Deck 11: Experimental Research Design
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Experimental Research Design
1
Exhibit 11.1: In the following items, select the experimental design that best fits the descriptive statement.
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.All subjects are entered into all experimental treatments.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest design control-group
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.All subjects are entered into all experimental treatments.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest design control-group
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design
E
2
A research study has a design with two groups receiving a pretest, one of which receives treatment, and two groups who are not pretested, one of which receives treatment.This is a
A) counterbalanced design.
B) multiple group pretest-posttest design.
C) Solomon design.
D) 2 * 2 factorial design.
A) counterbalanced design.
B) multiple group pretest-posttest design.
C) Solomon design.
D) 2 * 2 factorial design.
C
3
The Solomon three- and four-group designs were developed in order to control the threat of
A) differential measurement.
B) history.
C) maturation.
D) pretest sensitization.
A) differential measurement.
B) history.
C) maturation.
D) pretest sensitization.
D
4
In a randomized subjects pretest-posttest control group design, results might best be analyzed through
A) ANCOVA.
B) ANOVA.
C) change scores.
D) t tests.
A) ANCOVA.
B) ANOVA.
C) change scores.
D) t tests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Exhibit 11.1: In the following items, select the experimental design that best fits the descriptive statement.
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.Regression is controlled by random assignment, but the main effects of testing and the interaction of testing with X are not determinable.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest design control-group
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.Regression is controlled by random assignment, but the main effects of testing and the interaction of testing with X are not determinable.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest design control-group
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Counterbalanced designs
A) give the same treatments to all subjects.
B) may involve many groups and treatments.
C) rotate intact groups.
D) a and c
E) All of these are true.
A) give the same treatments to all subjects.
B) may involve many groups and treatments.
C) rotate intact groups.
D) a and c
E) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is an advantage of the factorial design? It
A) provides an opportunity to observe interaction.
B) accomplishes what might take many separate experiments.
C) provides a more powerful test of the hypothesis.
D) All of these are true.
A) provides an opportunity to observe interaction.
B) accomplishes what might take many separate experiments.
C) provides a more powerful test of the hypothesis.
D) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Exhibit 11.1: In the following items, select the experimental design that best fits the descriptive statement.
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.Recommended design unless there is some question relative to the randomness of the assignment of subjects.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest design control-group
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.Recommended design unless there is some question relative to the randomness of the assignment of subjects.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest design control-group
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
There is a need to be concerned with a carry-over effect when the design is a
A) times series design.
B) counterbalanced design.
C) randomized Solomon four-group design.
D) randomized control-group, posttest only design.
A) times series design.
B) counterbalanced design.
C) randomized Solomon four-group design.
D) randomized control-group, posttest only design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Exhibit 11.1: In the following items, select the experimental design that best fits the descriptive statement.
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.Includes more than one control group with one group receiving neither pretest nor treatment.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest, control-group design
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.Includes more than one control group with one group receiving neither pretest nor treatment.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest, control-group design
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Factorial designs are useful because they
A) allow multiple independent variables.
B) build in extraneous variables.
C) examine interaction of variables.
D) All of these are true.
A) allow multiple independent variables.
B) build in extraneous variables.
C) examine interaction of variables.
D) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Exhibit 11.1: In the following items, select the experimental design that best fits the descriptive statement.
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.Failure to control history and maturation is a definite weakness.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest design control-group
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.Failure to control history and maturation is a definite weakness.
A) One-group, pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest design control-group
D) Randomized Solomon four-group design
E) Counterbalanced design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
To investigate the interaction effect of several independent variables, a researcher would use a(n) _____ experimental design.
A) ABAB
B) factorial
C) Solomon four-group
D) single-subject
E) static group comparison
A) ABAB
B) factorial
C) Solomon four-group
D) single-subject
E) static group comparison

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Every subject receives every treatment in the
A) counterbalanced design.
B) randomized Solomon four-group design.
C) randomized subjects pretest-posttest, control group design.
D) randomized subjects posttest-only, control group design.
E) nonrandomized control group pretest-posttest design.
A) counterbalanced design.
B) randomized Solomon four-group design.
C) randomized subjects pretest-posttest, control group design.
D) randomized subjects posttest-only, control group design.
E) nonrandomized control group pretest-posttest design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a preexperimental design specific events may occur between the pretest and the posttest, which cause changes that are measured on the posttest.This represents a failure to control
A) randomization.
B) maturation.
C) pretest sensitivity.
D) reactivity.
E) history.
A) randomization.
B) maturation.
C) pretest sensitivity.
D) reactivity.
E) history.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which design can most easily be used with intact classes?
A) Solomon
B) Factorial
C) Randomized subjects posttest only
D) Counterbalanced
E) Randomized subjects pretest-posttest
A) Solomon
B) Factorial
C) Randomized subjects posttest only
D) Counterbalanced
E) Randomized subjects pretest-posttest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The main disadvantage of a counterbalanced design is the lack of control for
A) carry-over effect of treatment.
B) internal validity.
C) preexisting differences.
D) pretest sensitization.
A) carry-over effect of treatment.
B) internal validity.
C) preexisting differences.
D) pretest sensitization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A researcher is studying the effect of word games on spelling achievement.Of two randomly assigned groups one receives experience with word games, while the other does not.A spelling test is then administered.This design is
A) counterbalanced.
B) randomized subjects, posttest only control group.
C) a simple 2 * 2 factorial.
D) a static group
A) counterbalanced.
B) randomized subjects, posttest only control group.
C) a simple 2 * 2 factorial.
D) a static group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Consider the following designs: (1)Nonrandomized pretest-posttest design; (2) Solomon three-group design; (3) two-group static design; (4) one-group pretest-posttest design; (5) counterbalanced design.Which of these would you recommend for use in the ordinary classroom setting?
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
E) 4 and 5
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
E) 4 and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A static group comparison design has a control group, but
A) the posttest is not compared to anything.
B) the groups are not pretested to see change.
C) the equivalence of the groups is questionable.
D) b and c
A) the posttest is not compared to anything.
B) the groups are not pretested to see change.
C) the equivalence of the groups is questionable.
D) b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
(WWW) Which of the following would be the least acceptable research design?
A) Posttest only, control group design
B) One-group pretest-posttest design
C) Pretest-posttest control group design
D) Matched subjects, posttest only, control group design
A) Posttest only, control group design
B) One-group pretest-posttest design
C) Pretest-posttest control group design
D) Matched subjects, posttest only, control group design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The term "confounding" refers to the presence of
A) a variable which is controlled and does not affect the outcome of a study.
B) two independent variables in a study.
C) a variable that is not controlled which affects the outcome of a study.
D) two dependent variables in a study.
A) a variable which is controlled and does not affect the outcome of a study.
B) two independent variables in a study.
C) a variable that is not controlled which affects the outcome of a study.
D) two dependent variables in a study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Exhibit 11-2: The following means (graphs a - e) show some possible outcomes of a study investigating the relationship of two handwriting instruction methods, A and B, on the handwriting scores of boys and girls.The scale on the left shows dependent variable scores.
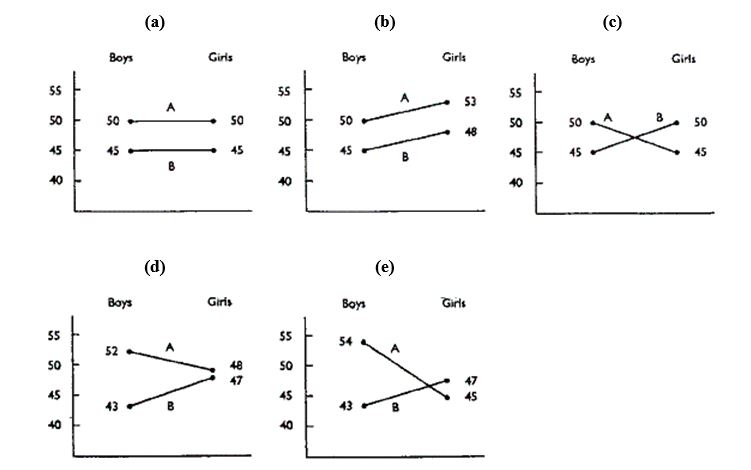
Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows interaction, gender difference, and method difference?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows interaction, gender difference, and method difference?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The major problem in single-subject research is
A) external validity.
B) extraneous variable control.
C) intersubject variability.
D) All of these are true.
A) external validity.
B) extraneous variable control.
C) intersubject variability.
D) All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Exhibit 11-2: The following means (graphs a - e) show some possible outcomes of a study investigating the relationship of two handwriting instruction methods, A and B, on the handwriting scores of boys and girls.The scale on the left shows dependent variable scores.

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows no interaction and no gender difference but does show method differences?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows no interaction and no gender difference but does show method differences?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The major disadvantage of a simple ABA single-subject design is that it
A) concludes with subjects under baseline conditions.
B) concludes with subjects under experimental conditions.
C) needs more than two different treatments.
D) requires an excessive amount of time to complete the experiment.
A) concludes with subjects under baseline conditions.
B) concludes with subjects under experimental conditions.
C) needs more than two different treatments.
D) requires an excessive amount of time to complete the experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Exhibit 11-2: The following means (graphs a - e) show some possible outcomes of a study investigating the relationship of two handwriting instruction methods, A and B, on the handwriting scores of boys and girls.The scale on the left shows dependent variable scores.

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows interaction but no gender or method difference?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows interaction but no gender or method difference?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The credibility of a single-subject experiment is based on
A) the extent of intersubject reliability.
B) the extent to which behavior changes as treatment changes.
C) how well regression as a threat to internal validity is controlled.
D) the extent to which there is random assignment to treatments.
A) the extent of intersubject reliability.
B) the extent to which behavior changes as treatment changes.
C) how well regression as a threat to internal validity is controlled.
D) the extent to which there is random assignment to treatments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a nonrandomized control group, pretest-posttest design, the recommended procedure for analyzing test results is a(n)
A) t-test of the difference between pretest and posttest means for both the experimental and the control group.
B) four-way analysis of variance.
C) analysis of covariance, in which the posttest means are compared using the pretest means as the covariate.
D) analysis of variance of the mean pretest-posttest change for the experimental and control groups.
A) t-test of the difference between pretest and posttest means for both the experimental and the control group.
B) four-way analysis of variance.
C) analysis of covariance, in which the posttest means are compared using the pretest means as the covariate.
D) analysis of variance of the mean pretest-posttest change for the experimental and control groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Single-case designs have been particularly useful in
A) theory testing.
B) laboratory studies.
C) classroom applications.
D) clinical applications.
A) theory testing.
B) laboratory studies.
C) classroom applications.
D) clinical applications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A simple reversal (ABA) design
A) concludes with subjects under baseline condition.
B) concludes with subjects under experimental condition.
C) employs more than two different treatments.
D) involves two groups.
A) concludes with subjects under baseline condition.
B) concludes with subjects under experimental condition.
C) employs more than two different treatments.
D) involves two groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Counterbalanced experimental designs are especially susceptible to the effect of
A) regression.
B) order.
C) instrumentation.
D) pretest sensitization.
A) regression.
B) order.
C) instrumentation.
D) pretest sensitization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A researcher wants to study the effect of three treatments, social class, and gender on a dependent variable.The best design to use is
A) counterbalanced.
B) one-group time series.
C) factorial.
D) randomized control group pretest-posttest.
A) counterbalanced.
B) one-group time series.
C) factorial.
D) randomized control group pretest-posttest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Exhibit 11-2: The following means (graphs a - e) show some possible outcomes of a study investigating the relationship of two handwriting instruction methods, A and B, on the handwriting scores of boys and girls.The scale on the left shows dependent variable scores.

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows no interaction but both gender and method difference?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows no interaction but both gender and method difference?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What are the two essential features of true experimental designs?
a.Dependent and attribute variables
b.Manipulation and random assignment
c.Blinding and counterbalancing
d.Theory and matching
e.Pretest and posttest
a.Dependent and attribute variables
b.Manipulation and random assignment
c.Blinding and counterbalancing
d.Theory and matching
e.Pretest and posttest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The control group time series design overcomes the one-group time series design problem of
A) maturation.
B) history.
C) nonrandomization.
D) all of these are true.
A) maturation.
B) history.
C) nonrandomization.
D) all of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Exhibit 11-2: The following means (graphs a - e) show some possible outcomes of a study investigating the relationship of two handwriting instruction methods, A and B, on the handwriting scores of boys and girls.The scale on the left shows dependent variable scores.

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows interaction and method difference but no gender difference?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Which diagram shows interaction and method difference but no gender difference?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)
C) graph (c)
D) graph (d)
E) graph (e)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A research study has a design with two groups receiving a pretest, one of which receives treatment and two groups who are not pretested, one of which receives treatment.This design is called a
A) counterbalanced design.
B) multiple group pretest-posttest design.
C) Solomon design.
D) 2 2 factorial design.
2 factorial design.
A) counterbalanced design.
B) multiple group pretest-posttest design.
C) Solomon design.
D) 2
 2 factorial design.
2 factorial design.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The first step in the ABAB design is
A) using random assignment to place subjects in groups.
B) selecting matched pairs for the study.
C) administering a pretest to all subjects.
D) measuring the behavior of interest before the treatment.
A) using random assignment to place subjects in groups.
B) selecting matched pairs for the study.
C) administering a pretest to all subjects.
D) measuring the behavior of interest before the treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For three weeks Mr.Gomez recorded the amount of homework his fourth grade students turned in.The next three weeks he rewarded those who turned in homework with free playtime and recorded the turn-in rate for these three weeks.Mr.Gomez is using which design?
A) Counterbalanced
B) One-group time series
C) 3*1*3 factorial
D) Multiple single-subject design
A) Counterbalanced
B) One-group time series
C) 3*1*3 factorial
D) Multiple single-subject design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a control group time series design, the experimental treatment is administered
A) prior to obtaining baseline measurements.
B) after all baseline measurements are obtained.
C) between two periodic series of measurements.
D) first to the experimental group and then to the control group.
A) prior to obtaining baseline measurements.
B) after all baseline measurements are obtained.
C) between two periodic series of measurements.
D) first to the experimental group and then to the control group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The single-subject experimental design is especially useful in
A) research on behavior modification.
B) research where the investigator cannot manipulate an independent variable.
C) research to determine the value of a clinical treatment.
D) All of these are true.
E) a and c
A) research on behavior modification.
B) research where the investigator cannot manipulate an independent variable.
C) research to determine the value of a clinical treatment.
D) All of these are true.
E) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Exhibit 11-4.Identify the major threat to internal validity in the following research studies.
Refer to Exhibit 11-4.A teacher researcher randomly assigned students within a classroom to two groups, one of which received some special instructional materials to take home with them to study and to use with homework assignments.The C group did not get the special materials.The researcher was surprised to find that there weren't significant differences between the two groups on achievement tests and other selected measures.
A) Regression
B) Diffusion
C) Mortality
D) Selection
E) History
Refer to Exhibit 11-4.A teacher researcher randomly assigned students within a classroom to two groups, one of which received some special instructional materials to take home with them to study and to use with homework assignments.The C group did not get the special materials.The researcher was surprised to find that there weren't significant differences between the two groups on achievement tests and other selected measures.
A) Regression
B) Diffusion
C) Mortality
D) Selection
E) History

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The best experimental design to use to determine the effect of a pretest on the dependent variable is a(n)
A) ABA design.
B) counterbalanced design.
C) Solomon four-group design.
D) randomized pretest-posttest, control group design.
A) ABA design.
B) counterbalanced design.
C) Solomon four-group design.
D) randomized pretest-posttest, control group design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Exhibit 11.3: The following graphs show the results of two studies comparing the effect of instructional Methods A and B in large and small social studies classes.The dependent variable was scores on a standardized social studies test.
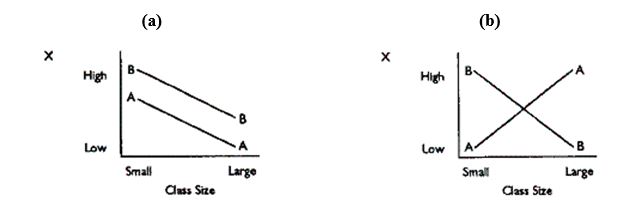
Refer to Exhibit 11-3.Which graph shows interaction but no main effects?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)

Refer to Exhibit 11-3.Which graph shows interaction but no main effects?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Under which of the following circumstances would a researcher use a quasi-experimental design?
A) Experimenter must employ a pretest.
B) Experimenter must collect all the data him/herself.
C) Experimenter cannot assign subjects to conditions.
D) There is more than one independent variable.
E) The pretest has a reactive effect.
A) Experimenter must employ a pretest.
B) Experimenter must collect all the data him/herself.
C) Experimenter cannot assign subjects to conditions.
D) There is more than one independent variable.
E) The pretest has a reactive effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Exhibit 11-4.Identify the major threat to internal validity in the following research studies.
Refer to Exhibit 11-4.A researcher used two classrooms in an experimental study.It was found that the E group had more high ability students than the C group before the study began.
A) Regression
B) Diffusion
C) Mortality
D) Selection
E) History
Refer to Exhibit 11-4.A researcher used two classrooms in an experimental study.It was found that the E group had more high ability students than the C group before the study began.
A) Regression
B) Diffusion
C) Mortality
D) Selection
E) History

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In contrast to time series designs, multiple baseline designs
A) involve observation of two or more target behaviors during the baseline condition.
B) do not reinstate initial baseline conditions following treatment.
C) use a control group to compare the effectiveness of the treatment.
D) All of these are true.
E) a and b
A) involve observation of two or more target behaviors during the baseline condition.
B) do not reinstate initial baseline conditions following treatment.
C) use a control group to compare the effectiveness of the treatment.
D) All of these are true.
E) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Exhibit 11.3: The following graphs show the results of two studies comparing the effect of instructional Methods A and B in large and small social studies classes.The dependent variable was scores on a standardized social studies test.

Refer to Exhibit 11-3.Which graph shows main effects but no interaction?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)

Refer to Exhibit 11-3.Which graph shows main effects but no interaction?
A) graph (a)
B) graph (b)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The main internal validity problem of the static-group comparison design is
A) observed posttest differences may be due to preexperimental differences between the groups rather than to the experimental treatment.
B) the interaction between the experimental and control treatments.
C) the pretest may sensitize subjects to the experimental treatment.
D) the matching procedure may result in the loss of too many subjects and thus introduce bias.
A) observed posttest differences may be due to preexperimental differences between the groups rather than to the experimental treatment.
B) the interaction between the experimental and control treatments.
C) the pretest may sensitize subjects to the experimental treatment.
D) the matching procedure may result in the loss of too many subjects and thus introduce bias.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In an experimental study using pre- and posttests, which of the following instruments is most likely to have a "reactive effect"?
A) Arithmetic pretest
B) Scholastic aptitude test used for matching purposes
C) Film showing prejudice toward minorities
D) Divergent thinking pretest
A) Arithmetic pretest
B) Scholastic aptitude test used for matching purposes
C) Film showing prejudice toward minorities
D) Divergent thinking pretest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The difference between the group means in a pretest-posttest control group experimental design can be tested for statistical significance most precisely by
A) analysis of variance of the groups' means on the posttest.
B) separate t-tests of the prepost difference for the experimental and for the control group.
C) analysis of covariance on the groups' posttest means with pretest as the covariate.
D) analysis of variance of the mean changes from pre- to posttest for the two groups.
A) analysis of variance of the groups' means on the posttest.
B) separate t-tests of the prepost difference for the experimental and for the control group.
C) analysis of covariance on the groups' posttest means with pretest as the covariate.
D) analysis of variance of the mean changes from pre- to posttest for the two groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A randomized matched subjects, control group design is beneficial whena.
A) small samples are to be used in the study.
B) classrooms are randomly assigned to different treatments.
C) subjects are exposed to more than one treatment.
D) the regression effect is likely to be a threat.
A) small samples are to be used in the study.
B) classrooms are randomly assigned to different treatments.
C) subjects are exposed to more than one treatment.
D) the regression effect is likely to be a threat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The major means of control in single-subject experimental research is
A) replication.
B) randomization.
C) homogeneous selection.
D) analysis of covariance.
A) replication.
B) randomization.
C) homogeneous selection.
D) analysis of covariance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following designs would probably be highest in internal validity?
A) Y1 X Y2
B) X Y2
--- Y2
C) (R) X Y2
(R) --- Y2
D) Y1 X Y2
Y1 --- Y2
A) Y1 X Y2
B) X Y2
--- Y2
C) (R) X Y2
(R) --- Y2
D) Y1 X Y2
Y1 --- Y2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A researcher wants to investigate the effectiveness of three versions of a computer-assisted instructional (CAI) program in math on the achievement of elementary school students in math.The researcher wants to know if the effectiveness of the program would depend on the math aptitude (classified as above and below average) and the gender of the students.What experimental design would you recommend for this study?
A) 1 * 2 * 3 factorial design
B) 3 * 2 * 2 factorial design
C) Solomon three-group design
D) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest, control group design
E) None of these is true.
A) 1 * 2 * 3 factorial design
B) 3 * 2 * 2 factorial design
C) Solomon three-group design
D) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest, control group design
E) None of these is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
This experimental design 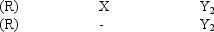
Is recommended for studies in which
A) pretest reactivity is likely to occur.
B) no control group is available.
C) a large sample is available.
D) only a small sample is available.
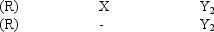
Is recommended for studies in which
A) pretest reactivity is likely to occur.
B) no control group is available.
C) a large sample is available.
D) only a small sample is available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A 2 * 2 * 2 factorial design indicates that the experiment includes
A) two dependent variables.
B) three dependent variables.
C) two independent variables.
D) three independent variables.
E) eight independent variables.
A) two dependent variables.
B) three dependent variables.
C) two independent variables.
D) three independent variables.
E) eight independent variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following experimental designs would have the strongest external validity?
A) One-group pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest-only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest, control-group design
D) Nonrandomized pretest-posttest, control-group design
A) One-group pretest-posttest design
B) Randomized subjects, posttest-only, control-group design
C) Randomized subjects, pretest-posttest, control-group design
D) Nonrandomized pretest-posttest, control-group design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A researcher might choose to use a counterbalanced design when
A) the interactive effect of different treatments is to be examined.
B) there is likely to be a carry-over effect of exposure to one treatment on a subsequent treatment.
C) there is a likelihood of pretest sensitization.
D) intact class groups are to be used.
A) the interactive effect of different treatments is to be examined.
B) there is likely to be a carry-over effect of exposure to one treatment on a subsequent treatment.
C) there is a likelihood of pretest sensitization.
D) intact class groups are to be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A baseline, treatment, baseline single-subject design would be represented as:
A)BAB
B)ABA
C)SAB
D)SBA
A)BAB
B)ABA
C)SAB
D)SBA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Exhibit 11-5: Indicate whether the following statements refer to internal validity or external validity.
Refer to Exhibit 11-5.Does this experiment represent reality?
A) internal validity
B) external validity.
Refer to Exhibit 11-5.Does this experiment represent reality?
A) internal validity
B) external validity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Experimental designs differ mainly in
A) number of independent variables.
B) method of assigning subjects to treatments.
C) number of pre-measurements of the dependent variable.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c
A) number of independent variables.
B) method of assigning subjects to treatments.
C) number of pre-measurements of the dependent variable.
D) a and b
E) a, b, and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Single-subject research would be described as
A) true experimental.
B) quasi-experimental.
C) ex post facto.
D) factorial.
A) true experimental.
B) quasi-experimental.
C) ex post facto.
D) factorial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The following experimental design would be recommended when 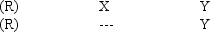
A) no control group is available.
B) matching is not feasible.
C) pre-existing groups must be used in a school setting.
D) a pretest may have an effect on the experimental treatment.
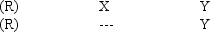
A) no control group is available.
B) matching is not feasible.
C) pre-existing groups must be used in a school setting.
D) a pretest may have an effect on the experimental treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The major means of control in single-subject experimental designs is
A) randomization.
B) replication.
C) statistical control.
D) None of these are true.
A) randomization.
B) replication.
C) statistical control.
D) None of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The relationship between internal and external validity in research can best be described as
A) If an experiment lacks external validity, it cannot have internal validity.
B) If an experiment lacks internal validity, it cannot have external validity.
C) Internal and external validity are not related at all.
A) If an experiment lacks external validity, it cannot have internal validity.
B) If an experiment lacks internal validity, it cannot have external validity.
C) Internal and external validity are not related at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a researcher compared left-handed versus right-handed girls on a reading test after giving half of them special training, then the attribute variable and one likely extraneous variable, would be respectively
A)special training; reading scores.
B)handedness; age of student.
C)reading scores; ability level.
D)special training; gender.
E)handedness; special training.
A)special training; reading scores.
B)handedness; age of student.
C)reading scores; ability level.
D)special training; gender.
E)handedness; special training.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A researcher used a pretest-posttest, control group quasi-experimental design.The experimental group had a mean achievement test score of 40 on the pretest and 70 on the posttest.The control group had a mean achievement score of 50 on the pretest and 60 on the posttest.What statistical technique should the researcher use to analyze these data?
A) t-test
B) ANOVA (analysis of variance)
C) ANCOVA (analysis of covariance)
D) chi-square
A) t-test
B) ANOVA (analysis of variance)
C) ANCOVA (analysis of covariance)
D) chi-square

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exhibit 11-5: Indicate whether the following statements refer to internal validity or external validity.
Refer to Exhibit 11-5.Are the findings of this study a result of the experimental treatment?
A) internal validity
B) external validity.
Refer to Exhibit 11-5.Are the findings of this study a result of the experimental treatment?
A) internal validity
B) external validity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following types of experimental designs would be strongest for establishing cause and effect?
A)Time series
B)Static-group comparison
C)Matched comparison group
D)Randomized posttest control group
E)One group pretest-posttest
A)Time series
B)Static-group comparison
C)Matched comparison group
D)Randomized posttest control group
E)One group pretest-posttest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A researcher has developed a series of in-service training programs for teachers that he believes will improve their effectiveness in the classroom.The researcher observes and compares teacher classroom behavior before and after the teachers attend the in-service training.If this design has a flaw, suggest a way(s) that you would improve it.
A) Use trained observers other than the researcher to make the before and after classroom observations.
B) Use videotapes of before and after teacher behavior and have trained observers in a blind technique evaluate the pre- and post-training tapes.
C) a or b
D) There is no serious flaw in the study.The researcher who developed the program and has an interest in its effectiveness should be the one making the observations.
A) Use trained observers other than the researcher to make the before and after classroom observations.
B) Use videotapes of before and after teacher behavior and have trained observers in a blind technique evaluate the pre- and post-training tapes.
C) a or b
D) There is no serious flaw in the study.The researcher who developed the program and has an interest in its effectiveness should be the one making the observations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Multiple baseline designs may use more than one
A) subject.
B) target behavior.
C) setting.
D) AB unit.
E) All of the these are true.
A) subject.
B) target behavior.
C) setting.
D) AB unit.
E) All of the these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Exhibit 11-5: Indicate whether the following statements refer to internal validity or external validity.
Refer to Exhibit 11-5.Can the results of the study be applied to elementary school students in rural settings?
A) internal validity
B) external validity.
Refer to Exhibit 11-5.Can the results of the study be applied to elementary school students in rural settings?
A) internal validity
B) external validity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A basic characteristic of single-subject experimental research is
A) measures of the independent variable are not repeated.
B) measures of the dependent variable are not repeated.
C) measures of the dependent variable are repeated
D) None of these are true.
A) measures of the independent variable are not repeated.
B) measures of the dependent variable are not repeated.
C) measures of the dependent variable are repeated
D) None of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Exhibit 11-4.Identify the major threat to internal validity in the following research studies.
Refer to Exhibit 11-4.Students who had low scores on a reading pretest were chosen for a special instructional program.This group showed significant gains on a reading achievement test administered after a period of four months.
A) Regression
B) Diffusion
C) Mortality
D) Selection
E) History
Refer to Exhibit 11-4.Students who had low scores on a reading pretest were chosen for a special instructional program.This group showed significant gains on a reading achievement test administered after a period of four months.
A) Regression
B) Diffusion
C) Mortality
D) Selection
E) History

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the fall semester, a professor compared a lecture approach to teaching statistics (using a sophomore class) with a problem-oriented approach (using a senior class).Both sections were given the same final exam.The professor repeated the same experiment in the spring semester.This study shows a confounding of
A)test scores with teaching approaches.
B)class levels with test scores.
C)teaching approaches with class level.
D)semester with teaching approaches.
A)test scores with teaching approaches.
B)class levels with test scores.
C)teaching approaches with class level.
D)semester with teaching approaches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A basic assumption of the multiple baseline design is that the
A) treatment affects different behaviors specifically.
B) treatment affects more than one behavior in the same way.
C) behaviors involved are independent of one another.
D) behaviors are correlated with one another.
E) a and c
A) treatment affects different behaviors specifically.
B) treatment affects more than one behavior in the same way.
C) behaviors involved are independent of one another.
D) behaviors are correlated with one another.
E) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Exhibit 11-4.Identify the major threat to internal validity in the following research studies.
Refer to Exhibit 11-4.A researcher conducted a semester-long experiment comparing two instructional programs in math.During the administration of tests during the semester, the researcher found that about ten percent of the experimental group and about five percent of the control group were absent for each administration.
A) Regression
B) Diffusion
C) Mortality
D) Selection
E) History
Refer to Exhibit 11-4.A researcher conducted a semester-long experiment comparing two instructional programs in math.During the administration of tests during the semester, the researcher found that about ten percent of the experimental group and about five percent of the control group were absent for each administration.
A) Regression
B) Diffusion
C) Mortality
D) Selection
E) History

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An elementary teacher had a student, Andy, who showed signs of hyperactivity in the classroom.The teacher wanted to "experiment" to find ways to reduce the hyperactivity and bring about behavior more conducive to learning.She began to record the number of incidences of hyperactive behavior.After a period of time, she started to praise Andy and gave him tokens when he stayed in his seat and showed other less hyperactive behavior.The praise and tokens continued during which time the teacher observed and recorded Andy's behavior.The teacher then stopped the praise and the tokens and took measures of Andy's behavior.What data would the teacher look for to determine the effectiveness of her "treatment"?
A) a decrease in hyperactivity during the treatment phase.
B) an increase in hyperactivity during the treatment phase.
C) an increase in hyperactivity during the "return to baseline" period.
D) an increase in hyperactivity when the B phase is reinstated.
E) a and c
A) a decrease in hyperactivity during the treatment phase.
B) an increase in hyperactivity during the treatment phase.
C) an increase in hyperactivity during the "return to baseline" period.
D) an increase in hyperactivity when the B phase is reinstated.
E) a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



