Deck 12: Gravity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/53
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Gravity
1
If Earth had twice its present mass but it orbited at the same distance from the sun as it does now,its orbital period would be
A)4 years.
B)3 years.
C)2 years.
D)1 year.
E)6 months.
A)4 years.
B)3 years.
C)2 years.
D)1 year.
E)6 months.
1 year.
2
If you stood on a planet having a mass four times that of Earth's mass,and a radius two times that of Earth's radius,you would weigh
A)the same as you do on Earth.
B)two times more than you do on Earth.
C)two times less than you do on Earth.
D)four times more than you do on Earth.
A)the same as you do on Earth.
B)two times more than you do on Earth.
C)two times less than you do on Earth.
D)four times more than you do on Earth.
the same as you do on Earth.
3
The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A is one-sixth what it is on Planet B,and the radius of the Planet A is one-fourth that of Planet B.The mass of Planet A is what fraction of the mass of Planet B?
A)1/6
B)1/16
C)1/24
D)1/96
E)1/12
A)1/6
B)1/16
C)1/24
D)1/96
E)1/12
1/96
4
A satellite encircles Mars at a distance above its surface equal to 3 times the radius of Mars.If gm is the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of Mars,what is the acceleration due to gravity at the location of the satellite?
A)gm/9
B)0
C)gm
D)gm/3
E)gm/16
A)gm/9
B)0
C)gm
D)gm/3
E)gm/16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When a spacecraft is launched from the earth toward the sun,at what distance from the earth will the gravitational forces due to the sun and the earth cancel? Earth's mass is 5.97 × 1024 kg,the sun's mass is 1.99 × 1030 kg,and the Earth-sun distance is 1.5 × 1011 m.
A)1.3 × 108 m
B)2.6 × 108 m
C)1.3 × 1010 m
D)2.6 × 1010 m
A)1.3 × 108 m
B)2.6 × 108 m
C)1.3 × 1010 m
D)2.6 × 1010 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Two planets have the same surface gravity,but planet B has twice the radius of planet A.If planet A has mass m,what is the mass of planet B?
A)m/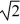
B)m
C)m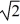
D)4m
E)m/4
A)m/
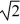
B)m
C)m
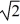
D)4m
E)m/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the gravitational force acting on a 59-kg person due to another 59-kg person standing 2.0 m away? We can model each person as a small sphere.(G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)5.8 × 10-8 N
B)8.5 × 103 N
C)1.2 × 10-7 N
D)9.8 × 10-10 N
E)2.0 × 10-9 N
A)5.8 × 10-8 N
B)8.5 × 103 N
C)1.2 × 10-7 N
D)9.8 × 10-10 N
E)2.0 × 10-9 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A spaceship is traveling to the Moon.At what point is it beyond the pull of Earth's gravity?
A)when it gets above the atmosphere
B)when it is half-way there
C)when it is closer to the Moon than it is to Earth
D)It is never beyond the pull of Earth's gravity.
A)when it gets above the atmosphere
B)when it is half-way there
C)when it is closer to the Moon than it is to Earth
D)It is never beyond the pull of Earth's gravity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Two small balls,A and B,attract each other gravitationally with a force of magnitude F.If we now double both masses and the separation of the balls,what will now be the magnitude of the attractive force on each one?
A)16F
B)8F
C)4F
D)F
E)F/4
A)16F
B)8F
C)4F
D)F
E)F/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Two planets have the same surface gravity,but planet B has twice the mass of planet A.If planet A has radius r,what is the radius of planet B?
A)r/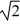
B)r
C)r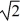
D)4r
E)2r
A)r/
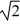
B)r
C)r
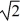
D)4r
E)2r

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The reason an astronaut in an earth satellite feels weightless is that
A)the astronaut is beyond the range of the earth's gravity.
B)the astronaut is falling.
C)the astronaut is at a point in space where the effects of the moon's gravity and the earth's gravity cancel.
D)this is a psychological effect associated with rapid motion.
E)the astronaut's acceleration is zero.
A)the astronaut is beyond the range of the earth's gravity.
B)the astronaut is falling.
C)the astronaut is at a point in space where the effects of the moon's gravity and the earth's gravity cancel.
D)this is a psychological effect associated with rapid motion.
E)the astronaut's acceleration is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Two small objects,with masses m and M,are originally a distance r apart,and the gravitational force on each one has magnitude F.The second object has its mass changed to 2M,and the distance is changed to r/4.What is the magnitude of the new gravitational force?
A)F/32
B)F/16
C)16F
D)32F
E)2F
A)F/32
B)F/16
C)16F
D)32F
E)2F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As a 70-kg person stands at the seashore gazing at the tides (which are caused by the Moon),how large is the gravitational force on that person due to the Moon? The mass of the Moon is 7.35 × 1022 kg,the distance to the Moon is 3.82 × 108 m,and G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2.
A)0.24 N
B)0.024 N
C)0.0024 N
D)0.00024 N
A)0.24 N
B)0.024 N
C)0.0024 N
D)0.00024 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Two small objects,with masses m and M,are originally a distance r apart,and the magnitude of the gravitational force on each one is F.The masses are changed to 2m and 2M,and the distance is changed to 4r.What is the magnitude of the new gravitational force?
A)F/16
B)F/4
C)16F
D)4F
E)F/2
A)F/16
B)F/4
C)16F
D)4F
E)F/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Satellite A has twice the mass of satellite B,and moves at the same orbital distance from Earth as satellite B.Compare the speeds of the two satellites.
A)The speed of B is twice the speed of A.
B)The speed of B is one-half the speed of A.
C)The speed of B is one-fourth the speed of A.
D)The speed of B is equal to the speed of A.
E)The speed of B is four times the speed of A.
A)The speed of B is twice the speed of A.
B)The speed of B is one-half the speed of A.
C)The speed of B is one-fourth the speed of A.
D)The speed of B is equal to the speed of A.
E)The speed of B is four times the speed of A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose our sun had 4 times its present mass but the earth orbited it at the same distance as it presently does.What would be the length of the year on the earth under those conditions?
A)1/4 as long as the present year
B)1/2 as long as the present year
C)the same as the present year
D)twice as long as the present year
E)four times as long as the present year
A)1/4 as long as the present year
B)1/2 as long as the present year
C)the same as the present year
D)twice as long as the present year
E)four times as long as the present year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Planet A has twice the mass of Planet B.From this information,what can we conclude about the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of Planet A compared to that at the surface of Planet B?
A)The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A must be twice as great as the acceleration due to gravity on Planet B.
B)The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A must be four times as great as the acceleration due to gravity on Planet B.
C)The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A is the same as the acceleration due to gravity on Planet B.
D)The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A is greater than the acceleration due to gravity on Planet B,but we cannot say how much greater.
E)We cannot conclude anything about the acceleration due to gravity on Planet A without knowing the radii of the two planets.
A)The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A must be twice as great as the acceleration due to gravity on Planet B.
B)The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A must be four times as great as the acceleration due to gravity on Planet B.
C)The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A is the same as the acceleration due to gravity on Planet B.
D)The acceleration due to gravity on Planet A is greater than the acceleration due to gravity on Planet B,but we cannot say how much greater.
E)We cannot conclude anything about the acceleration due to gravity on Planet A without knowing the radii of the two planets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A hypothetical planet has a mass of one-half that of the earth and a radius of twice that of the earth.What is the acceleration due to gravity on the planet in terms of g,the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth?
A)g
B)g/2
C)g/4
D)g/8
E)g/16
A)g
B)g/2
C)g/4
D)g/8
E)g/16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An piece of space debris is released from rest at an altitude that is two earth radii from the center of the earth.Compared to its weight on Earth,the weight of this debris is
A)zero.
B)the same as on the surface of the earth.
C)one-half of its weight on the surface of the earth.
D)one-third of its weight on the surface of the earth.
E)one-quarter of its weight on the surface of the earth.
A)zero.
B)the same as on the surface of the earth.
C)one-half of its weight on the surface of the earth.
D)one-third of its weight on the surface of the earth.
E)one-quarter of its weight on the surface of the earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

Mithra is an unknown planet that has two moons,A and B,in circular orbits around it.The table summarizes the hypothetical data about these moons.What is the magnitude of the maximum gravitational force that Moon A exerts on Moon B? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)1.6 × 1013 N
B)4.4 × 1013 N
C)1.0 × 1014 N
D)2.0 × 1014 N
E)4.0 × 1014 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What would be the weight of a 59.1-kg astronaut on a planet with the same density as Earth and having twice Earth's radius?
A)580 N
B)290 N
C)1160 N
D)2320 N
E)1200 N
A)580 N
B)290 N
C)1160 N
D)2320 N
E)1200 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The mass of Pluto is 1.31 × 1022 kg and its radius is 1.15 × 106 m.What is the acceleration of a freely-falling object at the surface of Pluto if it has no atmosphere? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)0.661 m/s2
B)9.81 m/s2
C)1.62 m/s2
D)3.72 m/s2
E)0.140 m/s2
A)0.661 m/s2
B)9.81 m/s2
C)1.62 m/s2
D)3.72 m/s2
E)0.140 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An astronaut goes out for a "space-walk" at a distance above the earth equal to the radius of the earth.What is her acceleration due to gravity at that point?
A)zero
B)g
C)g/2
D)g/4
E)g/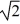
A)zero
B)g
C)g/2
D)g/4
E)g/

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
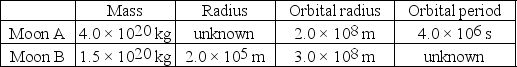
Mithra is an unknown planet that has two airless moons,A and B,in circular orbits around it.The table summarizes the hypothetical data about these moons.If you dropped a laser at the surface of Moon B,at what rate would it accelerate toward the ground? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)0.10 m/s2
B)0.15 m/s2
C)0.20 m/s2
D)0.25 m/s2
E)0.30 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Planet Z-34 has a mass equal to one-third that of Earth and a radius equal to one-third that of Earth.With g representing,as usual,the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of Earth,the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of Z-34 is
A)g/3.
B)3g.
C)6g.
D)g/9.
E)9g.
A)g/3.
B)3g.
C)6g.
D)g/9.
E)9g.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A spaceship with a mass of 2.8 × 106 kg is traveling toward two spherical asteroids,each with a mass of 5.0 × 1016 kg,that are 40 km apart center-to-center.Its path is perpendicular to the line joining the asteroids and is aimed at the midpoint of that line.What is the net gravitational force exerted by the asteroids on the spaceship when the spaceship is 30 km away from that midpoint? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)12,000 N
B)8,000 N
C)16,000 N
D)6,200 N
E)18,000 N
A)12,000 N
B)8,000 N
C)16,000 N
D)6,200 N
E)18,000 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The radius of the earth is R.At what distance above the earth's surface will the acceleration of gravity be 4.9 m/s2?
A)0.41 R
B)0.50 R
C)1.00 R
D)1.41 R
E)0.25 R
A)0.41 R
B)0.50 R
C)1.00 R
D)1.41 R
E)0.25 R

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The mass of the Moon is 7.4 × 1022 kg,its radius is 1.74 × 103 km,and it has no atmosphere.What is the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the Moon? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)2.8 × 106 m/s2
B)9.8 m/s2
C)4.9 m/s2
D)1.6 m/s2
E)0.80 m/s2
A)2.8 × 106 m/s2
B)9.8 m/s2
C)4.9 m/s2
D)1.6 m/s2
E)0.80 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
At a distance of 14,000 km from the center of Planet Z-99,the acceleration due to gravity is 32 m/s2.What is the acceleration due to gravity at a point 28,000 km from the center of this planet?
A)8.0 m/s2
B)16 m/s2
C)128 m/s2
D)4.0 m/s2
E)2.0 m/s2
A)8.0 m/s2
B)16 m/s2
C)128 m/s2
D)4.0 m/s2
E)2.0 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
At a given point above Earth's surface,the acceleration due to gravity is equal to 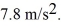
What is the altitude of this point above Earth's surface? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2,Mearth = 5.97 × 1024 kg,Rearth = 6.38 × 106 m)
A)770 km
B)970 km
C)1,500 km
D)2,000 km
E)2,400 km
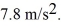
What is the altitude of this point above Earth's surface? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2,Mearth = 5.97 × 1024 kg,Rearth = 6.38 × 106 m)
A)770 km
B)970 km
C)1,500 km
D)2,000 km
E)2,400 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What would be the weight of a 59.1-kg astronaut on a planet twice as massive as Earth and having twice Earth's radius?
A)580 N
B)290 N
C)1160 N
D)118 N
E)1200 N
A)580 N
B)290 N
C)1160 N
D)118 N
E)1200 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
From what height above the surface of the earth should an object be dropped to initially experience an acceleration of 0.54g? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2,Mearth = 5.97 × 1024 kg,Rearth = 6.38 × 106 m)
A)2300 km
B)1700 km
C)5400 km
D)2900 km
A)2300 km
B)1700 km
C)5400 km
D)2900 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
At their closest approach,Venus and Earth are 4.20 × 1010 m apart.The mass of Venus is 4.87 × 1024 kg,the mass of Earth is 5.97 × 1024 kg,and G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2.What is the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by Venus on Earth at that point?
A)1.10 × 1018 N
B)4.62 × 1028 N
C)5.43 × 1026 N
D)6.30 × 1020 N
E)1.72 × 1019 N
A)1.10 × 1018 N
B)4.62 × 1028 N
C)5.43 × 1026 N
D)6.30 × 1020 N
E)1.72 × 1019 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The earth has radius R.A satellite of mass 100 kg is in orbit at an altitude of 3R above the earth's surface.What is the satellite's weight at the altitude of its orbit?
A)61 N
B)110 N
C)9000 N
D)16,000 N
A)61 N
B)110 N
C)9000 N
D)16,000 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An object weighs 432 N on the surface of the earth.The earth has radius R.If the object is raised to a height of 3R above the earth's surface,what is its weight?
A)108 N
B)48.0 N
C)27.0 N
D)305 N
E)144 N
A)108 N
B)48.0 N
C)27.0 N
D)305 N
E)144 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In another solar system,a planet has an airless moon Zygo that is 4.0 × 105 m in diameter.Experiments reveal that a freely falling object at the surface of Zygo accelerates at 0.20 m/s2.What is the mass of Zygo? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)2.4 × 1019 kg
B)4.8 × 1019 kg
C)1.2 × 1020 kg
D)2.4 × 1020 kg
E)4.8 × 1020 kg
A)2.4 × 1019 kg
B)4.8 × 1019 kg
C)1.2 × 1020 kg
D)2.4 × 1020 kg
E)4.8 × 1020 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
By how many newtons does the weight of a 100-kg person decrease when he goes from sea level to mountain top at an altitude of 5000 m? The mean radius of the earth is 6.38 × 106 m.
A)0.60 N
B)1.5 N
C)2.6 N
D)3.6 N
E)9.8 N
A)0.60 N
B)1.5 N
C)2.6 N
D)3.6 N
E)9.8 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the distance from the center of the Moon to the point between Earth and the Moon where the gravitational pulls of Earth and Moon are equal? The mass of Earth is 5.97 × 1024 kg,the mass of the Moon is 7.35 × 1022 kg,the center-to-center distance between Earth and the Moon is 3.84 × 108 m,and G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2.
A)3.45 × 108 m
B)3.84 × 107 m
C)4.69 × 106 m
D)3.83 × 106 m
E)4.69 × 107 m
A)3.45 × 108 m
B)3.84 × 107 m
C)4.69 × 106 m
D)3.83 × 106 m
E)4.69 × 107 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An astronaut drops a marble on the surface of the airless Planet Z-49 and observes that it takes 1.02 s for the marble to fall 2.00 m starting from rest.She also knows that the radius of Z-49 is 3.39 × 106 m.From this information,what will she determine for the mass of Z-49? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)3.30 ×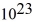 kg.
kg.
B)6.62 ×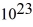 kg.
kg.
C)4.62 ×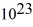 kg.
kg.
D)8.09 ×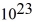 kg.
kg.
E)9.95 ×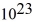 kg.
kg.
A)3.30 ×
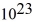 kg.
kg.B)6.62 ×
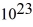 kg.
kg.C)4.62 ×
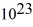 kg.
kg.D)8.09 ×
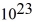 kg.
kg.E)9.95 ×
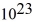 kg.
kg.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Three identical 50-kg balls are held at the corners of an equilateral triangle,30 cm on each side.If one of the balls is released,what is the magnitude of its initial acceleration if the only forces acting on it are the gravitational forces due to the other two masses? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)3.7 × 10-8 m/s2
B)2.5 × 10-8 m/s2
C)1.9 × 10-8 m/s2
D)4.2 × 10-8 m/s2
E)6.4 × 10-8 m/s2
A)3.7 × 10-8 m/s2
B)2.5 × 10-8 m/s2
C)1.9 × 10-8 m/s2
D)4.2 × 10-8 m/s2
E)6.4 × 10-8 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose NASA wants a satellite to revolve around Earth 5 times a day.What should be the radius of its orbit if we neglect the presence of the Moon? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2,Mearth = 5.97 × 1024 kg)
A)1.44 × 107 m
B)0.69 × 107 m
C)7.22 × 107 m
D)2.11 × 107 m
A)1.44 × 107 m
B)0.69 × 107 m
C)7.22 × 107 m
D)2.11 × 107 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A satellite that is in a circular orbit 230 km above the surface of the planet Zeeman-474 has an orbital period of 89 min.The radius of Zeeman-474 is 6.38 × 106 m.What is the mass of this planet? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)5.0 × 1024 kg
B)5.5 × 1024 kg
C)6.0 × 1024 kg
D)6.5 × 1024 kg
A)5.0 × 1024 kg
B)5.5 × 1024 kg
C)6.0 × 1024 kg
D)6.5 × 1024 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Find the orbital speed of an ice cube in the rings of Saturn.The mass of Saturn is 5.68 x 1026 kg,and use an orbital radius of 1.00 x 105 km.(G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)19.5 km/s
B)27.5 km/s
C)13.8 km/s
A)19.5 km/s
B)27.5 km/s
C)13.8 km/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A satellite having orbital speed V orbits a planet of mass M.If the planet had half as much mass,the orbital speed of the satellite at the same distance from the center would be
A)V .
.
B)2V.
C)V.
D)V/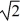 .
.
E)V/2.
A)V
 .
.B)2V.
C)V.
D)V/
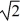 .
.E)V/2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A spherically symmetric planet has four times the earth's mass and twice its radius.If a jar of peanut butter weighs 12 N on the surface of the Earth,how much would it weigh on the surface of this planet?
A)3.0 N
B)6.0 N
C)12 N
D)24 N
E)36 N
A)3.0 N
B)6.0 N
C)12 N
D)24 N
E)36 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
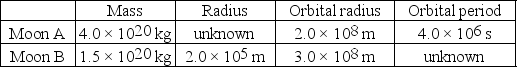
Mithra is an unknown planet that has two moons,A and B,in circular orbits around it.The table summarizes the hypothetical data about these moons.What is the mass of Mithra? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)1 × 1022 kg
B)3 × 1022 kg
C)1 × 1023 kg
D)3 × 1023 kg
E)1 × 1024 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Asteroid Ida was photographed by the Galileo spacecraft in 1993,and the photograph revealed that the asteroid has a small moon,which has been named Dactyl.From the dimensions of Ida and its general features,one can estimate the mass of Ida to be 4.5 × 1016 kg,and the distance between Dactyl and Ida is approximately 90 km.Assuming a circular orbit,what would be the orbital speed of Dactyl? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)5.8 m/s
B)11 m/s
C)2.3 m/s
D)2.9 m/s
E)30 m/s
A)5.8 m/s
B)11 m/s
C)2.3 m/s
D)2.9 m/s
E)30 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The innermost satellite of Jupiter orbits the planet with a radius of 422 × 103 km and a period of 1.77 days.What is the mass of Jupiter? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)1.33 × 1027 kg
B)1.50 × 1027 kg
C)1.72 × 1027 kg
D)1.89 × 1027 kg
E)3.08 × 1027 kg
A)1.33 × 1027 kg
B)1.50 × 1027 kg
C)1.72 × 1027 kg
D)1.89 × 1027 kg
E)3.08 × 1027 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A satellite of mass M takes time T to orbit a planet.If the satellite had twice as much mass,the time for it to orbit the planet at the same altitude would be
A)4T.
B)2T.
C)T.
D)T/2.
E)T/4.
A)4T.
B)2T.
C)T.
D)T/2.
E)T/4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
You are the science officer on a visit to a distant solar system.Prior to landing on a planet you measure its diameter to be 1.8 × 107 m.You have previously determined that the planet orbits 2.9 × 1011 m from its star with a period of 402 earth days.Once on the surface you find that the acceleration due to gravity is 19.5 m/s2.What are the masses of (a)the planet and (b)the star? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)(a)2.4 kg ×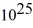 kg,(b)1.2 kg ×
kg,(b)1.2 kg ×
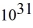 kg
kg
B)(a)4.3 kg ×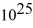 kg,(b)1.2 kg ×
kg,(b)1.2 kg ×
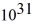 kg
kg
C)(a)2.4 kg ×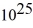 kg,(b)7.1 kg ×
kg,(b)7.1 kg ×
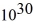 kg
kg
D)(a)4.3 kg ×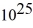 kg,(b)7.1 kg ×
kg,(b)7.1 kg ×
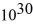 kg
kg
A)(a)2.4 kg ×
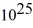 kg,(b)1.2 kg ×
kg,(b)1.2 kg ×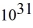 kg
kgB)(a)4.3 kg ×
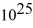 kg,(b)1.2 kg ×
kg,(b)1.2 kg ×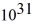 kg
kgC)(a)2.4 kg ×
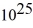 kg,(b)7.1 kg ×
kg,(b)7.1 kg ×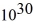 kg
kgD)(a)4.3 kg ×
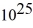 kg,(b)7.1 kg ×
kg,(b)7.1 kg ×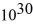 kg
kg
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In another solar system,a planet has a moon that is 4.0 × 105 m in diameter.Measurements reveal that this moon takes 3.0 x 105 s to make each orbit of diameter 1.8 × 108 m.What is the mass of the planet? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)1.2 × 1024 kg
B)1.7 × 1024 kg
C)2.4 × 1024 kg
D)3.4 × 1024 kg
E)4.8 × 1024 kg
A)1.2 × 1024 kg
B)1.7 × 1024 kg
C)2.4 × 1024 kg
D)3.4 × 1024 kg
E)4.8 × 1024 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Europa,a satellite of Jupiter,has an orbital diameter of 1.34 × 109 m and a period of 3.55 days.What is the mass of Jupiter? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)1.53 × 1027 kg
B)1.65 × 1027 kg
C)1.07 × 1027 kg
D)1.89 × 1027 kg
E)3.08 × 1027 kg
A)1.53 × 1027 kg
B)1.65 × 1027 kg
C)1.07 × 1027 kg
D)1.89 × 1027 kg
E)3.08 × 1027 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The captain of a spaceship orbiting planet X discovers that to remain in orbit at 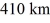
From the planet's center,she needs to maintain a speed of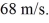
What is the mass of planet X? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)2.8 × 1019 kg
B)4.2 × 1017 kg
C)2.8 × 1016 kg
D)4.2 × 1014 kg
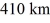
From the planet's center,she needs to maintain a speed of
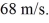
What is the mass of planet X? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ∙ m2/kg2)
A)2.8 × 1019 kg
B)4.2 × 1017 kg
C)2.8 × 1016 kg
D)4.2 × 1014 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 53 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



