Deck 21: Firm Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Firm Supply
1
A firm produces one output, using one input, with the production function 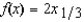 , where x is the amount of input. The cost function for this firm is proportional to the price of the input times the cube of the amount of output.
, where x is the amount of input. The cost function for this firm is proportional to the price of the input times the cube of the amount of output.
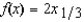 , where x is the amount of input. The cost function for this firm is proportional to the price of the input times the cube of the amount of output.
, where x is the amount of input. The cost function for this firm is proportional to the price of the input times the cube of the amount of output.True
2
In a perfectly competitive industry, the demand curve for the total output of the industry may be downward sloping.
True
3
The area under the marginal cost curve measures total variable costs.
True
4
A profit-maximizing firm continues to operate even though it is losing money. It sells its product at a price of $100.
A) Average total cost is less than $100.
B) Average fixed cost is less than $100.
C) Marginal cost is increasing.
D) Average variable cost is less than $100.
E) Marginal cost is decreasing.
A) Average total cost is less than $100.
B) Average fixed cost is less than $100.
C) Marginal cost is increasing.
D) Average variable cost is less than $100.
E) Marginal cost is decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The change in producer's surplus when the market price changes from p1 to p2 is half of the area to the left of the marginal cost curve between p1 and p2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Mr. O. Carr has the cost function c(y) = y2 + 100 if his output, y, is positive and c(0) = 0. If the price of output is 25, Mr. Carr's profit-maximizing output is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A firm with the cost function c(y) = 20y2 + 500 has a U-shaped cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A firm faces competitive markets both for its inputs and its outputs. If its long-run supply curve is q = 3p,then it cannot have constant returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Marge Costa produces plastic dog dishes using a process that requires only labor and plastic as inputs and has constant returns to scale. With the process she is currently using, a laborer can turn out 30 dog dishes an hour. The wage rate is $9 per hour. The plastic in a dog dish costs Marge $.10. She has no other costs besides labor and plastic. Marge faces a perfectly competitive market for plastic dog dishes, and she decides that she is maximizing profits when she makes 300 dog dishes an hour. What is the market price of dog dishes?
A) $.21
B) $.32
C) $.40
D) $.27
E) $.28
A) $.21
B) $.32
C) $.40
D) $.27
E) $.28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Mr. O. Carr has the cost function c(y) = y2 + 144 if his output, y, is positive and c(0) = 0. If the price of output is 18, Mr. Carr's profit-maximizing output is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Price equals marginal cost is a sufficient condition for profit maximization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A competitive firm has a continuous marginal cost curve. It finds that as output increases, its marginal cost curve first rises, then falls, then rises again. If it wants to maximize profits, the firm should never produce at a positive output where price equals marginal cost and marginal cost decreases as output increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A competitive firm uses two variable factors to produce its output, with a production function q = min{x1, x2}.The price of factor 1 is $4 and the price of factor 2 is $5. Due to a lack of warehouse space, the company cannot use more than 17 units of x1. The firm must pay a fixed cost of $136 if it produces any positive amount but doesn't have to pay this cost if it produces no output. What is the smallest integer price that would make a firm willing to produce a positive amount?
A) $36
B) $33
C) $21
D) $9
E) $17
A) $36
B) $33
C) $21
D) $9
E) $17

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A competitive firm uses two variable factors to produce its output, with a production function q = min{x1, x2}.The price of factor 1 is $8 and the price of factor 2 is $5. Due to a lack of warehouse space, the company cannot use more than 10 units of x1. The firm must pay a fixed cost of $80 if it produces any positive amount but doesn't have to pay this cost if it produces no output. What is the smallest integer price that would make a firm willing to produce a positive amount?
A) $44
B) $41
C) $29
D) $13
E) $21
A) $44
B) $41
C) $29
D) $13
E) $21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Mr. O. Carr has the cost function c(y) = y2 + 64 if his output, y, is positive and c(0) = 0. If the price of output is 12, Mr. Carr's profit-maximizing output is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A firm in a competitive industry takes account of the fact that the demand curve it confronts has a significant negative slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Average fixed costs never increase with output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A profit-maximizing dairy farm is currently producing 10,000 gallons of milk per day. The government is considering two alternative policies. One is to give the farm a lump sum subsidy of $500 per month. The other policy is to give the farm a subsidy of $.05 per gallon of output.
A) Both kinds of subsidy will increase production at this farm.
B) Neither subsidy will affect production at this farm, since output is determined by profit maximization.
C) Production at this farm will be increased if the per-unit subsidy is adopted but not if the lump sum subsidy is adopted.
D) Which subsidy has the greater effect on production at this farm depends on whether fixed costs are greater than variable costs.
E) Production will be increased by either kind of subsidy if and only if there are not decreasing returns to scale.
A) Both kinds of subsidy will increase production at this farm.
B) Neither subsidy will affect production at this farm, since output is determined by profit maximization.
C) Production at this farm will be increased if the per-unit subsidy is adopted but not if the lump sum subsidy is adopted.
D) Which subsidy has the greater effect on production at this farm depends on whether fixed costs are greater than variable costs.
E) Production will be increased by either kind of subsidy if and only if there are not decreasing returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A competitive firm uses two variable factors to produce its output, with a production function q = min{x1, x2}.The price of factor 1 is $4 and the price of factor 2 is $1. Due to a lack of warehouse space, the company cannot use more than 15 units of x1. The firm must pay a fixed cost of $90 if it produces any positive amount but doesn't have to pay this cost if it produces no output. What is the smallest integer price that would make a firm willing to produce a positive amount?
A) $15
B) $21
C) $5
D) $24
E) $11
A) $15
B) $21
C) $5
D) $24
E) $11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Two firms have the same technology and must pay the same wages for labor. They have identical factories, but firm 1 paid a higher price for its factory than firm 2 did. If they are both profit maximizers and have upward-sloping marginal cost curves, then we would expect firm 1 to have a higher output than firm 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A firm's production function is f(x1, x2) = 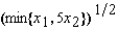 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 per unit and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $25 per unit, then its supply function is given by the equation S(p) =
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 per unit and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $25 per unit, then its supply function is given by the equation S(p) =
A) .
B) max{w1, 5w2}p.
C) min{w1, 5w2}p.
D) 10p.
E) min{5p, 125p}p.
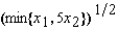 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 per unit and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $25 per unit, then its supply function is given by the equation S(p) =
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 per unit and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $25 per unit, then its supply function is given by the equation S(p) =A) .
B) max{w1, 5w2}p.
C) min{w1, 5w2}p.
D) 10p.
E) min{5p, 125p}p.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A competitive firm produces its output according to the production function y = min{x3, 1000}. Let p be the price of output, and let the price of input x be $1. The profit maximizing output for this firm is
A) 1,000 if p > 1 and 0 otherwise.
B) 10 for all p.
C) 1,000 for all p.
D) 0 if pE) None of the above.
A) 1,000 if p > 1 and 0 otherwise.
B) 10 for all p.
C) 1,000 for all p.
D) 0 if p

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that Dent Carr's long-run total cost of repairing s cars per week is c(s) = 3s2 + 108. If the price he receives for repairing a car is $18, then in the long run, how many cars will he fix per week if he maximizes profits?
A) 4.50
B) 0
C) 6
D) 3
E) 9
A) 4.50
B) 0
C) 6
D) 3
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A competitive firm has a single factory with the cost function c(y) = 4y2 + 89 and produces 28 units in order to maximize profits. Although the price of output does not change, the firm decides to build a second factory with the cost function c(y) = 8y2 + 39. To maximize its profits, how many units should it produce in the second factory?
A) 14
B) 21
C) 9
D) 13
E) None of the above.
A) 14
B) 21
C) 9
D) 13
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose that Dent Carr's long-run total cost of repairing s cars per week is c(s) = 3s2 + 75. If the price he receives for repairing a car is $18, then in the long run, how many cars will he fix per week if he maximizes profits?
A) 3
B) 0
C) 6
D) 4.50
E) 9
A) 3
B) 0
C) 6
D) 4.50
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Irma's production function is f(x1, x2) = 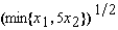 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $20, then her supply function is given by the equation
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $20, then her supply function is given by the equation
A) S(p) =.
B) S(p) = p(max{w1, 5w2})2.
C) S(p) = p(min{w1, 5w2})2.
D) S(p) = 9p.
E) S(p) = min{5p, 100p}.
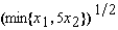 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $20, then her supply function is given by the equation
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $20, then her supply function is given by the equationA) S(p) =.
B) S(p) = p(max{w1, 5w2})2.
C) S(p) = p(min{w1, 5w2})2.
D) S(p) = 9p.
E) S(p) = min{5p, 100p}.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A competitive firm has a long-run total cost function c(y) = 3y2 + 675 for y > 0 and c(0) = 0. Its long-run supply function is described as
A) y =if p > 90, y = 0 if p < 90.
B) y =if p > 88, y = 0 if p < 88.
C) y =if p > 93, y = 0 if p < 99.
D) y =if p > 93, y = 0 if p < 93.
E) y =if p > 95, y = 0 if p < 85.
A) y =if p > 90, y = 0 if p < 90.
B) y =if p > 88, y = 0 if p < 88.
C) y =if p > 93, y = 0 if p < 99.
D) y =if p > 93, y = 0 if p < 93.
E) y =if p > 95, y = 0 if p < 85.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A firm's production function is f(x1, x2) = 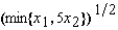 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 per unit and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $25 per unit, then its supply function is given by the equation S(p) =
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 per unit and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $25 per unit, then its supply function is given by the equation S(p) =
A) .
B) max{w1, 5w2}p.
C) min{w1, 5w2}p.
D) 10p.
E) min{5p, 125p}p.
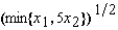 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 per unit and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $25 per unit, then its supply function is given by the equation S(p) =
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $5 per unit and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $25 per unit, then its supply function is given by the equation S(p) =A) .
B) max{w1, 5w2}p.
C) min{w1, 5w2}p.
D) 10p.
E) min{5p, 125p}p.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A firm has the long-run cost function C(q) = 3q2 + 27.In the long run, it will supply a positive amount of output, so long as the price is greater than
A) $36.
B) $44.
C) $9.
D) $18.
E) $23.
A) $36.
B) $44.
C) $9.
D) $18.
E) $23.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Irma's production function is f(x1, x2) = 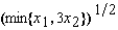 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $3 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $9, then her supply function is given by the equation
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $3 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $9, then her supply function is given by the equation
A) S(p) =.
B) S(p) = p(max{w1, 3w2})2.
C) S(p) = p(min{w1, 3w2})2.
D) S(p) = 6p.
E) S(p) = min{3p, 27p}.
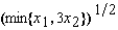 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $3 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $9, then her supply function is given by the equation
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $3 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $9, then her supply function is given by the equationA) S(p) =.
B) S(p) = p(max{w1, 3w2})2.
C) S(p) = p(min{w1, 3w2})2.
D) S(p) = 6p.
E) S(p) = min{3p, 27p}.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A competitive firm has a long-run total cost function c(y) = 2y2 + 288 for y > 0 and c(0) = 0. Its long-run supply function is described as
A) y =if p > 46, y = 0 if p < 46.
B) y =if p > 51, y = 0 if p < 54.
C) y =if p > 48, y = 0 if p < 48.
D) y =if p > 51, y = 0 if p < 51.
E) y =if p > 53, y = 0 if p < 43.
A) y =if p > 46, y = 0 if p < 46.
B) y =if p > 51, y = 0 if p < 54.
C) y =if p > 48, y = 0 if p < 48.
D) y =if p > 51, y = 0 if p < 51.
E) y =if p > 53, y = 0 if p < 43.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Irma's production function is f(x1, x2) = 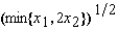 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $3 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $4, then her supply function is given by the equation
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $3 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $4, then her supply function is given by the equation
A) S(p) = p(min{w1, 2w2})2.
B) S(p) =.
C) S(p) = p(max{w1, 2w2})2.
D) S(p) = 5p.
E) S(p) = min{3p, 8p}.
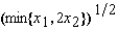 . If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $3 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $4, then her supply function is given by the equation
. If the price of factor 1 is w1 = $3 and the price of factor 2 is w2 = $4, then her supply function is given by the equationA) S(p) = p(min{w1, 2w2})2.
B) S(p) =.
C) S(p) = p(max{w1, 2w2})2.
D) S(p) = 5p.
E) S(p) = min{3p, 8p}.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A competitive firm is choosing an output level to maximize its profits in the short run. Which of the following is not necessarily true? (Assume that marginal cost is not constant and is well defined at all levels of output.)
A) Marginal cost is at least as large as average variable cost.
B) Total revenues are at least as large as total costs.
C) Price is at least as large as average variable cost.
D) Price equals marginal cost.
E) The marginal cost curve is rising.
A) Marginal cost is at least as large as average variable cost.
B) Total revenues are at least as large as total costs.
C) Price is at least as large as average variable cost.
D) Price equals marginal cost.
E) The marginal cost curve is rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A competitive firm produces its output according to the production function y = min{x2, 100}. Let w be the price of the factor x, and let the price of output be $1.The demand for x, when the price of x is w, is
A) 10 when w < 1 and 100 otherwise.
B) 100 for all w.
C) 10 for all w.
D) 0 if w > 10 and 10 otherwise.
E) None of the above.
A) 10 when w < 1 and 100 otherwise.
B) 100 for all w.
C) 10 for all w.
D) 0 if w > 10 and 10 otherwise.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A firm has the long-run cost function C(q) = 7q2 + 175.In the long run, it will supply a positive amount of output, so long as the price is greater than
A) $70.
B) $148.
C) $35.
D) $140.
E) $75.
A) $70.
B) $148.
C) $35.
D) $140.
E) $75.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A firm has the long-run cost function C(q) = 6q2 + 486.In the long run, it will supply a positive amount of output, so long as the price is greater than
A) $216.
B) $54.
C) $224.
D) $108.
E) $113.
A) $216.
B) $54.
C) $224.
D) $108.
E) $113.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose that Dent Carr's long-run total cost of repairing s cars per week is c(s) = 3s2 + 12. If the price he receives for repairing a car is $24, then in the long run, how many cars will he fix per week if he maximizes profits?
A) 6
B) 4
C) 0
D) 8
E) 12
A) 6
B) 4
C) 0
D) 8
E) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A competitive, capitalistic firm produces gift-wrapped pieces of the Berlin wall, using the standard Marxian inputs, K and L. The production function is 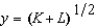 , where y is the number of pieces produced.Neglect the use of the wall itself. The price of capital, K, is r, and the price of labor, L, is w
, where y is the number of pieces produced.Neglect the use of the wall itself. The price of capital, K, is r, and the price of labor, L, is w
A) Regardless of w and r, cost minimization requires that K = L.
B) The technology has increasing returns to scale.
C) If r > w, then L = 0.
D) If r > w, then K = 0.
E) None of the above.
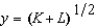 , where y is the number of pieces produced.Neglect the use of the wall itself. The price of capital, K, is r, and the price of labor, L, is w
, where y is the number of pieces produced.Neglect the use of the wall itself. The price of capital, K, is r, and the price of labor, L, is wA) Regardless of w and r, cost minimization requires that K = L.
B) The technology has increasing returns to scale.
C) If r > w, then L = 0.
D) If r > w, then K = 0.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A competitive firm has a long-run total cost function c(y) = 5y2 + 1,125 for y > 0 and c(0) = 0. Its long-run supply function is described as
A) y =if p > 148, y = 0 if p < 148.
B) y =if p > 150, y = 0 if p < 150.
C) y =if p > 153, y = 0 if p < 153.
D) y =if p > 153, y = 0 if p < 165.
E) y =if p > 155, y = 0 if p < 145.
A) y =if p > 148, y = 0 if p < 148.
B) y =if p > 150, y = 0 if p < 150.
C) y =if p > 153, y = 0 if p < 153.
D) y =if p > 153, y = 0 if p < 165.
E) y =if p > 155, y = 0 if p < 145.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A competitive firm produces its output according to the production function y = min{  , 10}. Let w be the price of the factor x, and let the price of output be $1.The demand for factor x, when the factor price is w, is
, 10}. Let w be the price of the factor x, and let the price of output be $1.The demand for factor x, when the factor price is w, is
A) x = min{, 10}
B) x = max{, 100}.
C) x = min{w2, 100}.
D) x = 10 +.
E) None of the above.
 , 10}. Let w be the price of the factor x, and let the price of output be $1.The demand for factor x, when the factor price is w, is
, 10}. Let w be the price of the factor x, and let the price of output be $1.The demand for factor x, when the factor price is w, isA) x = min{, 10}
B) x = max{, 100}.
C) x = min{w2, 100}.
D) x = 10 +.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Lost Mountains of northern Iowa are inhabited by the rare Marshallian deer. Patches of grass are far apart in this rugged land. If a deer finds a fresh patch of grass and spends h hours grazing it, it gets the square root of h units of grass. The deer compete for grass. When there are n deer, it takes a deer n 2 minutes to find a fresh patch. A deer can survive if it gets 1 unit of grass every 200 minutes.
a. Find the average cost in time of a unit of grass if a deer gets y units of grass from each patch.
b. How much time will an efficient deer spend in each patch when there are n deer? (Hint: Minimize aver-age cost.)
c. Since there is free entry into the deer business, the equilibrium population is the maximum number of efficient deer who can survive. How many is this?
a. Find the average cost in time of a unit of grass if a deer gets y units of grass from each patch.
b. How much time will an efficient deer spend in each patch when there are n deer? (Hint: Minimize aver-age cost.)
c. Since there is free entry into the deer business, the equilibrium population is the maximum number of efficient deer who can survive. How many is this?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



