Deck 2: Economics: Eight Powerful Ideas
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/197
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Economics: Eight Powerful Ideas
1
Scarcity is a problem faced by all but the wealthiest of citizens.
False
2
Marginal cost is the additional cost incurred as a result of an economic decision.
True
3
A country has a comparative advantage in the production of DVD players if it can produce DVD players at a lower opportunity cost than others.
True
4
The opportunity cost of a decision is the value of all of the available alternatives that were not chosen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Economists would predict that if salaries increased for engineers and decreased for MBAs that fewer people would go to graduate school in business and more would go in engineering,ceteris paribus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Government price controls make communication of information between buyers and sellers more effective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The opportunity cost of a decision is the value of the best foregone alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Everyone faces scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When considering whether or not to consume a second slice of cake,an individual is following marginal thinking if she compares the total cost of consuming both the first and second slices with their total benefit before making a decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Since it is possible to grow coffee in the United States,we should clearly create a U.S.coffee industry and no longer import coffee from Brazil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An entrepreneur organizes the other factors of production and bears the business risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The opportunity cost of attending college is likely higher for a high school graduate who leaves a job grilling hamburgers than it is for a high school dropout who leaves a job working as a computer network administrator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Market failure is a term used to describe what happens whenever governments intervene into markets (e.g.,the imposition of a price control).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Human capital consists of computers,tools,and equipment owned by private individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A permanent change to a much higher price of gasoline would lead us to expect fewer gas guzzlers on the road,ceteris paribus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If Xavier gives up a job in which he earns $23,000 per year in order to go to college full time,his foregone income is part of the opportunity cost of going to college.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Scarcity applies to our needs but does not apply to our wants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The market mechanism assures full employment and stable prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Small,developing countries must first become self-sufficient before they can benefit from international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Tractors,shovels,copy machines,and computer programming expertise are all examples of scarce resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Unemployment can be caused by downswings in the business cycle,people changing jobs,different skills needed by employers,or seasonal fluctuations in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Scarcity:
A) is only a problem in communist countries.
B) is a problem in both communist and socialist countries, but not in market economies.
C) does not exist in wealthy countries.
D) will never be eradicated because humans develop new wants as productive capabilities improve.
A) is only a problem in communist countries.
B) is a problem in both communist and socialist countries, but not in market economies.
C) does not exist in wealthy countries.
D) will never be eradicated because humans develop new wants as productive capabilities improve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following will not directly add to improvements in human capital?
A) increases in take home pay
B) a low-level manager is sent back to college to acquire an MBA degree
C) improved job training programs offered to employees
D) an increase in the computer-proficiency requirements of all high school graduates
A) increases in take home pay
B) a low-level manager is sent back to college to acquire an MBA degree
C) improved job training programs offered to employees
D) an increase in the computer-proficiency requirements of all high school graduates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Economic choices or tradeoffs are the result of:
A) basic human greed.
B) scarcity.
C) poverty.
D) private ownership of resources.
A) basic human greed.
B) scarcity.
C) poverty.
D) private ownership of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not a resource?
A) cash
B) entrepreneurship
C) land
D) labor
A) cash
B) entrepreneurship
C) land
D) labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is not a resource?
A) capital
B) entrepreneurship
C) legal institutions
D) labor
A) capital
B) entrepreneurship
C) legal institutions
D) labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Scarcity applies to:
A) only the poor.
B) the value of our time.
C) both the rich and poor.
D) both (b) and (c)
A) only the poor.
B) the value of our time.
C) both the rich and poor.
D) both (b) and (c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Additions to human capital can be made through:
A) increases in pension benefits
B) monthly deposits into a savings account.
C) improved education and on-the-job training.
D) the purchase of tools and equipment by workers.
A) increases in pension benefits
B) monthly deposits into a savings account.
C) improved education and on-the-job training.
D) the purchase of tools and equipment by workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An increase in population,ceteris paribus,will raise the standard of living.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Economic resources are also known as:
A) elements.
B) financial capital.
C) factors of production.
D) building blocks.
A) elements.
B) financial capital.
C) factors of production.
D) building blocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is an example of a resource?
A) land
B) capital
C) entrepreneurship
D) All of the above
A) land
B) capital
C) entrepreneurship
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The market mechanism assures full employment and stable prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The only way that an economy can increase its rate of consumption in the long run is by increasing the amount that it produces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is an example of a resource?
A) a river
B) a John Deere tractor
C) the chef at the city's best café
D) all of the above are resources
A) a river
B) a John Deere tractor
C) the chef at the city's best café
D) all of the above are resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Scarcity:
A) exists in command economies.
B) exists in market economies.
C) exists only in economies in which there is poverty.
D) (a) and (b) above are correct
A) exists in command economies.
B) exists in market economies.
C) exists only in economies in which there is poverty.
D) (a) and (b) above are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Because of scarcity:
A) we must sacrifice valuable alternatives to obtain more goods and services we desire.
B) the opportunity cost of consumption is zero.
C) we can obtain more of a desirable good without sacrificing other goods and services.
D) shortages of goods prevail at current market prices.
A) we must sacrifice valuable alternatives to obtain more goods and services we desire.
B) the opportunity cost of consumption is zero.
C) we can obtain more of a desirable good without sacrificing other goods and services.
D) shortages of goods prevail at current market prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Inflation is an increase in the overall price level in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Scarcity implies that:
A) consumers are too poor to afford the goods and services available.
B) at the current market price, consumers are willing to purchase more of a good than suppliers are willing to produce.
C) it is impossible to completely fulfill the unlimited human desire for goods and services with the limited resources available.
D) consumers would be willing to purchase the same quantity of a good at a higher price.
A) consumers are too poor to afford the goods and services available.
B) at the current market price, consumers are willing to purchase more of a good than suppliers are willing to produce.
C) it is impossible to completely fulfill the unlimited human desire for goods and services with the limited resources available.
D) consumers would be willing to purchase the same quantity of a good at a higher price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An economy's resources:
A) consist of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial skills.
B) are unlimited in a country like the United States.
C) are always efficiently utilized in wealthy nations.
D) consist of land, labor, and entrepreneurial skills but not capital.
A) consist of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial skills.
B) are unlimited in a country like the United States.
C) are always efficiently utilized in wealthy nations.
D) consist of land, labor, and entrepreneurial skills but not capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Scarcity means that:
A) human desires are limited.
B) resources are insufficient to satisfy all human desires.
C) choices are unnecessary.
D) all but the very wealthy must face choices.
A) human desires are limited.
B) resources are insufficient to satisfy all human desires.
C) choices are unnecessary.
D) all but the very wealthy must face choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following observations regarding economic goods is incorrect?
A) They are limited in supply.
B) They are desirable.
C) They are solely low-priced essential goods.
D) They are scarce goods created from scarce resources
A) They are limited in supply.
B) They are desirable.
C) They are solely low-priced essential goods.
D) They are scarce goods created from scarce resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An example of physical capital is:
A) a $100 bill.
B) a stock certificate.
C) a chainsaw.
D) a cheeseburger.
A) a $100 bill.
B) a stock certificate.
C) a chainsaw.
D) a cheeseburger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
All of the following are intangible except:
A) health.
B) love.
C) computer programming expertise.
D) All of the above are intangible goods.
A) health.
B) love.
C) computer programming expertise.
D) All of the above are intangible goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is an example of a capital resource?
A) an unskilled worker
B) a large coal deposit
C) a fishing boat
D) yellow-fin tuna
A) an unskilled worker
B) a large coal deposit
C) a fishing boat
D) yellow-fin tuna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Human capital is:
A) the same as labor.
B) a term describing the tools and equipment owned by households.
C) a worker's physical effort when working with machines.
D) the expertise or knowledge possessed by workers.
A) the same as labor.
B) a term describing the tools and equipment owned by households.
C) a worker's physical effort when working with machines.
D) the expertise or knowledge possessed by workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The expression,"There's no such thing as a free lunch" implies that:
A) everyone has to pay for his/her own lunch.
B) the person consuming a good must always pay for it.
C) costs are incurred when resources are used to produce goods and services.
D) no one has time for a good lunch anymore.
A) everyone has to pay for his/her own lunch.
B) the person consuming a good must always pay for it.
C) costs are incurred when resources are used to produce goods and services.
D) no one has time for a good lunch anymore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Human capital is:
A) machinery owned by firms, but not by individuals.
B) machinery owned by individuals, but not by firms.
C) machinery owned by individuals or firms, but not by the government.
D) the skill or knowledge of individuals.
A) machinery owned by firms, but not by individuals.
B) machinery owned by individuals, but not by firms.
C) machinery owned by individuals or firms, but not by the government.
D) the skill or knowledge of individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An example of an intangible good is:
A) an automobile.
B) a new house.
C) a snowplow.
D) friendship.
A) an automobile.
B) a new house.
C) a snowplow.
D) friendship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following would be categorized as capital resources for a college or university?
A) water, trees, and the acreage a campus rests on
B) chalkboards, overhead projectors, and the expertise of professors
C) exams, fuel oil (which heats the buildings), and electricity
D) the work effort of registrars, clerical assistants, and teaching assistants
A) water, trees, and the acreage a campus rests on
B) chalkboards, overhead projectors, and the expertise of professors
C) exams, fuel oil (which heats the buildings), and electricity
D) the work effort of registrars, clerical assistants, and teaching assistants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The function of an entrepreneur is to:
A) bear the business risks.
B) organize the other factors of production.
C) innovate.
D) do all of the above.
A) bear the business risks.
B) organize the other factors of production.
C) innovate.
D) do all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is not an example of a resource?
A) an office building
B) a product's price
C) the land plowed by a farmer in order to grow corn
D) the chief executive officer of a large corporation
A) an office building
B) a product's price
C) the land plowed by a farmer in order to grow corn
D) the chief executive officer of a large corporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Entrepreneurship is:
A) human capital.
B) another word for the financial capital that can be used to start a business.
C) the resource that organizes the other factors of production in order to produce goods and/or services.
D) another word for physical capital that is used to produce goods and services.
A) human capital.
B) another word for the financial capital that can be used to start a business.
C) the resource that organizes the other factors of production in order to produce goods and/or services.
D) another word for physical capital that is used to produce goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Every time an individual decides to try out new equipment,or finds better ways to manage money,he or she is exhibiting traits of:
A) money management.
B) entrepreneurship.
C) strategic management.
D) capital management.
A) money management.
B) entrepreneurship.
C) strategic management.
D) capital management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The similarity between all goods and services,whether tangible or intangible,is that they:
A) are not subject to economic analysis.
B) require technical expertise.
C) have no price tags.
D) are made from scarce resources and are subject to economic analysis.
A) are not subject to economic analysis.
B) require technical expertise.
C) have no price tags.
D) are made from scarce resources and are subject to economic analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
All of the following are tangible goods except:
A) a skateboard.
B) a desk.
C) a train locomotive.
D) fairness.
A) a skateboard.
B) a desk.
C) a train locomotive.
D) fairness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is not an example of a capital resource?
A) the expertise of a computer programmer
B) a pitch fork
C) a commercial sewing machine
D) 100 acres of farmland in central California
A) the expertise of a computer programmer
B) a pitch fork
C) a commercial sewing machine
D) 100 acres of farmland in central California

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is an example of a capital resource?
A) redwood trees
B) unskilled labor
C) stocks and bonds
D) an oil rig
A) redwood trees
B) unskilled labor
C) stocks and bonds
D) an oil rig

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An example of a capital resource is:
A) stock in a computer software company.
B) a bond issued by a company selling electric generators.
C) a dump truck.
D) an employee of a moving company.
A) stock in a computer software company.
B) a bond issued by a company selling electric generators.
C) a dump truck.
D) an employee of a moving company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Economic goods are:
A) only those commodities priced in monetary terms.
B) scarce products that are created from scarce resources.
C) the opposite of normative economic goods.
D) not subject to scarcity.
A) only those commodities priced in monetary terms.
B) scarce products that are created from scarce resources.
C) the opposite of normative economic goods.
D) not subject to scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Land as a resource can include all of the following except:
A) trees.
B) a sawmill.
C) a water body.
D) a limestone deposit.
A) trees.
B) a sawmill.
C) a water body.
D) a limestone deposit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Opportunity cost includes
A) monetary costs only.
B) non-monetary costs only.
C) both monetary and non-monetary costs.
D) neither monetary nor non-monetary costs.
A) monetary costs only.
B) non-monetary costs only.
C) both monetary and non-monetary costs.
D) neither monetary nor non-monetary costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Exhibit 2-1 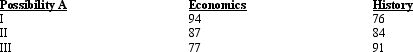 Refer to Exhibit 2-1.A student has only a few hours to prepare for two different exams tomorrow morning.The above table shows alternative possible exam outcomes with three alternative uses of the student's time.The opportunity cost of scoring an 84 on the history exam rather than 76 is:
Refer to Exhibit 2-1.A student has only a few hours to prepare for two different exams tomorrow morning.The above table shows alternative possible exam outcomes with three alternative uses of the student's time.The opportunity cost of scoring an 84 on the history exam rather than 76 is:
A) 10 points on the economics exam.
B) 7 points on the economics exam.
C) 8 points on the history exam.
D) 12 points on the economics exam.
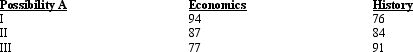 Refer to Exhibit 2-1.A student has only a few hours to prepare for two different exams tomorrow morning.The above table shows alternative possible exam outcomes with three alternative uses of the student's time.The opportunity cost of scoring an 84 on the history exam rather than 76 is:
Refer to Exhibit 2-1.A student has only a few hours to prepare for two different exams tomorrow morning.The above table shows alternative possible exam outcomes with three alternative uses of the student's time.The opportunity cost of scoring an 84 on the history exam rather than 76 is:A) 10 points on the economics exam.
B) 7 points on the economics exam.
C) 8 points on the history exam.
D) 12 points on the economics exam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The opportunity cost of an action is equal to:
A) only the monetary payment the action required.
B) the total time spent by all parties in carrying out the action.
C) the highest valued opportunity that must be sacrificed in order to take the action.
D) the value of all of the alternative actions that could have been taken.
A) only the monetary payment the action required.
B) the total time spent by all parties in carrying out the action.
C) the highest valued opportunity that must be sacrificed in order to take the action.
D) the value of all of the alternative actions that could have been taken.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Trent decides to spend an hour playing basketball rather than studying.His opportunity cost is:
A) nothing because he enjoys playing basketball more than studying.
B) the benefit to his grades from studying for an hour.
C) the increase in skill he obtains from playing basketball for that hour.
D) nothing because he had a free pass into the sports complex to play basketball.
A) nothing because he enjoys playing basketball more than studying.
B) the benefit to his grades from studying for an hour.
C) the increase in skill he obtains from playing basketball for that hour.
D) nothing because he had a free pass into the sports complex to play basketball.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The opportunity cost of going to college includes:
A) both tuition and the value of the student's time.
B) tuition, but not the value of the student's time, which is a monetary cost.
C) neither tuition nor the value of the student's time, since obtaining a college degree makes one's income higher in the future.
D) neither tuition nor the value of the student's time, at least at state-supported universities and colleges.
A) both tuition and the value of the student's time.
B) tuition, but not the value of the student's time, which is a monetary cost.
C) neither tuition nor the value of the student's time, since obtaining a college degree makes one's income higher in the future.
D) neither tuition nor the value of the student's time, at least at state-supported universities and colleges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The opportunity cost of an item is:
A) greater during periods of inflation and lower during periods of deflation.
B) the highest valued alternative you give up to get that item.
C) the value of all available alternatives you sacrifice to get that item.
D) always equal to the dollar value of the item.
A) greater during periods of inflation and lower during periods of deflation.
B) the highest valued alternative you give up to get that item.
C) the value of all available alternatives you sacrifice to get that item.
D) always equal to the dollar value of the item.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Opportunity costs:
A) only include explicit costs paid out-of-pocket.
B) never involve costs paid out-of-pocket.
C) may or may not involve costs paid out-of-pocket.
D) are always measured in time units.
A) only include explicit costs paid out-of-pocket.
B) never involve costs paid out-of-pocket.
C) may or may not involve costs paid out-of-pocket.
D) are always measured in time units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A student has a chance to see Taylor Swift in concert.The student also has a major economics exam in the morning.If the student goes to the concert:
A) she may receive a lower grade on the economics exam.
B) the opportunity cost of the concert is the value of the time spent studying.
C) the decision involves a tradeoff.
D) all of the above are correct.
A) she may receive a lower grade on the economics exam.
B) the opportunity cost of the concert is the value of the time spent studying.
C) the decision involves a tradeoff.
D) all of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The opportunity cost of a decision is equal to the explicit cost in monetary terms.
B) The opportunity cost of a decision is the value of the best foregone alternative.
C) Some economic decisions have zero opportunity cost.
D) The opportunity cost of attending college is the same for all students at the same university but may differ among students at different universities.
A) The opportunity cost of a decision is equal to the explicit cost in monetary terms.
B) The opportunity cost of a decision is the value of the best foregone alternative.
C) Some economic decisions have zero opportunity cost.
D) The opportunity cost of attending college is the same for all students at the same university but may differ among students at different universities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exhibit 2-1 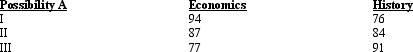 Refer to Exhibit 2-1.A student has only a few hours to prepare for two different exams this afternoon.The above table shows alternative possible exam scores with three alternative uses of the student's time.The opportunity cost of scoring a 94 on the economics exam rather than a 77 is:
Refer to Exhibit 2-1.A student has only a few hours to prepare for two different exams this afternoon.The above table shows alternative possible exam scores with three alternative uses of the student's time.The opportunity cost of scoring a 94 on the economics exam rather than a 77 is:
A) 8 points on the history exam.
B) 15 points on the history exam.
C) 76 points on the history exam.
D) 91 points on the history exam.
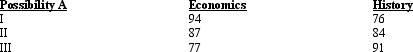 Refer to Exhibit 2-1.A student has only a few hours to prepare for two different exams this afternoon.The above table shows alternative possible exam scores with three alternative uses of the student's time.The opportunity cost of scoring a 94 on the economics exam rather than a 77 is:
Refer to Exhibit 2-1.A student has only a few hours to prepare for two different exams this afternoon.The above table shows alternative possible exam scores with three alternative uses of the student's time.The opportunity cost of scoring a 94 on the economics exam rather than a 77 is:A) 8 points on the history exam.
B) 15 points on the history exam.
C) 76 points on the history exam.
D) 91 points on the history exam.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
"Opportunity cost" refers to:
A) the dollar price paid for a good.
B) the value of the best foregone alternative.
C) the finder's fee paid to a job placement agency for locating employment for workers.
D) the membership fee paid to join a health club.
A) the dollar price paid for a good.
B) the value of the best foregone alternative.
C) the finder's fee paid to a job placement agency for locating employment for workers.
D) the membership fee paid to join a health club.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The opportunity cost of attending college is likely to include all except which of the following?
A) the cost of required textbooks
B) tuition fees
C) the income you forego in order to attend classes
D) the cost of haircuts received during the school term
A) the cost of required textbooks
B) tuition fees
C) the income you forego in order to attend classes
D) the cost of haircuts received during the school term

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The opportunity cost of attending a university for a year is measured by:
A) the tuition fees incurred.
B) the size of the student loans the student becomes responsible for.
C) the sum of all expenditures on rent, food, books, and tuition incurred during the school year.
D) the value of the best opportunity or opportunities foregone in order to enroll for the year.
A) the tuition fees incurred.
B) the size of the student loans the student becomes responsible for.
C) the sum of all expenditures on rent, food, books, and tuition incurred during the school year.
D) the value of the best opportunity or opportunities foregone in order to enroll for the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The opportunity cost of an action:
A) can be objectively determined only by economists.
B) is a subjective valuation that can only be determined by the individual who chooses the action.
C) can be determined by adding up the bills incurred as a result of the action.
D) can be determined by considering both the benefits that flow from as well as the monetary costs incurred as a result of the action.
A) can be objectively determined only by economists.
B) is a subjective valuation that can only be determined by the individual who chooses the action.
C) can be determined by adding up the bills incurred as a result of the action.
D) can be determined by considering both the benefits that flow from as well as the monetary costs incurred as a result of the action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The opportunity cost of an airplane flight:
A) differs across passengers only to the extent that each traveler pays a different airfare.
B) is identical for all passengers and equal to the number of hours a particular flight takes.
C) differs across passengers to the extent that both the airfare paid and the highest valued use of travel time vary.
D) is equal to the cost of a bus ticket, the next best form of alternative transportation to flying.
A) differs across passengers only to the extent that each traveler pays a different airfare.
B) is identical for all passengers and equal to the number of hours a particular flight takes.
C) differs across passengers to the extent that both the airfare paid and the highest valued use of travel time vary.
D) is equal to the cost of a bus ticket, the next best form of alternative transportation to flying.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The opportunity cost of attending a college basketball game is:
A) price of the admission to the game.
B) the sum of the value of all the alternative uses of your time while at the game.
C) the value of the highest alternative use of your time and money sacrificed as a result of attending the game.
D) less if your favorite team wins.
A) price of the admission to the game.
B) the sum of the value of all the alternative uses of your time while at the game.
C) the value of the highest alternative use of your time and money sacrificed as a result of attending the game.
D) less if your favorite team wins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
"If I didn't have class tonight,I would save the $4 campus parking fee and spend four hours at work where I earn $10 per hour." The opportunity cost of attending class this evening is:
A) $4.
B) $40.
C) $44.
D) $0.
A) $4.
B) $40.
C) $44.
D) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The opportunity cost of an action includes:
A) the monetary expenses incurred as a result of the action.
B) the highest valued alternative use of the time spent on the action.
C) the benefits received as a result of the action.
D) only a. and b.
A) the monetary expenses incurred as a result of the action.
B) the highest valued alternative use of the time spent on the action.
C) the benefits received as a result of the action.
D) only a. and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Jamie and Danny both attend the same college and incur the same expenses for tuition,books,and school supplies.Jamie gave up a lucrative modeling job in Paris to attend school full-time and Danny gave up a part-time job as a sales clerk in a department store.It follows that:
A) the opportunity cost of attending college is the same for both since they are enrolled at the same academic institution.
B) the opportunity cost of attending college is likely greater for Jamie than for Danny.
C) the opportunity cost of attending college is likely greater for Danny than for Jamie.
D) the opportunity cost is minimal for both since college graduates are paid much higher than high school graduates on average.
A) the opportunity cost of attending college is the same for both since they are enrolled at the same academic institution.
B) the opportunity cost of attending college is likely greater for Jamie than for Danny.
C) the opportunity cost of attending college is likely greater for Danny than for Jamie.
D) the opportunity cost is minimal for both since college graduates are paid much higher than high school graduates on average.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The opportunity cost of an action is equal to:
A) the monetary expense incurred as a result of the action.
B) the value of any alternative use of the time expended on the action.
C) the highest valued alternative sacrificed as a result of the action.
D) the sum of the benefits received as a result of the action.
A) the monetary expense incurred as a result of the action.
B) the value of any alternative use of the time expended on the action.
C) the highest valued alternative sacrificed as a result of the action.
D) the sum of the benefits received as a result of the action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 197 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



