Deck 55: Behavioral Biology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 55: Behavioral Biology
1
Interactions with individuals of the same or other species may be competitive or cooperative;collectively they are referred to as __________.
A)aggression
B)social behavior
C)neutrality
D)ecology
A)aggression
B)social behavior
C)neutrality
D)ecology
B
2
Learning is possible only within the boundaries set by an innate predisposition called _________.
A)instinct
B)free will
C)consciousness
D)ability
A)instinct
B)free will
C)consciousness
D)ability
A
3
The degree of parental investment required often results in the non-random mating behavior called ___________.
A)sexual selection
B)fidelity
C)mate choice
D)preferability
A)sexual selection
B)fidelity
C)mate choice
D)preferability
C
4
All of the following are examples of animal behavioral responses to environmental cues except
A)the feeding frenzy.
B)the mating ritual.
C)bee waggle-dance.
D)resistance to infection.
E)migration.
A)the feeding frenzy.
B)the mating ritual.
C)bee waggle-dance.
D)resistance to infection.
E)migration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The name of the study of behavior,behavioral genetics,and comparative psychology is _______.
A)ethology
B)demography
C)etiology
D)semanics
A)ethology
B)demography
C)etiology
D)semanics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
All of the following disciplines provide logical and natural linkages to the study of animal behavior except
A)genetics.
B)evolution.
C)philosophy.
D)physiology.
E)ecology.
A)genetics.
B)evolution.
C)philosophy.
D)physiology.
E)ecology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Tinbergen is credited with founding the field of behavioral _______,the study of how natural selection shapes behavior.
A)genetics
B)ecology
C)symptomology
D)demographics
A)genetics
B)ecology
C)symptomology
D)demographics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The genetic basis of behavior is supported by all of the following except
A)hybridization studies.
B)studies on the behavior of twins.
C)artificial selection.
D)studies of supernormal stimuli.
E)imprinting.
A)hybridization studies.
B)studies on the behavior of twins.
C)artificial selection.
D)studies of supernormal stimuli.
E)imprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Animals that acquire energy efficiently during foraging will increase their fitness by having more energy available for ________________.
A)competition
B)defenses
C)respiration
D)reproduction
A)competition
B)defenses
C)respiration
D)reproduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The processing of information and response in a manner that suggests thinking in the animal is called
A)endogenous behavior.
B)environmental induced behavior.
C)instinctive behavior.
D)associative behavior.
E)cognitive behavior.
A)endogenous behavior.
B)environmental induced behavior.
C)instinctive behavior.
D)associative behavior.
E)cognitive behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Chemical signals that mediate interactions between two or more members of a given species are called ________________.
A)pheromones
B)alarm signals
C)hormones
D)competitive exclusions
A)pheromones
B)alarm signals
C)hormones
D)competitive exclusions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A nonassociative learning called __________ can be defined as a decrease in response to a repeated stimulus that has no positive or negative consequences.
A)instinctive learning
B)imprinting
C)desensitization learning
D)habituation learning
E)cognitive learning
A)instinctive learning
B)imprinting
C)desensitization learning
D)habituation learning
E)cognitive learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Animals tend to feed on prey that maximize their net energy intake.This is called the __________ theory.
A)competitive exclusion
B)maximal consumption
C)optimal foraging
D)optimization
A)competitive exclusion
B)maximal consumption
C)optimal foraging
D)optimization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Current research in behavioral ecology focuses on the overall contribution that behavior makes to an animal's
A)fitness.
B)learning.
C)competitive strategies.
D)foraging efficiency.
E)length of lifE.
A)fitness.
B)learning.
C)competitive strategies.
D)foraging efficiency.
E)length of lifE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Artificial selection and hybridization can demonstrate the __________ basis of behavior.
A)cognitive
B)instinctive
C)genetic
D)associational
E)endogenous
A)cognitive
B)instinctive
C)genetic
D)associational
E)endogenous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The signal from the environment that triggers a stereotyped behavior is a
A)conditioned reflex.
B)fixed action pattern.
C)reinforcing stimulus.
D)releasing mechanism.
E)key stimulus (sign stimulus).
A)conditioned reflex.
B)fixed action pattern.
C)reinforcing stimulus.
D)releasing mechanism.
E)key stimulus (sign stimulus).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Animal behavioral researchers have identified some specific _________ that control behaviors.
A)environments
B)instincts
C)taxis
D)conditions
E)genes
A)environments
B)instincts
C)taxis
D)conditions
E)genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
As an animal matures,it forms attachments to other individuals and develops preferences.This process is called
A)instinct.
B)imprinting.
C)associational learning.
D)habituation.
E)sensitization.
A)instinct.
B)imprinting.
C)associational learning.
D)habituation.
E)sensitization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Alarm calling seems to be an example of ________,that is,it favors relatives.
A)sociology
B)demography
C)aggression
D)kin selection
A)sociology
B)demography
C)aggression
D)kin selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
By evaluating and selecting mates with superior qualities,an animal can increase its
A)reproductive success.
B)learning.
C)competitive strategies.
D)foraging efficiency.
E)length of lifE.
A)reproductive success.
B)learning.
C)competitive strategies.
D)foraging efficiency.
E)length of lifE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Insect workers propagate more of their own alleles by helping their mother reproduce rather than by reproducing themselves;thus,they share a larger fraction of their ___________ with the next generation.
A)food resources
B)time
C)genome
D)ability to defend their nest
E)home
A)food resources
B)time
C)genome
D)ability to defend their nest
E)home

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is an appropriate interpretation for these graphs? 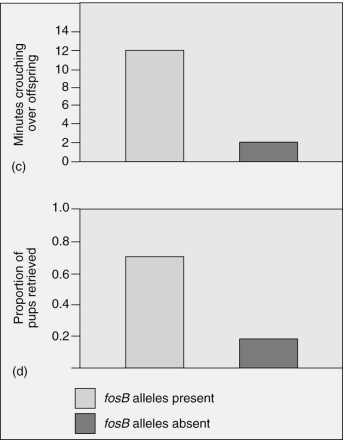
Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved)in female mice that have the fosB allele is
A)less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
B)greater than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
C)the same as the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
D)less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele;however,the graphs depict only minor differences,which are most likely not significant.
E)not possible to determine from the data.

Maternal care (as measured by minutes crouching over offspring and proportion of pups retrieved)in female mice that have the fosB allele is
A)less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
B)greater than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
C)the same as the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele.
D)less than the maternal care given by female mice without the fosB allele;however,the graphs depict only minor differences,which are most likely not significant.
E)not possible to determine from the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Young birds see objects flying overhead and respond by crouching down into the nest and remaining still.Over time some objects become familiar and the young birds do not crouch down.This type of learning is referred to as
A)sensitization.
B)associative learning.
C)operant conditioning.
D)habituation.
E)Pavlovian conditioning.
A)sensitization.
B)associative learning.
C)operant conditioning.
D)habituation.
E)Pavlovian conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a scientist is conducting a study of how an animal's senses provide a physiological basis for that behavior,she would be asking about the
A)ultimate causation.
B)proximate causation.
C)stereotyped causation.
D)ethnological causation.
E)fixed action pattern causation.
A)ultimate causation.
B)proximate causation.
C)stereotyped causation.
D)ethnological causation.
E)fixed action pattern causation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In birds,if the offspring require extensive care,usually involving both the male and female,they are called
A)semelparous species.
B)altricial species.
C)precocial species.
D)iteroparous species.
E)sympatric species.
A)semelparous species.
B)altricial species.
C)precocial species.
D)iteroparous species.
E)sympatric species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Social insect colonies are composed of highly integrated groups called
A)clines.
B)ecotypes.
C)castes.
D)species.
E)filial relatives.
A)clines.
B)ecotypes.
C)castes.
D)species.
E)filial relatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Habituation belongs to which of the following types of learning?
A)nonassociative
B)behavior modification
C)conditioning
D)innate release
E)cognitive
A)nonassociative
B)behavior modification
C)conditioning
D)innate release
E)cognitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
____________ conducted the now famous "imprinting" experiment on geese.
A)Mendel
B)Russel
C)Lorenz
D)Darwin
E)Raven
A)Mendel
B)Russel
C)Lorenz
D)Darwin
E)Raven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The scientist who described inclusive fitness as the effect an individual has on propagating its alleles through its own reproduction and through kin selection was
A)Mendel.
B)Darwin.
C)Wallace.
D)Tinbergen.
E)Hamilton.
A)Mendel.
B)Darwin.
C)Wallace.
D)Tinbergen.
E)Hamilton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Recent research revealed that the development of psychological well-being and growth is influenced by
A)imprinting.
B)physical contact.
C)sensitization.
D)associative learning.
E)pheromone levels.
A)imprinting.
B)physical contact.
C)sensitization.
D)associative learning.
E)pheromone levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Courtship is often dependent on
A)social releasers.
B)a stimulus/response chain.
C)an alarm call.
D)taxis.
E)size and colors.
A)social releasers.
B)a stimulus/response chain.
C)an alarm call.
D)taxis.
E)size and colors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Chemical messengers used for communication between animal species are called
A)hormones.
B)pheromones.
C)genes.
D)enzymes.
E)immune chemicals.
A)hormones.
B)pheromones.
C)genes.
D)enzymes.
E)immune chemicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The modification of behavior as a result of experience is called
A)association.
B)behavior modification.
C)habituation.
D)learning.
E)sensitization.
A)association.
B)behavior modification.
C)habituation.
D)learning.
E)sensitization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Foraging bees communicate with other bees in a waggle dance to give information about the food.The important cue in the dance that conveys information about the required flight direction to the food source relative to the hive-sun direction is the
A)angle between the food source and the hive in reference to the sun.
B)angle between the waggle run and the vertical axis within the hive.
C)angle between the waggle run in reference to the hive-sun angle.
D)angle between the waggle run in reference to the direction north from the hive.
E)speed of the waggle dancE.
A)angle between the food source and the hive in reference to the sun.
B)angle between the waggle run and the vertical axis within the hive.
C)angle between the waggle run in reference to the hive-sun angle.
D)angle between the waggle run in reference to the direction north from the hive.
E)speed of the waggle dancE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A behavior that has evolved to aid relatives,although at personal risk,and thus increases the chance of your genes being passed on to the next generation is known as
A)altricial behavior.
B)instinctive behavior.
C)kin selection.
D)operant conditioning.
E)adaptive behavior.
A)altricial behavior.
B)instinctive behavior.
C)kin selection.
D)operant conditioning.
E)adaptive behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
All of the following sources are used for orientation by some birds during migration except
A)the sun.
B)the stars.
C)magnetic fields.
D)landmarks.
E)phases of the moon.
A)the sun.
B)the stars.
C)magnetic fields.
D)landmarks.
E)phases of the moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If an unrelated stimulus,such as the ringing of a bell,was presented at the same time as the meat powder,over repeated trials,a dog would salivate in response to the sound of the bell alone.This kind of response is called
A)behavioral learning.
B)classical conditioning.
C)deviant behavior.
D)operant conditioning.
E)imprinting.
A)behavioral learning.
B)classical conditioning.
C)deviant behavior.
D)operant conditioning.
E)imprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
One type of evolutionary analysis of behavior pioneered by Tinbergen was the study of the
A)inheritance of behavior.
B)innate releasing mechanisms.
C)neural networks involved.
D)survival value of behavior.
E)timing of rhythmic behavior.
A)inheritance of behavior.
B)innate releasing mechanisms.
C)neural networks involved.
D)survival value of behavior.
E)timing of rhythmic behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a scientist is conducting a study of how a male bird's song and the female bird's response evolved,she would be asking about the
A)ultimate causation.
B)proximate causation.
C)stereotyped causation.
D)ethnological causation.
E)fixed action pattern causation.
A)ultimate causation.
B)proximate causation.
C)stereotyped causation.
D)ethnological causation.
E)fixed action pattern causation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An animal learns to associate its behavioral response with a reward or punishment in
A)behavioral learning.
B)classical conditioning.
C)deviant behavior.
D)operant conditioning.
E)imprinting.
A)behavioral learning.
B)classical conditioning.
C)deviant behavior.
D)operant conditioning.
E)imprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is the best interpretation of the graph below of mussel size (x-axis)versus energy gain (line graph,left y-axis),and number of mussels eaten per day (histogram,right y-axis)? 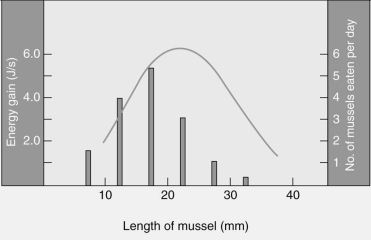
A)Mussels are selected as food sources by crabs.
B)Crabs select mussels in a way that maximizes their energy gain.
C)Mussel size does not seem to be a good predictor as to which mussel hungry crabs will select.
D)Crabs tend to consume most of the largest mussels.
E)Crabs prefer the mussels with the smallest length for their food resources.

A)Mussels are selected as food sources by crabs.
B)Crabs select mussels in a way that maximizes their energy gain.
C)Mussel size does not seem to be a good predictor as to which mussel hungry crabs will select.
D)Crabs tend to consume most of the largest mussels.
E)Crabs prefer the mussels with the smallest length for their food resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The vertical dive of a moth for cover when it hears the ultrasound chirps of an approaching bat is an example of a(n)
A)sign stimulus.
B)fixed action pattern.
C)innate releasing mechanism.
D)supernormal stimulus.
E)kinesis.
A)sign stimulus.
B)fixed action pattern.
C)innate releasing mechanism.
D)supernormal stimulus.
E)kinesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The area over which an animal moves in the course of daily activity,but which it does not necessarily defend against other animals,is its
A)family home.
B)foraging space.
C)home range.
D)nesting site.
E)territory.
A)family home.
B)foraging space.
C)home range.
D)nesting site.
E)territory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Konrad Lorenz demonstrated that newly hatched birds would direct their social behavior toward him if they saw him first after they hatched from their eggs.This is referred to as
A)cross-fostering behavior.
B)operant conditioning.
C)fixed action patterning.
D)habituation behavior.
E)imprinting behavior.
A)cross-fostering behavior.
B)operant conditioning.
C)fixed action patterning.
D)habituation behavior.
E)imprinting behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In species where the young are precocial,meaning requiring little parental care,males may be more likely to be
A)monogamous.
B)polygynous.
C)polyandrous.
D)polygamous.
E)altricial.
A)monogamous.
B)polygynous.
C)polyandrous.
D)polygamous.
E)altricial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In an experiment studying predator and prey relationships,a scientist offers a naïve toad a bumblebee as food.The bee stings the toad when the toad tries to catch and eat the bee.Subsequent feeding trials with the toad reveal that the toad avoids feeding on bumblebees.This is a demonstration of
A)non-associative learning on the toad's part.
B)associative learning on the toad's part.
C)ultimate learning on the toad's part.
D)proximate learning on the toad's part.
E)sign stimulus learning on the toad's part.
A)non-associative learning on the toad's part.
B)associative learning on the toad's part.
C)ultimate learning on the toad's part.
D)proximate learning on the toad's part.
E)sign stimulus learning on the toad's part.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Living as a member of a group may have all of the following advantages except
A)being more resistant to disease and parasites.
B)the feeding rate may be increased.
C)there may be greater protection from predators.
D)members learn about new food sources from other members.
E)more individuals scan the environment for dangers.
A)being more resistant to disease and parasites.
B)the feeding rate may be increased.
C)there may be greater protection from predators.
D)members learn about new food sources from other members.
E)more individuals scan the environment for dangers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A friend of yours is wondering about the differences between the words orientation and navigation when these two terms are used in descriptions of bird migrations.Since you have studied and know something about animal behavior,you tell your friend that
A)orientation is adjusting a bearing,while navigation is actually following a bearing.
B)orientation and navigation are used interchangeably when referring to avian migrations.
C)orientation is following a bearing,while navigation is setting or adjusting a bearing.
D)orientation is following the sun in the day as starling do,while navigation is following a bearing with a small amount of magnetite,which is found in the heads of some migratory birds.
E)orientation is the ability to find true east,navigation is the ability to find a bearing while crossing water.
A)orientation is adjusting a bearing,while navigation is actually following a bearing.
B)orientation and navigation are used interchangeably when referring to avian migrations.
C)orientation is following a bearing,while navigation is setting or adjusting a bearing.
D)orientation is following the sun in the day as starling do,while navigation is following a bearing with a small amount of magnetite,which is found in the heads of some migratory birds.
E)orientation is the ability to find true east,navigation is the ability to find a bearing while crossing water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Haldane pointed out that if he received a certain allele,the chance that one of his brothers would receive that allele would be
A)100%.
B)50%.
C)10%.
D)random.
E)0%.
A)100%.
B)50%.
C)10%.
D)random.
E)0%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The flash pattern used by female fireflies to attract males of their species is an example of
A)a sign stimulus.
B)a fixed action pattern.
C)an innate releasing mechanism.
D)a supernormal stimulus.
E)sexual imprinting.
A)a sign stimulus.
B)a fixed action pattern.
C)an innate releasing mechanism.
D)a supernormal stimulus.
E)sexual imprinting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Pea fowl (peacocks and peahens)show sexual dimorphism.Which statement best describes the graphed data? 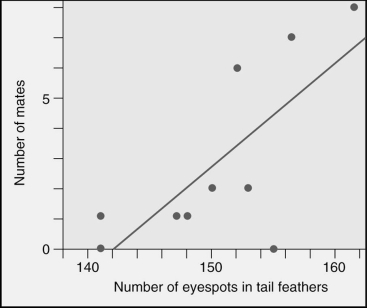
A)There are no peacocks with less than 140 eyespots.
B)The fewer eyespots that a peacock has in his tail,the more mates he attracts.
C)Actually eyespots have very little to do with mate-attracting activities.
D)The more eyespots that a peacock has in his tail,the more mates he attracts.
E)There are no peacocks with more than 165 eyespots.

A)There are no peacocks with less than 140 eyespots.
B)The fewer eyespots that a peacock has in his tail,the more mates he attracts.
C)Actually eyespots have very little to do with mate-attracting activities.
D)The more eyespots that a peacock has in his tail,the more mates he attracts.
E)There are no peacocks with more than 165 eyespots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The evolution of foraging behaviors that maximize the amount of energy gained per unit of time spent foraging is favored by
A)natural selection.
B)artificial selection.
C)specialization.
D)altruism.
E)territoriality.
A)natural selection.
B)artificial selection.
C)specialization.
D)altruism.
E)territoriality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Eusocial (true social)insects include all of the following except
A)honeybees.
B)ants.
C)termites.
D)fruit flies.
E)wasps.
A)honeybees.
B)ants.
C)termites.
D)fruit flies.
E)wasps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Hamilton explained the origin of altruism in selected insect societies with his kin selection model of sex determination.Since males are haploid and females are diploid,the workers share a very high proportion of alleles,theoretically as high as 75%;this model is called
A)diploidy.
B)haploidy.
C)haplodiploidy.
D)parthenogenesis.
E)altruism.
A)diploidy.
B)haploidy.
C)haplodiploidy.
D)parthenogenesis.
E)altruism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The neural pattern that allows a male stickleback fish to orient and behave aggressively towards an inanimate object with a red stripe is an example of a(n)
A)sign stimulus.
B)fixed action pattern.
C)innate releasing mechanism.
D)supernormal stimulus.
E)stimulus-response chain.
A)sign stimulus.
B)fixed action pattern.
C)innate releasing mechanism.
D)supernormal stimulus.
E)stimulus-response chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Foraging behaviors are those having to do with all of the following except
A)what an animal eats.
B)when an animal eats.
C)how an animal finds its food.
D)how much food an animal eats.
E)how an animal avoids becoming the prey of a larger predator.
A)what an animal eats.
B)when an animal eats.
C)how an animal finds its food.
D)how much food an animal eats.
E)how an animal avoids becoming the prey of a larger predator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Selection that favors altruism toward relatives is called
A)kin selection.
B)mate choice.
C)group selection.
D)nepotism.
E)reciprocal altruism.
A)kin selection.
B)mate choice.
C)group selection.
D)nepotism.
E)reciprocal altruism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Male Mormon crickets choose larger females as mate choices.Which of the following statements best interprets the graph? 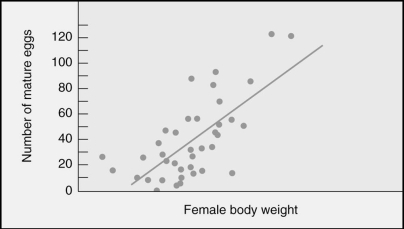
A)Larger females live longer and thus produce more eggs.
B)Larger females are capable of storing sperm.
C)Larger females reproduce earlier than smaller females.
D)Larger females lay more eggs.
E)Larger females defend themselves better.

A)Larger females live longer and thus produce more eggs.
B)Larger females are capable of storing sperm.
C)Larger females reproduce earlier than smaller females.
D)Larger females lay more eggs.
E)Larger females defend themselves better.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Recently the focus of research in behavioral ecology has been on the contribution by behavior to an animal's reproductive success.This is called its
A)average number of mates.
B)fitness.
C)foraging efficiency.
D)longevity.
E)rate of growth to sexual maturity.
A)average number of mates.
B)fitness.
C)foraging efficiency.
D)longevity.
E)rate of growth to sexual maturity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A friend asks you the following question: "would you please explain the differences between home range and territory?" Which choice would be the best response to your friend's question?
A)Territory is the entire area that an animal can utilize for its resources,such as shelter,food,and mates.Home range is near its nest or den.
B)Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources,such as shelter,food and mates and will defend against other members of its species.Home range is near its nest or den.
C)Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources,such as shelter,food and mates,and will defend against other members of its species.Home range is the area that an animal may roam over on a daily basis.
D)Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources,such as shelter,food and mates,and will defend against others members of its species.Home range is a smaller area within the territory that the animal is found in when it is resting or hiding from predators.
A)Territory is the entire area that an animal can utilize for its resources,such as shelter,food,and mates.Home range is near its nest or den.
B)Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources,such as shelter,food and mates and will defend against other members of its species.Home range is near its nest or den.
C)Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources,such as shelter,food and mates,and will defend against other members of its species.Home range is the area that an animal may roam over on a daily basis.
D)Territory is the area that an animal can utilize for its resources,such as shelter,food and mates,and will defend against others members of its species.Home range is a smaller area within the territory that the animal is found in when it is resting or hiding from predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The development of normal maternal behavior in female mice depends on interactions between the female and her young and the presence of a gene called fosB.In mice with functional fosB genes a sequence of events occurs.Arrange the following events in their normal sequence and select the event that would occur fourth.
A)fosB genes are activated to produce a protein.
B)Female crouches over and retrieves displaced young.
C)Auditory,olfactory,and tactile signals about the young are sent to the hypothalamus.
D)Female inspects newborns.
E)Neural circuitry within the hypothalamus is modified.
A)fosB genes are activated to produce a protein.
B)Female crouches over and retrieves displaced young.
C)Auditory,olfactory,and tactile signals about the young are sent to the hypothalamus.
D)Female inspects newborns.
E)Neural circuitry within the hypothalamus is modified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of the following examples describes a communication mode that would be best for signaling over the greatest distance in a dark,densely forested environment?
A)display of plumage of a male bird to attract females
B)waggle dance of a honeybee in a colony within the forest
C)pheromones released by a female moth
D)territorial song of a male bird to repel other males
E)flashing of a male firefly to attract conspecific females
A)display of plumage of a male bird to attract females
B)waggle dance of a honeybee in a colony within the forest
C)pheromones released by a female moth
D)territorial song of a male bird to repel other males
E)flashing of a male firefly to attract conspecific females

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which choice best completes the following? Learning that occurs only during a brief period early in life and results in a behavior that is difficult to modify is called
A)imprinting.
B)filial imprinting.
C)innate behavior.
D)instinct.
E)operant conditioning.
A)imprinting.
B)filial imprinting.
C)innate behavior.
D)instinct.
E)operant conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Choose the letter of the best match from the following:
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
A form of communication in honeybees.
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
A form of communication in honeybees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following statements best defines an altruistic act?
A)benefits the performer and another individual
B)benefits another individual at some cost to the performer
C)benefits another,related individual at some cost to the performer
D)imposes a cost on the performer and another individual
E)imposes a cost on the performer without benefiting another individual
A)benefits the performer and another individual
B)benefits another individual at some cost to the performer
C)benefits another,related individual at some cost to the performer
D)imposes a cost on the performer and another individual
E)imposes a cost on the performer without benefiting another individual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which one of the following is not an example of associative learning?
A)imprinting
B)classical conditioning
C)Pavlovian conditioning
D)operant conditioning
E)cognition
A)imprinting
B)classical conditioning
C)Pavlovian conditioning
D)operant conditioning
E)cognition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which one of the following statements comparing the naked mole rat social system with social insect societies is false?
A)As with social insect societies,colony members are kin.
B)As with social insect societies,it is based on haplodiploidy.
C)Unlike social insect societies,all colony members are diploid.
D)As with social insect societies,there is one queen and several reproductive males per colony.
E)As with social insect societies,there is a division of labor within the colony.
A)As with social insect societies,colony members are kin.
B)As with social insect societies,it is based on haplodiploidy.
C)Unlike social insect societies,all colony members are diploid.
D)As with social insect societies,there is one queen and several reproductive males per colony.
E)As with social insect societies,there is a division of labor within the colony.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
You place an empty dog-food dish across the room from a puppy that then goes over to investigate the dish.You pick the dish up and ten minutes later you place it in a different part of the room,and you keep repeating this pattern.After the fifth time the puppy no longer goes over to the empty dish.Which of the following terms best describes this form of learning?
A)trial and error learning
B)habituation
C)classical conditioning
D)operant conditioning
E)imprinting
A)trial and error learning
B)habituation
C)classical conditioning
D)operant conditioning
E)imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
It is 6:00 PM and the sun is due west of the hive.A honeybee has just returned to its hive from a patch of flowers that are due north of the hive.Which of the following best describes the type of waggle dance that this bee should perform? Note: The waggle run is the straight part of the dance.
A)The waggle run should be straight down the vertical axis.
B)The waggle run should be straight up the vertical axis.
C)The waggle run should be 90 to the left of the vertical axis.
D)The waggle run should be 90 to the right of the vertical axis.
E)The waggle run should be 45 to the right of the vertical axis.
A)The waggle run should be straight down the vertical axis.
B)The waggle run should be straight up the vertical axis.
C)The waggle run should be 90 to the left of the vertical axis.
D)The waggle run should be 90 to the right of the vertical axis.
E)The waggle run should be 45 to the right of the vertical axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Choose the letter of the best match from the following:
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
Information processing that suggests thinking.
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
Information processing that suggests thinking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In which of the following examples has communication not occurred?
A)A bird signs from the top of a tree in its territory keeping other birds of the same species from trespassing.
B)A queen bee emits a chemical that keeps worker bees from becoming reproductive.
C)A waggle dancing bee feeds some of the nectar she is carrying to bees attending her dance;they now know what type of flowers she has visited.
D)A bird signs from the top of a tree in its territory attracting a female of the same species to it.
E)A bird gives an alarm call when a hawk approaches,but no other birds are in the area.
A)A bird signs from the top of a tree in its territory keeping other birds of the same species from trespassing.
B)A queen bee emits a chemical that keeps worker bees from becoming reproductive.
C)A waggle dancing bee feeds some of the nectar she is carrying to bees attending her dance;they now know what type of flowers she has visited.
D)A bird signs from the top of a tree in its territory attracting a female of the same species to it.
E)A bird gives an alarm call when a hawk approaches,but no other birds are in the area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Choose the letter of the best match from the following:
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
Move long distances using sun and stars.
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
Move long distances using sun and stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When a parent herring gull arrives at the nest with food,a chick will orient to and peck at the red spot on the parent's bill.The parent will then regurgitate the food into the chick's open mouth and the chick swallows it.This is an example of a(n)
A)sign stimulus.
B)fixed action pattern.
C)innate releasing mechanism.
D)taxis.
E)stimulus-response chain.
A)sign stimulus.
B)fixed action pattern.
C)innate releasing mechanism.
D)taxis.
E)stimulus-response chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Choose the letter of the best match from the following:
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
Social attachments are formed between parents and offspring.
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
Social attachments are formed between parents and offspring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Choose the letter of the best match from the following:
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
Innate motor program.
A.cognition
B.waggle dance
C.navigation
D.filial imprinting
E.fixed action pattern
Innate motor program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following treatment outcomes would not be expected based on our current understanding of the genetic basis of pair bonding in the prairie vole (Microtus ochrogaster)and montane voles (Microtus montanus)?
A)Prairie voles mate and form pair bonds.
B)Montane voles mate and do not form pair bonds.
C)Montane voles injected with oxytocin and vasopressin form pair bonds.
D)Prairie voles with blocked oxytocin and vasopressin do not form pair bonds.
E)Transgenic montane voles with the prairie vole version of the "pair bonding" gene form pair bonds.
A)Prairie voles mate and form pair bonds.
B)Montane voles mate and do not form pair bonds.
C)Montane voles injected with oxytocin and vasopressin form pair bonds.
D)Prairie voles with blocked oxytocin and vasopressin do not form pair bonds.
E)Transgenic montane voles with the prairie vole version of the "pair bonding" gene form pair bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



