Deck 13: Monopoly and Antitrust
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/189
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Monopoly and Antitrust
1
Monopolists,unlike perfectly competitive firms,can continue to earn positive economic profits over time.
True
2
Monopolies will tend to produce a greater quantity and charge higher prices than perfectly competitive industries.
False
3
A natural monopolist will voluntarily choose to produce at the point of allocative efficiency.
False
4
When a monopolist practices price discrimination,consumer surplus tends to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Control of a scarce resource or input can serve as an entry barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In order to implement average cost pricing regulation,it is necessary to provide a natural monopolist with a subsidy equal to the economic loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The demand curve faced by a monopolist is the same as the marginal revenue curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A price-discriminating monopoly firm will tend to charge a higher price to customers with a greater willingness to pay than it does to customers with a lower willingness to pay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A monopoly firm can sell as much output as it wants at whatever price it sets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The U.S.Postal Service historically has had a monopoly over the market for the delivery of first-class letters in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A welfare loss occurs when a monopolist chooses not to produce units of output that are of greater marginal value to consumers than the marginal cost of producing them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The welfare loss from monopoly is not really a loss to society as a whole,since it is just a transfer from consumers to producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Monopoly profits cannot persist in the long run,because there are barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The monopolist,like the perfect competitor,maximizes profits at the output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Peak load pricing - which causes consumers to pay higher prices at certain times - leads to greater efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A profit-maximizing monopolist will choose to operate along the inelastic portion of its demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A monopolist restricts output and charges a higher price relative to what would occur if a market were perfectly competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A natural monopoly exists when one large firm can produce a product at a lower per unit cost than can smaller firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In order for a firm to be able to price discriminate it must not be a price taker,there must be different demand from different groups of consumers,and there must be an ability to prevent resale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
One difficulty associated with average cost pricing regulation of natural monopolies is that firms have little or no incentive to minimize production costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is inconsistent with a monopoly?
A) a single seller
B) a downward-sloping demand curve
C) marginal revenue exceeds price
D) a U-shaped average total cost curve
A) a single seller
B) a downward-sloping demand curve
C) marginal revenue exceeds price
D) a U-shaped average total cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following can serve as a barrier to entry?
A) legal restrictions
B) patents
C) control of scarce inputs or resources
D) all of the above
A) legal restrictions
B) patents
C) control of scarce inputs or resources
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not a source of monopoly?
A) technologies that allow each of many small firms to produce at the same per-unit costs as one large firm
B) patents
C) control of crucial inputs
D) government licensing requirements
A) technologies that allow each of many small firms to produce at the same per-unit costs as one large firm
B) patents
C) control of crucial inputs
D) government licensing requirements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the average total cost curve is always above the demand curve of a monopolist:
A) that monopolist will suffer economic losses.
B) entry will occur, forcing the monopolist to reduce price and expand output.
C) the monopolist will earn an economic profit.
D) the monopolist must be producing inefficiently.
A) that monopolist will suffer economic losses.
B) entry will occur, forcing the monopolist to reduce price and expand output.
C) the monopolist will earn an economic profit.
D) the monopolist must be producing inefficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Graphically which of the following is true for a monopoly?
A) The marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve and is steeper than the demand curve.
B) The marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve and is steeper than the demand curve.
C) The marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve and is flatter than the demand curve.
D) The marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve and is flatter than the demand curve.
A) The marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve and is steeper than the demand curve.
B) The marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve and is steeper than the demand curve.
C) The marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve and is flatter than the demand curve.
D) The marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve and is flatter than the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why does the government allow some markets to be monopolized by granting patents?
A) to promote a more equal distribution of income
B) to correct for negative externalities
C) to promote technological progress
D) to ensure lower prices for consumers in the short run
A) to promote a more equal distribution of income
B) to correct for negative externalities
C) to promote technological progress
D) to ensure lower prices for consumers in the short run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not potentially a barrier to entry into a product market?
A) patent protection on the design of the product
B) the absence of economies of scale in the product market
C) government licensing of the product's producers
D) the control of a crucial input necessary to produce the product
A) patent protection on the design of the product
B) the absence of economies of scale in the product market
C) government licensing of the product's producers
D) the control of a crucial input necessary to produce the product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Pure monopoly:
A) is characterized by a single supplier.
B) is a market structure in which no close substitute products are available.
C) exists when entry and survival of potential competitors is extremely unlikely.
D) is characterized by all of the above.
A) is characterized by a single supplier.
B) is a market structure in which no close substitute products are available.
C) exists when entry and survival of potential competitors is extremely unlikely.
D) is characterized by all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of these contributes to the existence of monopoly power?
A) the control of critical resources
B) legal barriers
C) patents
D) All of the above contribute to the existence of monopoly power.
A) the control of critical resources
B) legal barriers
C) patents
D) All of the above contribute to the existence of monopoly power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Graphically,the marginal revenue curve of a monopolist:
A) lies below the demand curve of a monopolist.
B) is the same as the demand curve of a monopolist.
C) lies above the demand curve of a monopolist.
D) is the same as the marginal cost curve of a monopolist.
A) lies below the demand curve of a monopolist.
B) is the same as the demand curve of a monopolist.
C) lies above the demand curve of a monopolist.
D) is the same as the marginal cost curve of a monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is generally true of monopoly?
A) Price exceeds marginal cost.
B) Marginal revenue is less than price.
C) Output is restricted relative to the socially efficient level.
D) All of the above are generally true of monopoly.
A) Price exceeds marginal cost.
B) Marginal revenue is less than price.
C) Output is restricted relative to the socially efficient level.
D) All of the above are generally true of monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A monopolist will operate at the quantity where:
A) MR = MC and charge a price equal to marginal revenue.
B) MR = MC and charge a price equal to average variable cost.
C) MR = MC and charge a price corresponding to demand at that level.
D) MR = MC and charge a price corresponding to average total cost at that level.
A) MR = MC and charge a price equal to marginal revenue.
B) MR = MC and charge a price equal to average variable cost.
C) MR = MC and charge a price corresponding to demand at that level.
D) MR = MC and charge a price corresponding to average total cost at that level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A monopolistic firm is a:
A) price taker that faces the market supply curve.
B) price taker that faces the market demand curve.
C) price maker that faces the market supply curve.
D) price maker that faces the market demand curve.
A) price taker that faces the market supply curve.
B) price taker that faces the market demand curve.
C) price maker that faces the market supply curve.
D) price maker that faces the market demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Many communities have granted monopoly rights to cable companies.This is an example of a monopoly created through:
A) government licensing.
B) ownership of the cable resources.
C) patent protection.
D) smart business practices by shrewd entrepreneurs.
A) government licensing.
B) ownership of the cable resources.
C) patent protection.
D) smart business practices by shrewd entrepreneurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following best explains why a monopolist's marginal revenue is less than the sale price?
A) To sell more units, a monopolist must increase the price on all units sold.
B) As a monopolist expands output, its average total cost declines.
C) When a firm has a monopoly, consumers have no choice other than to pay the price set by the monopolist.
D) When a monopolist reduces price in order to sell more units, it must lower the price of some units that could otherwise have been sold at a higher price.
A) To sell more units, a monopolist must increase the price on all units sold.
B) As a monopolist expands output, its average total cost declines.
C) When a firm has a monopoly, consumers have no choice other than to pay the price set by the monopolist.
D) When a monopolist reduces price in order to sell more units, it must lower the price of some units that could otherwise have been sold at a higher price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Barriers that prevent the entry of new firms may arise because:
A) economies of scale exist over a substantial range of industry demand.
B) marginal revenue is less than average total cost.
C) the government protects some firms from competition.
D) of both (a) and (c).
A) economies of scale exist over a substantial range of industry demand.
B) marginal revenue is less than average total cost.
C) the government protects some firms from competition.
D) of both (a) and (c).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The demand curve of a monopolist is:
A) is identical to the marginal cost curve.
B) downward sloping and above the marginal revenue curve.
C) downward sloping and below the marginal revenue curve.
D) kinked because of recognized interdependence with other firms.
A) is identical to the marginal cost curve.
B) downward sloping and above the marginal revenue curve.
C) downward sloping and below the marginal revenue curve.
D) kinked because of recognized interdependence with other firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The DeBeers Diamond Company,which owns most of the South African diamond production,has market power over the diamond trade.This market power was obtained through:
A) illegal means.
B) control of a scarce resource.
C) patent protection.
D) government licensing.
A) illegal means.
B) control of a scarce resource.
C) patent protection.
D) government licensing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A natural gas monopoly currently sells 100 cubic feet of gas at $1.10 per cubic foot.To sell one more cubic foot,the natural gas company must lower the price of gas to $1.09.Which of the following best describes the marginal revenue of the 101st cubic foot of natural gas?
A) The marginal revenue equals the price, or $1.09.
B) The marginal revenue equals the change in price, or $ 0.01.
C) The marginal revenue is less than $1.09.
D) The marginal revenue is greater than $1.09.
A) The marginal revenue equals the price, or $1.09.
B) The marginal revenue equals the change in price, or $ 0.01.
C) The marginal revenue is less than $1.09.
D) The marginal revenue is greater than $1.09.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is a characteristic of a monopoly?
A) a large number of sellers
B) homogeneous products
C) large barriers to entry
D) price taking firms
A) a large number of sellers
B) homogeneous products
C) large barriers to entry
D) price taking firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Exhibit 13-1 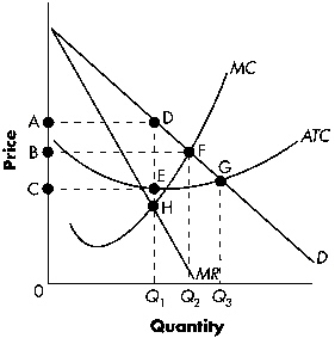 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The profit-maximizing firm's total revenue is indicated in the diagram as area:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The profit-maximizing firm's total revenue is indicated in the diagram as area:
A) 0CEQ1.
B) 0BFQ2.
C) 0ADQ1.
D) CADE.
 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The profit-maximizing firm's total revenue is indicated in the diagram as area:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The profit-maximizing firm's total revenue is indicated in the diagram as area:A) 0CEQ1.
B) 0BFQ2.
C) 0ADQ1.
D) CADE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is likely in a monopolized market?
A) a price that exceeds marginal cost
B) a price that exceeds marginal revenue
C) a welfare loss due to the restriction of output
D) all of the above
A) a price that exceeds marginal cost
B) a price that exceeds marginal revenue
C) a welfare loss due to the restriction of output
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Monopoly results in a welfare loss because:
A) marginal revenue does not equal marginal cost.
B) the monopolist restricts output below the socially efficient level.
C) average variable cost is not minimized.
D) total cost is not minimized.
A) marginal revenue does not equal marginal cost.
B) the monopolist restricts output below the socially efficient level.
C) average variable cost is not minimized.
D) total cost is not minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Profit-maximizing monopolists choose a level of output such that:
A) average total cost is minimized.
B) price equals marginal revenue but exceeds average variable cost.
C) price equals marginal cost but exceeds average variable cost.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A) average total cost is minimized.
B) price equals marginal revenue but exceeds average variable cost.
C) price equals marginal cost but exceeds average variable cost.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Exhibit 13-1 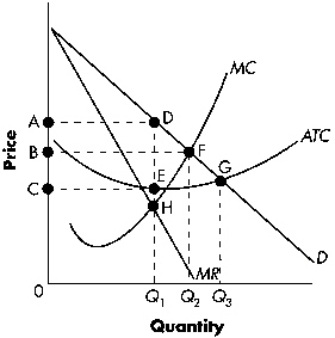 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The socially efficient level of output equals:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The socially efficient level of output equals:
A) 0Q1.
B) 0Q2.
C) 0Q3.
D) none of the above.
 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The socially efficient level of output equals:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The socially efficient level of output equals:A) 0Q1.
B) 0Q2.
C) 0Q3.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
At his current level of output,a monopolist has a MR of $10,a MC of $6,and an economic profit of zero.If the market demand curve is downward sloping and his marginal cost curve is upward sloping,the monopolist:
A) is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output.
B) could increase profit by increasing output.
C) could increase profit by increasing his price.
D) should exit the market if significant fixed costs have been incurred.
A) is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output.
B) could increase profit by increasing output.
C) could increase profit by increasing his price.
D) should exit the market if significant fixed costs have been incurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a profit-maximizing monopolist finds that marginal cost is increasing and exceeds marginal revenue,it should:
A) increase output and decrease price.
B) increase price and decrease output.
C) decrease both price and output.
D) increase both price and output.
A) increase output and decrease price.
B) increase price and decrease output.
C) decrease both price and output.
D) increase both price and output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following accurately describes a major difference between a monopolist and firms in perfectly competitive markets?
A) The monopolist maximizes profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets maximize sales.
B) The monopolist may earn long-run economic profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets cannot.
C) The monopolist is a price taker; firms in other markets are price searchers.
D) The monopolist may earn short-run profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets cannot.
A) The monopolist maximizes profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets maximize sales.
B) The monopolist may earn long-run economic profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets cannot.
C) The monopolist is a price taker; firms in other markets are price searchers.
D) The monopolist may earn short-run profit; firms in perfectly competitive markets cannot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Exhibit 13-1 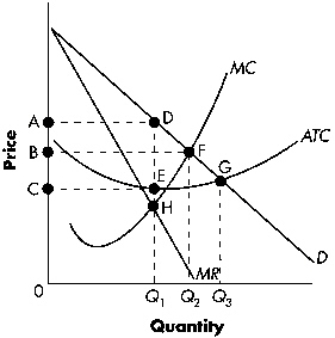 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The profit-maximizing firm will produce at what level of output?
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The profit-maximizing firm will produce at what level of output?
A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) None of the above.
 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The profit-maximizing firm will produce at what level of output?
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The profit-maximizing firm will produce at what level of output?A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
At a given output level,a monopolist earns a profit only if:
A) the slope of the total revenue curve exceeds the slope of the total cost curve.
B) the height of the marginal revenue curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the marginal cost curve at that output.
C) the height of the demand curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the marginal revenue curve at that output.
D) the height of the demand curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the average total cost curve at that output.
A) the slope of the total revenue curve exceeds the slope of the total cost curve.
B) the height of the marginal revenue curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the marginal cost curve at that output.
C) the height of the demand curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the marginal revenue curve at that output.
D) the height of the demand curve at the output produced exceeds the height of the average total cost curve at that output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Based on the table below what is the marginal revenue of the 28th unit of output? 
A) -$16.50
B) -$13.50
C) $13.50
D) $16.50

A) -$16.50
B) -$13.50
C) $13.50
D) $16.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If marginal revenue on the tenth unit of output equals $4 for a non-discriminating,profit-maximizing monopolist,then price:
A) equals $4.
B) is less than $4.
C) is greater than $4.
D) must be equal to average total cost.
A) equals $4.
B) is less than $4.
C) is greater than $4.
D) must be equal to average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
For a profit-maximizing monopolist,the price of a product is:
A) always equal to marginal revenue.
B) always greater than marginal revenue.
C) always less than marginal revenue.
D) always equal to the average total cost of production.
A) always equal to marginal revenue.
B) always greater than marginal revenue.
C) always less than marginal revenue.
D) always equal to the average total cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is not generally true about a profit-maximizing monopolist?
A) The monopolist faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B) The monopolist can potentially continue to earn economic profits in the long run.
C) The monopolist charges a price that exceeds marginal cost.
D) The monopolist chooses output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A) The monopolist faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B) The monopolist can potentially continue to earn economic profits in the long run.
C) The monopolist charges a price that exceeds marginal cost.
D) The monopolist chooses output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a firm seeks to maximize total revenue,it should produce the quantity where:
A) marginal revenue equals zero.
B) elasticity of demand is less than one.
C) elasticity of demand is greater than one.
D) marginal revenue is maximized.
A) marginal revenue equals zero.
B) elasticity of demand is less than one.
C) elasticity of demand is greater than one.
D) marginal revenue is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Exhibit 13-1 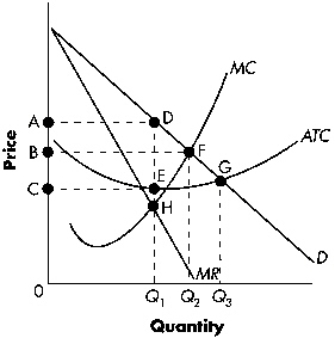 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.If the firm is profit maximizing,the region bounded by CADE represents:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.If the firm is profit maximizing,the region bounded by CADE represents:
A) total costs.
B) total losses.
C) total profits.
D) total consumer surplus.
 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.If the firm is profit maximizing,the region bounded by CADE represents:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.If the firm is profit maximizing,the region bounded by CADE represents:A) total costs.
B) total losses.
C) total profits.
D) total consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Based on the table below what is the marginal revenue of the 14th unit of output? 
A) $0.25
B) $46.00
C) $46.50
D) $49.75

A) $0.25
B) $46.00
C) $46.50
D) $49.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following best explains why marginal revenue for a monopolist is less than the sales price?
A) To sell more units, the monopolist must reduce price on all units sold.
B) As the monopolist expands output, the average total cost of production declines.
C) The monopolist charges each consumer the highest possible price.
D) When a firm has a monopoly, consumers have no choice other than to pay the price set by the monopolist.
A) To sell more units, the monopolist must reduce price on all units sold.
B) As the monopolist expands output, the average total cost of production declines.
C) The monopolist charges each consumer the highest possible price.
D) When a firm has a monopoly, consumers have no choice other than to pay the price set by the monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Exhibit 13-1 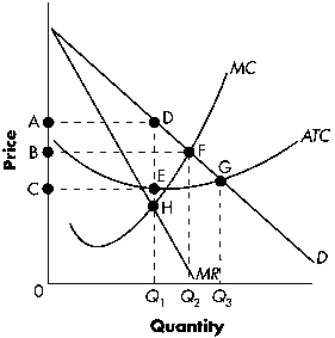 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The welfare loss due to monopoly is indicated in the diagram as area:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The welfare loss due to monopoly is indicated in the diagram as area:
A) DGE.
B) DFH.
C) DFQ2Q1.
D) EGQ3Q1.
 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The welfare loss due to monopoly is indicated in the diagram as area:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.The welfare loss due to monopoly is indicated in the diagram as area:A) DGE.
B) DFH.
C) DFQ2Q1.
D) EGQ3Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Exhibit 13-1 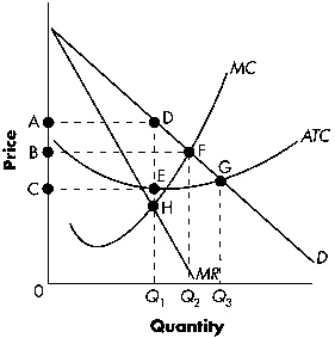 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.Total cost when the monopolist is maximizing profits is indicated by area:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.Total cost when the monopolist is maximizing profits is indicated by area:
A) 0CEQ1.
B) 0BFQ2.
C) 0ADQ1.
D) CADE.
 Refer to Exhibit 13-1.Total cost when the monopolist is maximizing profits is indicated by area:
Refer to Exhibit 13-1.Total cost when the monopolist is maximizing profits is indicated by area:A) 0CEQ1.
B) 0BFQ2.
C) 0ADQ1.
D) CADE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A profit-maximizing monopolist,if producing at all,chooses a level of output where:
A) total revenue is maximized.
B) total cost is minimized.
C) average total cost is minimized.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A) total revenue is maximized.
B) total cost is minimized.
C) average total cost is minimized.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If a monopoly firm is at a level of output where MC equals $10 and is increasing,MR equals $10,and average variable cost equals $9.To maximize profits,the firm should:
A) increase both output and price.
B) increase output but decrease the price.
C) decrease output and increase the price.
D) not change either the output or the price.
A) increase both output and price.
B) increase output but decrease the price.
C) decrease output and increase the price.
D) not change either the output or the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A monopolist will shut down in the short run if:
A) price exceeds marginal revenue.
B) price is less than marginal revenue.
C) price is less than average total cost.
D) total revenue is less than total variable cost.
A) price exceeds marginal revenue.
B) price is less than marginal revenue.
C) price is less than average total cost.
D) total revenue is less than total variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exhibit 13-3 A monopoly producer of canned iced coffee produces with the following costs:
 Consumers demand iced coffee according to the following demand schedule:
Consumers demand iced coffee according to the following demand schedule:
 Refer to Exhibit 13-3.What would the monopolist's profit-maximizing level of output be?
Refer to Exhibit 13-3.What would the monopolist's profit-maximizing level of output be?
A) 2 cans of iced coffee
B) 3 cans of iced coffee
C) 4 cans of iced coffee
D) 5 cans of iced coffee
 Consumers demand iced coffee according to the following demand schedule:
Consumers demand iced coffee according to the following demand schedule: Refer to Exhibit 13-3.What would the monopolist's profit-maximizing level of output be?
Refer to Exhibit 13-3.What would the monopolist's profit-maximizing level of output be?A) 2 cans of iced coffee
B) 3 cans of iced coffee
C) 4 cans of iced coffee
D) 5 cans of iced coffee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A monopoly firm is charging the price the market will bear at a level of output where MC equals $22 and is increasing,MR equals $20,and average variable cost equals $17.To maximize profits,the firm should:
A) increase both output and price.
B) increase output but decrease the price.
C) decrease output and increase the price.
D) decrease both output and price.
A) increase both output and price.
B) increase output but decrease the price.
C) decrease output and increase the price.
D) decrease both output and price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following would likely be an example of a monopolistic industry?
A) fast-food restaurants
B) wireless phone service
C) auto manufacturing
D) none of the above
A) fast-food restaurants
B) wireless phone service
C) auto manufacturing
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What is the maximum amount of profit that the firm below could generate? 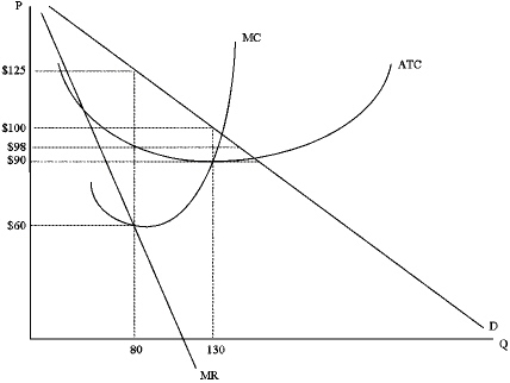
A) -$2,800
B) $2,400
C) $2,480
D) $2,880

A) -$2,800
B) $2,400
C) $2,480
D) $2,880

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The consumer surplus lost because monopolists restrict the production of output represents a welfare loss because:
A) it is transferred to producers in the form of profit.
B) consumers pay a higher price than they would in a more competitive market.
C) society is not using its scarce resources in the best way possible.
D) of both a. and b., but not c.
A) it is transferred to producers in the form of profit.
B) consumers pay a higher price than they would in a more competitive market.
C) society is not using its scarce resources in the best way possible.
D) of both a. and b., but not c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A profit-maximizing monopolist will never produce at an output level where:
A) demand is elastic.
B) it suffers economic losses in the short run.
C) demand is inelastic.
D) marginal cost is less than average total cost.
A) demand is elastic.
B) it suffers economic losses in the short run.
C) demand is inelastic.
D) marginal cost is less than average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a monopolist's marginal revenue is less than zero over a range of output,then price elasticity of demand must be:
A) greater than one.
B) equal to one.
C) less than one.
D) equal to zero.
A) greater than one.
B) equal to one.
C) less than one.
D) equal to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exhibit 13-2 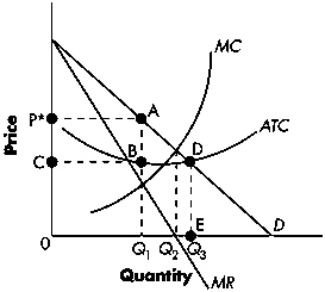 Refer to Exhibit 13-2.The profit-maximizing firm will produce at what level of output?
Refer to Exhibit 13-2.The profit-maximizing firm will produce at what level of output?
A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) zero units
 Refer to Exhibit 13-2.The profit-maximizing firm will produce at what level of output?
Refer to Exhibit 13-2.The profit-maximizing firm will produce at what level of output?A) 0Q1
B) 0Q2
C) 0Q3
D) zero units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Exhibit 13-3 A monopoly producer of canned iced coffee produces with the following costs:
 Consumers demand iced coffee according to the following demand schedule:
Consumers demand iced coffee according to the following demand schedule:
 Refer to Exhibit 13-3.At the profit-maximizing level of output,the firm's profits equal:
Refer to Exhibit 13-3.At the profit-maximizing level of output,the firm's profits equal:
A) $2.35.
B) $8.25.
C) $10.00.
D) $10.25.
 Consumers demand iced coffee according to the following demand schedule:
Consumers demand iced coffee according to the following demand schedule: Refer to Exhibit 13-3.At the profit-maximizing level of output,the firm's profits equal:
Refer to Exhibit 13-3.At the profit-maximizing level of output,the firm's profits equal:A) $2.35.
B) $8.25.
C) $10.00.
D) $10.25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A monopoly firm is charging the price the market will bear at a level of output where MC equals $6 and is increasing,MR equals $9,and average variable cost equals $5.To maximize profits,the firm should:
A) increase both output and price.
B) increase output but decrease the price.
C) decrease output and increase the price.
D) decrease both output and price.
A) increase both output and price.
B) increase output but decrease the price.
C) decrease output and increase the price.
D) decrease both output and price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If an unregulated monopolist operates in a market,then:
A) customers will pay higher prices than if the market were competitive.
B) customers will purchase fewer units of output than if the market were competitive.
C) society will not be allocating its resources efficiently.
D) all of the above will occur.
A) customers will pay higher prices than if the market were competitive.
B) customers will purchase fewer units of output than if the market were competitive.
C) society will not be allocating its resources efficiently.
D) all of the above will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The following represents a portion of the demand schedule faced by a monopoly firm.  The marginal revenue of the third unit of output equals:
The marginal revenue of the third unit of output equals:
A) $12.
B) $10.
C) $8.
D) $1.
 The marginal revenue of the third unit of output equals:
The marginal revenue of the third unit of output equals:A) $12.
B) $10.
C) $8.
D) $1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In the short run,a monopolist:
A) always suffers an economic loss.
B) always earns an economic profit.
C) always earns a normal rate of return.
D) may make an economic loss, an economic profit, or zero economic profits.
A) always suffers an economic loss.
B) always earns an economic profit.
C) always earns a normal rate of return.
D) may make an economic loss, an economic profit, or zero economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A monopoly is inefficient because:
A) consumers are forced to pay higher prices for products.
B) firms are able to earn economic profits.
C) the cost of increased production is less than the value that society places on it.
D) price exceeds marginal revenue.
A) consumers are forced to pay higher prices for products.
B) firms are able to earn economic profits.
C) the cost of increased production is less than the value that society places on it.
D) price exceeds marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Exhibit 13-2 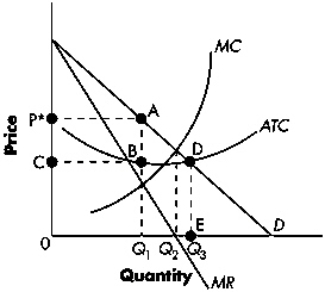 Refer to Exhibit 13-2.The region bounded by P*ABC represents:
Refer to Exhibit 13-2.The region bounded by P*ABC represents:
A) total costs.
B) total losses.
C) total profits.
D) total consumer surplus.
 Refer to Exhibit 13-2.The region bounded by P*ABC represents:
Refer to Exhibit 13-2.The region bounded by P*ABC represents:A) total costs.
B) total losses.
C) total profits.
D) total consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the maximum amount of profit that the firm below could generate? 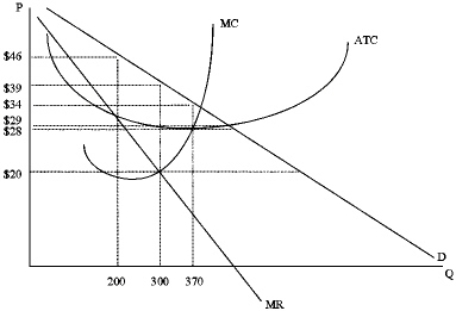
A) $2,220
B) $3,000
C) $3,300
D) $3,700

A) $2,220
B) $3,000
C) $3,300
D) $3,700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A price-taking firm and a monopoly firm are alike in that:
A) price equals marginal revenue for both.
B) both maximize profits by choosing an output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) price exceeds marginal cost at the profit-maximizing level of output for both.
D) in the long run, both earn zero economic profits.
A) price equals marginal revenue for both.
B) both maximize profits by choosing an output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) price exceeds marginal cost at the profit-maximizing level of output for both.
D) in the long run, both earn zero economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 189 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



