Deck 56: Population Ecology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 56: Population Ecology
1
Demographic studies include all of the following except
A)age structure.
B)growth rates.
C)mortality and survivorship curves.
D)sex ratio.
E)measurements of interspecific competition.
A)age structure.
B)growth rates.
C)mortality and survivorship curves.
D)sex ratio.
E)measurements of interspecific competition.
E
2
A small group of mice are released on an island without mice but with abundant food for mice and no predators.After the population size stabilizes for several years,a hurricane drastically reduces it,we can now say that
A)the biotic potential of the population has been reduced.
B)its new population size is a result of density-dependent regulation.
C)its new population size is a result of density-independent regulation.
D)it can now act as a sink metapopulation.
E)it can now act as a source metapopulation.
A)the biotic potential of the population has been reduced.
B)its new population size is a result of density-dependent regulation.
C)its new population size is a result of density-independent regulation.
D)it can now act as a sink metapopulation.
E)it can now act as a source metapopulation.
C
3
A group of individuals of a single species living together is a
A)deme.
B)phenotype.
C)genome.
D)biotic community.
E)population.
A)deme.
B)phenotype.
C)genome.
D)biotic community.
E)population.
E
4
A small group of mice are released on an island without mice but with abundant food for mice and no predators.When the population stabilizes
A)the birth rate is zero.
B)the birth rate plus the death rate is zero.
C)the population has reached its biotic potential.
D)the population size equals the carrying capacity.
E)the intrinsic rate of increase is zero.
A)the birth rate is zero.
B)the birth rate plus the death rate is zero.
C)the population has reached its biotic potential.
D)the population size equals the carrying capacity.
E)the intrinsic rate of increase is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Effects that are dependent on the size of the population and regulate the growth of populations are called ___________ effects.
A)K-related
B)density-independent
C)environmental resistance
D)density-dependent
E)demographic
A)K-related
B)density-independent
C)environmental resistance
D)density-dependent
E)demographic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The statistical study of populations including sex ratio,age structure,and predicting growth rates is called __________.
A)ethology
B)demography
C)population genetics
D)biometrics
A)ethology
B)demography
C)population genetics
D)biometrics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The size at which a population stabilizes in a particular place is defined as the __________ for that species.
A)growth potential
B)optimum
C)range
D)carrying capacity
A)growth potential
B)optimum
C)range
D)carrying capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The trade-off between investments in current reproduction and in growth that promotes future reproduction is referred to as the total cost of
A)adaptation.
B)selection.
C)reproduction.
D)genetic change.
E)fitness.
A)adaptation.
B)selection.
C)reproduction.
D)genetic change.
E)fitness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A community and the nonliving factors with which it interacts is called a(n)
A)population.
B)race.
C)cline.
D)environment.
E)ecosystem.
A)population.
B)race.
C)cline.
D)environment.
E)ecosystem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A small group of mice are released on an island without mice but with abundant food for mice and no predators.Initially,the growth of the mouse population will be limited mainly by
A)the carrying capacity.
B)its birth rate.
C)its biotic potential.
D)only density-dependent factors.
E)only independent-dependent factors.
A)the carrying capacity.
B)its birth rate.
C)its biotic potential.
D)only density-dependent factors.
E)only independent-dependent factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Life history adaptations of ____ selected populations are characterized by an early age of first reproduction and short maturation time and life span.
A)r-
B)K-
A)r-
B)K-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Species that have a delayed reproductive stage,are competing for limited resources,and have smaller numbers of slowly maturing large offspring show ______ selected adaptations.
A)K-
B)r-
A)K-
B)r-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The rate at which a population of a given species will increase when no limits are placed on its rate of growth is called its __________.
A)maximum growth
B)carrying capacity
C)biotic potential
D)optimal growth
A)maximum growth
B)carrying capacity
C)biotic potential
D)optimal growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Population studies include all of the following features except
A)size.
B)biodiversity.
C)density.
D)dispersion.
E)demography.
A)size.
B)biodiversity.
C)density.
D)dispersion.
E)demography.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Clumped or patched populations that undergo local periodic extinction and recolonization are called
A)randomly spaced populations.
B)uniformly spaced populations.
C)metapopulations.
D)over sized populations.
E)endangered populations.
A)randomly spaced populations.
B)uniformly spaced populations.
C)metapopulations.
D)over sized populations.
E)endangered populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A group of population members all of the same age is called a _________.
A)deme
B)species
C)cohort
D)tribe
A)deme
B)species
C)cohort
D)tribe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Organisms such as lizards that need to maintain body temperature through external means do so by
A)shivering to produce heat.
B)sunbathing.
C)swimming in geothermal pools.
D)running frequently to warm up.
E)eating large meals to provide calories for heat production.
A)shivering to produce heat.
B)sunbathing.
C)swimming in geothermal pools.
D)running frequently to warm up.
E)eating large meals to provide calories for heat production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Populations of endotherms that live in colder climates tend to have shorter ears and limbs than populations of the same species in warm climates.This is called ____________ Rule.
A)Allen's
B)the K-Selected
C)the r-Selected
D)Edward's
A)Allen's
B)the K-Selected
C)the r-Selected
D)Edward's

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Based on surface-area to volume considerations,we would predict that populations of mammals that live in colder climates should have _______ bodies than populations of the same species in warm climates.
A)smaller
B)larger
C)leaner
D)taller
A)smaller
B)larger
C)leaner
D)taller

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Organisms that produce offspring several times over many seasons exhibit a life history adaptation called
A)semelparity.
B)iteroparity.
C)biparity.
D)polyparity.
E)alloparity.
A)semelparity.
B)iteroparity.
C)biparity.
D)polyparity.
E)alloparity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the logistic growth model,as the number of individuals in the population (N)approaches the carrying capacity (K),the rate of growth (dN/dt)
A)increases rapidly until N far surpasses K.
B)increases rapidly until N reaches K and then stops.
C)increases at the same rate it has been,continuing on until N is beyond K for some distance before regulating.
D)approaches zero as N approaches K.
E)stops well before N reaches K and stabilizes.
A)increases rapidly until N far surpasses K.
B)increases rapidly until N reaches K and then stops.
C)increases at the same rate it has been,continuing on until N is beyond K for some distance before regulating.
D)approaches zero as N approaches K.
E)stops well before N reaches K and stabilizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All of the following apply to density-dependent factors except that they
A)affect the size of the population.
B)act to regulate population growth.
C)ultimately cause adaptation as competition for limiting factors increases.
D)are especially important in K-selected populations.
E)never involve biological interactions.
A)affect the size of the population.
B)act to regulate population growth.
C)ultimately cause adaptation as competition for limiting factors increases.
D)are especially important in K-selected populations.
E)never involve biological interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Ranges of a population
A)are very fluid and change frequently in a random fashion.
B)are stable and almost never change.
C)only change after a disaster has wiped out a former range.
D)change over time due to external events.
E)only change due to iteroparity.
A)are very fluid and change frequently in a random fashion.
B)are stable and almost never change.
C)only change after a disaster has wiped out a former range.
D)change over time due to external events.
E)only change due to iteroparity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Populations have three basic types of dispersal patterns-clumped,random,and uniform.One can observe random distributions because
A)individuals of the populations do not interact strongly with one another.
B)individuals of the population are usually in competition for resources.
C)individuals of the population are reacting to uneven distribution of resources.
D)individuals of the population with random distribution display social interactions.
A)individuals of the populations do not interact strongly with one another.
B)individuals of the population are usually in competition for resources.
C)individuals of the population are reacting to uneven distribution of resources.
D)individuals of the population with random distribution display social interactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The r-selected populations are characterized by all of the following except
A)early age of first reproduction.
B)large brood size/numerous offspring.
C)little or no parental care.
D)short generation time.
E)Type I survivorship curves.
A)early age of first reproduction.
B)large brood size/numerous offspring.
C)little or no parental care.
D)short generation time.
E)Type I survivorship curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the sigmoid growth curve,the number of individuals at any one time is
A)r.
B)N.
C)K.
D)dN/dt.
E)N/K.
A)r.
B)N.
C)K.
D)dN/dt.
E)N/K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Populations of organisms that have sigmoid growth curves limited by the carrying capacity are called
A)K-selected.
B)r-selected.
C)predators.
D)parasites.
E)perennials.
A)K-selected.
B)r-selected.
C)predators.
D)parasites.
E)perennials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The number of individuals of a species that can be supported indefinitely in a particular place is called its
A)niche.
B)biotic potential.
C)carrying capacity.
D)maximum size.
E)habitat usagE.
A)niche.
B)biotic potential.
C)carrying capacity.
D)maximum size.
E)habitat usagE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
There are three aspects of entire populations that are important and often studied.Select the best choice from the ones listed.
A)a population's range,the dispersal of individuals within the range,and the size that the population
B)a population's range,the amount of food available within the range,and the size that the population attains
C)a population's range,the parental care received by each offspring within the population,and the size that the population attains
D)a population's range,the size home range of an individual in the population,and the parental care expended for each offspring
A)a population's range,the dispersal of individuals within the range,and the size that the population
B)a population's range,the amount of food available within the range,and the size that the population attains
C)a population's range,the parental care received by each offspring within the population,and the size that the population attains
D)a population's range,the size home range of an individual in the population,and the parental care expended for each offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Examples of organisms showing K-selected adaptations include all of the following except
A)dandelions.
B)whooping cranes.
C)whales.
D)humans.
E)coconut palms.
A)dandelions.
B)whooping cranes.
C)whales.
D)humans.
E)coconut palms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Many times species are composed of networks of distinct populations called metapopulations.Metapopulations occur in areas where
A)a population in better habitats continually sends out dispersers to bolster populations in poorer habitats.
B)a population in poor habitat continually sends out dispersers to bolster populations in better habitats.
C)a population in better habitats does not send out colonizers into poorer habitats.
D)suitable habitat is patchily distributed and separated by areas of unsuitable habitat.
A)a population in better habitats continually sends out dispersers to bolster populations in poorer habitats.
B)a population in poor habitat continually sends out dispersers to bolster populations in better habitats.
C)a population in better habitats does not send out colonizers into poorer habitats.
D)suitable habitat is patchily distributed and separated by areas of unsuitable habitat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the sigmoid growth curve,the carrying capacity of the environment is
A)r.
B)N.
C)K.
D)dN/dt.
E)N/K.
A)r.
B)N.
C)K.
D)dN/dt.
E)N/K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In the logistic growth model,as the number of individuals in the population (N)approaches the carrying capacity (K),the intrinsic rate of growth (r)
A)will be affected by an increased birth rate.
B)will be affected by a decreased death rate from predation.
C)will be affected by increased competition with other species.
D)will be affected by increased competition within the species.
E)will not changE.
A)will be affected by an increased birth rate.
B)will be affected by a decreased death rate from predation.
C)will be affected by increased competition with other species.
D)will be affected by increased competition within the species.
E)will not changE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements is true about the graph?
A)Oysters live longer than HydrA.
B)Hydra and humans have parallel life spans.
C)Humans and oysters have similar life spans.
D)Humans have low mortality rates late in life.
E)Oysters have high mortality rates late in lifE.
A)Oysters live longer than HydrA.
B)Hydra and humans have parallel life spans.
C)Humans and oysters have similar life spans.
D)Humans have low mortality rates late in life.
E)Oysters have high mortality rates late in lifE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is not an example of organisms displaying r-selected adaptations?
A)dandelions
B)whales
C)aphids
D)mice
E)cockroaches
A)dandelions
B)whales
C)aphids
D)mice
E)cockroaches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The biotic potential representing growth without limits at its maximal rate is given the symbol
A)r.
B)N.
C)K.
D)dN/dt.
E)N/K.
A)r.
B)N.
C)K.
D)dN/dt.
E)N/K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During the late 1800s,cattle egrets arrived in South America from Africa and began to colonize.Their range has expanded dramatically over the years.They were able to do this because
A)the habitats that they left in Africa were not suitable for any further colonization;thus,they were forced to immigrate.
B)the habitats that they encountered in South America were suitable to them and unoccupied.
C)there were abundant cattle for the birds to gather around in South America;furthermore,various animals that the egrets had lived around in Africa had become quite scarce because of over hunting and poaching,causing the birds to extend their range.
D)the food resources in South America were far superior to those in Africa,allowing the egrets more opportunity to grow and reproduce and ultimately expand their range.
A)the habitats that they left in Africa were not suitable for any further colonization;thus,they were forced to immigrate.
B)the habitats that they encountered in South America were suitable to them and unoccupied.
C)there were abundant cattle for the birds to gather around in South America;furthermore,various animals that the egrets had lived around in Africa had become quite scarce because of over hunting and poaching,causing the birds to extend their range.
D)the food resources in South America were far superior to those in Africa,allowing the egrets more opportunity to grow and reproduce and ultimately expand their range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following factors is not one that increases the likelihood of population extinction?
A)Small population size is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.
B)Isolation of a population from sources of immigrants is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.
C)Isolation of a population from sinks of immigrants is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.
D)Low resource availability is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.
E)Lack of genetic diversity is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.
A)Small population size is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.
B)Isolation of a population from sources of immigrants is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.
C)Isolation of a population from sinks of immigrants is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.
D)Low resource availability is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.
E)Lack of genetic diversity is a factor contributing to a population's extinction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Density-independent factors do not include
A)weather.
B)earthquakes.
C)intraspecific competition.
D)volcanism.
E)introduction of non-native species.
A)weather.
B)earthquakes.
C)intraspecific competition.
D)volcanism.
E)introduction of non-native species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An example of clumped distribution of a population is
A)an introduction of a new species into a new environment.
B)a herd of antelope.
C)a behavioral interaction between two members of the same species.
D)not very common in nature.
A)an introduction of a new species into a new environment.
B)a herd of antelope.
C)a behavioral interaction between two members of the same species.
D)not very common in nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Parental care of the young is usually associated with species with a Type ___ survivorship curve.
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)I or II (depending on the sex ratio)
E)I or III (depending on whether the reproductive strategy if iteroparous or semelparous)
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)I or II (depending on the sex ratio)
E)I or III (depending on whether the reproductive strategy if iteroparous or semelparous)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What point on the graph (marked by A,B,C,D,or E)shows the result of a density independent change in the size of the population?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
All of the following apply to the demography of human populations today except
A)we use almost half of the Earth's land.
B)we use over half of all renewable fresh water sources.
C)we are unevenly distributed and the difference is increasing.
D)we are using distributed resources unevenly-less than 20% of us use over 80% of the energy.
E)our ecological footprint is decreasing.
A)we use almost half of the Earth's land.
B)we use over half of all renewable fresh water sources.
C)we are unevenly distributed and the difference is increasing.
D)we are using distributed resources unevenly-less than 20% of us use over 80% of the energy.
E)our ecological footprint is decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Allee effect occurs when
A)a density-dependent factor decreases a population.
B)a density-independent factor decreases a population.
C)a density-dependent factor increases a population.
D)a density-independent factor increases a population.
E)a density-independent factor holds a population at its carrying capacity.
A)a density-dependent factor decreases a population.
B)a density-independent factor decreases a population.
C)a density-dependent factor increases a population.
D)a density-independent factor increases a population.
E)a density-independent factor holds a population at its carrying capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Spacing within a population for a species that is strongly territorial would be expected to be
A)uniform.
B)clumped.
C)random.
D)uniform or clumped depending if it is a source or sink metapopulation.
E)uniform or clumped depending on the life history strategy of the species.
A)uniform.
B)clumped.
C)random.
D)uniform or clumped depending if it is a source or sink metapopulation.
E)uniform or clumped depending on the life history strategy of the species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
You construct a life table for a plant species and find that in all cases about the same proportion of the cohort survive to the beginning of the next time interval.Such a plant would have
A)a Type I survivorship curve.
B)a Type II survivorship curve.
C)a Type III survivorship curve.
D)a semelparous life history adaptation.
E)populations regulated by density-independent events.
A)a Type I survivorship curve.
B)a Type II survivorship curve.
C)a Type III survivorship curve.
D)a semelparous life history adaptation.
E)populations regulated by density-independent events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which one of the following is not a correct distinction about source-sink metapopulations?
A)Source populations usually occupy better habitats.
B)Source populations are less likely to go extinct.
C)Sink populations near source populations are less likely to go extinct.
D)Sink populations without access to immigrants from source populations are less likely to go extinct.
E)The emigration rate from source populations exceeds that from sink populations.
A)Source populations usually occupy better habitats.
B)Source populations are less likely to go extinct.
C)Sink populations near source populations are less likely to go extinct.
D)Sink populations without access to immigrants from source populations are less likely to go extinct.
E)The emigration rate from source populations exceeds that from sink populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A species whose population growth is not well described by the logistic growth equation is likely to have all of the following traits except
A)first reproduction is early in life.
B)it has a long life span.
C)it provides little parental care.
D)semelparous reproduction.
E)it produces many,small young.
A)first reproduction is early in life.
B)it has a long life span.
C)it provides little parental care.
D)semelparous reproduction.
E)it produces many,small young.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Select the feature that is not an important characteristic of a population.
A)a population's geographic distribution
B)dispersion of individuals within the population
C)the life history of the population
D)the demography of the population
E)if and how the population interacts with a metapopulation
A)a population's geographic distribution
B)dispersion of individuals within the population
C)the life history of the population
D)the demography of the population
E)if and how the population interacts with a metapopulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which one of the following factors that affects population growth is not a direct part of the logistic growth equation?
A)intraspecific competition
B)interspecific competition
C)floods and droughts
D)predation
E)disease
A)intraspecific competition
B)interspecific competition
C)floods and droughts
D)predation
E)disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The human population growth rate has declined over the past 30 years.This means
A)improved status of women and increased family planning have had an effect.
B)actual population numbers of humans are declining in nearly all countries.
C)density-dependent factors have taken effect as we neared our carrying capacity.
D)density-independent factors have taken effect as we neared our carrying capacity.
E)all of thesE.
A)improved status of women and increased family planning have had an effect.
B)actual population numbers of humans are declining in nearly all countries.
C)density-dependent factors have taken effect as we neared our carrying capacity.
D)density-independent factors have taken effect as we neared our carrying capacity.
E)all of thesE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Allen's rule states that mammals from colder climates have shorter ears and appendages than individuals of the same species from warmer areas.The related Bergman's rule states that mammal body size varies with latitude,with larger body size in populations located closer to the poles and smaller body size in populations located closer to the equator.Both Allen's and Bergman's rule has to do with the fact that
A)larger bodies can store proportionally more fat as insulation than smaller bodies.
B)smaller bodies can store proportionally more fat as insulation than larger bodies.
C)larger bodies have a proportionally smaller surface area,and heat radiation varies with surface area.
D)larger bodies have a proportionally smaller surface area,and heat radiation varies with volume.
E)smaller bodies have a proportionally smaller surface area,and heat radiation varies with surface area.
A)larger bodies can store proportionally more fat as insulation than smaller bodies.
B)smaller bodies can store proportionally more fat as insulation than larger bodies.
C)larger bodies have a proportionally smaller surface area,and heat radiation varies with surface area.
D)larger bodies have a proportionally smaller surface area,and heat radiation varies with volume.
E)smaller bodies have a proportionally smaller surface area,and heat radiation varies with surface area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The change that begins at point C could be caused by
A)increased predation by wolves.
B)a wet year with increased vegetative growth.
C)increased competition from moose herds.
D)a dry year with decreased vegetative growth.
E)lower than normal birth rates.
A)increased predation by wolves.
B)a wet year with increased vegetative growth.
C)increased competition from moose herds.
D)a dry year with decreased vegetative growth.
E)lower than normal birth rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Organisms with a Type III life history are probably
A)K-selected.
B)r-selected.
C)idiopathiC.
D)at their carrying capacity.
E)subject to low predation rates.
A)K-selected.
B)r-selected.
C)idiopathiC.
D)at their carrying capacity.
E)subject to low predation rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Population pyramids are primarily used to show
A)death rates.
B)birth rates.
C)competition.
D)sex and age composition of a population.
E)the carrying capacity.
A)death rates.
B)birth rates.
C)competition.
D)sex and age composition of a population.
E)the carrying capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A __________ would probably have a Type III life history.
A)whale
B)coconut palm
C)lion
D)gorilla
E)pine tree
A)whale
B)coconut palm
C)lion
D)gorilla
E)pine tree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
At what point in a population will zero population growth occur?
A)when N equals K
B)when N is less than K
C)when dN/dt equals zero
D)when r equals zero
E)when N equals zero
A)when N equals K
B)when N is less than K
C)when dN/dt equals zero
D)when r equals zero
E)when N equals zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which one of the following is not a physical environmental factor that determines where an organism can live?
A)temperature
B)water
C)insolation (sunlight)
D)soil type
E)intraspecific competition
A)temperature
B)water
C)insolation (sunlight)
D)soil type
E)intraspecific competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Some population parameters vary directly (as one increases,the second increases)and some vary inversely (as one increases,the second decreases)with population density.Which one of the following would be expected to vary inversely with population density?
A)mortality (death)rate
B)fecundity (birth)rate
C)intraspecific competition
D)predation
E)parasitism
A)mortality (death)rate
B)fecundity (birth)rate
C)intraspecific competition
D)predation
E)parasitism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which one of the following expressions from the logistic equation (dN/dt = rN ((K - N)/K)represents the proportion of unused resources remaining for use by the population?
A)the carrying capacity (K)
B)the population size (N)
C)the biotic potential (rN)
D)(K - N)/K
E)the growth rate (dN/dt)
A)the carrying capacity (K)
B)the population size (N)
C)the biotic potential (rN)
D)(K - N)/K
E)the growth rate (dN/dt)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Select the description of a population pyramid for a population that has the largest potential for exponential growth.
A)broad at the base,narrow at the top,with more females than males
B)broad at the base,narrow at the top,with more males than females
C)uniform at all age classes,with more females than males
D)broad at the top,narrow at the base,with more males than females
E)broad at the top,narrow at the base,with more females than males
A)broad at the base,narrow at the top,with more females than males
B)broad at the base,narrow at the top,with more males than females
C)uniform at all age classes,with more females than males
D)broad at the top,narrow at the base,with more males than females
E)broad at the top,narrow at the base,with more females than males

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the most reasonable conclusion that can be made from data graphed in the figure. 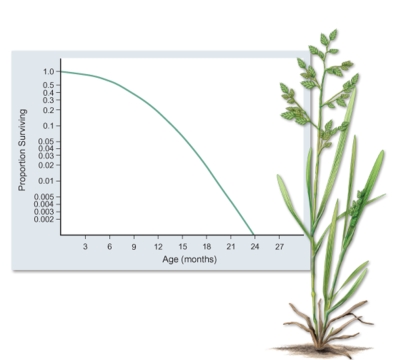
A)After high mortality early in life,survivorship becomes constant for the rest of life.
B)After high mortality late in life,survivorship becomes constant for the rest of life.
C)After high mortality early in life,survivorship increases at a constant rate for the rest of life.
D)After high mortality late in life,survivorship increases at a constant rate for the rest of life.
E)After high mortality early in life,survivorship decreases at a constant rate for the rest of lifE.

A)After high mortality early in life,survivorship becomes constant for the rest of life.
B)After high mortality late in life,survivorship becomes constant for the rest of life.
C)After high mortality early in life,survivorship increases at a constant rate for the rest of life.
D)After high mortality late in life,survivorship increases at a constant rate for the rest of life.
E)After high mortality early in life,survivorship decreases at a constant rate for the rest of lifE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Most density-dependent factors show negative feedback relative to population size.Which one of the following is more likely to show positive feedback relative to population size?
A)competition in small,sink populations
B)competition in large,source populations
C)fecundity in small,sink populations
D)fecundity in large,source populations
E)mortality in large,source populations
A)competition in small,sink populations
B)competition in large,source populations
C)fecundity in small,sink populations
D)fecundity in large,source populations
E)mortality in large,source populations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the most reasonable conclusion that can be made from data graphed in the figure. 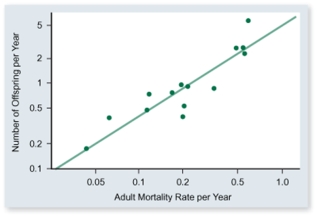
A)Adults that are likely to die soon have more offspring than those not likely to die.
B)Adults with greater fecundity are less likely to die than adults with smaller fecundity.
C)Adults with greater fecundity are more likely to die than adults with smaller fecundity.
D)If the probability that an adult is likely to die is great,its fecundity rate is great.
E)If the probability that an adult is likely to die is great,its fecundity rate is small.

A)Adults that are likely to die soon have more offspring than those not likely to die.
B)Adults with greater fecundity are less likely to die than adults with smaller fecundity.
C)Adults with greater fecundity are more likely to die than adults with smaller fecundity.
D)If the probability that an adult is likely to die is great,its fecundity rate is great.
E)If the probability that an adult is likely to die is great,its fecundity rate is small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The figure included shows the body temperature of lizards versus air temperature in two different habitats-open and shaded forest.Which one of the following conclusions is best supported by these data. 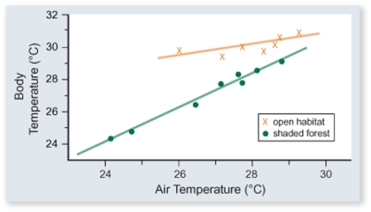
A)Lizards are more active in open habitats.
B)Lizards sunbath more in open habitats.
C)Lizards in shaded forest habitats eat more to maintain their temperature.
D)The body temperature of lizards is more constant in open than in shaded forest habitats.
E)The negative effect of air temperature on body temperature is less in shaded forest habitats because the temperature varies less therE.

A)Lizards are more active in open habitats.
B)Lizards sunbath more in open habitats.
C)Lizards in shaded forest habitats eat more to maintain their temperature.
D)The body temperature of lizards is more constant in open than in shaded forest habitats.
E)The negative effect of air temperature on body temperature is less in shaded forest habitats because the temperature varies less therE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



