Deck 20: International Financial Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: International Financial Management
1
Which theory states that the exchange rate between two currencies adjusts to reflect the relative inflation rates in the two currencies?
A)Interest rate parity.
B)Unbiased forward rates.
C)International fisher effect.
D)Purchasing power parity.
A)Interest rate parity.
B)Unbiased forward rates.
C)International fisher effect.
D)Purchasing power parity.
Purchasing power parity.
2
Bonds denominated in US dollars and issued in the US by non-US companies are known as:
A)American bonds.
B)USA bonds.
C)Yankee bonds.
D)Bulldog bonds.
A)American bonds.
B)USA bonds.
C)Yankee bonds.
D)Bulldog bonds.
Yankee bonds.
3
Which theory states that a forward exchange rate is given by relative interest rates in the two currencies?
A)Interest rate parity.
B)Purchasing power parity.
C)International fisher effect.
D)Unbiased forward rates.
A)Interest rate parity.
B)Purchasing power parity.
C)International fisher effect.
D)Unbiased forward rates.
Interest rate parity.
4
The price at which Australian dollars can be converted into,say,US dollars is known as the:
A)spot exchange rate.
B)direct exchange rate.
C)exchange rate between Australian dollars and US dollars.
D)gold standard.
A)spot exchange rate.
B)direct exchange rate.
C)exchange rate between Australian dollars and US dollars.
D)gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The difference between spot and forward rates is known as:
A)spot margin.
B)margin.
C)future margin.
D)forward margin.
A)spot margin.
B)margin.
C)future margin.
D)forward margin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If $A1 buys US$0.5200,how many Australian dollars can be exchanged for US$1000?
A)A$1000
B)A$520
C)A$1945
D)A$1923
A)A$1000
B)A$520
C)A$1945
D)A$1923

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which theory states that the difference in interest rates between two countries is an unbiased predictor of the future change in the spot exchange rate?
A)Interest rate parity.
B)Unbiased forward rates.
C)International Fisher effect.
D)Purchasing power parity.
A)Interest rate parity.
B)Unbiased forward rates.
C)International Fisher effect.
D)Purchasing power parity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Exchange rate between two currencies derived from the exchange rates between the currencies and a third currency is known as:
A)spot rate.
B)unbiased forward rate.
C)triangular rate.
D)cross rate.
A)spot rate.
B)unbiased forward rate.
C)triangular rate.
D)cross rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A difference between the 'buy' and 'sell' rates of foreign currency occurs because of:
A)timing differences between 'buy' and 'sell' trades.
B)profit making by the foreign exchange dealer.
C)arbitrage opportunities available to non-foreign exchange dealers.
D)none of the given options.
A)timing differences between 'buy' and 'sell' trades.
B)profit making by the foreign exchange dealer.
C)arbitrage opportunities available to non-foreign exchange dealers.
D)none of the given options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The forward rate refers to:
A)the spot exchange rate.
B)the exchange rate that is determined at a specified future date.
C)the exchange rate that is determined now but with payment and delivery to occur at a specified future date.
D)the upper bound of a currency.
A)the spot exchange rate.
B)the exchange rate that is determined at a specified future date.
C)the exchange rate that is determined now but with payment and delivery to occur at a specified future date.
D)the upper bound of a currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The difference between the spot rate and the forward rate is referred to as the:
A)forward margin.
B)interest rate parity.
C)exchange rate arbitrage.
D)law of one price.
A)forward margin.
B)interest rate parity.
C)exchange rate arbitrage.
D)law of one price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The current spot exchange rate between Australian dollars and UK pounds is A$1 = 0.400 pounds.Interest rates for one year are 5 per cent for pounds and 15 per cent for dollars.What is the expected spot exchange rate in one year's time?
A)0.3652
B)0.4600
C)0.4200
D)0.4380
A)0.3652
B)0.4600
C)0.4200
D)0.4380

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An exchange rate that is established now but with payment and delivery to occur on a specified future date is known as:
A)forward margin.
B)future rate.
C)forward rate.
D)unbiased rate.
A)forward margin.
B)future rate.
C)forward rate.
D)unbiased rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The spot rate can be defined as:
A)the exchange rate where delivery of currency is almost immediate.
B)the exchange rate where delivery of currency is not required.
C)the exchange rate between two currencies.
D)none of the given options.
A)the exchange rate where delivery of currency is almost immediate.
B)the exchange rate where delivery of currency is not required.
C)the exchange rate between two currencies.
D)none of the given options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The highest figure that the daily market turnover in foreign currency in Australia frequently exceeds is:
A)90 billion Australian dollars.
B)100 billion Australian dollars.
C)110 billion Australian dollars.
D)125 billion Australian dollars.
A)90 billion Australian dollars.
B)100 billion Australian dollars.
C)110 billion Australian dollars.
D)125 billion Australian dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which theory states that the forward rate is an unbiased predictor of the future spot rate?
A)Interest rate parity
B)Unbiased forward rates
C)International fisher effect
D)Uncovered interest parity
A)Interest rate parity
B)Unbiased forward rates
C)International fisher effect
D)Uncovered interest parity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Bonds denominated in UK pounds and issued in the UK by non-UK companies are known as:
A)British bonds.
B)Brit bonds.
C)Bulldog bonds.
D)Kangaroo bonds.
A)British bonds.
B)Brit bonds.
C)Bulldog bonds.
D)Kangaroo bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Australian dollar was floated in:
A)1982.
B)1983.
C)1984.
D)1985.
A)1982.
B)1983.
C)1984.
D)1985.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A bond issued by a non-Japanese entity in a currency other than yen but sold in the Japanese retail market is known as:
A)Dashi bond.
B)Sumo bond.
C)Uridashi bond.
D)None of the given options.
A)Dashi bond.
B)Sumo bond.
C)Uridashi bond.
D)None of the given options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose that the spot rate is A$1 = 0.3325 pounds.If the inflation rate next year is expected to be 9 per cent in Australia and 4 per cent in the UK what is next year's spot rate expected to be?
A)0.1732
B)0.3712
C)0.3172
D)The spot rate cannot be calculated as not enough information is provided.
A)0.1732
B)0.3712
C)0.3172
D)The spot rate cannot be calculated as not enough information is provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Calculate the expected exchange rate in one year's time if the present exchange rate is AUD 1 = JPY 80 and if the expected inflation rates in Australia and Japan are 2 per cent and 8 per cent,respectively.
A)AUD 1 = JPY 82.50
B)JPY 1 = AUD 0.0132
C)AUD 1 = JPY 78.20
D)JPY 1 = AUD 0.0118
A)AUD 1 = JPY 82.50
B)JPY 1 = AUD 0.0132
C)AUD 1 = JPY 78.20
D)JPY 1 = AUD 0.0118

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The law of one price states that:
A)the dollar price of any given commodity should be the same everywhere in the world.
B)the expected change in the exchange rate is due to differences in expected inflation rates in the respective countries.
C)arbitrage can be undertaken in situations where the market value departs from the true value.
D)the difference in price of gold around the world can only be due to different exchange rates.
A)the dollar price of any given commodity should be the same everywhere in the world.
B)the expected change in the exchange rate is due to differences in expected inflation rates in the respective countries.
C)arbitrage can be undertaken in situations where the market value departs from the true value.
D)the difference in price of gold around the world can only be due to different exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Covered interest arbitrage is expected to continue:
A)until interest rates between two investments and/or exchange rates between two different countries' rates do not adjust to eliminate further arbitrage.
B)in an efficient market.
C)unless markets become deregulated.
D)until interest rates between two investments and/or exchange rates between two different countries' rates adjust to eliminate further arbitrage.
A)until interest rates between two investments and/or exchange rates between two different countries' rates do not adjust to eliminate further arbitrage.
B)in an efficient market.
C)unless markets become deregulated.
D)until interest rates between two investments and/or exchange rates between two different countries' rates adjust to eliminate further arbitrage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following companies is more likely to benefit from exchange rate hedging?
A)An importer.
B)A local manufacturer with a 'one-off' export deal.
C)A company with a division in a country that is expected to have its currency devalued relative to the Australian dollars in the future.
D)A company with divisions in many different countries.
A)An importer.
B)A local manufacturer with a 'one-off' export deal.
C)A company with a division in a country that is expected to have its currency devalued relative to the Australian dollars in the future.
D)A company with divisions in many different countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Interest rate parity states that:
A)relative forward exchange rates determine the relativity between the forward interest rate and the spot interest rate.
B)relative spot exchange rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the forward interest rate.
C)relative interest rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange rate.
D)relative forward exchange rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the spot interest rate.
A)relative forward exchange rates determine the relativity between the forward interest rate and the spot interest rate.
B)relative spot exchange rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the forward interest rate.
C)relative interest rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange rate.
D)relative forward exchange rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the spot interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Covered interest arbitrage describes:
A)the movement of funds between two currencies to profit from interest rate differences.
B)the movement of funds between two currencies to profit from interest rate differences while using forward contracts to eliminate exchange risk.
C)the difference in interest rates on two different government securities.
D)none of the given options.
A)the movement of funds between two currencies to profit from interest rate differences.
B)the movement of funds between two currencies to profit from interest rate differences while using forward contracts to eliminate exchange risk.
C)the difference in interest rates on two different government securities.
D)none of the given options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The general principle of exchange rate hedging is to:
A)transact in the currency of the country with which you are dealing.
B)deposit foreign currency in a cash deposit until commitment is due.
C)enter into an offsetting commitment in another foreign currency.
D)enter into an offsetting commitment in the same foreign currency.
A)transact in the currency of the country with which you are dealing.
B)deposit foreign currency in a cash deposit until commitment is due.
C)enter into an offsetting commitment in another foreign currency.
D)enter into an offsetting commitment in the same foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The Fisher equation holds that:
A)relative interest rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange rate.
B)for any given interest rate,one currency will be set by the market such that it covers expected inflation and provides a real return.
C)the expected change in the exchange rate is due to differences in expected inflation rates in respective countries.
D)for any given currency,the nominal interest rate will be set by the market such that it covers expected inflation and provides a real return.
A)relative interest rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange rate.
B)for any given interest rate,one currency will be set by the market such that it covers expected inflation and provides a real return.
C)the expected change in the exchange rate is due to differences in expected inflation rates in respective countries.
D)for any given currency,the nominal interest rate will be set by the market such that it covers expected inflation and provides a real return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Calculate how much risk-free profit,in Australian dollars,can be obtained for a dealer with A$10 000 if the following exchange rates apply: 
A)A$1243.52
B)A$10 766.67
C)US$950.34
D)A$766.67

A)A$1243.52
B)A$10 766.67
C)US$950.34
D)A$766.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following represents an appropriate hedge for an Australian exporter expecting payment of US$100 000 in three months' time?
A)Lend the Australian dollar equivalent for three months.
B)Borrow the Australian dollar equivalent for three months.
C)Lend US$100 000 for three months.
D)Borrow the present value of US$100 000 for three months and buy Australian dollars spot.
A)Lend the Australian dollar equivalent for three months.
B)Borrow the Australian dollar equivalent for three months.
C)Lend US$100 000 for three months.
D)Borrow the present value of US$100 000 for three months and buy Australian dollars spot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Transactions in which dealers in foreign exchange markets enter simultaneously into spot and forward transactions are referred to as:
A)arbitrage profits.
B)swaps.
C)foreign currency swaps.
D)exchange rate risk taking.
A)arbitrage profits.
B)swaps.
C)foreign currency swaps.
D)exchange rate risk taking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following transactions minimises exchange rate risk for an importer that buys computer equipment from the US?
A)Taking out a forward contract to buy US dollars in the future when payment is required.
B)Transacting all trades in Australian dollars.
C)Lending US dollars to be repaid when payment is required.
D)All of the given options.
A)Taking out a forward contract to buy US dollars in the future when payment is required.
B)Transacting all trades in Australian dollars.
C)Lending US dollars to be repaid when payment is required.
D)All of the given options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The current exchange rates between Australian dollars and US dollars is AUD 1 = USD 0.7500.Interest rates for one year are 5 per cent in Australia and 8 per cent in the US.What is the expected spot exchange rate?
A)AUD 1 = USD 0.7700
B)USD 1 = AUD 1.3000
C)USD 1 = AUD 1.3700
D)AUD 1 = USD 0.7700 and USD 1 = AUD 1.3000
A)AUD 1 = USD 0.7700
B)USD 1 = AUD 1.3000
C)USD 1 = AUD 1.3700
D)AUD 1 = USD 0.7700 and USD 1 = AUD 1.3000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If an Australian exporter receives US$23 120 in payment for goods and the exchange rate is A$1 = US$0.5150 how many Australian dollars will it buy?
A)$11 906.80
B)$44 893.20
C)$4489.32
D)$1190.68
A)$11 906.80
B)$44 893.20
C)$4489.32
D)$1190.68

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the real interest rate if the nominal interest rate is 10 per cent and the expected inflation rate is 3 per cent?
A)7%
B)6.36%
C)6.8%
D)7.2%
A)7%
B)6.36%
C)6.8%
D)7.2%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Purchasing power parity states that:
A)interest rates must compensate for expected inflation.
B)the expected change in the exchange rate between two currencies is due to differences in expected inflation rates in the respective countries.
C)relative interest rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange rate.
D)the expected change in the exchange rate is due to differences in expected interest rates in the respective countries.
A)interest rates must compensate for expected inflation.
B)the expected change in the exchange rate between two currencies is due to differences in expected inflation rates in the respective countries.
C)relative interest rates determine the relativity between the forward exchange rate and the spot exchange rate.
D)the expected change in the exchange rate is due to differences in expected interest rates in the respective countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the expected one-year forward exchange rate between $A (AUD)and UK pounds (GBP)that maintains interest parity if interest rates on government securities in Australia yield 5.2% p.a.and 4.6% p.a.in the UK,and the spot exchange rate is AUD 1 = GBP 0.45?
A)AUD 1 = GBP 0.4474
B)AUD 1 = GBP 0.3113
C)AUD 1 = GBP 0.4532
D)AUD 1 = GBP 0.4500
A)AUD 1 = GBP 0.4474
B)AUD 1 = GBP 0.3113
C)AUD 1 = GBP 0.4532
D)AUD 1 = GBP 0.4500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An Australian importer wishes to exchange Australian dollars for Japanese yen to pay for goods.How many Australian dollars are needed to pay for a bill of 500 000 yen if A$1 = 70 yen?
A)$350 000
B)$3 500 000
C)$71 428.57
D)$7 142.86
A)$350 000
B)$3 500 000
C)$71 428.57
D)$7 142.86

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Calculate the exchange rate between Australian dollars and UK pounds (GBP)if A$1 = US$0.753 and US$1 = GBP 0.629?
A)A$1 = GBP 1.20
B)A$1 = GBP 0.74
C)GBP 1 = A$2.11
D)GBP 1 = A$0.83
A)A$1 = GBP 1.20
B)A$1 = GBP 0.74
C)GBP 1 = A$2.11
D)GBP 1 = A$0.83

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How many Australian dollars can one US dollar buy if the exchange rate is A$1 = US$0.782?
A)$1.28
B)$1.32
C)$1.00
D)$0.782
A)$1.28
B)$1.32
C)$1.00
D)$0.782

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A negotiable,unsecured,short-term promissory note that is issued in Euromarkets and in several domestic markets is known as:
A)a eurobond.
B)a Eurocurrency term loan.
C)commercial paper.
D)a bearer security.
A)a eurobond.
B)a Eurocurrency term loan.
C)commercial paper.
D)a bearer security.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In which of the following events will an Australian borrower benefit from borrowing Swiss francs?
A)If the Australian dollar appreciates or the Swiss franc depreciates.
B)If the Australian dollar depreciates or the Swiss franc appreciates.
C)The Australian dollar and the Swiss franc both appreciate.
D)The Australian dollar and the Swiss franc both depreciate.
A)If the Australian dollar appreciates or the Swiss franc depreciates.
B)If the Australian dollar depreciates or the Swiss franc appreciates.
C)The Australian dollar and the Swiss franc both appreciate.
D)The Australian dollar and the Swiss franc both depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Companies who are only entering into foreign currency markets for a one-off transaction have no need to hedge against exchange risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A _____________ loan is debt that is raised in a country other than the currency of the country in which the loan was raised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the rate of return to an Australian investor who purchases US dollars with A$100 000 when the exchange rate is AUD 1 = USD 0.74 then invests in a US bank at 7% p.a.interest for 12 months and converts the investment back to Australian dollars when the exchange rate is AUD 1 = USD 0.76?
A)A$4184.21
B)1.418%
C)40.8%
D)4.18%
A)A$4184.21
B)1.418%
C)40.8%
D)4.18%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Foreign currency ___________ are a suitable way to undertake contingent hedging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The intercountry correlation coefficients for share price indices between Australia and other countries are as follows: 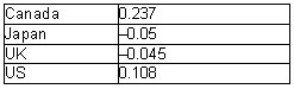
Which country is likely to offer the best diversification benefits for an Australian investor?
A)Canada
B)Japan
C)UK
D)US

Which country is likely to offer the best diversification benefits for an Australian investor?
A)Canada
B)Japan
C)UK
D)US

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the equivalent Australian dollar interest rate for a company that borrows US$10 million for one year at an interest rate of 10% p.a.if the exchange rate was AUD 1 = USD 0.8000 at the time and it was AUD 1 = USD 0.7800 at the repayment date?
A)10%
B)12.8%
C)10.25%
D)14.3%
A)10%
B)12.8%
C)10.25%
D)14.3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The foreign exchange market has a physical marketplace based in New York.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Unbiased forward theory states that the forward rate is an unbiased predictor of the _____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Potential disadvantages of international diversification include adverse taxation implications,increased transaction costs and political risks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The difference between spot and forwards rates is called the ______________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
________________ risk is the variability of an entity's value that is due to possible appreciation or depreciation of the currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is not an overseas borrowing by BHP Billiton?
A)BHP Billiton purchases debentures from a US company.
B)BHP Billiton sells Eurocommercial paper in overseas markets.
C)BHP Billiton sells debentures to overseas investors denominated in Swiss francs.
D)BHP Billiton organises a loan through the Bundesberg Bank in Germany.
A)BHP Billiton purchases debentures from a US company.
B)BHP Billiton sells Eurocommercial paper in overseas markets.
C)BHP Billiton sells debentures to overseas investors denominated in Swiss francs.
D)BHP Billiton organises a loan through the Bundesberg Bank in Germany.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements regarding purchasing power parity (PPP)is true?
A)Overseas evidence mostly supports PPP,provided that transaction costs are factored into the model.
B)International comparisons using current exchange rates can be misleading because deviations from PPP are substantially larger in the long run than in the short run.
C)Under PPP,a country with a low inflation rate will have an appreciating exchange rate.
D)None of the given options.
A)Overseas evidence mostly supports PPP,provided that transaction costs are factored into the model.
B)International comparisons using current exchange rates can be misleading because deviations from PPP are substantially larger in the long run than in the short run.
C)Under PPP,a country with a low inflation rate will have an appreciating exchange rate.
D)None of the given options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements is true of international diversification?
A)International diversification is more beneficial to an investor because he/she can trade at any time of the day.
B)Greater diversification benefits arise from holding a portfolio of shares in companies from countries with stable governments,rather than from emerging countries with greater political risk.
C)Holding a portfolio of shares traded on foreign exchanges increases the likelihood that the correlation between the shares is lower because of the larger number of assets that an investor can choose from.
D)Greater diversification benefits arise from holding a portfolio of shares in companies from countries with stable governments,rather than from emerging countries with greater political risk and holding a portfolio of shares traded on foreign exchanges increases the likelihood that the correlation between the shares is lower because of the larger number of assets that an investor can choose from.
A)International diversification is more beneficial to an investor because he/she can trade at any time of the day.
B)Greater diversification benefits arise from holding a portfolio of shares in companies from countries with stable governments,rather than from emerging countries with greater political risk.
C)Holding a portfolio of shares traded on foreign exchanges increases the likelihood that the correlation between the shares is lower because of the larger number of assets that an investor can choose from.
D)Greater diversification benefits arise from holding a portfolio of shares in companies from countries with stable governments,rather than from emerging countries with greater political risk and holding a portfolio of shares traded on foreign exchanges increases the likelihood that the correlation between the shares is lower because of the larger number of assets that an investor can choose from.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Swaps are agreements:
A)in which two counterparties undertake to exchange risks.
B)which are medium to long-term international securities.
C)which include securities such as euronotes.
D)in which two counterparties undertake to exchange a series of future cash flows.
A)in which two counterparties undertake to exchange risks.
B)which are medium to long-term international securities.
C)which include securities such as euronotes.
D)in which two counterparties undertake to exchange a series of future cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
You observe the following spot exchange rates:
A$1 = £0.4
A$1 = US$0.85
£1 = US$2.125
Assuming no transaction costs,an arbitrage opportunity is possible in this instance.
A$1 = £0.4
A$1 = US$0.85
£1 = US$2.125
Assuming no transaction costs,an arbitrage opportunity is possible in this instance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



