Deck 8: Firms in the Global Economy: Export Decisions, Outsourcing, and Multinational Enterprises
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Firms in the Global Economy: Export Decisions, Outsourcing, and Multinational Enterprises
1
Imperfectly competitive firms have a demand curve that ________ and a marginal revenue curve that ________ and is ________ the demand curve.
A)slopes downward;slopes downward;below
B)is horizontal;is horizontal;the same as
C)slopes downward;is horizontal;above
D)is horizontal;slopes downward;below
E)slopes downward;slopes downward;the same as
A)slopes downward;slopes downward;below
B)is horizontal;is horizontal;the same as
C)slopes downward;is horizontal;above
D)is horizontal;slopes downward;below
E)slopes downward;slopes downward;the same as
A
2
An imperfectly competitive firm has the following demand curve: Q = 100 - 2P.What is marginal revenue equal to when P = 30?
Q = 40,so MR = 30 - (40/2)= 10.
3
An imperfectly competitive firm has the following demand curve: Q = 100 - 2P.What is marginal revenue equal to when P = 40?
Q = 20,so MR = 40 - (20/2)= 30.
4
Under the model of monopolistic competition,a(an)________ in the number of firms in the industry will cause ________ to ________.
A)increase;average price;decrease
B)increase;average price;increase
C)increase;average cost;decrease
D)decrease;markup;decrease
E)increase;marginal cost;decrease
A)increase;average price;decrease
B)increase;average price;increase
C)increase;average cost;decrease
D)decrease;markup;decrease
E)increase;marginal cost;decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If there are a large number of firms in a monopolistically competitive industry
A)long-run profit will be equal to zero.
B)the country in which the firms are located can be expected to export the goods they produce.
C)there will be barriers to entry that prevent addition firms from entering the industry.
D)the firms will converge production on a standardized product.
E)there will be a small number of firms that are very large and the rest will be very small.
A)long-run profit will be equal to zero.
B)the country in which the firms are located can be expected to export the goods they produce.
C)there will be barriers to entry that prevent addition firms from entering the industry.
D)the firms will converge production on a standardized product.
E)there will be a small number of firms that are very large and the rest will be very small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An imperfectly competitive firm has the following total cost curve: C = 100 + 4Q.What is marginal cost equal to when Q = 10?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Modeling trade in imperfectly competitive industries is problematic because
A)there is no single generally accepted model of behavior by imperfectly competitive firms.
B)there are no models of imperfectly competitive behavior.
C)it is difficult to find an imperfectly competitive firm in the real world.
D)collusion among imperfectly competitive firms makes usable data rare.
E)there is only a single model of imperfect competition (monopoly)but imperfect competition can take many forms in the real world.
A)there is no single generally accepted model of behavior by imperfectly competitive firms.
B)there are no models of imperfectly competitive behavior.
C)it is difficult to find an imperfectly competitive firm in the real world.
D)collusion among imperfectly competitive firms makes usable data rare.
E)there is only a single model of imperfect competition (monopoly)but imperfect competition can take many forms in the real world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If a firm increases its output in the ________ and unit costs ________,then the firm is experiencing ________ of scale.
A)long-run;increase;diseconomies
B)short-run;decrease;economies
C)long-run;decrease;diseconomies
D)short-run;decrease;diseconomies
E)long-run;increase;economies
A)long-run;increase;diseconomies
B)short-run;decrease;economies
C)long-run;decrease;diseconomies
D)short-run;decrease;diseconomies
E)long-run;increase;economies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A monopolistic firm
A)will never sell a product whose demand is inelastic at the quantity sold.
B)can sell as much as it wants for any price it determines in the market.
C)cannot determine the price,which is determined by consumer demand.
D)cannot sell additional quantity unless it raises the price on each unit.
E)will always earn a profit in the long run.
A)will never sell a product whose demand is inelastic at the quantity sold.
B)can sell as much as it wants for any price it determines in the market.
C)cannot determine the price,which is determined by consumer demand.
D)cannot sell additional quantity unless it raises the price on each unit.
E)will always earn a profit in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
It is possible that trade based on external scale economies may leave a country worse off than it would have been without trade.Explain how this could happen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An imperfectly competitive firm has the following total cost curve: C = 100 + 4Q.What is average fixed cost equal to when Q = 10?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Monopolistic competition is associated with
A)product differentiation.
B)price-taking behavior.
C)explicit consideration at the firm level of the strategic impact of other firms' pricing decisions.
D)high profit margins in the long run.
E)increasing returns to scale.
A)product differentiation.
B)price-taking behavior.
C)explicit consideration at the firm level of the strategic impact of other firms' pricing decisions.
D)high profit margins in the long run.
E)increasing returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An imperfectly competitive firm has the following total cost curve: C = 100 + 4Q.What is total cost equal to when Q = 10?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An imperfectly competitive firm has the following total cost curve: C = 100 + 4Q.What is average total cost equal to when Q = 10?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When a country both exports and imports a type of commodity,the country is engaged in
A)intra-industry trade.
B)increasing returns to scale.
C)imperfect competition.
D)inter-industry trade.
E)an attempt to monopolize the relevant industry.
A)intra-industry trade.
B)increasing returns to scale.
C)imperfect competition.
D)inter-industry trade.
E)an attempt to monopolize the relevant industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If a firm that uses a production process that yields economies of scale charges a price equal to ________,then profit will be ________.
A)marginal cost;negative
B)marginal revenue;maximized
C)marginal cost;maximized
D)marginal revenue;positive
E)marginal cost;positive
A)marginal cost;negative
B)marginal revenue;maximized
C)marginal cost;maximized
D)marginal revenue;positive
E)marginal cost;positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Under oligopoly,firms' pricing policies are ________ and,under monopolistic competition,they are ________.
A)interdependent;independent
B)independent;interdependent
C)cooperative;uncooperative
D)uncooperative;cooperative
E)profit maximizing;revenue maximizing
A)interdependent;independent
B)independent;interdependent
C)cooperative;uncooperative
D)uncooperative;cooperative
E)profit maximizing;revenue maximizing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Firms that produce ________ products must be ________ competitive.
A)differentiated;imperfectly
B)differentiated;perfectly
C)standardized;imperfectly
D)standardized;perfectly
E)exported;imperfectly
A)differentiated;imperfectly
B)differentiated;perfectly
C)standardized;imperfectly
D)standardized;perfectly
E)exported;imperfectly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If a firm increases its output in the ________ and unit costs ________,then the firm is experiencing ________ of scale.
A)long-run;decrease;economies
B)short-run;decrease;economies
C)long-run;decrease;diseconomies
D)short-run;decrease;diseconomies
E)long-run;increase;economies
A)long-run;decrease;economies
B)short-run;decrease;economies
C)long-run;decrease;diseconomies
D)short-run;decrease;diseconomies
E)long-run;increase;economies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The simultaneous export and import of widgets by the United States is an example of
A)intra-industry trade.
B)increasing returns to scale.
C)imperfect competition.
D)inter-industry trade.
E)the effect of a monopoly on international trade.
A)intra-industry trade.
B)increasing returns to scale.
C)imperfect competition.
D)inter-industry trade.
E)the effect of a monopoly on international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An industry is characterized by scale economies and exists in two countries.In order for consumers of its products to enjoy both lower prices and more variety of choice
A)the two countries must engage in international trade with each other.
B)each country's marginal cost must equal that of the other country.
C)the marginal cost of this industry must equal marginal revenue in the other.
D)the monopoly must lower prices in order to sell more.
E)they must combine to become a multinational corporation.
A)the two countries must engage in international trade with each other.
B)each country's marginal cost must equal that of the other country.
C)the marginal cost of this industry must equal marginal revenue in the other.
D)the monopoly must lower prices in order to sell more.
E)they must combine to become a multinational corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
International trade based solely on internal scale economies in both countries is likely to be carried out by
A)monopolists in each country.
B)a relatively large number of price competing firms.
C)a relatively small number of price competing firms.
D)a relatively small number of imperfect competitors.
E)a large number of oligopolists in each country.
A)monopolists in each country.
B)a relatively large number of price competing firms.
C)a relatively small number of price competing firms.
D)a relatively small number of imperfect competitors.
E)a large number of oligopolists in each country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Refer to above figure.While selling exports it would also maximize its domestic sales by equating its marginal (opportunity)cost to its marginal revenue of $5.How much steel would the firm sell domestically,and at what price?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
International trade based on external scale economies in both countries is likely to be carried out by
A)a relatively large number of price competing firms.
B)a relatively small number of price competing firms.
C)a relatively small number of imperfect competitors.
D)monopolists in each country.
E)a large number of oligopolists in each country.
A)a relatively large number of price competing firms.
B)a relatively small number of price competing firms.
C)a relatively small number of imperfect competitors.
D)monopolists in each country.
E)a large number of oligopolists in each country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A product is produced in a monopolistically competitive industry with scale economies.If this industry exists in two countries,and these two countries engage in trade with each other,then we would expect
A)each country will export different varieties of the product to the other.
B)the country in which the price of the product is lower will export the product.
C)the country with a relative abundance of the factor of production in which production of the product is intensive will export this product.
D)neither country will export this product since there is no comparative advantage.
E)the countries will trade only with other nations they are not in competition with.
A)each country will export different varieties of the product to the other.
B)the country in which the price of the product is lower will export the product.
C)the country with a relative abundance of the factor of production in which production of the product is intensive will export this product.
D)neither country will export this product since there is no comparative advantage.
E)the countries will trade only with other nations they are not in competition with.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Intra-industry trade will tend to dominate trade flows when which of the following exists?
A)small differences between relative country factor availabilities
B)large differences between relative country factor availabilities
C)homogeneous products that cannot be differentiated
D)constant cost industries
E)uneven distribution of abundant resources between two countries
A)small differences between relative country factor availabilities
B)large differences between relative country factor availabilities
C)homogeneous products that cannot be differentiated
D)constant cost industries
E)uneven distribution of abundant resources between two countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Two countries engaged in trade in products with scale economies,produced under conditions of monopolistic competition,are likely to be engaged in
A)intra-industry trade.
B)price competition.
C)inter-industry trade.
D)Heckscher-Ohlinean trade.
E)immiserizing trade.
A)intra-industry trade.
B)price competition.
C)inter-industry trade.
D)Heckscher-Ohlinean trade.
E)immiserizing trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An industry is characterized by scale economies,and exists in two countries.Should these two countries engage in trade such that the combined market is supplied by one country's industry,then
A)consumers in both countries would have more varieties and lower prices.
B)consumers in both countries would have higher prices and fewer varieties.
C)consumers in the importing country only would have higher prices and fewer varieties.
D)consumers in the exporting country only would have higher prices and fewer varieties.
E)consumers in both countries would have fewer varieties at lower prices.
A)consumers in both countries would have more varieties and lower prices.
B)consumers in both countries would have higher prices and fewer varieties.
C)consumers in the importing country only would have higher prices and fewer varieties.
D)consumers in the exporting country only would have higher prices and fewer varieties.
E)consumers in both countries would have fewer varieties at lower prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
We often observe "pseudo-intra-industry trade" between the United States and Mexico.Actually,such trade is consistent with
A)comparative advantage associated with Heckscher-Ohlin model.
B)oligopolistic markets.
C)optimal tariff issues.
D)the Ricardian model of trade.
E)the specific factors model of trade.
A)comparative advantage associated with Heckscher-Ohlin model.
B)oligopolistic markets.
C)optimal tariff issues.
D)the Ricardian model of trade.
E)the specific factors model of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Imagine scale economies were not only external to firms,but were also external to individual countries.That is,the larger the worldwide industry (regardless of where firms or plants are located),the cheaper would be the per-unit cost of production.Describe what world trade would look like in this case.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A monopoly firm will maximize profits by producing where
A)marginal revenue is the same in domestic and foreign markets.
B)prices are the same in domestic and foreign markets.
C)marginal revenue is higher in foreign markets.
D)marginal revenue is higher in the domestic market.
E)total revenue from domestic and foreign sales is maximized.
A)marginal revenue is the same in domestic and foreign markets.
B)prices are the same in domestic and foreign markets.
C)marginal revenue is higher in foreign markets.
D)marginal revenue is higher in the domestic market.
E)total revenue from domestic and foreign sales is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A monopoly firm engaged in international trade will
A)equate marginal costs with marginal revenues in both domestic and foreign markets.
B)equate average to local costs.
C)equate marginal costs with foreign marginal revenues.
D)equate marginal costs with the highest price the market will bear.
E)equate marginal costs with the relative world prices.
A)equate marginal costs with marginal revenues in both domestic and foreign markets.
B)equate average to local costs.
C)equate marginal costs with foreign marginal revenues.
D)equate marginal costs with the highest price the market will bear.
E)equate marginal costs with the relative world prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Under the model of monopolistic competition,a(an)________ in the number of firms in the industry will cause ________ to ________.
A)increase;markup;decrease
B)increase;average price;increase
C)increase;average cost;decrease
D)decrease;markup;decrease
E)increase;marginal cost;decrease
A)increase;markup;decrease
B)increase;average price;increase
C)increase;average cost;decrease
D)decrease;markup;decrease
E)increase;marginal cost;decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
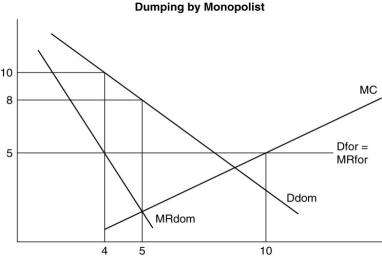
Refer to above figure.The monopolist can export as much as it likes of its steel at the world price of $5/ton.How much steel will the monopolist sell,and at what price?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the market for products produced by firms in a monopolistically competitive industry becomes ________,then there will be ________ firms and each firm will produce ________ output and charge a ________ price.
A)larger;more;more;lower
B)larger;fewer;more;lower
C)larger;fewer;more;higher
D)larger;more;more;higher
E)larger;more;less;higher
A)larger;more;more;lower
B)larger;fewer;more;lower
C)larger;fewer;more;higher
D)larger;more;more;higher
E)larger;more;less;higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A firm in long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition will earn
A)zero economic profits because of free entry.
B)positive monopoly profits because each sells a differentiated product.
C)positive oligopoly profits because each firm sells a differentiated product.
D)negative economic profits because it has economies of scale.
E)positive economic profit if it engages in international trade.
A)zero economic profits because of free entry.
B)positive monopoly profits because each sells a differentiated product.
C)positive oligopoly profits because each firm sells a differentiated product.
D)negative economic profits because it has economies of scale.
E)positive economic profit if it engages in international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Two countries engaged in trade in products with no scale economies,produced under conditions of perfect competition,are likely to be engaged in
A)inter-industry trade.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)intra-industry trade.
D)Heckscher-Ohlin trade.
E)oligopolistic competition
A)inter-industry trade.
B)monopolistic competition.
C)intra-industry trade.
D)Heckscher-Ohlin trade.
E)oligopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Intra-industry trade is most common in the trade patterns of
A)the industrial countries of Western Europe.
B)the developing countries of Asia and Africa.
C)raw material producers.
D)China with the rest of the world.
E)labor-intensive products.
A)the industrial countries of Western Europe.
B)the developing countries of Asia and Africa.
C)raw material producers.
D)China with the rest of the world.
E)labor-intensive products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Trade without serious income distribution effects is most likely to happen
A)in sophisticated manufactures trade between rich countries.
B)in simple manufactures trade between developing countries.
C)in sophisticated manufactures trade between rich and poor countries.
D)in agricultural trade between rich countries.
E)in labor-intensive industries like clothing.
A)in sophisticated manufactures trade between rich countries.
B)in simple manufactures trade between developing countries.
C)in sophisticated manufactures trade between rich and poor countries.
D)in agricultural trade between rich countries.
E)in labor-intensive industries like clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Refer to above figure.Given the opportunity to sell at world prices,the marginal (opportunity)cost of selling a ton domestically is what?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
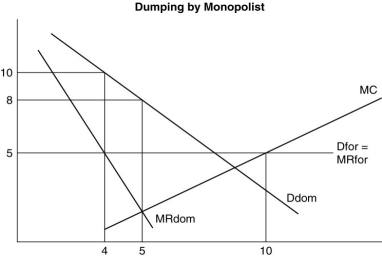
The figure above represents the demand and cost functions facing a Brazilian Steel producing monopolist.If it were unable to export,and was constrained by its domestic market,what quantity would it sell at what price?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the model of monopolistic competition,an increase in industry output will ________ producers of ________ higher-priced goods and ________ producers of lower-priced goods.
A)harm;benefit
B)benefit;harm
C)harm;harm
D)benefit;benefit
E)benefit;have no effect on
A)harm;benefit
B)benefit;harm
C)harm;harm
D)benefit;benefit
E)benefit;have no effect on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Complaints are often made to the International Trade Commission concerning foreign "dumping" practices.These complaints typically claim that
A)U.S.firms are harmed by the unfair pricing of foreign exporters.
B)foreign companies are charging exorbitant prices that are higher than the true value of the products.
C)foreign companies are charging prices that are lower than prices they charge countries other than the U.S.
D)U.S.consumers are harmed by the lack of quality control or health concerns in foreign countries.
E)U.S.consumers cannot differentiate between the foreign and domestic goods.
A)U.S.firms are harmed by the unfair pricing of foreign exporters.
B)foreign companies are charging exorbitant prices that are higher than the true value of the products.
C)foreign companies are charging prices that are lower than prices they charge countries other than the U.S.
D)U.S.consumers are harmed by the lack of quality control or health concerns in foreign countries.
E)U.S.consumers cannot differentiate between the foreign and domestic goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the market for products produced by firms in a monopolistically competitive industry becomes ________,then there will be ________ firms and each firm will produce ________ output and charge a ________ price.
A)smaller;fewer;less;higher
B)smaller;more;less;higher
C)smaller;more;less;lower
D)smaller;fewer;less;lower
E)smaller;fewer;more;higher
A)smaller;fewer;less;higher
B)smaller;more;less;higher
C)smaller;more;less;lower
D)smaller;fewer;less;lower
E)smaller;fewer;more;higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A corporation is considered a multinational ________ if ________.
A)affiliate;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
B)parent;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
C)child;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
D)child;more than 50% of its stock is held by a foreign company
E)monopolist;it owns more than 50% of a foreign firm
A)affiliate;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
B)parent;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
C)child;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
D)child;more than 50% of its stock is held by a foreign company
E)monopolist;it owns more than 50% of a foreign firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The most common form of price discrimination in international trade is
A)dumping.
B)non-tariff barriers.
C)Voluntary Export Restraints.
D)preferential trade arrangements.
E)product boycotts.
A)dumping.
B)non-tariff barriers.
C)Voluntary Export Restraints.
D)preferential trade arrangements.
E)product boycotts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A corporation is considered a multinational ________ if ________.
A)parent;it owns more than 10% of a foreign firm
B)parent;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
C)child;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
D)child;more than 50% of its stock is held by a foreign company
E)monopolist;it owns more than 50% of a foreign firm
A)parent;it owns more than 10% of a foreign firm
B)parent;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
C)child;more than 10% of its stock is held by a foreign company
D)child;more than 50% of its stock is held by a foreign company
E)monopolist;it owns more than 50% of a foreign firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If an industry is imperfectly competitive,and markets are segmented then
A)a firm may find that it is profitable to engage in dumping.
B)a firm may find that international trade is unprofitable.
C)a firm may find that it should promote scale economies.
D)a firm may find that it has lost its comparative advantage.
E)a firm may find that it should become more specialized.
A)a firm may find that it is profitable to engage in dumping.
B)a firm may find that international trade is unprofitable.
C)a firm may find that it should promote scale economies.
D)a firm may find that it has lost its comparative advantage.
E)a firm may find that it should become more specialized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the following two cases.In the first,a U.S.firm purchases 18% of a foreign firm.In the second,a U.S.firm builds a new production facility in a foreign country.Both are ________,with the first referred to as ________ and the second as ________.
A)foreign direct investment (FDI)outflows;greenfield;brownfield
B)foreign direct investment (FDI)inflows;greenfield;brownfield
C)foreign direct investment (FDI)outflows;brownfield;greenfield
D)foreign direct investment (FDI)inflows;brownfield;greenfield
E)foreign direct investment (FDI);inflows;outflows
A)foreign direct investment (FDI)outflows;greenfield;brownfield
B)foreign direct investment (FDI)inflows;greenfield;brownfield
C)foreign direct investment (FDI)outflows;brownfield;greenfield
D)foreign direct investment (FDI)inflows;brownfield;greenfield
E)foreign direct investment (FDI);inflows;outflows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the model of monopolistic competition,compared to a firm with a higher marginal cost,a firm with a lower marginal cost will set a ________ price,produce ________ output,and earn ________ profits.
A)lower;more;more
B)higher;more;more
C)lower;less;less
D)higher;less;less
E)higher;less;more
A)lower;more;more
B)higher;more;more
C)lower;less;less
D)higher;less;less
E)higher;less;more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the model of monopolistic competition,an increase in industry output will cause individual firms' demand curves to become ________,which will ________ demand for higher-priced goods and ________ demand for lower-priced goods.
A)flatter;reduce;increase
B)steeper;reduce;increase
C)flatter;increase;reduce
D)steeper;increase;reduce
E)horizontal;reduce;reduce
A)flatter;reduce;increase
B)steeper;reduce;increase
C)flatter;increase;reduce
D)steeper;increase;reduce
E)horizontal;reduce;reduce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the model of monopolistic competition,if firms have ________ average cost curves,then opening trade will ________ the total number of firms and ________ the average price.
A)downward sloping;decrease;decrease
B)downward sloping;decrease;increase
C)downward sloping;increase;decrease
D)upward sloping;decrease;increase
E)upward sloping;increase;decrease
A)downward sloping;decrease;decrease
B)downward sloping;decrease;increase
C)downward sloping;increase;decrease
D)upward sloping;decrease;increase
E)upward sloping;increase;decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In an industry where firms experience internal scale economies,the long-run cost of production will depend on
A)the size of the market.
B)the size of the labor force.
C)whether the country engages in intra-industry trade.
D)individual firms' fixed costs.
E)whether the country engages in inter-industry trade.
A)the size of the market.
B)the size of the labor force.
C)whether the country engages in intra-industry trade.
D)individual firms' fixed costs.
E)whether the country engages in inter-industry trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54

The figure above represents the demand and cost functions facing a Brazilian Steel producing monopolist.The Brazilian firm is charging its foreign (U.S. )customers one half the price it is charging its domestic customers.Is this good or bad for the real income or economic welfare of the United States? Is the Brazilian firm engaged in dumping? Is this predatory behavior on the part of the Brazilian steel company?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the model of monopolistic competition,if firms have ________ average cost curves,then opening trade will cause ________ firms to ________ the industry.
A)different;less efficient;exit
B)different;more efficient;enter
C)symmetric;less efficient;exit
D)symmetric;more efficient;enter
E)symmetric;less efficient;enter
A)different;less efficient;exit
B)different;more efficient;enter
C)symmetric;less efficient;exit
D)symmetric;more efficient;enter
E)symmetric;less efficient;enter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the model of monopolistic competition,compared to a firm with a lower marginal cost,a firm with a higher marginal cost will set a ________ price,produce ________ output,and earn ________ profits.
A)higher;less;less
B)lower;more;more
C)higher;more;more
D)lower;less;less
E)higher;less;more
A)higher;less;less
B)lower;more;more
C)higher;more;more
D)lower;less;less
E)higher;less;more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the model of monopolistic competition,trade costs between countries cause
A)some firms that can earn a profit on domestic sales to refrain from exporting their goods.
B)prices of goods sold domestically to exceed the prices of exported goods.
C)marginal costs of goods sold domestically to exceed the marginal costs of exported goods.
D)all firms that can earn a profit on domestic sales to export their goods at higher prices.
E)countries to negotiate the elimination of trade costs by mutual subsidization of trade.
A)some firms that can earn a profit on domestic sales to refrain from exporting their goods.
B)prices of goods sold domestically to exceed the prices of exported goods.
C)marginal costs of goods sold domestically to exceed the marginal costs of exported goods.
D)all firms that can earn a profit on domestic sales to export their goods at higher prices.
E)countries to negotiate the elimination of trade costs by mutual subsidization of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the model of monopolistic competition,trade costs between countries will cause domestic and foreign markets to have ________ prices,________ quantities sold,and ________ profit levels.
A)different;different;different
B)identical;different;different
C)different;different;identical
D)identical;different;identical
E)identical;identical;different
A)different;different;different
B)identical;different;different
C)different;different;identical
D)identical;different;identical
E)identical;identical;different

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the model of monopolistic competition,an increase in industry output will ________ market shares and ________ profits of producers of higher-priced goods and will ________ market shares and ________ profits of producers of lower-priced goods.
A)reduce;reduce;increase;increase
B)increase;increase;reduce;reduce
C)increase;reduce;increase;reduce
D)reduce;increase;reduce;increase
E)reduce;increase;increase;reduce
A)reduce;reduce;increase;increase
B)increase;increase;reduce;reduce
C)increase;reduce;increase;reduce
D)reduce;increase;reduce;increase
E)reduce;increase;increase;reduce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the model of monopolistic competition,trade costs between countries cause
A)marginal costs of exported goods to exceed the marginal costs of goods sold domestically.
B)marginal costs of goods sold domestically to exceed the marginal costs of exported goods.
C)all firms that can earn a profit on domestic sales to export their goods at lower prices.
D)all firms that can earn a profit on domestic sales to export their goods at higher prices.
E)countries to negotiate the elimination of trade costs by mutual subsidization of trade.
A)marginal costs of exported goods to exceed the marginal costs of goods sold domestically.
B)marginal costs of goods sold domestically to exceed the marginal costs of exported goods.
C)all firms that can earn a profit on domestic sales to export their goods at lower prices.
D)all firms that can earn a profit on domestic sales to export their goods at higher prices.
E)countries to negotiate the elimination of trade costs by mutual subsidization of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the nature of the proximity-concentration tradeoff that firms have to deal with then making decisions regarding foreign direct investment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What are the consequences of outsourcing production on the welfare of countries?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A firm is more likely to engage in horizontal foreign direct investment if
A)trade costs are high and there are internal economies of scale.
B)trade costs are low and there are internal economies of scale.
C)trade costs are high and there are external economies of scale.
D)trade costs are low and there are external economies of scale.
E)trade costs are low and firms experience constant returns to scale in production.
A)trade costs are high and there are internal economies of scale.
B)trade costs are low and there are internal economies of scale.
C)trade costs are high and there are external economies of scale.
D)trade costs are low and there are external economies of scale.
E)trade costs are low and firms experience constant returns to scale in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When a multinational affiliate replicates elements of a production process in a foreign country it is called ________ foreign direct investment.
A)vertical
B)horizontal
C)transitional
D)bisectional
E)direct
A)vertical
B)horizontal
C)transitional
D)bisectional
E)direct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Product differentiation and internal economies of scale yield gains from trade in the form of
A)lower production costs and a greater variety of goods.
B)higher profits and lower trade costs.
C)the proximity-concentration effect.
D)a proliferation of competitive firms.
E)the substitution of immigration for foreign direct investment.
A)lower production costs and a greater variety of goods.
B)higher profits and lower trade costs.
C)the proximity-concentration effect.
D)a proliferation of competitive firms.
E)the substitution of immigration for foreign direct investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
During the past decade,U.S.imports of business services have ________,U.S.exports of business services have ________,and U.S.net exports of business services have ________.
A)increased;increased;increased
B)increased;decreased;decreased
C)decreased;increased;increased
D)increased;increased;not changed
E)decreased;decreased;increased
A)increased;increased;increased
B)increased;decreased;decreased
C)decreased;increased;increased
D)increased;increased;not changed
E)decreased;decreased;increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A firm's foreign direct investment.decisions are,in the case of horizontal FDI,strongly influenced by ________ and,in the case of vertical FDI,strongly influenced by ________.
A)trade costs;production costs
B)materials costs;labor costs
C)production costs;materials costs
D)production costs;trade costs
E)labor costs;trade costs
A)trade costs;production costs
B)materials costs;labor costs
C)production costs;materials costs
D)production costs;trade costs
E)labor costs;trade costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Foreign outsourcing is
A)the transfer of operations to foreign contractors.
B)an example of internalization.
C)an example of foreign direct investment.
D)currently illegal in the U.S.
E)the substitution of immigration for foreign direct investment.
A)the transfer of operations to foreign contractors.
B)an example of internalization.
C)an example of foreign direct investment.
D)currently illegal in the U.S.
E)the substitution of immigration for foreign direct investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When a multinational affiliate replicates production in a foreign country it is called ________ foreign direct investment.
A)horizontal
B)vertical
C)transitional
D)bisectional
E)direct
A)horizontal
B)vertical
C)transitional
D)bisectional
E)direct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 69 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



