Deck 26: Oligopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Oligopoly
1
A city has two major league baseball teams, A and B. The number of tickets sold by either team depends on the price of the team's own tickets and the price of the other team's tickets. If team A charges Pa for its tickets and team B charges Pb for its tickets, then ticket sales, measured in hundreds of thousands per season, are 10 - 2Pa + Pb for team A and 5 + Pa - 2Pb for team B. The marginal cost of an extra spectator is zero for both teams. Each team believes the other's price is independent of its own choice of price, and each team sets its own price so as to maximize its revenue. What price do they charge per ticket?
A) Team A charges 3 and team B charges 2.
B) Team A charges 3 and team B charges 4.
C) Team A charges 4 and team B charges 4.
D) Team A charges 5 and team B charges 1.
E) None of the above.
A) Team A charges 3 and team B charges 2.
B) Team A charges 3 and team B charges 4.
C) Team A charges 4 and team B charges 4.
D) Team A charges 5 and team B charges 1.
E) None of the above.
A
2
In Bertrand competition between two firms, each firm believes that if it changes its output, the rival firm will change its output by the same amount.
False
3
A city has two newspapers. Demand for either paper depends on its own price and the price of its rival. Demand functions for papers A and B respectively, measured in tens of thousands of subscriptions, are 21 - 2Pa + Pb and 21 + Pa 2 2Pb. The marginal cost of printing and distributing an extra paper just equals the extra advertising revenue from another reader, so each paper treats marginal costs as zero. Each paper maximizes its revenue assuming that the other's price is independent of its own price. If the papers enter a joint operating agreement where they set prices to maximize total revenue, by how much will newspaper prices rise?
A) $3
B) $2
C) $0
D) $3.50
E) $2.50
A) $3
B) $2
C) $0
D) $3.50
E) $2.50
D
4
A city has two major league baseball teams, A and B. The number of tickets sold by either team depends on the price of the team's own tickets and the price of the other team's tickets. If team A charges Pa for its tickets and team B charges Pb for its tickets, then ticket sales, measured in hundreds of thousands per season, are 10 - 2Pa + Pb for team A and 20 + Pa - 2Pb for team B. The marginal cost of an extra spectator is zero for both teams. Each team believes the other's price is independent of its own choice of price, and each team sets its own price so as to maximize its revenue. What price do they charge per ticket?
A) Team A charges 4 and team B charges 6.
B) Team A charges 6 and team B charges 5.
C) Team A charges 5 and team B charges 8.
D) Team A charges 4 and team B charges 12.
E) None of the above.
A) Team A charges 4 and team B charges 6.
B) Team A charges 6 and team B charges 5.
C) Team A charges 5 and team B charges 8.
D) Team A charges 4 and team B charges 12.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
One unit of zinc and one unit of copper are needed to produce a unit of brass. The world's supply of zinc and the world's supply of copper are owned by two different monopolists. For simplicity assume that it costs nothing to mine zinc and copper, that no other inputs are needed to produce brass, and that the brass industry operates competitively. Then the price of a unit of brass equals the cost of the inputs used to make it. The demand function for brass is q = 900 - 2p, where p is the price of brass. The zinc and copper monopolists each set a price, believing that the other monopolist will not change its price. What is the equilibrium price of brass?
A) $100
B) $200
C) $300
D) $50
E) $25
A) $100
B) $200
C) $300
D) $50
E) $25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
There are two major producers of corncob pipes in the world, both located in Herman, Missouri. Suppose that the inverse demand function for corncob pipes is described by p = 160 - 3q, where q is total industry output, and marginal costs are zero. What is the Cournot reaction function of firm 1 to the output, q2, of firm 2?
A) 160 - 3q22
B) 160 - 3q2
C) 26.67 - .5q2
D) 53.33 - 3q2
E) 163 - 6q2
A) 160 - 3q22
B) 160 - 3q2
C) 26.67 - .5q2
D) 53.33 - 3q2
E) 163 - 6q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Conjectural variation refers to the fact that in a single market there is variation among firms in their estimates of the demand function in future periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A duopoly faces the inverse demand curve p = 160 - 2q. Both firms in the industry have constant costs of $10 per unit of output. In a Cournot equilibrium how much output will each duopolist sell?
A) 75
B) 54
C) 25
D) 35
E) 48
A) 75
B) 54
C) 25
D) 35
E) 48

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An industry has two firms. The inverse demand function for this industry is p = 74 - 4q. Both firms produce at a constant unit cost of $26 per unit. What is the Cournot equilibrium price for this industry?
A) $21
B) $29
C) $42
D) $26
E) None of the above.
A) $21
B) $29
C) $42
D) $26
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An industry has two firms each of which produces output at a constant unit cost of $10 per unit. The demand function for the industry is q = 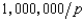 . The Cournot equilibrium price for this industry is
. The Cournot equilibrium price for this industry is
A) $5.
B) $10.
C) $15.
D) $20.
E) $25.
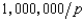 . The Cournot equilibrium price for this industry is
. The Cournot equilibrium price for this industry isA) $5.
B) $10.
C) $15.
D) $20.
E) $25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In Cournot equilibrium each firm chooses the quantity that maximizes its own profits assuming that the firm's rival will continue to sell at the same price as before.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A duopoly in which two identical firms are engaged in Bertrand competition will not distort prices from their competitive levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A Stackelberg leader chooses his actions on the assumption that his rival will adjust to the leader's actions in such a way as to maximize the rival's profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A Stackelberg leader will necessarily make at least as much profit as he would if he acted as a Cournot oligopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the Cournot model, each firm chooses its actions on the assumption that its rivals will react by changing their quantities in such a way as to maximize their own profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An industry has two firms producing at a constant unit cost of $10 per unit. The inverse demand curve for the industry is p = 110 - .5q. Suppose that firm 1 is a Stackelberg leader in choosing its quantity (i.e., firm 1 chooses its quantity first, knowing that firm 2 will observe firm 1's quantity when it chooses its own output.) How much output will firm 2, the follower, produce?
A) 40 units.
B) 15 units.
C) 20 units.
D) 50 units.
E) 30 units.
A) 40 units.
B) 15 units.
C) 20 units.
D) 50 units.
E) 30 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An industry has two firms. The inverse demand function for this industry is p = 263 - 6q. Both firms produce at a constant unit cost of $29 per unit. What is the Cournot equilibrium price for this industry?
A) $29
B) $31
C) $107
D) $53.50
E) None of the above.
A) $29
B) $31
C) $107
D) $53.50
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the Bertrand model of duopoly, each firm sets its price, believing that the other's price will not change. When both firms have identical production functions and produce with constant returns to scale, the Bertrand equilibrium price is equal to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
There are two major producers of corncob pipes in the world, both located in Herman, Missouri. Suppose that the inverse demand function for corncob pipes is described by p = 160 - 4q, where q is total industry output, and marginal costs are zero. What is the Cournot reaction function of firm 1 to the output, q2, of firm 2?
A) 40 - 4q2
B) 160 - 4q22
C) 20 - .5q2
D) 160 - 4q2
E) 164 - 8q2
A) 40 - 4q2
B) 160 - 4q22
C) 20 - .5q2
D) 160 - 4q2
E) 164 - 8q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose that the demand curve for an industry's output is a downward-sloping straight line and there is constant marginal cost. Then the larger the number of identical firms producing in Cournot equilibrium, the lower will be the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose that the market demand curve for bean sprouts is given by P = 880 - 4Q, where P is the price and Q is the total industry output. Suppose that the industry has two firms, a Stackelberg leader and a follower. Each firm has a constant marginal cost of $80 per unit of output. In equilibrium, total output by the two firms will be
A)100
B)50
C)150
D)200
E) 25.
A)100
B)50
C)150
D)200
E) 25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider a market with one large firm and many small firms. The supply function of all of the small firms together is S(p) = 200 + p, the market demand curve is D(p) = 400 - p, and the cost function for the large firm is C(y) = 20y. The residual demand curve for the large firm, where DL is the large firm's demand and yL is the large firm's output, is
A) DL(p) = 400 - 21yL.
B) DL(p) = 200 - 2p.
C) DL(p) = 600 - 2p.
D) DL(yL) = 200 - 2p - 20yL.
E) DL(yL) = 200 + p + 20yL.
A) DL(p) = 400 - 21yL.
B) DL(p) = 200 - 2p.
C) DL(p) = 600 - 2p.
D) DL(yL) = 200 - 2p - 20yL.
E) DL(yL) = 200 + p + 20yL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The demand for y is given by 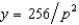 . Only two firms produce y. They have identical costs c(y) = y2. If they agree to collude and maximize their joint profits, how much output will each firm produce?
. Only two firms produce y. They have identical costs c(y) = y2. If they agree to collude and maximize their joint profits, how much output will each firm produce?
A) 2
B) 5
C) 10
D) 12
E) 16
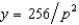 . Only two firms produce y. They have identical costs c(y) = y2. If they agree to collude and maximize their joint profits, how much output will each firm produce?
. Only two firms produce y. They have identical costs c(y) = y2. If they agree to collude and maximize their joint profits, how much output will each firm produce?A) 2
B) 5
C) 10
D) 12
E) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The duopolists Carl and Simon face a demand function for pumpkins of Q = 2,200 - 400P, where Q is the total number of pumpkins that reach the market and P is the price of pumpkins. Suppose further that each farmer has a constant marginal cost of $1.50 for each pumpkin produced. If Carl believes that Simon is going to produce Qs pumpkins this year, then the reaction function tells us how many pumpkins Carl should produce in order to maximize his profits. Carl's reaction function is
A) RC(Qs) = 400 -.
B) RC(Qs) = 2,200 - 800Qs.
C) RC(Qs) = 800 -.
D) RC(Qs) = 2,200 - 400Qs.
E) RC(Qs) = 1,200 - Qs.
A) RC(Qs) = 400 -.
B) RC(Qs) = 2,200 - 800Qs.
C) RC(Qs) = 800 -.
D) RC(Qs) = 2,200 - 400Qs.
E) RC(Qs) = 1,200 - Qs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose that two airlines are Cournot duopolists serving the Peoria-Dubuque route, and the demand curve for tickets per day is Q = 220 - 2p (so p = 110 - 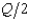 ). Total costs of running a flight on this route are 1,400 + 20q, where q is the number of passengers on the flight. Each flight has a capacity of 80 passengers. In Cournot equilibrium, each duopolist will run one flight per day and will make a daily profit of
). Total costs of running a flight on this route are 1,400 + 20q, where q is the number of passengers on the flight. Each flight has a capacity of 80 passengers. In Cournot equilibrium, each duopolist will run one flight per day and will make a daily profit of
A) $400.
B) $800.
C) $220.
D) $700.
E) $3,000.
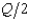 ). Total costs of running a flight on this route are 1,400 + 20q, where q is the number of passengers on the flight. Each flight has a capacity of 80 passengers. In Cournot equilibrium, each duopolist will run one flight per day and will make a daily profit of
). Total costs of running a flight on this route are 1,400 + 20q, where q is the number of passengers on the flight. Each flight has a capacity of 80 passengers. In Cournot equilibrium, each duopolist will run one flight per day and will make a daily profit ofA) $400.
B) $800.
C) $220.
D) $700.
E) $3,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A duopoly faces the inverse demand curve p = 160 - 2q. Firm 1's total cost function is given by C1(q1) = 8q1 and firm 2's total cost function is given by C2(q2) = 10q2. In a Cournot equilibrium,
A) the firm with the lower marginal cost produces more.
B) both firms will produce the same amount.
C) the firm with the higher marginal cost produces more to cover the higher costs.
D) the reaction function for both firms is the same since both firms have a constant marginal cost.
E) More than one of the above is correct.
A) the firm with the lower marginal cost produces more.
B) both firms will produce the same amount.
C) the firm with the higher marginal cost produces more to cover the higher costs.
D) the reaction function for both firms is the same since both firms have a constant marginal cost.
E) More than one of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Two firms decide to form a cartel and collude in a way that maximizes industry profits. Each firm has zero production costs and each firm is given a positive output quota by the cartel. Which of the following statements is not true?
A) Each firm would want to produce more than its quota if it knew that the other would continue to produce at its quota.
B) The price elasticity of demand will be 21 at the output level chosen.
C) Output would be lower than if the firms behaved as Cournot firms.
D) Output would be lower than if the firms behaved as competitors.
E) All of the other statements are false.
A) Each firm would want to produce more than its quota if it knew that the other would continue to produce at its quota.
B) The price elasticity of demand will be 21 at the output level chosen.
C) Output would be lower than if the firms behaved as Cournot firms.
D) Output would be lower than if the firms behaved as competitors.
E) All of the other statements are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose that two airlines are Cournot duopolists serving the Peoria-Dubuque route, and the demand curve for tickets per day is Q = 230 - 2p (so p = 115 - 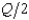 ). Total costs of running a flight on this route are 450 + 40q, where q is the number of passengers on the flight. Each flight has a capacity of 80 passengers. In Cournot equilibrium, each duopolist will run one flight per day and will make a daily profit of
). Total costs of running a flight on this route are 450 + 40q, where q is the number of passengers on the flight. Each flight has a capacity of 80 passengers. In Cournot equilibrium, each duopolist will run one flight per day and will make a daily profit of
A) $800.
B) $225.
C) $230.
D) $1,600.
E) $3,250.
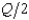 ). Total costs of running a flight on this route are 450 + 40q, where q is the number of passengers on the flight. Each flight has a capacity of 80 passengers. In Cournot equilibrium, each duopolist will run one flight per day and will make a daily profit of
). Total costs of running a flight on this route are 450 + 40q, where q is the number of passengers on the flight. Each flight has a capacity of 80 passengers. In Cournot equilibrium, each duopolist will run one flight per day and will make a daily profit ofA) $800.
B) $225.
C) $230.
D) $1,600.
E) $3,250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The duopolists Carl and Simon face a demand function for pumpkins of Q = 8,200 - 400P, where Q is the total number of pumpkins that reach the market and P is the price of pumpkins. Suppose further that each farmer has a constant marginal cost of $.50 for each pumpkin produced. If Carl believes that Simon is going to produce Qs pumpkins this year, then the reaction function tells us how many pumpkins Carl should produce in order to maximize his profits. Carl's reaction function is
A) RC(Qs) = 4,000 -.
B) RC(Qs) = 8,200 - 400Qs.
C) RC(Qs) = 8,200 - 800Qs.
D) RC(Qs) = 2,000 -.
E) RC(Qs) = 6,000 - Qs.
A) RC(Qs) = 4,000 -.
B) RC(Qs) = 8,200 - 400Qs.
C) RC(Qs) = 8,200 - 800Qs.
D) RC(Qs) = 2,000 -.
E) RC(Qs) = 6,000 - Qs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose that Grinch and Grubb go into the wine business in a small country where wine is difficult to grow. The demand for wine is given by p = $300 - .2Q, where p is the price and Q is the total quantity sold. The industry consists of just the two Cournot duopolists, Grinch and Grubb. Imports are prohibited. Grinch has constant marginal costs of $45 and Grubb has marginal costs of $30. How much is Grinch's output in equilibrium?
A) 400
B) 800
C) 200
D) 600
E) 1,200
A) 400
B) 800
C) 200
D) 600
E) 1,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An industry has two firms. Firm 1's cost function is c(y) = 2y + 500 and firm 2's cost function is c(y) = 2y + 400. The demand curve for the output of this industry is a downward-sloping straight line. In a Cournot equilibrium, where both firms produce positive amounts of output,
A) the firm with lower fixed costs produces more.
B) the firm with higher fixed costs produces more.
C) both firms produce the same amount of output.
D) there is less output than there would be if the firms colluded to maximize joint profits.
E) firm 1 always operates in the region where the demand curve is inelastic.
A) the firm with lower fixed costs produces more.
B) the firm with higher fixed costs produces more.
C) both firms produce the same amount of output.
D) there is less output than there would be if the firms colluded to maximize joint profits.
E) firm 1 always operates in the region where the demand curve is inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The inverse demand function for fuzzy dice is p = 20 - q. There are constant returns to scale in this industry with unit costs of $8. Which of the following sets of statements is completely true?
A) Monopoly output is 6. Cournot duopoly total output is 8. A Stackelberg leader's output is 8.
B) Monopoly output is 8. Cournot duopoly total output is 8. A Stackelberg leader's output is 8.
C) Monopoly output is 6. Cournot duopoly total output is 6. A Stackelberg follower's output is 3.
D) Monopoly output is 6. Cournot duopoly total output is 8. A Stackelberg follower's output is 3.
E) Monopoly output is 6. Cournot duopoly total output is 8. A Stackelberg follower's output is 4.
A) Monopoly output is 6. Cournot duopoly total output is 8. A Stackelberg leader's output is 8.
B) Monopoly output is 8. Cournot duopoly total output is 8. A Stackelberg leader's output is 8.
C) Monopoly output is 6. Cournot duopoly total output is 6. A Stackelberg follower's output is 3.
D) Monopoly output is 6. Cournot duopoly total output is 8. A Stackelberg follower's output is 3.
E) Monopoly output is 6. Cournot duopoly total output is 8. A Stackelberg follower's output is 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A certain type of mushroom used to be produced on 50 farms, each of which had a cost function c(y) = y2 + 1, where y > 0 and c(0) = 0. The firms operated as competitors. The demand curve for this kind of mushroom is given by D(p) = 52 - p. Marauding deviant Ninja turtles invaded many of the mushroom farms leaving absolute devastation and loathsome slime in their wake. (The turtles had no effect on the cost functions of farms that were not invaded.)
A) If all of the farms but one were invaded and that farm became a monopolist, total output of mushrooms would fall to half of the preinvasion output.
B) If all of the farms but one were invaded and that farm became a monopolist, total output of mushrooms would fall toth of the preinvasion output.
C) If all of the farms but two were invaded and the two undamaged farms became Cournot duopolists, total output of mushrooms would beof the preinvasion output.
D) If half of the farms were invaded and the industry remained competitive, industry output would fall to half of the preinvasion output.
E) If half of the farms were invaded and the industry remained competitive, industry output would fall but would be greater than half of the preinvasion output.
A) If all of the farms but one were invaded and that farm became a monopolist, total output of mushrooms would fall to half of the preinvasion output.
B) If all of the farms but one were invaded and that farm became a monopolist, total output of mushrooms would fall toth of the preinvasion output.
C) If all of the farms but two were invaded and the two undamaged farms became Cournot duopolists, total output of mushrooms would beof the preinvasion output.
D) If half of the farms were invaded and the industry remained competitive, industry output would fall to half of the preinvasion output.
E) If half of the farms were invaded and the industry remained competitive, industry output would fall but would be greater than half of the preinvasion output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose that Grinch and Grubb go into the wine business in a small country where wine is difficult to grow. The demand for wine is given by p = $480 - .2Q, where p is the price and Q is the total quantity sold. The industry consists of just the two Cournot duopolists, Grinch and Grubb. Imports are prohibited. Grinch has constant marginal costs of $30 and Grubb has marginal costs of $60. How much is Grinch's output in equilibrium?
A) 1,600
B) 1,200
C) 800
D) 400
E) 2,400
A) 1,600
B) 1,200
C) 800
D) 400
E) 2,400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The price elasticity of demand for melocotones is constant and equal to -2. The melocotone market is controlled by two Cournot duopolists who have different cost functions. One of the duopolists has a constant marginal cost of $675 per ton and produces 50% of the total number of melocotones sold. The equilibrium price of a ton of melocotones must be
A) $1,800.
B) $450.
C) $900.
D) $675.
E) $1,350.
A) $1,800.
B) $450.
C) $900.
D) $675.
E) $1,350.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose that the inverse demand for bean sprouts is given by P(Y) = 750 - 2Y and the total cost of producing Y units for any firm is TC(Y) = 30Y. If the industry consists of two Cournot duopolists, then in equilibrium each firm's production is
A) 60 units.
B) 120 units.
C) 180 units.
D) 90 units.
E) 93.75 units.
A) 60 units.
B) 120 units.
C) 180 units.
D) 90 units.
E) 93.75 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The price elasticity of demand for melocotones is constant and equal to -2. The melocotone market is controlled by two Cournot duopolists who have different cost functions. One of the duopolists has a constant marginal cost of $975 per ton and produces 70% of the total number of melocotones sold. The equilibrium price of a ton of melocotones must be
A) $1,500.
B) $750.
C) $975.
D) $3,000.
E) $2,250.
A) $1,500.
B) $750.
C) $975.
D) $3,000.
E) $2,250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A duopoly faces the demand curve D(p) = 30 - .5p. Both firms in the industry have a total cost function given by C(q) = 4q. Suppose that firm 1 is a Stackelberg leader in choosing its quantity first. Firm 1's profit function can be written as
A) q1 = 14 - .5q2.
B) q2 = 14 - .5q1.
C) 28q1 - q21.
D) 56q1 - q21.
E) 60q - q2.
A) q1 = 14 - .5q2.
B) q2 = 14 - .5q1.
C) 28q1 - q21.
D) 56q1 - q21.
E) 60q - q2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Suppose that the inverse demand for bean sprouts is given by P(Y) = 370 - 4Y and the total cost of producing Y units for any firm is TC(Y) = 10Y. If the industry consists of two Cournot duopolists, then in equilibrium each firm's production is
A) 45 units.
B) 22.50 units.
C) 15 units.
D) 30 units.
E) 23.13 units.
A) 45 units.
B) 22.50 units.
C) 15 units.
D) 30 units.
E) 23.13 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The cartel of copper exporting countries is called COPEC. As part of an international marketing agreement, the United States has agreed to buy all the copper that COPEC wants to sell the United States at a constant price of $100 per ton. COPEC also sells copper in Europe at a price of $150 per ton. COPEC acts just like a monopolist. If COPEC finds it profitable to sell in the United States at $100 per ton and simultaneously to sell in Europe for $150 a ton, what is the price elasticity of demand of COPEC's copper in the European market? (Hint: What is COPEC's marginal revenue in the U.S. market?)
A) -1
B) -2
C) -3
D) -
E) -
A) -1
B) -2
C) -3
D) -
E) -

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An industry has two firms-a Stackelberg leader and a follower. The price of the industry output is given by P = 84 - Q, where Q is the total output of the two firms. The follower has a marginal cost of $0. The leader has a marginal cost of $21. How much should the leader produce in order to maximize profits?
A) 21
B) 24
C) 42
D) 19
E) None of the above.
A) 21
B) 24
C) 42
D) 19
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Roach Motors is the dominant used-car dealer in a small Midwestern city. After paying $50,000 for overhead, Roach Motors' cost per car is $500. There are 5 other small used-car lots in this town, but since they are not large enough to purchase cars through the same discount sources as Roach, each firm faces the cost function C = 5,000 + 700Q + 5Q2. The demand for used cars is Q = 200 - 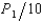 . Assuming Roach is aware of its competitors' costs, what price should Roach set for a used car?
. Assuming Roach is aware of its competitors' costs, what price should Roach set for a used car?
A) $708.33
B) $575
C) $616.67
D) $604.17
E) $925
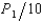 . Assuming Roach is aware of its competitors' costs, what price should Roach set for a used car?
. Assuming Roach is aware of its competitors' costs, what price should Roach set for a used car?A) $708.33
B) $575
C) $616.67
D) $604.17
E) $925

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Roach Motors is the dominant used-car dealer in a small Midwestern city. After paying $50,000 for overhead, Roach Motors' cost per car is $500. There are 4 other small used-car lots in this town, but since they are not large enough to purchase cars through the same discount sources as Roach, each firm faces the cost function C = 5,000 + 600Q + 5Q2. The demand for used cars is Q = 600 - 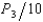 . Assuming Roach sets the market price so as to maximize its profit, how many cars will each of the follower firms supply?
. Assuming Roach sets the market price so as to maximize its profit, how many cars will each of the follower firms supply?
A) 25
B) 33
C) 28
D) 29
E) 27
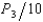 . Assuming Roach sets the market price so as to maximize its profit, how many cars will each of the follower firms supply?
. Assuming Roach sets the market price so as to maximize its profit, how many cars will each of the follower firms supply?A) 25
B) 33
C) 28
D) 29
E) 27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Ann and Bruce each own a pizza store in Frostbite Falls, Minnesota. Demand for pizza is given by Q = 200 - 10P. Having the only two pizza stores in Frostbite Falls, they attempt to profitably split the market without violating the Sherman Antitrust Act. Each has the cost function C = 50 + 5Q. If Ann and Bruce behave as duopolists, each earns a profit of
A) $0.
B) $200.
C) $500.
D) $500.
E) $562.50.
A) $0.
B) $200.
C) $500.
D) $500.
E) $562.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Ann and Bruce each own a pizza store in Frostbite Falls, Minnesota. Demand for pizza is given by Q = 400 2 40P. Having the only two pizza stores in Frostbite Falls, they attempt to profitably split the market without violating the Sherman Antitrust Act. Each has the cost function C = 50 + 2Q. If Ann and Bruce behave as duopolists, each earns a profit of
A) $568.89.
B) $497.78.
C) $0.
D) $234.44.
E) $640.
A) $568.89.
B) $497.78.
C) $0.
D) $234.44.
E) $640.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An industry has two colluding firms that act so as to maximize total profit in the industry and then split the profits equally. Firm 1 has cost function c(y) = 8y. Firm 2 has cost function c(y) = y2. Each firm produces an integer number of units. Market demand is given by Y(p) = 72 - p.
A) Each firm should produce 16 units.
B) Firm 1 should produce 32 units and firm 2 should produce 2 units.
C) Firm 1 should produce 14 units and firm 2 should produce 14 units.
D) Firm 1 should produce 28 units and firm 2 should produce 4 units.
E) None of the above.
A) Each firm should produce 16 units.
B) Firm 1 should produce 32 units and firm 2 should produce 2 units.
C) Firm 1 should produce 14 units and firm 2 should produce 14 units.
D) Firm 1 should produce 28 units and firm 2 should produce 4 units.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
North Bend currently has one McDonald's fast-food franchise. Demand for hamburgers in North Bend is given by Q = 300 - 10P. Any McDonald's franchise has costs of C = 70 + 2Q for producing Q hamburgers. If a second McDonald's franchise were to move into North Bend (and both behaved as duopolists), the profit of the original McDonald's would fall from
A) $1,890 to $1,602.22.
B) $1,960 to $1,602.22.
C) $2,240 to $1,057.78.
D) $1,890 to $801.11.
E) $1,960 to $1,672.22.
A) $1,890 to $1,602.22.
B) $1,960 to $1,602.22.
C) $2,240 to $1,057.78.
D) $1,890 to $801.11.
E) $1,960 to $1,672.22.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
There are two firms in the blastopheme industry. The demand curve for blastophemes is given by p = 3,600 - 4q. Each firm has one manufacturing plant and each firm i has a cost function C(qi) = q2i, where qi is the output of firm i. The two firms form a cartel and arrange to split total industry profits equally. Under this cartel arrangement, they will maximize joint profits if
A) and only if each firm produces 200 units in its plant.
B) they produce a total of 400 units, no matter which firm produces them.
C) and only if they each produce a total of 450 units.
D) they produce a total of 300 units, no matter which firm produces them.
E) they shut down one of the two plants, having the other operate as a monopoly and splitting the profits.
A) and only if each firm produces 200 units in its plant.
B) they produce a total of 400 units, no matter which firm produces them.
C) and only if they each produce a total of 450 units.
D) they produce a total of 300 units, no matter which firm produces them.
E) they shut down one of the two plants, having the other operate as a monopoly and splitting the profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An industry has two colluding firms that act so as to maximize total profit in the industry and then split the profits equally. Firm 1 has cost function c(y) = 8y. Firm 2 has cost function c(y) = y2. Each firm produces an integer number of units. Market demand is given by Y(p) = 56 - p.
A) Firm 1 should produce 10 units and firm 2 should produce 10 units.
B) Firm 1 should produce 20 units and firm 2 should produce 4 units.
C) Each firm should produce 12 units.
D) Firm 1 should produce 24 units and firm 2 should produce 2 units.
E) None of the above.
A) Firm 1 should produce 10 units and firm 2 should produce 10 units.
B) Firm 1 should produce 20 units and firm 2 should produce 4 units.
C) Each firm should produce 12 units.
D) Firm 1 should produce 24 units and firm 2 should produce 2 units.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An industry has two firms-a Stackelberg leader and a follower. The price of the industry output is given by P = 36 - Q, where Q is the total output of the two firms. The follower has a marginal cost of $0. The leader has a marginal cost of $9. How much should the leader produce in order to maximize profits?
A) 12
B) 18
C) 9
D) 7
E) None of the above.
A) 12
B) 18
C) 9
D) 7
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A Stackelberg leader and follower choose their outputs to maximize their own profits. Local property taxes which constitute a lump sum tax for each of them are reduced by $500 per year for the leader and by $200 a year for the follower. In consequence, the firms
A) both increase their output, with the leader increasing its output by more.
B) both increase their output, with the follower increasing its output by more.
C) increase their output by equal amounts for each firm.
D) leave their outputs unchanged.
E) There is not enough information in the question to determine what the firms will do.
A) both increase their output, with the leader increasing its output by more.
B) both increase their output, with the follower increasing its output by more.
C) increase their output by equal amounts for each firm.
D) leave their outputs unchanged.
E) There is not enough information in the question to determine what the firms will do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose that the market demand curve for bean sprouts is given by P = 820 - 2Q, where P is the price and Q is the total industry output. Suppose that the industry has two firms, a Stackelberg leader and a follower. Each firm has a constant marginal cost of $20 per unit of output. In equilibrium, total output by the two firms will be
A)200
B)100
C)300
300)d.
E) 50.
A)200
B)100
C)300
300)d.
E) 50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
North Bend currently has one McDonald's fast-food franchise. Demand for hamburgers in North Bend is given by Q = 400 - 10P. Any McDonald's franchise has costs of C = 60 + 3Q for producing Q hamburgers. If a second McDonald's franchise were to move into North Bend (and both behaved as duopolists), the profit of the original McDonald's would fall from
A) $3,362.50 to $2,922.22.
B) $3,977.50 to $1,891.11.
C) $3,422.50 to $2,922.22.
D) $3,362.50 to $1,461.11.
E) $3,422.50 to $2,982.22.
A) $3,362.50 to $2,922.22.
B) $3,977.50 to $1,891.11.
C) $3,422.50 to $2,922.22.
D) $3,362.50 to $1,461.11.
E) $3,422.50 to $2,982.22.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Roach Motors is the dominant used-car dealer in a small Midwestern city. After paying $50,000 for overhead, Roach Motors' cost per car is $500. There are 5 other small used-car lots in this town, but since they are not large enough to purchase cars through the same discount sources as Roach, each firm faces the cost function C = 5,000 + 700Q + 5Q2. The demand for used cars is Q = 500 - 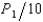 . Assuming Roach is aware of its competitors' costs, what price should Roach set for a used car?
. Assuming Roach is aware of its competitors' costs, what price should Roach set for a used car?
A) $1,325
B) $616.67
C) $958.33
D) $729.17
E) $1,675
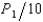 . Assuming Roach is aware of its competitors' costs, what price should Roach set for a used car?
. Assuming Roach is aware of its competitors' costs, what price should Roach set for a used car?A) $1,325
B) $616.67
C) $958.33
D) $729.17
E) $1,675

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Roach Motors is the dominant used-car dealer in a small Midwestern city. After paying $50,000 for overhead, Roach Motors' cost per car is $500. There are 4 other small used-car lots in this town, but since they are not large enough to purchase cars through the same discount sources as Roach, each firm faces the cost function C = 5,000 + 700Q + 5Q2. The demand for used cars is Q = 300 - 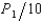 . Assuming Roach sets the market price so as to maximize its profit, how many cars will each of the follower firms supply?
. Assuming Roach sets the market price so as to maximize its profit, how many cars will each of the follower firms supply?
A) 19
B) 13
C) 9
D) 16
E) 8
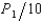 . Assuming Roach sets the market price so as to maximize its profit, how many cars will each of the follower firms supply?
. Assuming Roach sets the market price so as to maximize its profit, how many cars will each of the follower firms supply?A) 19
B) 13
C) 9
D) 16
E) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
There are two firms in the blastopheme industry. The demand curve for blastophemes is given by p = 4,200 - 3q. Each firm has one manufacturing plant and each firm i has a cost function C(qi) = q2i, where qi is the output of firm i. The two firms form a cartel and arrange to split total industry profits equally. Under this cartel arrangement, they will maximize joint profits if
A) they produce a total of 600 units, no matter which firm produces them.
B) they produce a total of 466.67 units, no matter which firm produces them.
C) and only if they each produce a total of 700 units.
D) and only if each firm produces of 300 units in its plant.
E) they shut down one of the two plants, having the other operate as a monopoly and splitting the profits.
A) they produce a total of 600 units, no matter which firm produces them.
B) they produce a total of 466.67 units, no matter which firm produces them.
C) and only if they each produce a total of 700 units.
D) and only if each firm produces of 300 units in its plant.
E) they shut down one of the two plants, having the other operate as a monopoly and splitting the profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



