Deck 25: A: Factor Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: A: Factor Markets
1
Suppose that the labor supply curve for a large university in a small town is given by w = 160 + 0.05L, where L is number of units of labor per week and w is the weekly wage paid per unit of labor. If the university is currently hiring 1,000 units of labor per week, the marginal cost of an additional unit of labor
A) equals the wage rate.
B) equals the wage rate plus $50.
C) is twice the wage rate.
D) equals the wage rate plus $100.
E) equals the wage rate plus $150.
A) equals the wage rate.
B) equals the wage rate plus $50.
C) is twice the wage rate.
D) equals the wage rate plus $100.
E) equals the wage rate plus $150.
B
2
Suppose that in Problem 2, the demand curve for mineral water is given by p = 60 - 8q, where p is the price per bottle paid by consumers and q is the number of bottles purchased by consumers. Mineral water is supplied to consumers by a monopolistic distributor, who buys from a monopolist producer who is able to produce mineral water at zero cost. The producer charges the distributor a price of c per bottle, that will maximize the producer's total revenue. Given his marginal cost of c, the distributor chooses an output to maximize profits. The price paid by consumers under this arrangement is
A) $30.
B) $45.
C) $3.75.
D) $7.50.
E) $15.
A) $30.
B) $45.
C) $3.75.
D) $7.50.
E) $15.
B
3
Suppose that the labor supply curve for a large university in a small town is given by w = 160 + 0.03L, where L is number of units of labor per week and w is the weekly wage paid per unit of labor. If the university is currently hiring 1,000 units of labor per week, the marginal cost of an additional unit of labor
A) equals the wage rate.
B) is twice the wage rate.
C) equals the wage rate plus $60.
D) equals the wage rate plus $30.
E) equals the wage rate plus $90.
A) equals the wage rate.
B) is twice the wage rate.
C) equals the wage rate plus $60.
D) equals the wage rate plus $30.
E) equals the wage rate plus $90.
D
4
In Problem 1, suppose that the demand curve for antimacassars is p 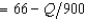 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
A) 14,625 antimacassars.
B) 7,312.50 antimacassars.
C) 21,937.50 antimacassars.
D) 4,826.25 antimacassars.
E) 3,656.25 antimacassars.
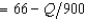 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest toA) 14,625 antimacassars.
B) 7,312.50 antimacassars.
C) 21,937.50 antimacassars.
D) 4,826.25 antimacassars.
E) 3,656.25 antimacassars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In Problem 1, suppose that the demand curve for antimacassars is p 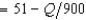 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
A) 16,875 antimacassars.
B) 5,625 antimacassars.
C) 3,712.50 antimacassars.
D) 11,250 antimacassars.
E) 2,812.50 antimacassars.
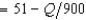 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest toA) 16,875 antimacassars.
B) 5,625 antimacassars.
C) 3,712.50 antimacassars.
D) 11,250 antimacassars.
E) 2,812.50 antimacassars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose that the labor supply curve for a large university in a small town is given by w = 140 + 0.02L, where L is number of units of labor per week and w is the weekly wage paid per unit of labor. If the university is currently hiring 1,000 units of labor per week, the marginal cost of an additional unit of labor
A) equals the wage rate plus $40.
B) is twice the wage rate.
C) equals the wage rate plus $20.
D) equals the wage rate.
E) equals the wage rate plus $60.
A) equals the wage rate plus $40.
B) is twice the wage rate.
C) equals the wage rate plus $20.
D) equals the wage rate.
E) equals the wage rate plus $60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Rabelaisian Restaurants has a monopoly in the town of Upper Glutton. Its production function is Q = 10L, where L is the amount of labor it uses and Q is the number of meals produced. Rabelaisian Restaurants finds that in order to hire L units of labor, it must pay a wage of 10 + .1L per unit of labor. The demand curve for meals at Rabelaisian Restaurants is given by P 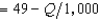 . The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
A) 24,000 meals.
B) 2,500 meals.
C) 3,000 meals.
D) 12,000 meals.
E) 1,500 meals.
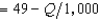 . The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants isA) 24,000 meals.
B) 2,500 meals.
C) 3,000 meals.
D) 12,000 meals.
E) 1,500 meals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Suppose that in Problem 2, the demand curve for mineral water is given by p = 20 - 16q, where p is the price per bottle paid by consumers and q is the number of bottles purchased by consumers. Mineral water is supplied to consumers by a monopolistic distributor, who buys from a monopolist producer who is able to produce mineral water at zero cost. The producer charges the distributor a price of c per bottle, that will maximize the producer's total revenue. Given his marginal cost of c, the distributor chooses an output to maximize profits. The price paid by consumers under this arrangement is
A) $10.
B) $15.
C) $1.25.
D) $.63.
E) $5.
A) $10.
B) $15.
C) $1.25.
D) $.63.
E) $5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In Problem 1, suppose that the demand curve for antimacassars is p 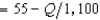 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
A) 4,900.50 antimacassars.
B) 22,275 antimacassars.
C) 7,425 antimacassars.
D) 14,850 antimacassars.
E) 3,712.50 antimacassars.
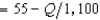 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest toA) 4,900.50 antimacassars.
B) 22,275 antimacassars.
C) 7,425 antimacassars.
D) 14,850 antimacassars.
E) 3,712.50 antimacassars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Rabelaisian Restaurants has a monopoly in the town of Upper Glutton. Its production function is Q = 40L, where L is the amount of labor it uses and Q is the number of meals produced. Rabelaisian Restaurants finds that in order to hire L units of labor, it must pay a wage of 40 + .1L per unit of labor. The demand curve for meals at Rabelaisian Restaurants is given by P 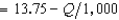 . The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
A) 12,000 meals.
B) 1,000 meals.
C) 6,000 meals.
D) 1,500 meals.
E) 750 meals.
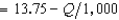 . The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants isA) 12,000 meals.
B) 1,000 meals.
C) 6,000 meals.
D) 1,500 meals.
E) 750 meals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Rabelaisian Restaurants has a monopoly in the town of Upper Glutton. Its production function is Q = 10L, where L is the amount of labor it uses and Q is the number of meals produced. Rabelaisian Restaurants finds that in order to hire L units of labor, it must pay a wage of 10 + .1L per unit of labor. The demand curve for meals at Rabelaisian Restaurants is given by P 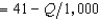 =. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
=. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
A) 2,500 meals.
B) 20,000 meals.
C) 10,000 meals.
D) 2,000 meals.
E) 1,250 meals.
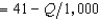 =. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
=. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants isA) 2,500 meals.
B) 20,000 meals.
C) 10,000 meals.
D) 2,000 meals.
E) 1,250 meals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose that the labor supply curve for a large university in a small town is given by w = 60 + 0.08L, where L is number of units of labor per week and w is the weekly wage paid per unit of labor. If the university is currently hiring 1,000 units of labor per week, the marginal cost of an additional unit of labor
A) equals the wage rate.
B) is twice the wage rate.
C) equals the wage rate plus $160.
D) equals the wage rate plus $80.
E) equals the wage rate plus $240.
A) equals the wage rate.
B) is twice the wage rate.
C) equals the wage rate plus $160.
D) equals the wage rate plus $80.
E) equals the wage rate plus $240.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose that in Problem 2, the demand curve for mineral water is given by p = 20 - 12q, where p is the price per bottle paid by consumers and q is the number of bottles purchased by consumers. Mineral water is supplied to consumers by a monopolistic distributor, who buys from a monopolist producer who is able to produce mineral water at zero cost. The producer charges the distributor a price of c per bottle, that will maximize the producer's total revenue. Given his marginal cost of c, the distributor chooses an output to maximize profits. The price paid by consumers under this arrangement is
A) $15.
B) $.83.
C) $1.67.
D) $10.
E) $5.
A) $15.
B) $.83.
C) $1.67.
D) $10.
E) $5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose that in Problem 2, the demand curve for mineral water is given by p = 40 - 16q, where p is the price per bottle paid by consumers and q is the number of bottles purchased by consumers. Mineral water is supplied to consumers by a monopolistic distributor, who buys from a monopolist producer who is able to produce mineral water at zero cost. The producer charges the distributor a price of c per bottle, that will maximize the producer's total revenue. Given his marginal cost of c, the distributor chooses an output to maximize profits. The price paid by consumers under this arrangement is
A) $2.50.
B) $20.
C) $1.25.
D) $30.
E) $10.
A) $2.50.
B) $20.
C) $1.25.
D) $30.
E) $10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Rabelaisian Restaurants has a monopoly in the town of Upper Glutton. Its production function is Q = 30L, where L is the amount of labor it uses and Q is the number of meals produced. Rabelaisian Restaurants finds that in order to hire L units of labor, it must pay a wage of 30 + .1L per unit of labor. The demand curve for meals at Rabelaisian Restaurants is given by P 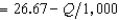 . The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
A) 12,000 meals.
B) 24,000 meals.
C) 3,000 meals.
D) 2,500 meals.
E) 1,500 meals.
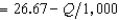 . The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants isA) 12,000 meals.
B) 24,000 meals.
C) 3,000 meals.
D) 2,500 meals.
E) 1,500 meals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose that in Problem 2, the demand curve for mineral water is given by p = 70 - 16q, where p is the price per bottle paid by consumers and q is the number of bottles purchased by consumers. Mineral water is supplied to consumers by a monopolistic distributor, who buys from a monopolist producer who is able to produce mineral water at zero cost. The producer charges the distributor a price of c per bottle, that will maximize the producer's total revenue. Given his marginal cost of c, the distributor chooses an output to maximize profits. The price paid by consumers under this arrangement is
A) $52.50.
B) $35.
C) $4.38.
D) $2.19.
E) $17.50.
A) $52.50.
B) $35.
C) $4.38.
D) $2.19.
E) $17.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Rabelaisian Restaurants has a monopoly in the town of Upper Glutton. Its production function is Q = 10L, where L is the amount of labor it uses and Q is the number of meals produced. Rabelaisian Restaurants finds that in order to hire L units of labor, it must pay a wage of 10 + .1L per unit of labor. The demand curve for meals at Rabelaisian Restaurants is given by P 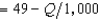 . The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
A) 3,000 meals.
B) 12,000 meals.
C) 2,500 meals.
D) 24,000 meals.
E) 1,500 meals.
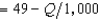 . The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants is
. The profit-maximizing output for Rabelaisian Restaurants isA) 3,000 meals.
B) 12,000 meals.
C) 2,500 meals.
D) 24,000 meals.
E) 1,500 meals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Suppose that the labor supply curve for a large university in a small town is given by w = 140 + 0.05L, where L is number of units of labor per week and w is the weekly wage paid per unit of labor. If the university is currently hiring 1,000 units of labor per week, the marginal cost of an additional unit of labor
A) is twice the wage rate.
B) equals the wage rate plus $50.
C) equals the wage rate plus $100.
D) equals the wage rate.
E) equals the wage rate plus $150.
A) is twice the wage rate.
B) equals the wage rate plus $50.
C) equals the wage rate plus $100.
D) equals the wage rate.
E) equals the wage rate plus $150.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In Problem 1, suppose that the demand curve for antimacassars is p 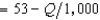 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
A) 6,500 antimacassars.
B) 13,000 antimacassars.
C) 19,500 antimacassars.
D) 4,290 antimacassars.
E) 3,250 antimacassars.
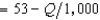 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest toA) 6,500 antimacassars.
B) 13,000 antimacassars.
C) 19,500 antimacassars.
D) 4,290 antimacassars.
E) 3,250 antimacassars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In Problem 1, suppose that the demand curve for antimacassars is p 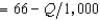 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
A) 24,375 antimacassars.
B) 16,250 antimacassars.
C) 5,362.50 antimacassars.
D) 8,125 antimacassars.
E) 4,062.50 antimacassars.
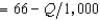 . The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest to
. The firm's profit-maximizing output is closest toA) 24,375 antimacassars.
B) 16,250 antimacassars.
C) 5,362.50 antimacassars.
D) 8,125 antimacassars.
E) 4,062.50 antimacassars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



