Deck 35: Public Goods
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 35: Public Goods
1
Remember Bonnie and Clyde from your workbook? Suppose that their total profits are 40H, where H is the number of hours they work per year. Their utility functions are, respectively, UB(CB, H) = CB - 0.02H2 and UC(CC, H) = CC - 0.03H2, where CB and CC are their private goods consumptions and H is the number of hours they work per year. If they find a Pareto optimal choice of hours of work and income distribution, the number of hours they work per year must be
A)500
B)400
C)150
D) 250.
A)500
B)400
C)150
D) 250.
C
2
If preferences are single peaked, then pairwise majority voting among alternative options will not lead to voting cycles.
True
3
Economists define public goods to be those goods that are supplied by the government and private goods to be those goods that are supplied by the private sector.
False
4
Which of the following is the best example of a public good as defined in your text?
A) Cable television
B) Day care
C) Radio broadcasts
D) Medical care
E) Disneyland
A) Cable television
B) Day care
C) Radio broadcasts
D) Medical care
E) Disneyland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Anton, Bertha, and Cecilia all consume crackers and music. Crackers are a pure private good and music is a pure public good. Their utility functions are U A (c A, m) = c A m, U B (c B, m) = c B m, and U B (c C, m) = 2c C m, where c A is Antons cracker consumption, c B is Berthas cracker consumption, c C is Cecilias cracker consumption, and where m is the amount of music jointly consumed by all three of them. Music is measured in hours. Crackers cost $1 each. Music costs $10 an hour. Antons wealth is $30, Berthas wealth is $50, and Cecilias wealth is $20. What is the efficient amount of music for them to consume?
A) 2 hours
B) 3 hours
C) 4 hours
D) 5 hours
E) 6 hours
A) 2 hours
B) 3 hours
C) 4 hours
D) 5 hours
E) 6 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
One of the problems with the Clarke tax mechanism is that when it is used, people have an incentive to lie about their preferences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Nadia Comaneci and Mr. X have preferences defined over pizza, p, and trampolines, t. They have identical utility functions, U(p, t) = 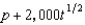 . Each pizza costs $1 and each trampoline costs $1,000. Nadia and Mr. X like to share, and indeed trampolines are a public good for them. Pizza, however, is a private good. We don't know their exact incomes, but we do know that each of them earns at least $10,000.
. Each pizza costs $1 and each trampoline costs $1,000. Nadia and Mr. X like to share, and indeed trampolines are a public good for them. Pizza, however, is a private good. We don't know their exact incomes, but we do know that each of them earns at least $10,000.
A) The Pareto efficient number of trampolines for them is 4.
B) The Pareto efficient number of trampolines for them is 1.
C) The Pareto efficient number of trampolines for them cannot be determined without knowing how the costs will be shared.
D) The Pareto efficient number of trampolines for them is 2.
E) Since their preferences are homothetic, their income elasticity of demand for pizza is -1.
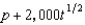 . Each pizza costs $1 and each trampoline costs $1,000. Nadia and Mr. X like to share, and indeed trampolines are a public good for them. Pizza, however, is a private good. We don't know their exact incomes, but we do know that each of them earns at least $10,000.
. Each pizza costs $1 and each trampoline costs $1,000. Nadia and Mr. X like to share, and indeed trampolines are a public good for them. Pizza, however, is a private good. We don't know their exact incomes, but we do know that each of them earns at least $10,000.A) The Pareto efficient number of trampolines for them is 4.
B) The Pareto efficient number of trampolines for them is 1.
C) The Pareto efficient number of trampolines for them cannot be determined without knowing how the costs will be shared.
D) The Pareto efficient number of trampolines for them is 2.
E) Since their preferences are homothetic, their income elasticity of demand for pizza is -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Sons of Knute had a hunting lodge up on Loon Lake that burned down last winter. They plan to rebuild it this summer and are trying to decide how large the new lodge should be. The organization has 50 members. The marginal rate of substitution of each of them between square feet of hunting lodge and money for other goods is 1.2 - 0.0004y, where y is the size of the hunting lodge in square feet. What is the efficient size for the new hunting lodge?
A) 1,000 square feet
B) 1,200 square feet
C) 2,000 square feet
D) 2,400 square feet
E) None of the above.
A) 1,000 square feet
B) 1,200 square feet
C) 2,000 square feet
D) 2,400 square feet
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A quiet town in Kansas has 2,000 people, all of whom have the same preferences. There is one private good and one public good. Each person I in town has utility U(x i, y) = x i + y .5, where x i is private good for person i and y is the amount of public good that the town provides. If the private good costs $1 per unit and the public good costs $10 per unit, then the Pareto optimal amount of public good for the town to provide is
A) 100 units.
B) 500 units.
C) 2,000 units.
D) 8,000 units.
E) 10,000 units.
A) 100 units.
B) 500 units.
C) 2,000 units.
D) 8,000 units.
E) 10,000 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
To say that preferences are single peaked means that everybody either prefers more public goods to less or everybody prefers less public goods to more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A Pareto optimal amount of public goods is shown on a graph (with quantities of public goods on the x axis) by the point at which the horizontal sum of the marginal rate of substitution curves meets the marginal cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Bob and Ray are thinking of buying a sofa. Bob's utility function is UB(S, MB) = (1 + S)MB and Ray's utility function is UR(S, MR) = (3 + S)MR, where S = 0 if they don't get the sofa and S = 1 if they do and where MB and MR are the amounts of money they have respectively to spend on their private consumptions. Bob has a total of $800 to spend on the sofa and other stuff. Ray has a total of $1,600 to spend on the sofa and other stuff. The maximum amount that they could pay for the sofa and still arrange to both be better off than without it is
A) $533.33.
B) $800.
C) $1,200.
D) $450.
E) $1,600.
A) $533.33.
B) $800.
C) $1,200.
D) $450.
E) $1,600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Just north of the town of Muskrat, Ontario, is the town of Brass Monkey, population 6,400. Brass Monkey, like Muskrat, has a single public good, the town skating rink, and a single private good, Labatt Ale. Everyone's utility function is Ui(Xi, Y) = Xi - 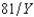 , where Xi is the number of bottles of ale consumed by i and Y is the size of the skating rink in square meters. The price of ale is $1 per bottle. The cost of the skating rink to the city is $4 per square meter. Everyone has an income of at least $5,000. What is the Pareto efficient size for the town skating rink?
, where Xi is the number of bottles of ale consumed by i and Y is the size of the skating rink in square meters. The price of ale is $1 per bottle. The cost of the skating rink to the city is $4 per square meter. Everyone has an income of at least $5,000. What is the Pareto efficient size for the town skating rink?
A) 360 square meters
B) 480 square meters
C) 240 square meters
D) 725 square meters
E) None of the above.
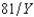 , where Xi is the number of bottles of ale consumed by i and Y is the size of the skating rink in square meters. The price of ale is $1 per bottle. The cost of the skating rink to the city is $4 per square meter. Everyone has an income of at least $5,000. What is the Pareto efficient size for the town skating rink?
, where Xi is the number of bottles of ale consumed by i and Y is the size of the skating rink in square meters. The price of ale is $1 per bottle. The cost of the skating rink to the city is $4 per square meter. Everyone has an income of at least $5,000. What is the Pareto efficient size for the town skating rink?A) 360 square meters
B) 480 square meters
C) 240 square meters
D) 725 square meters
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A small coffee company roasts coffee beans in its shop. The unroasted beans cost the company $2 per pound. The marginal cost of roasting coffee beans is $ 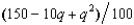 per pound when q pounds are roasted. The smell of roasting beans imposes costs on the company's neighbors. The total amount that neighbors would be willing to pay to have the shop stop roasting altogether is 5q2, where q is the number of pounds being roasted. The company sells its output in a competitive market at $4.50 per pound. What is the socially efficient amount of coffee for the company to roast?
per pound when q pounds are roasted. The smell of roasting beans imposes costs on the company's neighbors. The total amount that neighbors would be willing to pay to have the shop stop roasting altogether is 5q2, where q is the number of pounds being roasted. The company sells its output in a competitive market at $4.50 per pound. What is the socially efficient amount of coffee for the company to roast?
A) 10 pounds.
B) 15 pounds.
C) the square root of 10 pounds.
D) 45 pounds.
E) None of the above.
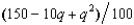 per pound when q pounds are roasted. The smell of roasting beans imposes costs on the company's neighbors. The total amount that neighbors would be willing to pay to have the shop stop roasting altogether is 5q2, where q is the number of pounds being roasted. The company sells its output in a competitive market at $4.50 per pound. What is the socially efficient amount of coffee for the company to roast?
per pound when q pounds are roasted. The smell of roasting beans imposes costs on the company's neighbors. The total amount that neighbors would be willing to pay to have the shop stop roasting altogether is 5q2, where q is the number of pounds being roasted. The company sells its output in a competitive market at $4.50 per pound. What is the socially efficient amount of coffee for the company to roast?A) 10 pounds.
B) 15 pounds.
C) the square root of 10 pounds.
D) 45 pounds.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A tax imposed on polluters to give them an incentive to make an efficient reduction in pollution is called a Clarke tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Bob and Ray are thinking of buying a sofa. Bob's utility function is UB(S, MB) = (1 + S)MB and Ray's utility function is UR(S, MR) = (3 + S)MR, where S = 0 if they don't get the sofa and S = 1 if they do and where MB and MR are the amounts of money they have respectively to spend on their private consumptions. Bob has a total of $2,000 to spend on the sofa and other stuff. Ray has a total of $2,400 to spend on the sofa and other stuff. The maximum amount that they could pay for the sofa and still arrange to both be better off than without it is
A) $2,400.
B) $800.
C) $1,600.
D) $850.
E) $3,200.
A) $2,400.
B) $800.
C) $1,600.
D) $850.
E) $3,200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Bob and Ray are thinking of buying a sofa. Bob's utility function is UB(S, MB) = (1 + S)MB and Ray's utility function is UR(S, MR) = (3 + S)MR, where S = 0 if they don't get the sofa and S = 1 if they do and where MB and MR are the amounts of money they have respectively to spend on their private consumptions. Bob has a total of $1,200 to spend on the sofa and other stuff. Ray has a total of $1,600 to spend on the sofa and other stuff. The maximum amount that they could pay for the sofa and still arrange to both be better off than without it is
A) $1,500.
B) $533.33.
C) $550.
D) $1,000.
E) $2,000.
A) $1,500.
B) $533.33.
C) $550.
D) $1,000.
E) $2,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the supply of public goods is determined by majority vote, then the outcome must be Pareto optimal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If preferences are single peaked, then everyone will agree about the right amount of public goods to be supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a pure public good is provided by voluntary contributions, economic theory predicts that in general too little will be supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Lucy's utility function is 2XL + G and Melvin's utility function is XMG, where G is their expenditures on the public goods they share in their apartment and where XL and XM are their respective private consumption expenditures. The total amount they have to spend on private goods and public goods is $28,000. They agree on a Pareto optimal pattern of expenditures in which the amount that is spent on Lucy's private consumption is $10,000. How much do they spent on public goods?
A) $12,000
B) $3,000
C) $6,000
D) $8,050
E) There is not enough information here to be able to determine the answer.
A) $12,000
B) $3,000
C) $6,000
D) $8,050
E) There is not enough information here to be able to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Remember Bonnie and Clyde from your workbook? Suppose that their total profits are 160H, where H is the number of hours they work per year. Their utility functions are, respectively, UB(CB, H) = CB - 0.04H2 and UC(CC, H) = CC - 0.01H2, where CB and CC are their private goods consumptions and H is the number of hours they work per year. If they find a Pareto optimal choice of hours of work and income distribution, the number of hours they work per year must be
A)750
B) 1,600.
C)850
)d. 1,700.
A)750
B) 1,600.
C)850
)d. 1,700.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An otherwise charming island is inhabited by two religious groups who hate each other. The island is presided over by a benevolent monarch who is extremely concerned about envy between groups. He chooses the distribution of income on the island so as to maximize the social welfare function, W(x, y) = min{2x - y,2y - x}, where x is the utility of the average member of group X and y is the utility of the average member of group Y.
a. If the monarch can accomplish any distribution of utility such that x + 3y = 24, diagram the utility possibilities frontier and the monarchs isowelfare lines.
b. What income distribution maximizes W?
c. Show that an equal increase in both groups income will always please the monarch.
d. If the initial incomes are equal, when do increases in both groups utility reduce W?
a. If the monarch can accomplish any distribution of utility such that x + 3y = 24, diagram the utility possibilities frontier and the monarchs isowelfare lines.
b. What income distribution maximizes W?
c. Show that an equal increase in both groups income will always please the monarch.
d. If the initial incomes are equal, when do increases in both groups utility reduce W?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Lucy's utility function is 2XL + G and Melvin's utility function is XMG, where G is their expenditures on the public goods they share in their apartment and where XL and XM are their respective private consumption expenditures. The total amount they have to spend on private goods and public goods is $30,000. They agree on a Pareto optimal pattern of expenditures in which the amount that is spent on Lucy's private consumption is $9,000. How much do they spent on public goods?
A) $7,000
B) $14,000
C) $8,050
D) $3,500
E) There is not enough information here to be able to determine the answer.
A) $7,000
B) $14,000
C) $8,050
D) $3,500
E) There is not enough information here to be able to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Lucy's utility function is 2XL + G and Melvin's utility function is XMG, where G is their expenditures on the public goods they share in their apartment and where XL and XM are their respective private consumption expenditures. The total amount they have to spend on private goods and public goods is $33,000. They agree on a Pareto optimal pattern of expenditures in which the amount that is spent on Lucy's private consumption is $9,000. How much do they spent on public goods?
A) $4,000
B) $16,000
C) $8,550
D) $8,000
E) There is not enough information here to be able to determine the answer.
A) $4,000
B) $16,000
C) $8,550
D) $8,000
E) There is not enough information here to be able to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Remember Bonnie and Clyde from your workbook? Suppose that their total profits are 112H, where H is the number of hours they work per year. Their utility functions are, respectively, UB(CB, H) = CB - 0.02H2 and UC(CC, H) = CC - 0.02H2, where CB and CC are their private goods consumptions and H is the number of hours they work per year. If they find a Pareto optimal choice of hours of work and income distribution, the number of hours they work per year must be
A) 1,400.
B)750
C)650 1,500.
D) 650.
A) 1,400.
B)750
C)650 1,500.
D) 650.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



