Deck 17: Futures Contracts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Futures Contracts
1
If someone enters into a contract with the intention of taking delivery of a commodity set out in the contract for a price that was determined before delivery,they are likely to be:
A)a broker.
B)a speculator.
C)a hedger.
D)a speculator or hedger.
A)a broker.
B)a speculator.
C)a hedger.
D)a speculator or hedger.
a hedger.
2
A futures contract can be defined as:
A)a contract which provides something to be sold at a future date at a price decided today.
B)a contract which provides something to be sold at a future date at a price decided upon expiry of the contract.
C)a right given to a buyer to sell something at a price determined in advance.
D)a contract that expires when the object of the transaction changes hands.
A)a contract which provides something to be sold at a future date at a price decided today.
B)a contract which provides something to be sold at a future date at a price decided upon expiry of the contract.
C)a right given to a buyer to sell something at a price determined in advance.
D)a contract that expires when the object of the transaction changes hands.
a contract which provides something to be sold at a future date at a price decided today.
3
Which concept is similar to a spread but refers to positions in futures contracts on different commodities rather than on the same commodity for different months?
A)Short spread.
B)Long spread.
C)Straddling.
D)Scalping.
A)Short spread.
B)Long spread.
C)Straddling.
D)Scalping.
Straddling.
4
The process of adjusting traders account balances to reflect changes in market prices is known as:
A)margin call.
B)marking to call.
C)marking to market.
D)spread.
A)margin call.
B)marking to call.
C)marking to market.
D)spread.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The time period during which a scalper holds a futures contract is usually measured in:
A)hours.
B)minutes.
C)seconds.
D)minutes or seconds.
A)hours.
B)minutes.
C)seconds.
D)minutes or seconds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The spot price of a commodity is:
A)the cost of holding a commodity for a specified period of time.
B)the price that a commodity was traded for on the previous trading day.
C)the agreed price that a commodity will be traded for at some point in time in the future.
D)the price of the commodity when the buyer pays immediately and the seller delivers immediately.
A)the cost of holding a commodity for a specified period of time.
B)the price that a commodity was traded for on the previous trading day.
C)the agreed price that a commodity will be traded for at some point in time in the future.
D)the price of the commodity when the buyer pays immediately and the seller delivers immediately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider a bond with exactly three years to maturity,a face value of $100 and a coupon interest rate of 6.6% p.a. ,payable half yearly.If the required yield is 7.2% p.a. ,what is the price of the bond?
A)$98.40
B)$98.04
C)$98.00
D)Cannot be calculated as not enough information is provided.
A)$98.40
B)$98.04
C)$98.00
D)Cannot be calculated as not enough information is provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The first futures contract in Australia was on:
A)cotton.
B)wheat.
C)wool.
D)greasy wool.
A)cotton.
B)wheat.
C)wool.
D)greasy wool.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not a major function of the clearing house:
A)establish and collect deposits.
B)determine the price of all futures contracts.
C)call in margins as required.
D)apportion the gains and losses.
A)establish and collect deposits.
B)determine the price of all futures contracts.
C)call in margins as required.
D)apportion the gains and losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If two parties enter into the same futures contract,one as a buyer and the other as a seller,how many contracts are formed?
A)One,between the two parties.
B)Two,one between the buyer and seller and the other with the exchange.
C)Two,each with the clearinghouse of the exchange.
D)Three,two between each party and the clearinghouse and one between each party.
A)One,between the two parties.
B)Two,one between the buyer and seller and the other with the exchange.
C)Two,each with the clearinghouse of the exchange.
D)Three,two between each party and the clearinghouse and one between each party.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A personalised contract between two parties whereby one party agrees to sell a bale of wool to another party in the future at a price determined today is an example of a:
A)futures contract.
B)forward contract.
C)wool option.
D)spot contract.
A)futures contract.
B)forward contract.
C)wool option.
D)spot contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A futures contract can be differentiated from a forward contract in that a futures contract:
A)is organised through an exchange.
B)can be 'closed out' or 'reversed' at any time.
C)is exactly the same as a forward contract.
D)is organised through an exchange and can be 'closed out' or 'reversed' at any time.
A)is organised through an exchange.
B)can be 'closed out' or 'reversed' at any time.
C)is exactly the same as a forward contract.
D)is organised through an exchange and can be 'closed out' or 'reversed' at any time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A hedger can be described as someone who enters into a futures contract:
A)with the purpose of making a profit.
B)with the purpose of minimising risk.
C)as a seller with the purpose of minimising risk.
D)with the purpose of buying or selling a commodity defined in the futures contract.
A)with the purpose of making a profit.
B)with the purpose of minimising risk.
C)as a seller with the purpose of minimising risk.
D)with the purpose of buying or selling a commodity defined in the futures contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
To prevent arbitrage,the futures price must be:
A)less than (or equal to)the current spot price plus the carrying price.
B)greater than (or equal to)the current spot price plus the carrying price.
C)less than the present value of all carrying costs.
D)greater than the present value of all carrying costs.
A)less than (or equal to)the current spot price plus the carrying price.
B)greater than (or equal to)the current spot price plus the carrying price.
C)less than the present value of all carrying costs.
D)greater than the present value of all carrying costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A speculator can be described as someone who enters into a futures contract:
A)with the purpose of making a profit.
B)with the purpose of minimising risk.
C)as a seller with the purpose of minimising risk.
D)with the purpose of buying or selling a commodity defined in the futures contract.
A)with the purpose of making a profit.
B)with the purpose of minimising risk.
C)as a seller with the purpose of minimising risk.
D)with the purpose of buying or selling a commodity defined in the futures contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Individuals and companies who enter into contracts in order to reduce risk are known as:
A)speculators.
B)hedgers.
C)dealers.
D)scalpers.
A)speculators.
B)hedgers.
C)dealers.
D)scalpers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The cost of holding a commodity from one period to another is known as:
A)carrying cost.
B)commodity cost.
C)holding cost.
D)exercise cost.
A)carrying cost.
B)commodity cost.
C)holding cost.
D)exercise cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Sydney Futures Exchange opened for trading in:
A)1957.
B)1958.
C)1960.
D)1962.
A)1957.
B)1958.
C)1960.
D)1962.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Individuals and companies who enter into contracts in order to profit from correctly anticipating price movements are known as:
A)speculators.
B)hedgers.
C)dealers.
D)scalpers.
A)speculators.
B)hedgers.
C)dealers.
D)scalpers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A demand for extra funds to be deposited into a trader's account is called a:
A)call option.
B)deposit demand.
C)margin call.
D)short selling.
A)call option.
B)deposit demand.
C)margin call.
D)short selling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Calculate the price of a bank bill with 90 days remaining to maturity,with face value of $100 000 and priced to yield 10% p.a.
A)$90 909
B)$97 594
C)$96 656
D)$98 424
A)$90 909
B)$97 594
C)$96 656
D)$98 424

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Calculate the profit (loss)to a short hedger due to basis risk from the following information: 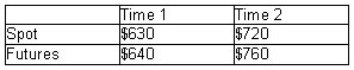
A)$30
B)$10
C)$40
D)($30)

A)$30
B)$10
C)$40
D)($30)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The financial controller of Nointerest Ltd has planned that the company borrow using a 90-day bank bill facility with face value of $500 000 in four weeks.Interest rates on 90-day bank bills are currently 12% p.a.As a protection against possible interest rate increases,she has entered into a futures contract by selling one bank bill futures contract at a price of $88.50.After the four-week period,she reverses the futures position at $86.50 and issues a bank bill at a rate of 14% p.a.Calculate the net dollar shortfall/gain.
A)$2432
B)$70
C)$203
D)$6
A)$2432
B)$70
C)$203
D)$6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The financial controller of No interest Ltd has planned that the company borrow using a 90-day bank bill facility with face value of $500 000 in four weeks.Interest rates on 90-day bank bills are currently 12% p.a.As a protection against possible interest rate increases,she has entered into a futures contract by selling one bank bill futures contract at a price of $88.50.After the four-week period,she reverses the futures position at $86.50 and issues a bank bill at a rate of 14% p.a.Calculate the dollar shortfall that Nointerest would have faced had it not entered into the futures contract.
A)$1148
B)$2315
C)$3087
D)$7832
A)$1148
B)$2315
C)$3087
D)$7832

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A call option on a futures contract:
A)gives the buyer the right to assume a sold position in the futures.
B)gives the seller the right to assume a sold position in the futures.
C)gives the buyer the right to assume a buy position in the futures.
D)gives the seller the right to assume a buy position in the futures.
A)gives the buyer the right to assume a sold position in the futures.
B)gives the seller the right to assume a sold position in the futures.
C)gives the buyer the right to assume a buy position in the futures.
D)gives the seller the right to assume a buy position in the futures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is true regarding a futures contract?
A)Few contracts end in delivery of a commodity.
B)Most contracts end in delivery of a commodity.
C)All contracts end in delivery of a commodity.
D)No contracts end in delivery of a commodity.
A)Few contracts end in delivery of a commodity.
B)Most contracts end in delivery of a commodity.
C)All contracts end in delivery of a commodity.
D)No contracts end in delivery of a commodity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
'Marking to market' is a process of the clearinghouse whereby:
A)funds are demanded from each trader that incurs a loss.
B)funds are returned to each trader that earns a profit.
C)each trader's position is updated according to the average market price determined on that day.
D)each trader's position is adjusted according to the market price determined at the close of each trading day.
A)funds are demanded from each trader that incurs a loss.
B)funds are returned to each trader that earns a profit.
C)each trader's position is updated according to the average market price determined on that day.
D)each trader's position is adjusted according to the market price determined at the close of each trading day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If an individual who takes a position as a buyer in a futures contract wishes to realise a profit from their position,they should:
A)find a buyer and sell their position.
B)offset their original contract by entering into another as a seller.
C)offset their original contract by entering into another as a buyer.
D)take delivery of the commodity.
A)find a buyer and sell their position.
B)offset their original contract by entering into another as a seller.
C)offset their original contract by entering into another as a buyer.
D)take delivery of the commodity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
It is expected that the price of a futures contract with a term to maturity of zero be:
A)close to zero.
B)less than the spot price.
C)equal to the spot price.
D)more than the spot price.
A)close to zero.
B)less than the spot price.
C)equal to the spot price.
D)more than the spot price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The financial controller of Nointerest Ltd has planned that the company borrow using a 90-day bank bill facility with face value of $500 000 in four weeks.Interest rates on 90-day bank bills are currently 12% p.a.As a protection against possible interest rate increases,she has entered into a futures contract by selling one bank bill futures contract at a price of $88.50.After the four-week period,she reverses the futures position at $86.50 and issues a bank bill at a rate of 14% p.a.Calculate the gain/loss made on the futures contract.
A)$2321 gain.
B)$2111 gain.
C)$7902 loss.
D)$3580 loss.
A)$2321 gain.
B)$2111 gain.
C)$7902 loss.
D)$3580 loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Calculate the dollar price implicit in a bank-accepted bill futures contract with a face value of $1 000 000,a reported price of $95.00 (the price of the trade),and 90 days to maturity.
A)$998 252
B)$952 381
C)$960 242
D)$987 821
A)$998 252
B)$952 381
C)$960 242
D)$987 821

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The prime function of a futures clearinghouse is to:
A)be the counterparty in each contract.
B)bring together the buyer and seller in each contract.
C)determine the futures price.
D)check the creditworthiness of each party in a contract.
A)be the counterparty in each contract.
B)bring together the buyer and seller in each contract.
C)determine the futures price.
D)check the creditworthiness of each party in a contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A margin call refers to:
A)the payment of profit by the clearinghouse to the trader.
B)the demand of funds by the clearinghouse from each trader to cover losses.
C)the difference between the futures market price and the contract price.
D)the close of a futures contract.
A)the payment of profit by the clearinghouse to the trader.
B)the demand of funds by the clearinghouse from each trader to cover losses.
C)the difference between the futures market price and the contract price.
D)the close of a futures contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the spot price and futures price on a gold contract are $553 and $555,respectively,then theoretically the carrying cost should be equal to:
A)$2 or more.
B)between $0 and $2.
C)cannot be determined.
D)$2.
A)$2 or more.
B)between $0 and $2.
C)cannot be determined.
D)$2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The objective of a hedger is to:
A)minimise possible losses and still receive profits.
B)minimise possible losses at the expense of foregoing possible profits.
C)make arbitrage profits.
D)none of the given options.
A)minimise possible losses and still receive profits.
B)minimise possible losses at the expense of foregoing possible profits.
C)make arbitrage profits.
D)none of the given options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Assuming perfect convergence,a spot price will be:
A)greater than the futures price,which has a term to maturity of zero.
B)less than the futures price,which has a term to maturity of zero.
C)the cost of holding a commodity in a futures contract from one time period to another.
D)the price of a commodity in a futures contract,which expires today.
A)greater than the futures price,which has a term to maturity of zero.
B)less than the futures price,which has a term to maturity of zero.
C)the cost of holding a commodity in a futures contract from one time period to another.
D)the price of a commodity in a futures contract,which expires today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Calculate how much a trader,who enters into a 90-day bank bill futures contract on 20 June with a reported price of $94.00,will need to pay on settlement date (30 June)if the face value of the underlying bill is $500 000.
A)$497 289
B)$499 179
C)$500 000
D)$492 711
A)$497 289
B)$499 179
C)$500 000
D)$492 711

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Buying a June bank bill futures contract and simultaneously selling a March bond futures contract is:
A)a typical trading strategy for a scalper.
B)a typical trading strategy for a hedger.
C)an example of a spread.
D)an example of a straddle.
A)a typical trading strategy for a scalper.
B)a typical trading strategy for a hedger.
C)an example of a spread.
D)an example of a straddle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Given the following information,calculate the expected arbitrage profit or loss from buying an ounce of gold today for $553 and selling a futures contract that matures in six months' time at a price of $570.Assume interest rates are 10% p.a. ,insurance costs are $20,the risk factor is 5 per cent on the cost of gold,and projected gold production over the next 12 months is 5000 ounces.
A)$0
B)($31)
C)$17
D)$31
A)$0
B)($31)
C)$17
D)$31

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If an individual who has entered a futures contract to buy one ounce of gold for $553 decides to reverse their position when the futures price is $555,they will:
A)effectively now have two positions with the exchange.
B)will still have one contract with the exchange.
C)make a profit of $2.
D)make a loss of $2.
A)effectively now have two positions with the exchange.
B)will still have one contract with the exchange.
C)make a profit of $2.
D)make a loss of $2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A farmer plans to sell 800 bales of greasy wool (21 micron)in four weeks time.The current spot price is 1300 for a contract of 20 bales and the eight week futures price is 1320 (20 bales per contract).If the farmer hedges how many futures contracts should be purchased?
A)50
B)49
C)39
D)28
A)50
B)49
C)39
D)28

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements is true for a 10-year bond future contract?
A)Trading ceases on the 15th day of the settlement month.
B)Trading ceases on the last business day of the contract month.
C)Settlement day is the third business day after the day when trading ceases.
D)Settlement day is the second business day after the day when trading ceases.
A)Trading ceases on the 15th day of the settlement month.
B)Trading ceases on the last business day of the contract month.
C)Settlement day is the third business day after the day when trading ceases.
D)Settlement day is the second business day after the day when trading ceases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
On 31 December 2001,the All Ordinaries Index closed at 3427 points and the September 2002 SPI 200 futures was priced at 3473 points.A speculator believes that share prices are likely to fall and so decides to sell September 2002 SPI 200 futures immediately.One week later,when the All Ordinaries Index rises to 3435 points and the September 2002 SPI 200 futures falls to 3471 points,the speculator decides to reverse her position.How much profit/loss does the speculator make?
A)$200 loss.
B)$1100 gain.
C)$950 gain.
D)$50 gain.
A)$200 loss.
B)$1100 gain.
C)$950 gain.
D)$50 gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Calculate the price of a 10-year bond that has five years to maturity,with face value of $100 000,and coupon interest rate of 8.9% p.a.paid semi-annually,if the required rate of return is 9.9% p.a.(simple interest).
A)$96 130
B)$90 992
C)$95 752
D)$93 193
A)$96 130
B)$90 992
C)$95 752
D)$93 193

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Basis risk occurs when the spot and futures prices do not move in perfect unison.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
_____________________ refers to the fact that the commodity that is the subject of the futures contract is not precisely the same as the commodity that is of interest to the hedger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Entering into a contract to sell and later entering into a contract to buy is called _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The value of a bank bill futures price can be expressed as:
A)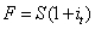
B)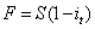
C)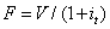
D)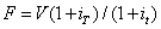
A)
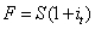
B)
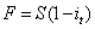
C)
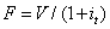
D)
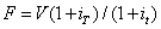

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Runaway Bank Ltd is expecting a cash inflow of $500 000 in one month,which it intends to invest in 90-day bank bills.Management of the company has chosen to hedge against fluctuations in interest rates by hedging with a bank bill futures contract.When the company enters the hedged position,the yields are 10.4% p.a.(spot)and 10.6% p.a.(futures).When the hedge is reversed,the yields are 7.6% p.a.(spot)and 7.78% p.a.(futures).Including the gain from the futures,what will be the implied yield that Runaway Bank Ltd receives?
A)8.63%
B)7.72%
C)10.42%
D)10.55%
A)8.63%
B)7.72%
C)10.42%
D)10.55%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A hedger is an individual or company who enters into financial contracts in order to profit from correctly anticipating price movements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The 10-year bond futures contract can be useful in hedging against an exposure to changes in ____________ fixed-interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
'Short selling' refers to:
A)selling a contract allowing the holder to sell the underlying asset back to the seller at maturity.
B)a process that is used when stock prices are expected to gradually increase over time.
C)selling an asset that does not belong to you,and buying it back at a later date.
D)none of the given options.
A)selling a contract allowing the holder to sell the underlying asset back to the seller at maturity.
B)a process that is used when stock prices are expected to gradually increase over time.
C)selling an asset that does not belong to you,and buying it back at a later date.
D)none of the given options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The SPI 200 futures contract is only used for speculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The face value of a 90-day bank bill is $ _______________.(Enter numbers only,no spaces or thousands separators. )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Many companies prefer forward rate agreements (FRAs)to futures contracts as:
A)an FRA allows the company to close out the agreement before settlement.
B)an FRA allows flexibility to reverse the contract.
C)an FRA can be more closely tailored to the companies specific needs.
D)None of the given answers.
A)an FRA allows the company to close out the agreement before settlement.
B)an FRA allows flexibility to reverse the contract.
C)an FRA can be more closely tailored to the companies specific needs.
D)None of the given answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
On 6 January 2002,the All Ordinaries Index closed at 3435 points and the June 2002 SPI 200 futures was priced at 3457 points.A speculator believes that share prices are likely to fall and so decides to sell June 2002 SPI 200 futures.One week later,when the All Ordinaries Index falls to 3417 points and the June 2002 SPI 200 futures falls to 3436 points,the speculator decides to reverse her position.How much profit/loss does the speculator make?
A)$450 gain.
B)$475 gain.
C)$525 gain.
D)$525 loss.
A)$450 gain.
B)$475 gain.
C)$525 gain.
D)$525 loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Day traders are prepared to trade as they see fit during a trading day,but regard an overnight position as _____________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An investor purchased 100 SPI200 futures contracts when the price was 6450.Twelve months later the investor reversed out when the price was 5960.The investor made a loss of $_____________.
(Enter numbers only,no spaces or thousands separators. )
(Enter numbers only,no spaces or thousands separators. )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Over hedging is the equivalent of speculating.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Basis equals futures price minus spot price.
B)Futures contracts are usually closed out at maturity although they are settled daily through marking to market,because the futures price is based on final delivery.
C)While the bank bill contract is used for operations involving short-term interest rates,the 10-year Treasury bond contract can be used for both short-term and long-term interest rates.
D)None of the given options.
A)Basis equals futures price minus spot price.
B)Futures contracts are usually closed out at maturity although they are settled daily through marking to market,because the futures price is based on final delivery.
C)While the bank bill contract is used for operations involving short-term interest rates,the 10-year Treasury bond contract can be used for both short-term and long-term interest rates.
D)None of the given options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Forward Rate Agreements (FRAs)lack flexibility due to the difficulty to reverse out of the contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How can a hedging strategy lead to losses?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Forward Rate Agreements (FRAs)are traded on the Australian Securities Exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A futures price must be greater than or equal to the current spot price,plus the carrying cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
You are the financial manager of a company that plans to issue long-term bonds in 6 months' time.However,you are worried that interest rates may rise before then.How would you use financial futures to protect against a rise in interest rates?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Distinguish between a forward-rate agreement (FRA)and a futures contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



