those that would have occurred in the absence of these agreements.
C)was a group of restrictive trade treaties between individual countries,and agreements exempting others from the restrictions.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If England buys hockey sticks from Canada,it tells us:
A)England has an absolute advantage over Canada in making hockey sticks.
B)Canada has an absolute advantage over England in making hockey sticks.
C)England has the comparative advantage over Canada in making hockey sticks.
D)Canada has the comparative advantage over England in making hockey sticks.
A)England has an absolute advantage over Canada in making hockey sticks.
B)Canada has an absolute advantage over England in making hockey sticks.
C)England has the comparative advantage over Canada in making hockey sticks.
D)Canada has the comparative advantage over England in making hockey sticks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When two countries specialize and trade:
A)both can enjoy more output than either could produce on its own.
B)they can have consumption possibilities beyond their production possibilities.
C)surplus can be gained by both countries.
D)All of these are true.
A)both can enjoy more output than either could produce on its own.
B)they can have consumption possibilities beyond their production possibilities.
C)surplus can be gained by both countries.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Multifibre Arrangement (MFA):
A)was a group of separate treaties between individual countries.
B)set limits on how much of what type of clothing could be traded between which countries.
C)was written on a level of detail that seems ridiculous in retrospect.
D)All of these are true.
A)was a group of separate treaties between individual countries.
B)set limits on how much of what type of clothing could be traded between which countries.
C)was written on a level of detail that seems ridiculous in retrospect.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If Spain sells soccer balls to the United States,it tells us:
A)Spain has an absolute advantage over the United States in making soccer balls.
B)Spain can produce more soccer balls than the United States given the same resources.
C)Spain has the ability to produce soccer balls at a lower opportunity cost than the United States can.
D)All of these are true.
A)Spain has an absolute advantage over the United States in making soccer balls.
B)Spain can produce more soccer balls than the United States given the same resources.
C)Spain has the ability to produce soccer balls at a lower opportunity cost than the United States can.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
International trade affects:
A)prices in different countries.
B)workers in different countries.
C)consumers in different countries.
D)All of these are true.
A)prices in different countries.
B)workers in different countries.
C)consumers in different countries.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When a country has the ability to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than others can,they:
A)have an absolute advantage.
B)have a comparative advantage.
C)are free-traders.
D)should remain self-sufficient.
A)have an absolute advantage.
B)have a comparative advantage.
C)are free-traders.
D)should remain self-sufficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Absolute advantage is the ability to produce:
A)more of a good than others with a given amount of resources.
B)relatively more than any other good with a given amount of resources.
C)a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than others can.
D)None of these is true.
A)more of a good than others with a given amount of resources.
B)relatively more than any other good with a given amount of resources.
C)a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than others can.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If Colombia has a comparative advantage over Mexico in the production of coffee,it means:
A)Colombia probably sells coffee to Mexico.
B)Mexico is more productive at making coffee than Colombia.
C)Colombia has the ability to produce more coffee than Mexico with the same resources.
D)None of these is true.
A)Colombia probably sells coffee to Mexico.
B)Mexico is more productive at making coffee than Colombia.
C)Colombia has the ability to produce more coffee than Mexico with the same resources.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When each country specializes in producing the good for which it has a comparative advantage:
A)both countries can benefit.
B)both countries always enjoy equal gains from trade.
C)the country that is bigger will gain more surplus.
D)All of these are true.
A)both countries can benefit.
B)both countries always enjoy equal gains from trade.
C)the country that is bigger will gain more surplus.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Voluntary exchanges between ____________ generates surplus.
A)firms
B)countries
C)individuals
D)All of these are true.
A)firms
B)countries
C)individuals
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Both countries can benefit from trade when:
A)at least one country produces the good for which it has an absolute advantage.
B)each specializes in producing the good for which it has a comparative advantage.
C)each specializes in producing the good for which it has an absolute advantage.
D)It is not possible for both countries to benefit.
A)at least one country produces the good for which it has an absolute advantage.
B)each specializes in producing the good for which it has a comparative advantage.
C)each specializes in producing the good for which it has an absolute advantage.
D)It is not possible for both countries to benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If Japan has an absolute advantage over the United States in making TVs,it means:
A)Japan probably sells TVs to the United States.
B)Japan is more productive at making TVs than the United States,when both countries use the same quantity of resources in TV production.
C)Japan has the ability to produce TVs at a lower opportunity cost than the United States.
D)None of these is true.
A)Japan probably sells TVs to the United States.
B)Japan is more productive at making TVs than the United States,when both countries use the same quantity of resources in TV production.
C)Japan has the ability to produce TVs at a lower opportunity cost than the United States.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A country with a lot of land relative to its population may have a comparative advantage in:
A)land-intensive activities.
B)capital-intensive activities.
C)labor-intensive activities.
D)technology-intensive activities.
A)land-intensive activities.
B)capital-intensive activities.
C)labor-intensive activities.
D)technology-intensive activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As workforces become more educated in countries with comparative advantage in labor-intensive products,the comparative advantage for the production of those goods:
A)shifts toward other countries with more cheap labor relative to the other factors of production.
B)shifts toward other countries with less cheap labor relative to the other factors of production.
C)shifts away from countries with more cheap labor relative to other factors of production.
D)None of these is true.
A)shifts toward other countries with more cheap labor relative to the other factors of production.
B)shifts toward other countries with less cheap labor relative to the other factors of production.
C)shifts away from countries with more cheap labor relative to other factors of production.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A country is likely to have a comparative advantage in a land-intensive activity if it has:
A)a lot of land relative to its population.
B)a large population relative to its landmass.
C)a higher opportunity cost of producing technology.
D)None of these is true.
A)a lot of land relative to its population.
B)a large population relative to its landmass.
C)a higher opportunity cost of producing technology.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In reality,trade requires:
A)governments to get together and agree on who is going to specialize in what.
B)governments employ an economic super-planner to crunch the numbers to find comparative advantage for different products.
C)that the day-to-day business decision making is carried out almost entirely by firms and individuals,not by governments.
D)None of these is true.
A)governments to get together and agree on who is going to specialize in what.
B)governments employ an economic super-planner to crunch the numbers to find comparative advantage for different products.
C)that the day-to-day business decision making is carried out almost entirely by firms and individuals,not by governments.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
As workforces become more educated in countries with comparative advantages in labor-intensive products,cheap labor becomes:
A)less abundant relative to skilled labor.
B)more abundant relative to skilled labor.
C)more abundant relative to capital.
D)None of these is true.
A)less abundant relative to skilled labor.
B)more abundant relative to skilled labor.
C)more abundant relative to capital.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Over time,technology tends to:
A)spread from country to country,equalizing opportunity costs.
B)set countries apart in terms of productivity.
C)allow developing nations to experience the "catch-up" effect.
D)None of these is true.
A)spread from country to country,equalizing opportunity costs.
B)set countries apart in terms of productivity.
C)allow developing nations to experience the "catch-up" effect.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In reality,international free trade:
A)allows everyone involved to gain surplus.
B)can have individual winners and losers of surplus within a country.
C)creates surplus only for the producers in a country.
D)creates surplus only for the consumers in a country.
A)allows everyone involved to gain surplus.
B)can have individual winners and losers of surplus within a country.
C)creates surplus only for the producers in a country.
D)creates surplus only for the consumers in a country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When we say that a country enjoys gains from trade,we mean:
A)everyone in that country benefits from the trade.
B)the net gain of surplus is positive for that country.
C)the total producer surplus increased in the country.
D)the total consumer surplus increased in the country.
A)everyone in that country benefits from the trade.
B)the net gain of surplus is positive for that country.
C)the total producer surplus increased in the country.
D)the total consumer surplus increased in the country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
We might predict that Hawaii has a comparative advantage compared to Russia in the production of pineapples because:
A)Hawaii's climate is more suitable.
B)Hawaii has more land available to grow them on.
C)Hawaii has more advanced farming technology.
D)All of these are true.
A)Hawaii's climate is more suitable.
B)Hawaii has more land available to grow them on.
C)Hawaii has more advanced farming technology.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A country is likely to have a comparative advantage in a capital-intensive activity if it has:
A)a lot of land relative to its population.
B)a large amount of capital relative to its landmass.
C)a higher opportunity cost of producing technology.
D)None of these is true.
A)a lot of land relative to its population.
B)a large amount of capital relative to its landmass.
C)a higher opportunity cost of producing technology.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Only a firm with ______________ will be able to make their output profitably.
A)a comparative advantage at producing their output
B)the highest opportunity cost of production
C)an absolute advantage at producing their output
D)None of these is true.
A)a comparative advantage at producing their output
B)the highest opportunity cost of production
C)an absolute advantage at producing their output
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A country may gain a temporary comparative advantage if:
A)it is the first to discover and implement a new technology or production process.
B)it remains self-sufficient until it stockpiles enough inventory to supply the world.
C)it remains a political ally to all.
D)All of these are true.
A)it is the first to discover and implement a new technology or production process.
B)it remains self-sufficient until it stockpiles enough inventory to supply the world.
C)it remains a political ally to all.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If there are big gains to be had from specialization and trade,why doesn't every country produce just one good?
A)Specialization is limited by trade agreements.
B)No national economy is a perfectly free market.
C)There is no perfectly free trade between national economies.
D)All of these are true.
A)Specialization is limited by trade agreements.
B)No national economy is a perfectly free market.
C)There is no perfectly free trade between national economies.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
We might predict that Japan has a comparative advantage compared to Russia in the production of hi-tech electronics because:
A)Japan's climate is more suitable.
B)Japan has more land available to build manufacturing plants on.
C)Japan has more advanced electronics technology.
D)All of these are true.
A)Japan's climate is more suitable.
B)Japan has more land available to build manufacturing plants on.
C)Japan has more advanced electronics technology.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An important determinant of comparative advantage is:
A)diversity in climate and natural resources.
B)endowment of factors of production.
C)technology.
D)All of these are important determinants of comparative advantage.
A)diversity in climate and natural resources.
B)endowment of factors of production.
C)technology.
D)All of these are important determinants of comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A country with plenty of capital and little land may have a comparative advantage in:
A)land-intensive activities.
B)capital-intensive activities.
C)labor-intensive activities.
D)technology-intensive activities.
A)land-intensive activities.
B)capital-intensive activities.
C)labor-intensive activities.
D)technology-intensive activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Technology or production processes developed in a particular country:
A)may give that country a temporary comparative advantage.
B)may set that country back until they earn back the research and development costs.
C)will give that country a permanent comparative advantage.
D)None of these is true.
A)may give that country a temporary comparative advantage.
B)may set that country back until they earn back the research and development costs.
C)will give that country a permanent comparative advantage.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Once a new technology spreads and is adopted by many countries,
A)the first country to use it may lose its comparative advantage.
B)the first country to use it will lose its absolute advantage.
C)other countries will perfect it,putting them at an absolute advantage.
D)the country will have to have strict intellectual property rights protections in place.
A)the first country to use it may lose its comparative advantage.
B)the first country to use it will lose its absolute advantage.
C)other countries will perfect it,putting them at an absolute advantage.
D)the country will have to have strict intellectual property rights protections in place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A national characteristic that affects the cost of producing goods in a particular country is:
A)natural resources and climate.
B)endowment of factors of production.
C)technology.
D)All of these affect the cost of producing goods.
A)natural resources and climate.
B)endowment of factors of production.
C)technology.
D)All of these affect the cost of producing goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The right decision about what to produce and who to trade with happens:
A)automatically.
B)when governments publish comparative advantage numbers.
C)only after firms research the cost of inputs such as labor and raw materials,and the sale prices of different goods you could produce,and calculate the most profitable option.
D)None of these is true.
A)automatically.
B)when governments publish comparative advantage numbers.
C)only after firms research the cost of inputs such as labor and raw materials,and the sale prices of different goods you could produce,and calculate the most profitable option.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 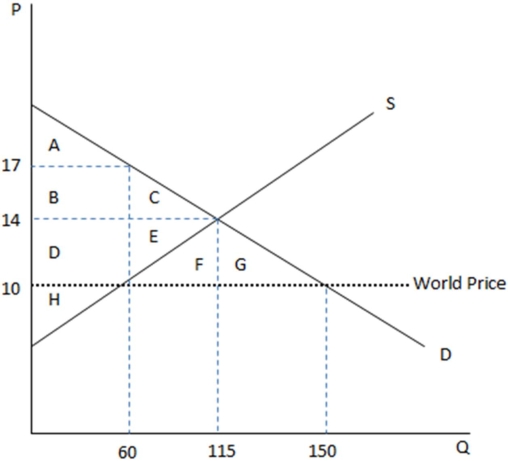
According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,domestic consumers would consume how many units?
A)60
B)115
C)150
D)90

According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,domestic consumers would consume how many units?
A)60
B)115
C)150
D)90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 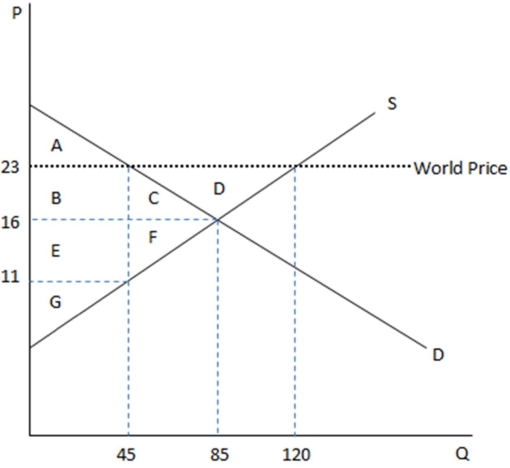
According to given graph shown,what is the world price?
A)$23
B)$16
C)$11
D)$45

According to given graph shown,what is the world price?
A)$23
B)$16
C)$11
D)$45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 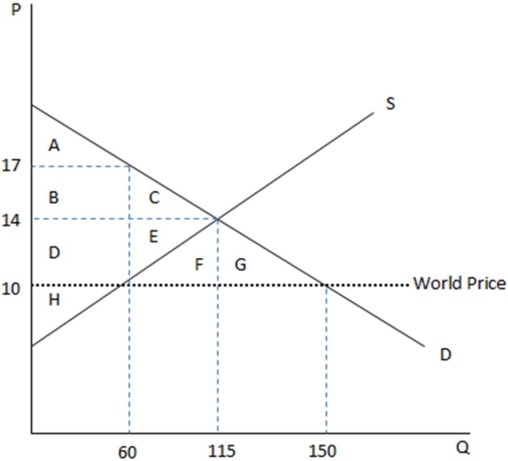
According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,how many units would be imported?
A)60
B)115
C)150
D)90

According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,how many units would be imported?
A)60
B)115
C)150
D)90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 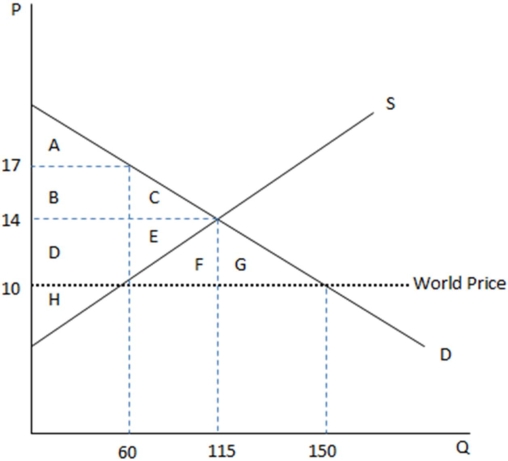
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic prices would:
A)remain $14 for domestically produced goods,and be $10 for those units imported.
B)drop to $10 for all units.
C)remain $14,with more units sold overall.
D)None of these is true.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic prices would:
A)remain $14 for domestically produced goods,and be $10 for those units imported.
B)drop to $10 for all units.
C)remain $14,with more units sold overall.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 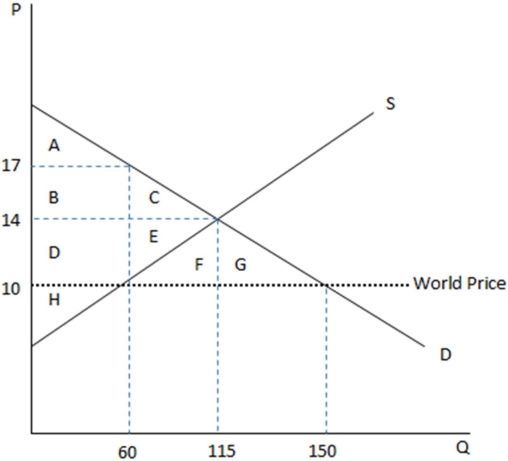
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic producers would:
A)transfer surplus in area DE to consumers.
B)transfer surplus in area DE to foreign producers.
C)lose surplus in area FG to deadweight loss.
D)lose surplus in area FG to foreign producers.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic producers would:
A)transfer surplus in area DE to consumers.
B)transfer surplus in area DE to foreign producers.
C)lose surplus in area FG to deadweight loss.
D)lose surplus in area FG to foreign producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Imports are goods and services that are:
A)produced in other countries and consumed domestically.
B)produced domestically and consumed in other countries.
C)produced and consumed in other countries.
D)produced and consumed domestically.
A)produced in other countries and consumed domestically.
B)produced domestically and consumed in other countries.
C)produced and consumed in other countries.
D)produced and consumed domestically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 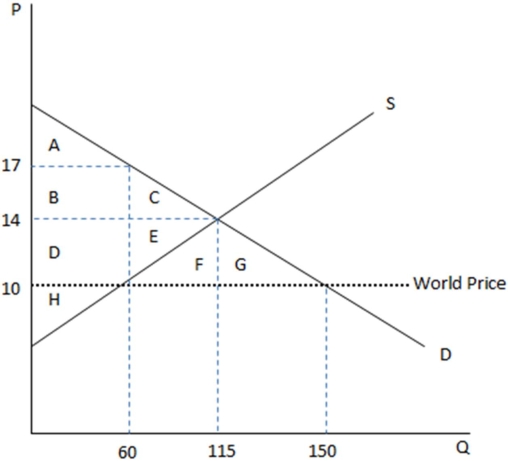
According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the amount being sold domestically is:
A)60.
B)115.
C)160.
D)90.

According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the amount being sold domestically is:
A)60.
B)115.
C)160.
D)90.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 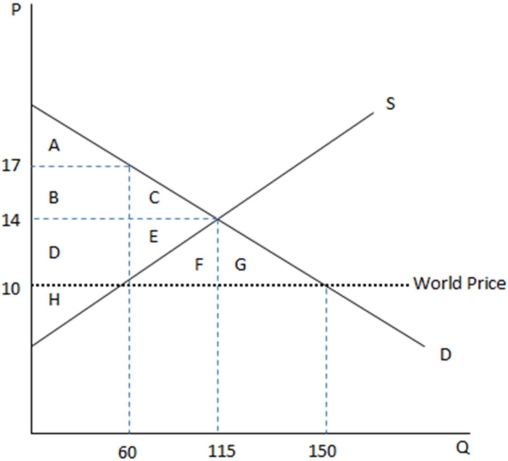
According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the amount being bought domestically is:
A)60 at $10 each.
B)60 at $17 each.
C)115 at $14 each.
D)150 at $10 each.

According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the amount being bought domestically is:
A)60 at $10 each.
B)60 at $17 each.
C)115 at $14 each.
D)150 at $10 each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 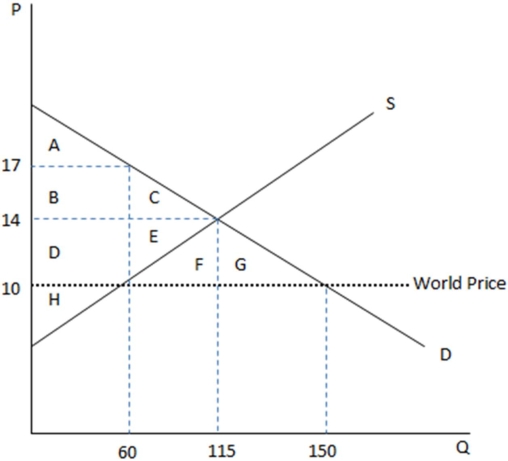
According to the graph shown,if this economy were an autarky,consumers would get area:
A)A in consumer surplus.
B)ABC in consumer surplus.
C)ABCDE in consumer surplus.
D)ABCDEFG in consumer surplus.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were an autarky,consumers would get area:
A)A in consumer surplus.
B)ABC in consumer surplus.
C)ABCDE in consumer surplus.
D)ABCDEFG in consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
We call an economy that is self-contained and does not engage in any trade with outsiders:
A)an autarky.
B)an oligopoly.
C)an oligarchy.
D)a monarchy.
A)an autarky.
B)an oligopoly.
C)an oligarchy.
D)a monarchy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 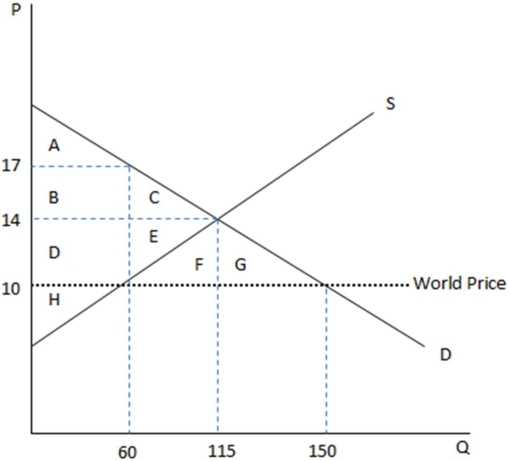
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,the amount consumed domestically would:
A)increase by 35.
B)increase by 90.
C)decrease by 35.
D)decrease by 90.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,the amount consumed domestically would:
A)increase by 35.
B)increase by 90.
C)decrease by 35.
D)decrease by 90.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 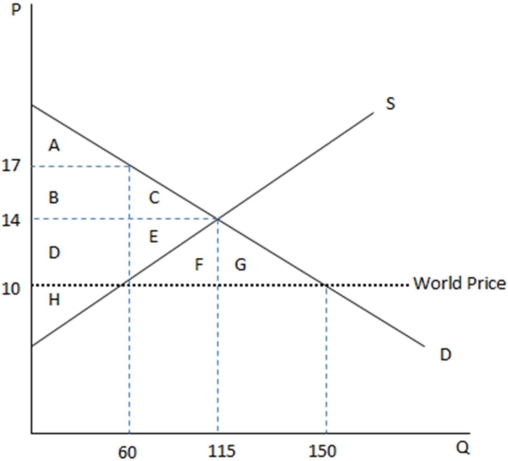
According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,domestic producers would produce how many units?
A)60
B)115
C)150
D)90

According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,domestic producers would produce how many units?
A)60
B)115
C)150
D)90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exports are goods and services that are:
A)produced in other countries and consumed domestically.
B)produced domestically and consumed in other countries.
C)produced and consumed in other countries.
D)produced and consumers domestically.
A)produced in other countries and consumed domestically.
B)produced domestically and consumed in other countries.
C)produced and consumed in other countries.
D)produced and consumers domestically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 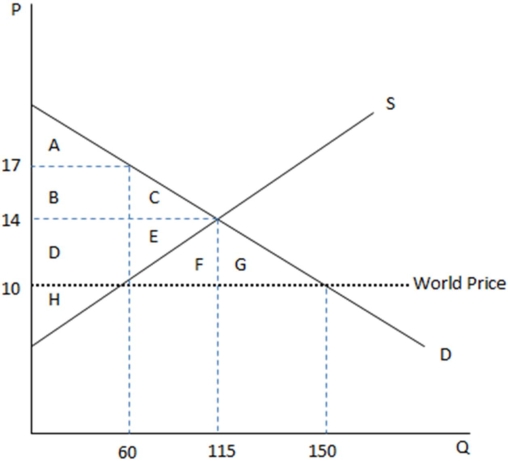
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,consumers would:
A)enjoy a net gain to surplus of DEFG.
B)suffer a net loss to surplus of DEFG.
C)suffer a transfer of surplus to the producer of DEFG.
D)experience deadweight loss of FG.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,consumers would:
A)enjoy a net gain to surplus of DEFG.
B)suffer a net loss to surplus of DEFG.
C)suffer a transfer of surplus to the producer of DEFG.
D)experience deadweight loss of FG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 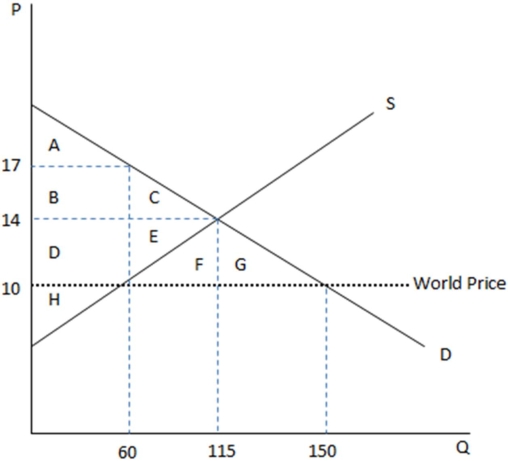
According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the equilibrium price would be:
A)$10.
B)$14.
C)$17.
D)$4.

According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the equilibrium price would be:
A)$10.
B)$14.
C)$17.
D)$4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 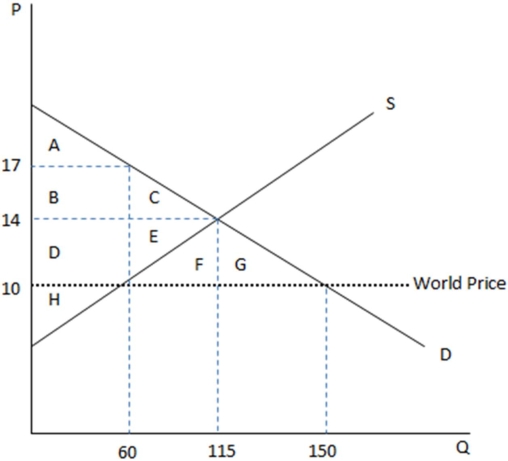
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to become a free trade nation,this good would:
A)be imported.
B)be exported.
C)no longer be produced domestically.
D)not imported or exported,but only produced domestically.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to become a free trade nation,this good would:
A)be imported.
B)be exported.
C)no longer be produced domestically.
D)not imported or exported,but only produced domestically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 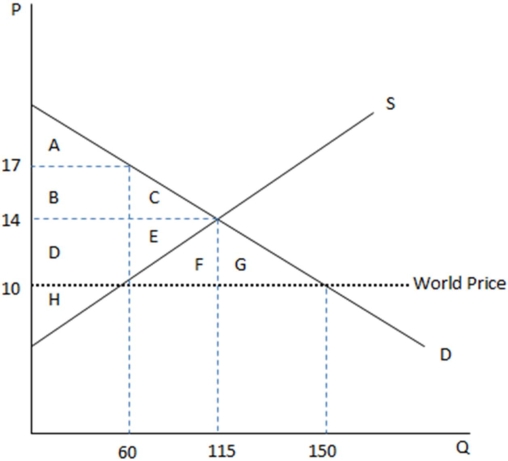
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic producers would have to cut:
A)production by 55 units.
B)production by 90 units.
C)prices by $3.
D)prices by $7.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic producers would have to cut:
A)production by 55 units.
B)production by 90 units.
C)prices by $3.
D)prices by $7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 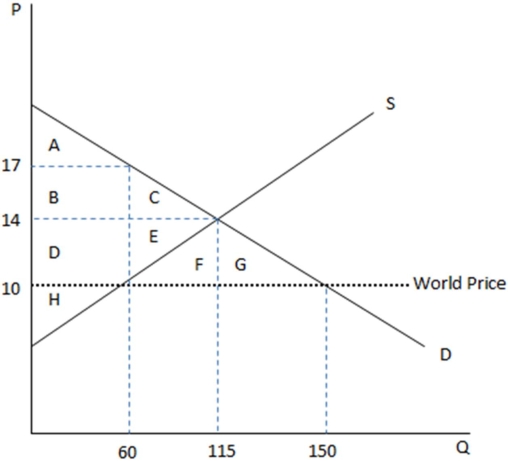
According the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,it would:
A)import this good,because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
B)export this good,because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
C)import this good,because the world price is greater than the domestic price.
D)export this good,because the world price is greater than the domestic price.

According the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,it would:
A)import this good,because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
B)export this good,because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
C)import this good,because the world price is greater than the domestic price.
D)export this good,because the world price is greater than the domestic price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 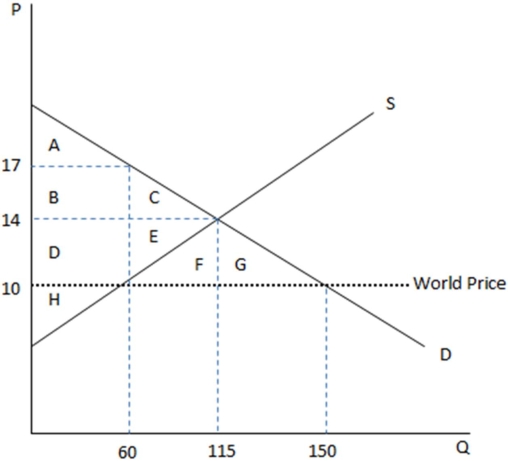
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,surplus would:
A)increase overall.
B)decrease for the producer.
C)transfer from producer to consumer.
D)All of these are true.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,surplus would:
A)increase overall.
B)decrease for the producer.
C)transfer from producer to consumer.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 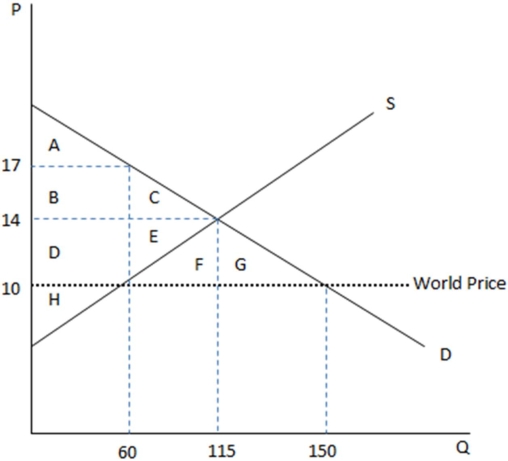
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,which amount of surplus would be transferred?
A)Area FG would be transferred to the consumer.
B)Area DE would be transferred to the consumer.
C)Area DEFG would be transferred to the consumer.
D)Area FG would be transferred to the producer.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,which amount of surplus would be transferred?
A)Area FG would be transferred to the consumer.
B)Area DE would be transferred to the consumer.
C)Area DEFG would be transferred to the consumer.
D)Area FG would be transferred to the producer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 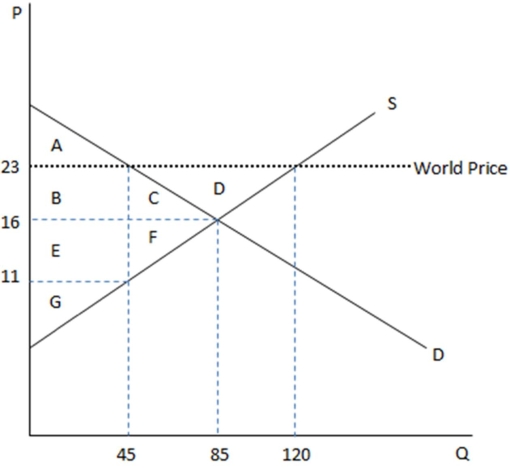
According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,how many units would be exported?
A)35
B)85
C)120
D)75

According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,how many units would be exported?
A)35
B)85
C)120
D)75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 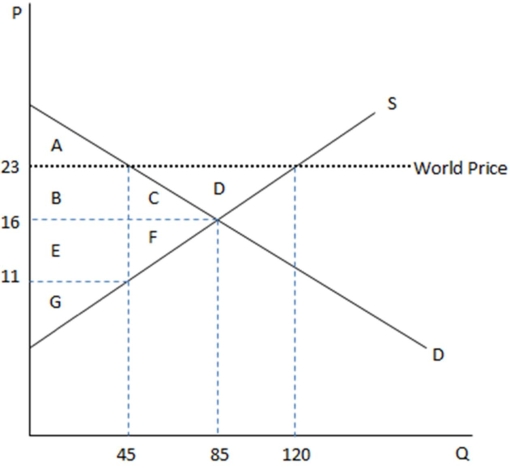
According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,domestic consumers would consume how many units?
A)45
B)85
C)120
D)75

According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,domestic consumers would consume how many units?
A)45
B)85
C)120
D)75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 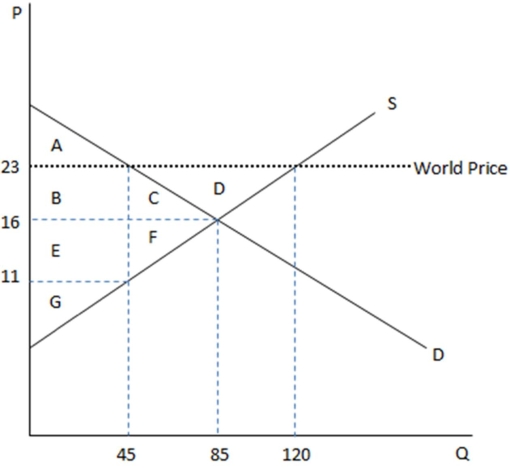
According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the amount being bought domestically is:
A)45 at $11 each.
B)45 at $23 each.
C)85 at $16 each.
D)120 at $23 each.

According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the amount being bought domestically is:
A)45 at $11 each.
B)45 at $23 each.
C)85 at $16 each.
D)120 at $23 each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 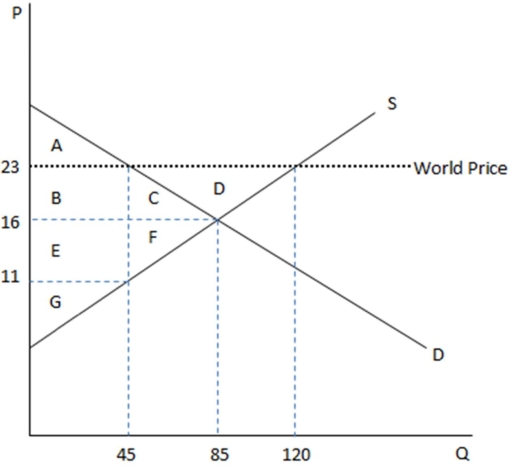
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,surplus would:
A)increase overall.
B)decrease for the producer.
C)transfer from producer to consumer.
D)All of these are true.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,surplus would:
A)increase overall.
B)decrease for the producer.
C)transfer from producer to consumer.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 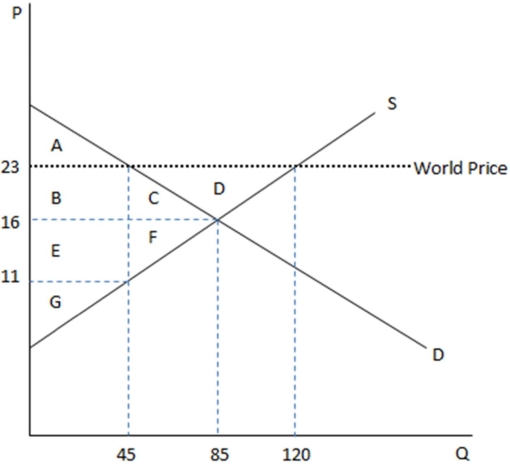
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,which amount of surplus would be transferred?
A)Area BC would be transferred to the consumer.
B)Area BCD would be transferred to the producer.
C)Area BCD would be transferred to the consumer.
D)Area BC would be transferred to the producer.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,which amount of surplus would be transferred?
A)Area BC would be transferred to the consumer.
B)Area BCD would be transferred to the producer.
C)Area BCD would be transferred to the consumer.
D)Area BC would be transferred to the producer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
For a single country to influence the price of some good in the global market:
A)it must be considered a price taker.
B)the quantity it produces and consumes must be small relative to the total amount of that good bought and sold worldwide.
C)the quantity it produces and consumes must be large relative to the total amount of that good bought and sold worldwide.
D)None of these is true.
A)it must be considered a price taker.
B)the quantity it produces and consumes must be small relative to the total amount of that good bought and sold worldwide.
C)the quantity it produces and consumes must be large relative to the total amount of that good bought and sold worldwide.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 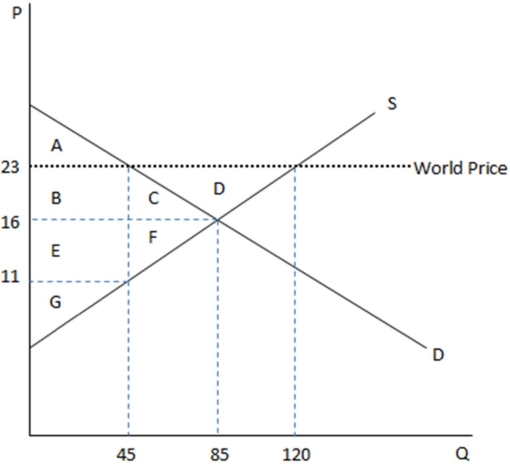
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic producers would:
A)transfer surplus in area BC to consumers.
B)transfer surplus in area BCD to foreign producers.
C)lose surplus in area BCD to foreign consumers.
D)None of these is true.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic producers would:
A)transfer surplus in area BC to consumers.
B)transfer surplus in area BCD to foreign producers.
C)lose surplus in area BCD to foreign consumers.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 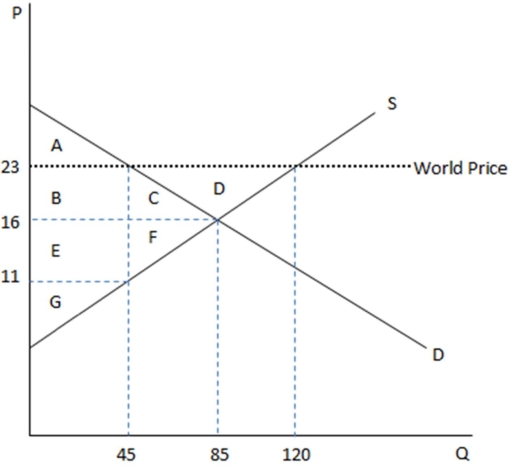
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic prices would:
A)remain $16 for domestically produced goods,and be $23 for those units imported.
B)increase to $23 for all units.
C)remain $16,with more units sold overall.
D)None of these is true.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic prices would:
A)remain $16 for domestically produced goods,and be $23 for those units imported.
B)increase to $23 for all units.
C)remain $16,with more units sold overall.
D)None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 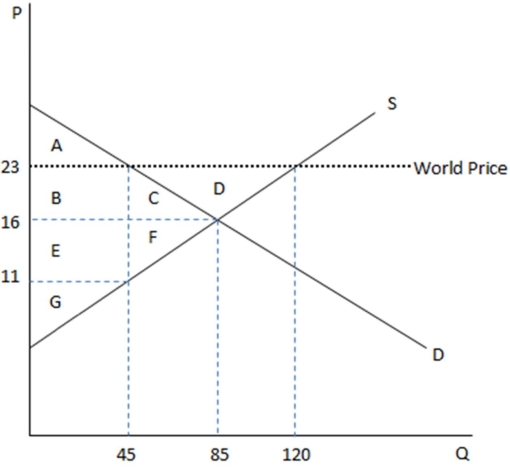
According to the graph shown,if this economy were an autarky,producers would enjoy area:
A)BCEFG
B)BCDEFG
C)G
D)EFG

According to the graph shown,if this economy were an autarky,producers would enjoy area:
A)BCEFG
B)BCDEFG
C)G
D)EFG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 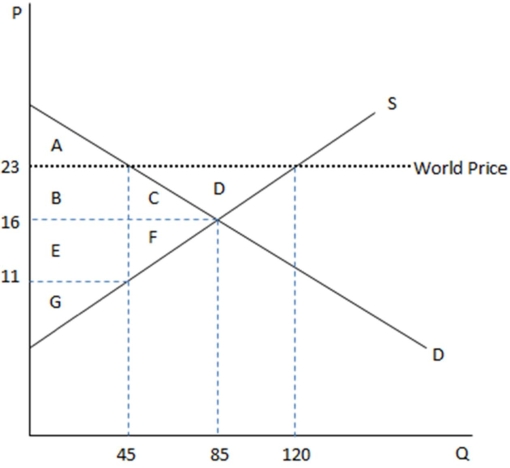
According to the graph shown,if this economy were an autarky,consumers would get area:
A)A in consumer surplus.
B)ABC in consumer surplus.
C)ABCD in consumer surplus.
D)ABCDEFG in consumer surplus.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were an autarky,consumers would get area:
A)A in consumer surplus.
B)ABC in consumer surplus.
C)ABCD in consumer surplus.
D)ABCDEFG in consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When a price-taking country joins the global market for some good,it:
A)shifts the world demand and supply to the right.
B)has a negligible effect on the world equilibrium.
C)shifts the world demand and supply to the left.
D)shifts the world demand to the right,and the world supply to the left.
A)shifts the world demand and supply to the right.
B)has a negligible effect on the world equilibrium.
C)shifts the world demand and supply to the left.
D)shifts the world demand to the right,and the world supply to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 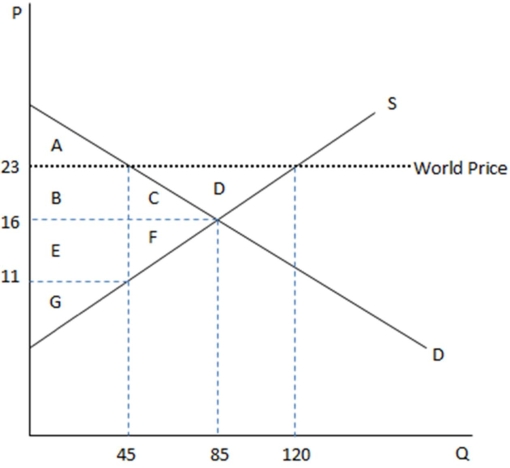
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,the amount consumed domestically would:
A)increase by 35.
B)increase by 40.
C)decrease by 40.
D)increase by 75.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,the amount consumed domestically would:
A)increase by 35.
B)increase by 40.
C)decrease by 40.
D)increase by 75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 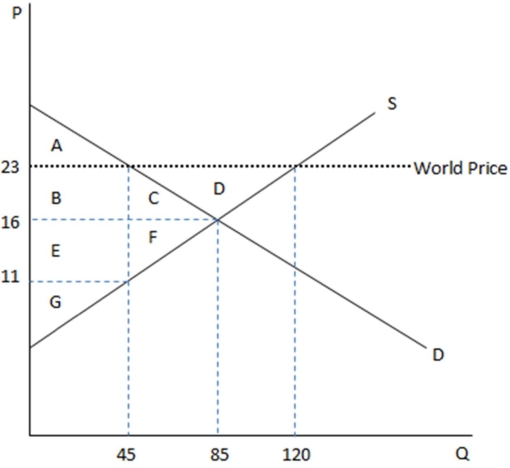
According the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,it would:
A)import this good because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
B)export this good because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
C)import this good because the world price is greater than the domestic price.
D)export this good because the world price is greater than the domestic price.

According the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,it would:
A)import this good because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
B)export this good because the domestic price is greater than the world price.
C)import this good because the world price is greater than the domestic price.
D)export this good because the world price is greater than the domestic price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 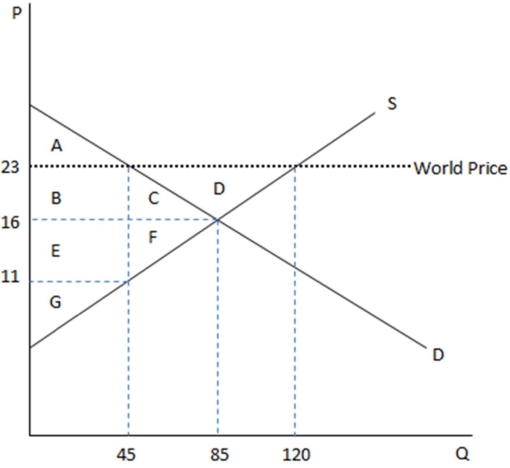
According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the amount being sold domestically is:
A)45.
B)85.
C)120.
D)75.

According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the amount being sold domestically is:
A)45.
B)85.
C)120.
D)75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 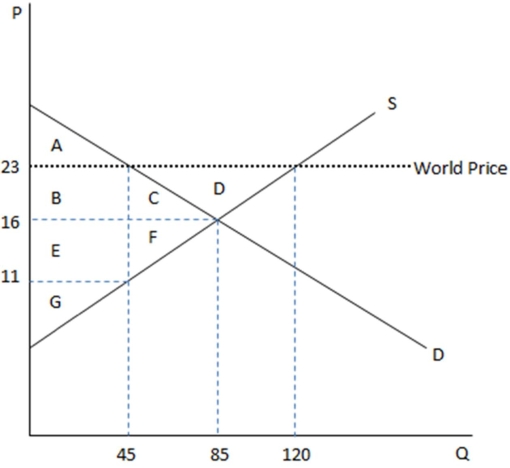
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to become a free trade nation,this good would:
A)be imported.
B)be exported.
C)no longer be produced domestically.
D)not imported or exported,but only produced domestically.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to become a free trade nation,this good would:
A)be imported.
B)be exported.
C)no longer be produced domestically.
D)not imported or exported,but only produced domestically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 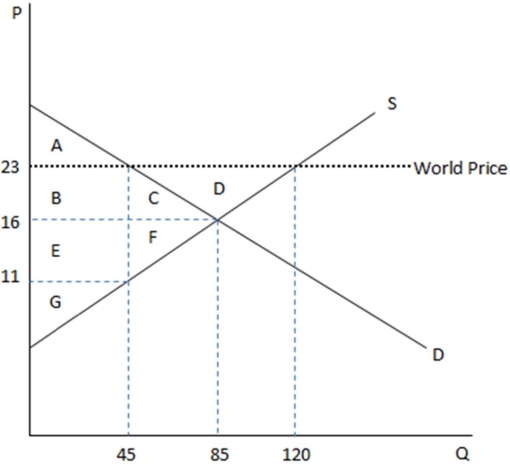
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic producers would increase:
A)production by 75 units.
B)production by 35 units.
C)prices by $5.
D)prices by $11.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,domestic producers would increase:
A)production by 75 units.
B)production by 35 units.
C)prices by $5.
D)prices by $11.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 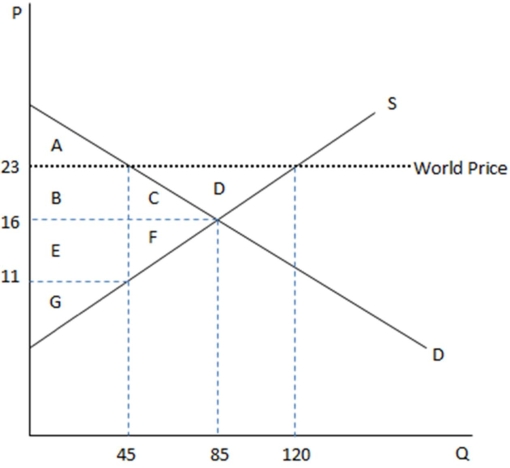
According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,consumers would:
A)enjoy a net gain to surplus of BC.
B)suffer a net loss to surplus of BCD.
C)suffer a transfer of surplus to the producer of BC.
D)experience deadweight loss of FG.

According to the graph shown,if this economy were to open to trade,consumers would:
A)enjoy a net gain to surplus of BC.
B)suffer a net loss to surplus of BCD.
C)suffer a transfer of surplus to the producer of BC.
D)experience deadweight loss of FG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 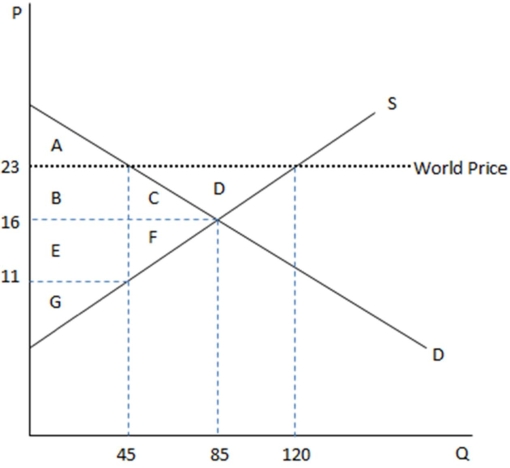
According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the equilibrium price would be:
A)$23
B)$16
C)$11
D)$45

According to the graph shown,if this were depicting an autarky,the equilibrium price would be:
A)$23
B)$16
C)$11
D)$45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
This graph demonstrates the domestic demand and supply for a good,as well as the world price for that good. 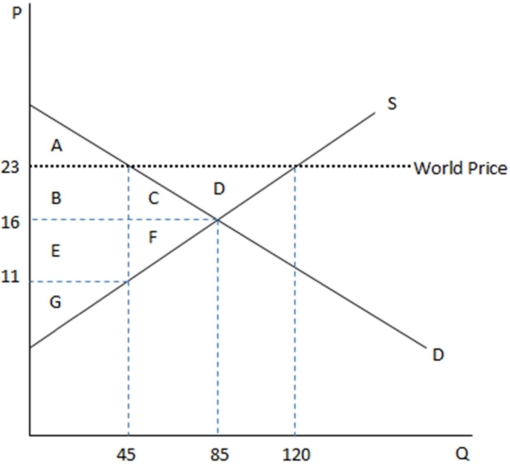
According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,domestic producers would produce how many units?
A)45
B)85
C)120
D)75

According to the graph shown,if this economy were open to free trade,domestic producers would produce how many units?
A)45
B)85
C)120
D)75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
For a country to be a price taker in the global market for some good:
A)the quantity it produces and consumes must be very small relative to the total amount of that good bought and sold worldwide.
B)the quantity it produces and consumes must be very large relative to the total amount of that good bought and sold worldwide.
C)there must be many sellers all supplying a very significant amount to the market.
D)there must be many buyers all buying a large amount from the market.
A)the quantity it produces and consumes must be very small relative to the total amount of that good bought and sold worldwide.
B)the quantity it produces and consumes must be very large relative to the total amount of that good bought and sold worldwide.
C)there must be many sellers all supplying a very significant amount to the market.
D)there must be many buyers all buying a large amount from the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



