Deck 34: Plant Structure, Nutrition, and Transport
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 34: Plant Structure, Nutrition, and Transport
1
A tendril on a grapevine is a modified
A) leaf.
B) bud.
C) root.
D) stem.
A) leaf.
B) bud.
C) root.
D) stem.
D
2
Chemicals that dissolve a plant's cuticle typically result in the death of the plant as it loses its ability to
A) photosynthesize.
B) resist herbivore grazing.
C) retain water.
D) repair wounds.
A) photosynthesize.
B) resist herbivore grazing.
C) retain water.
D) repair wounds.
C
3
Examine the plant in the figure below.

The plant shown is most likely a dicot because of the presence of
A) a taproot.
B) veins within the leaves.
C) five leaves.
D) both root and shoot systems.

The plant shown is most likely a dicot because of the presence of
A) a taproot.
B) veins within the leaves.
C) five leaves.
D) both root and shoot systems.
A
4
Water and nutrients are taken up from soil by
A) guard cells.
B) root hairs.
C) root caps.
D) xylem in taproots.
A) guard cells.
B) root hairs.
C) root caps.
D) xylem in taproots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Dermal hairs are more common on plants living at high elevations because at higher elevations
A) fewer herbivores are present.
B) water evaporates quickly.
C) competition for space is more intense.
D) ultraviolet radiation is more intense.
A) fewer herbivores are present.
B) water evaporates quickly.
C) competition for space is more intense.
D) ultraviolet radiation is more intense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What observation would indicate that the thorns on a rosebush are actually modified stems?
A) the presence of stomata
B) vascular bundles arranged in a ring
C) a centrally located vascular bundle
D) the presence of a cuticle
A) the presence of stomata
B) vascular bundles arranged in a ring
C) a centrally located vascular bundle
D) the presence of a cuticle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Worldwide,humans obtain more than 80 percent of their calories from
A) mosses.
B) flowering plants.
C) ferns.
D) conifers.
A) mosses.
B) flowering plants.
C) ferns.
D) conifers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A plant's root cap would be found
A) where the soil meets the air.
B) between the active growing area of the root and the soil.
C) within and just behind the active growing area of the root.
D) at the base of each root hair,near the main root.
A) where the soil meets the air.
B) between the active growing area of the root and the soil.
C) within and just behind the active growing area of the root.
D) at the base of each root hair,near the main root.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The typical leaf is broad and flat.This structure maximizes the amount of
A) light the leaf can capture for photosynthesis.
B) area available for the plant to absorb carbon dioxide.
C) area available for the plant to absorb water.
D) light the leaf can capture for photosynthesis and the area available for the plant to absorb carbon dioxide.
A) light the leaf can capture for photosynthesis.
B) area available for the plant to absorb carbon dioxide.
C) area available for the plant to absorb water.
D) light the leaf can capture for photosynthesis and the area available for the plant to absorb carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A cotyledon is the
A) food-storing organ found in the seeds of flowering plants.
B) embryonic root of a seedling.
C) reproductive organ of a plant.
D) type of ground tissue in mechanical reinforcement of stem structure.
A) food-storing organ found in the seeds of flowering plants.
B) embryonic root of a seedling.
C) reproductive organ of a plant.
D) type of ground tissue in mechanical reinforcement of stem structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The vascular tissue responsible for transporting sugars is known as
A) phloem.
B) xylem.
C) sclerenchyma.
D) collenchyma.
A) phloem.
B) xylem.
C) sclerenchyma.
D) collenchyma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
While walking in the forest,you come across a plant with a flower that has three petals and leaves with parallel veins.You would classify this plant as a
A) dicot.
B) monocot.
C) tricot.
D) cotyledon.
A) dicot.
B) monocot.
C) tricot.
D) cotyledon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The outer waxy covering on plants is called
A) dermal tissue.
B) the trichome layer.
C) the guard cell layer.
D) the cuticle.
A) dermal tissue.
B) the trichome layer.
C) the guard cell layer.
D) the cuticle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which combination of conditions will cause a plant's stomata to open?
A) high moisture and daylight
B) high moisture and darkness
C) dehydration and darkness
D) dehydration and daylight
A) high moisture and daylight
B) high moisture and darkness
C) dehydration and darkness
D) dehydration and daylight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Dermal tissues typically
A) regulate what enters and leaves the plant.
B) participate in wound healing.
C) transport food and water.
D) carry out photosynthesis.
A) regulate what enters and leaves the plant.
B) participate in wound healing.
C) transport food and water.
D) carry out photosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Examine the diagram below of a root tip.Which letter in the diagram indicates the zone of cell division?
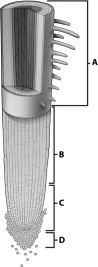
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In terms of their energy needs,solar energy is converted to chemical energy primarily within the plant's
A) stems.
B) leaves.
C) roots.
D) flowers.
A) stems.
B) leaves.
C) roots.
D) flowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is NOT a function of stems?
A) positioning the leaves for photosynthesis
B) supporting the overall shape of the plant
C) water and mineral absorption
D) vertical growth
A) positioning the leaves for photosynthesis
B) supporting the overall shape of the plant
C) water and mineral absorption
D) vertical growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Roots perform all of the following functions EXCEPT
A) the transport of water.
B) photosynthesis.
C) the transport of nutrients.
D) the storage of food.
A) the transport of water.
B) photosynthesis.
C) the transport of nutrients.
D) the storage of food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the diagram below of a leaf,which letter indicates dermal tissue?

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a plant leaf,photosynthesis occurs in the ________ cells.
A) collenchyma
B) parenchyma
C) sclerenchyma
D) collenchyma,parenchyma,and sclerenchyma
A) collenchyma
B) parenchyma
C) sclerenchyma
D) collenchyma,parenchyma,and sclerenchyma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The figure below illustrates how food is transported in phloem tissue.
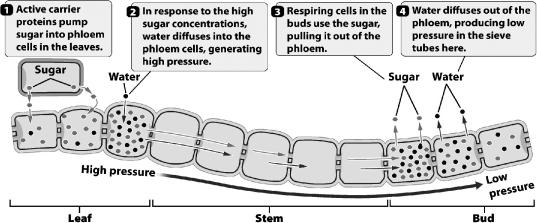
At what step(s)during the movement of sugar does the plant provide metabolic energy?
A) steps 2 and 4,when water enters and leaves the phloem
B) step 1,when sugars are loaded into the phloem
C) step 3,when sugar diffuses into respiring cells
D) All of the steps require the expenditure of metabolic energy.

At what step(s)during the movement of sugar does the plant provide metabolic energy?
A) steps 2 and 4,when water enters and leaves the phloem
B) step 1,when sugars are loaded into the phloem
C) step 3,when sugar diffuses into respiring cells
D) All of the steps require the expenditure of metabolic energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following does NOT contain ground tissue?
A) stems
B) roots
C) leaves
D) guard cells
A) stems
B) roots
C) leaves
D) guard cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Like other organisms,plants are composed of proteins,lipids,carbohydrates,and nucleic acids.Based on this,which of the following would be a micronutrient?
A) carbon
B) zinc
C) oxygen
D) nitrogen
A) carbon
B) zinc
C) oxygen
D) nitrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Vessel elements in plants are found in
A) guard cells.
B) root caps.
C) phloem.
D) xylem.
A) guard cells.
B) root caps.
C) phloem.
D) xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Like other organisms,plants are composed of proteins,lipids,carbohydrates,and nucleic acids.Based on this,which of the following would be a macronutrient?
A) zinc
B) copper
C) iron
D) carbon
A) zinc
B) copper
C) iron
D) carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Plants can generate the pressures needed to transport sugars produced by photosynthesis great distances by
A) manipulating the concentration of amino acids in phloem.
B) active transport of water.
C) actively transporting sugars into phloem and cells.
D) building up high water pressures in root hairs.
A) manipulating the concentration of amino acids in phloem.
B) active transport of water.
C) actively transporting sugars into phloem and cells.
D) building up high water pressures in root hairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the figure below,the line with the arrows indicates the cell-wall pathway for an absorbed nutrient.
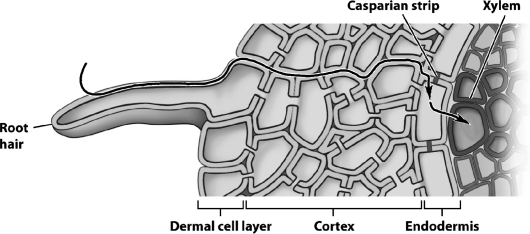
What structure actually regulates the entry of nutrients into the plant's interior?
A) the root cap
B) the plasma membrane of root hair
C) the plasma membrane of endodermal wall
D) the cell wall of root hair

What structure actually regulates the entry of nutrients into the plant's interior?
A) the root cap
B) the plasma membrane of root hair
C) the plasma membrane of endodermal wall
D) the cell wall of root hair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Sieve pores are a modification seen in vascular tissue that facilitate the movement of
A) water.
B) salts.
C) sugar and organic compounds.
D) dissolved minerals.
A) water.
B) salts.
C) sugar and organic compounds.
D) dissolved minerals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
From root hair to xylem,which of the following describes the journey of water entering a plant?
A) cortex to endodermis to dermal cell layer
B) endodermis to dermal cell layer to cortex
C) cortex to dermal cell layer to endodermis
D) dermal cell layer to cortex to endodermis
A) cortex to endodermis to dermal cell layer
B) endodermis to dermal cell layer to cortex
C) cortex to dermal cell layer to endodermis
D) dermal cell layer to cortex to endodermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is an example of a plant tissue?
A) root
B) stem
C) leaves
D) vascular
A) root
B) stem
C) leaves
D) vascular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The uptake of nutrients by roots requires energy because the
A) concentrations of nutrients in the soil are greater than the concentrations in root cells.
B) concentrations of nutrients in the soil are much more dilute than the concentrations in root cells.
C) concentrations of nutrients in the soil and in root cells are equal.
D) root hairs are covered by a waxy layer.
A) concentrations of nutrients in the soil are greater than the concentrations in root cells.
B) concentrations of nutrients in the soil are much more dilute than the concentrations in root cells.
C) concentrations of nutrients in the soil and in root cells are equal.
D) root hairs are covered by a waxy layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A benefit of using organic fertilizers over inorganic fertilizers is that organic fertilizers
A) supply energy to plant roots.
B) provide large quantities of potassium.
C) help soil hold water within which nutrients can dissolve.
D) help rid soil of harmful minerals.
A) supply energy to plant roots.
B) provide large quantities of potassium.
C) help soil hold water within which nutrients can dissolve.
D) help rid soil of harmful minerals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Plants rely on exoskeletons for support.
B) Plants rely on cell walls for support.
C) Plants rely on endoskeletons for support.
D) Plants do not require a support system.
A) Plants rely on exoskeletons for support.
B) Plants rely on cell walls for support.
C) Plants rely on endoskeletons for support.
D) Plants do not require a support system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which plant does NOT capture prey?
A) Venus flytraps
B) the bladderworts in the genus Utricularia
C) pitcher plants
D) Malayan urn vine
A) Venus flytraps
B) the bladderworts in the genus Utricularia
C) pitcher plants
D) Malayan urn vine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Tracheids in plants are found in
A) phloem.
B) xylem.
C) root caps.
D) guard cells.
A) phloem.
B) xylem.
C) root caps.
D) guard cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Companion cells in plants
A) are found next to guard cells.
B) are found in phloem.
C) lie next to tracheids in xylem.
D) are the basic components of tracheids.
A) are found next to guard cells.
B) are found in phloem.
C) lie next to tracheids in xylem.
D) are the basic components of tracheids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Why do some plants,like beans and peas,contain bacteria in compartments in their roots?
A) These friendly bacteria help the plant fight off disease-causing bacteria in the soil.
B) These bacteria are capable of nitrogen fixation and will provide the plant with nitrogen in exchange for carbohydrates.
C) Peas and beans form these compartments in their roots to block these bacteria from infecting the rest of the plant.
D) These bacteria increase the efficiency of root hairs' absorption of water.
A) These friendly bacteria help the plant fight off disease-causing bacteria in the soil.
B) These bacteria are capable of nitrogen fixation and will provide the plant with nitrogen in exchange for carbohydrates.
C) Peas and beans form these compartments in their roots to block these bacteria from infecting the rest of the plant.
D) These bacteria increase the efficiency of root hairs' absorption of water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A typical fertilizer contains no carbon because carbon is
A) not a plant nutrient.
B) obtained from the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
C) produced when the plant metabolizes nitrogen.
D) plentiful in all soils.
A) not a plant nutrient.
B) obtained from the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
C) produced when the plant metabolizes nitrogen.
D) plentiful in all soils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Within its vascular tissue,sieve tube elements and companion cells are connected by the
A) guard cells.
B) central vacuoles.
C) plasmodesmata.
D) Casparian strip.
A) guard cells.
B) central vacuoles.
C) plasmodesmata.
D) Casparian strip.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Most aboveground plant growth occurs with the repeated addition of ________ units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The most abundant plant cell type in ground tissue is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Some insects obtain nutrition by poking a mouthpart into the stem of a plant.Once the insect's mouthpart is inserted,fluid from the plant is actually pushed through the digestive tract of the insect by pressure.The mouthpart of the insect has most likely penetrated the ________ of the plant.
A) xylem
B) phloem
C) companion cells
D) endodermis
A) xylem
B) phloem
C) companion cells
D) endodermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Plants have two types of vascular tissue: xylem,which transports ________ and ________,and phloem,which transports ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Some plants house bacteria in compartments in their roots.These bacteria benefit the plant because they are capable of performing ________,making the macronutrient nitrogen available to the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is true of phloem transport?
A) Pressure in the sugar-loading zone is greater than pressure in the phloem-unloading zone.
B) Pressure in the sugar-loading zone is less than pressure in the phloem-unloading zone.
C) Pressure in the sugar-loading zone is equal to pressure in the phloem-unloading zone.
D) Pressure is not involved in phloem transport.
A) Pressure in the sugar-loading zone is greater than pressure in the phloem-unloading zone.
B) Pressure in the sugar-loading zone is less than pressure in the phloem-unloading zone.
C) Pressure in the sugar-loading zone is equal to pressure in the phloem-unloading zone.
D) Pressure is not involved in phloem transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Plants are protected from herbivores by ________ tissue,which also controls gas exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Most carnivorous plants obtain energy through photosynthesis;they consume insects to obtain ________ and ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
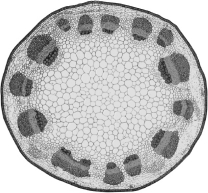
49
A plant with the arrangement of vascular bundles shown in the image below would be classified as a(n)________.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Leafhoppers feed on the contents of tracheids and vessels.The concentration of organic material in these plant components is
A) very high.
B) very low.
C) non-existent.
D) high only in spring.
A) very high.
B) very low.
C) non-existent.
D) high only in spring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The cells of the xylem are dead at functional maturity.This allows
A) osmosis into the xylem.
B) transpiration to occur in the stem.
C) the water molecules in the xylem to form a continuous column from root to shoot.
D) sugars to be actively transported into the xylem.
A) osmosis into the xylem.
B) transpiration to occur in the stem.
C) the water molecules in the xylem to form a continuous column from root to shoot.
D) sugars to be actively transported into the xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The basic plant body consists of a root system and a ________ system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Most of the dry biomass of a plant comes from ________ absorbed from the air by its leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the xylem,water is transported
A) in "cables" of a sugary water solution.
B) as evaporation from leaves pulls water "cables" from the root.
C) as evaporation of "cables" pulls water from root hairs.
D) through concentrated sugar solutions in phloem.
A) in "cables" of a sugary water solution.
B) as evaporation from leaves pulls water "cables" from the root.
C) as evaporation of "cables" pulls water from root hairs.
D) through concentrated sugar solutions in phloem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What best explains why sugar maple trees are tapped on the sun-warmed south side of the trunk?
A) Sap on the north side of the tree is still frozen in early spring.
B) During the summer most photosynthesis occurs on the south side of the tree.
C) The reaction rate for the enzymes that convert starch to sucrose is temperature dependent.
D) The sap expands as it is warmed and flows upward through the trunk.
A) Sap on the north side of the tree is still frozen in early spring.
B) During the summer most photosynthesis occurs on the south side of the tree.
C) The reaction rate for the enzymes that convert starch to sucrose is temperature dependent.
D) The sap expands as it is warmed and flows upward through the trunk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What process powers water transport from the root to shoot of a plant?
A) osmosis
B) nitrogen fixation
C) differences in pressure as a result of active transport
D) transpiration
A) osmosis
B) nitrogen fixation
C) differences in pressure as a result of active transport
D) transpiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Although plants require nine macronutrients,plant fertilizers typically provide just nitrogen,phosphorus,and ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Once sugars have been actively transported into the phloem,
A) the sugars move to other parts of the phloem by diffusion.
B) water is actively transported into the phloem to prevent diffusion.
C) water enters the phloem through osmosis.
D) pressure decreases in the phloem.
A) the sugars move to other parts of the phloem by diffusion.
B) water is actively transported into the phloem to prevent diffusion.
C) water enters the phloem through osmosis.
D) pressure decreases in the phloem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The presence of root hairs in the region of this root tip labeled with the letter A suggests that we are looking at the zone of ________.
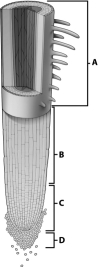


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Why is it important that the cells of the phloem remain alive?
A) Active transport and osmosis require a functional plasma membrane to take place.
B) Transpiration depends on the presence of a central vacuole.
C) Photosynthesis only occurs in vascular tissue.
D) All the mitochondria in a plant are found in the phloem.
A) Active transport and osmosis require a functional plasma membrane to take place.
B) Transpiration depends on the presence of a central vacuole.
C) Photosynthesis only occurs in vascular tissue.
D) All the mitochondria in a plant are found in the phloem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Plants use microscopic muscles to push sugars through their organs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Aristotle showed that plants get most of what they need to grow from the air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The type of plant tissue indicated by the letter A in the diagram below of a plant stem is ground tissue.
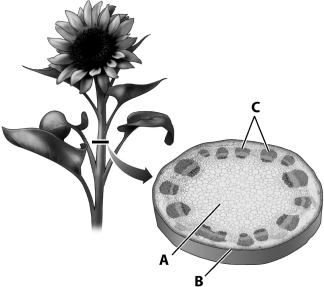


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The reason that the cell walls of tracheids are so thick is to prevent them from collapsing under the tension created by transpiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
________ is the evaporation of water from the surface of a leaf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Venus flytraps are known to have captured and consumed small mammals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Root caps are aided by mucilage in order to move in abrasive soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The roots of a plant are covered with a waxy cuticle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Flowers are an example of a plant organ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Many plants and animals move water and nutrients within internal vessels.Animals use the energy of muscle contraction;however,no metabolic energy is expended when water and minerals move within a plant's xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A flowering plant with leaves containing parallel veins is most likely a dicot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Fungi can clog tracheids and vessels,which causes a plant's ________ system to wilt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Carnivorous plants are often found in habitats deficient in nitrogen and phosphorus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The difference in ________ between the sugar-loading zone and the sugar-unloading zone drives the long-distance transport of sugars through the phloem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Trees,although immobile,can take defensive measures against harmful insects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A high-quality soil provides everything needed for plant growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When tension is produced during ________,a column of water is able to extend and move all the way from the roots through the xylem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Fibrous root systems have one predominant root and many smaller roots near the top of the main root.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Plant spines or thorns are examples of modified leaves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A carrot is an example of a taproot system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



