Deck 20: Financial Globalization: Opportunity and Crisis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/131
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Financial Globalization: Opportunity and Crisis
1
What would best describe the international capital markets?
A)the market of exchange of bonds
B)the market of exchange of stocks
C)the market of exchange of real-estate
D)the market in which residents of different countries trade assets
E)the currency market
A)the market of exchange of bonds
B)the market of exchange of stocks
C)the market of exchange of real-estate
D)the market in which residents of different countries trade assets
E)the currency market
D
2
For the following question assume the following facts: (1)Balance of Payments = 0 prior to the transactions.
(2)Person A (who lives in the United States)purchases an airplane from British Airways for $150,000.
(3)Person A pays with a check from his account at First Union Bank in the United States.
(4)British airways,since it will need dollars in 1 month,deposits the check at the Bank of England.
(5)Bank of England deposits the $150,000 at Commonwealth bank,which is located in the United States.
Due to the transactions above,what are the effects on the balance of payments?
A)-$150,000 due to import of good (current account debit)
B)+$150,000 due to import of good (current account credit)
C)-$150,000 due to deposit of Bank of England (capital account debit)
D)+$150,000 due to deposit of Bank of England (capital account credit)
E)No effect (150,000 current account debit and 150,000 capital account credit)
(2)Person A (who lives in the United States)purchases an airplane from British Airways for $150,000.
(3)Person A pays with a check from his account at First Union Bank in the United States.
(4)British airways,since it will need dollars in 1 month,deposits the check at the Bank of England.
(5)Bank of England deposits the $150,000 at Commonwealth bank,which is located in the United States.
Due to the transactions above,what are the effects on the balance of payments?
A)-$150,000 due to import of good (current account debit)
B)+$150,000 due to import of good (current account credit)
C)-$150,000 due to deposit of Bank of England (capital account debit)
D)+$150,000 due to deposit of Bank of England (capital account credit)
E)No effect (150,000 current account debit and 150,000 capital account credit)
E
3
People who are risk averse
A)value a collection of assets only on the basis of its expected returns.
B)value a collection of assets only on the basis of the risk of that return.
C)value a collection of assets not only on the basis of its expected returns but also on the basis of the risk of that return.
D)are less likely to invest in life insurance.
E)are less likely to have a diverse portfolio.
A)value a collection of assets only on the basis of its expected returns.
B)value a collection of assets only on the basis of the risk of that return.
C)value a collection of assets not only on the basis of its expected returns but also on the basis of the risk of that return.
D)are less likely to invest in life insurance.
E)are less likely to have a diverse portfolio.
C
4
Asset trades that deal with debt instruments are best described as
A)share of stock.
B)exchange rate.
C)receipts.
D)factors.
E)bonds or bank deposits.
A)share of stock.
B)exchange rate.
C)receipts.
D)factors.
E)bonds or bank deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If you are offered a gamble in which you win 500 dollars 3/8 of the time and you lose 500 dollars 5/8 of the time,what is your expected payoff and your behavior given that you are a risk-lover?
A)$500,take the gamble
B)-$125,take the gamble
C)-$125,it is unclear what you would do without further information
D)$500,decline the gamble
E)-$125,decline the gamble
A)$500,take the gamble
B)-$125,take the gamble
C)-$125,it is unclear what you would do without further information
D)$500,decline the gamble
E)-$125,decline the gamble

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Intertemporal trade is
A)the exchange of goods but not services for claims to future goods.
B)the exchange of services but not goods for claims to future services.
C)the exchange of good and services for claims to future goods and services.
D)the exchange of domestic goods and services for foreign goods and services.
E)the type of trade that the U.S.government focuses most upon.
A)the exchange of goods but not services for claims to future goods.
B)the exchange of services but not goods for claims to future services.
C)the exchange of good and services for claims to future goods and services.
D)the exchange of domestic goods and services for foreign goods and services.
E)the type of trade that the U.S.government focuses most upon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Equity Instruments include
A)stocks.
B)bonds.
C)banks deposits.
D)receipts.
E)bank statements.
A)stocks.
B)bonds.
C)banks deposits.
D)receipts.
E)bank statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The two types of trade,intertemporal and pure asset swap ________ perfect substitutes,because ________.
A)are;they both offer considerable payoff and are equal in the long run
B)are;they both involve the smoothing out of now and future consumption
C)are not;asset swapping is immediate and involves only assets,while intertemporal trade takes two time periods and involves both assets and goods/services
D)could possibly be;different economic states occur at different points in time
E)are not;asset swapping never relates to intertemporal trade
A)are;they both offer considerable payoff and are equal in the long run
B)are;they both involve the smoothing out of now and future consumption
C)are not;asset swapping is immediate and involves only assets,while intertemporal trade takes two time periods and involves both assets and goods/services
D)could possibly be;different economic states occur at different points in time
E)are not;asset swapping never relates to intertemporal trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The international capital market is:
A)the international currency exchange.
B)a market in which capital assets are exchanged for services.
C)the market that is subject to intense regulation and must file a report to the Basel committee on a biannual basis.
D)not really a single market,but a group of closely interconnected markets in which asset exchanges with some international dimension take place.
E)an organization of fiscal policies that dictate international trade.
A)the international currency exchange.
B)a market in which capital assets are exchanged for services.
C)the market that is subject to intense regulation and must file a report to the Basel committee on a biannual basis.
D)not really a single market,but a group of closely interconnected markets in which asset exchanges with some international dimension take place.
E)an organization of fiscal policies that dictate international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Asset trades that deal with equity instruments are best described as
A)share of stock.
B)exchange rate.
C)bonds.
D)bank deposits.
E)factors.
A)share of stock.
B)exchange rate.
C)bonds.
D)bank deposits.
E)factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For most practical matters,economists assume that
A)individuals are risk neutral.
B)individuals are risk lovers.
C)individuals are risk averse.
D)most individuals are risk lovers.
E)most individuals are risk neutral.
A)individuals are risk neutral.
B)individuals are risk lovers.
C)individuals are risk averse.
D)most individuals are risk lovers.
E)most individuals are risk neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose one is offered a gamble in which you win $1,000 half the time but lose $1,000 half the time.Since in this case one is as likely to win as to lose the $1,000,the average payoff on this gamble-its expected value-is: 0.5 ∗ $1,000 + 0.5 ∗ (-$1,000)= 0.
Under such circumstances:
A)no one will take the gamble.
B)risk averse individuals will take the gamble.
C)risk lovers individuals will not take the gamble.
D)risk neutral individuals will not take the gamble.
E)risk lovers and risk neutral individuals may take the gamble.
Under such circumstances:
A)no one will take the gamble.
B)risk averse individuals will take the gamble.
C)risk lovers individuals will not take the gamble.
D)risk neutral individuals will not take the gamble.
E)risk lovers and risk neutral individuals may take the gamble.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Imagine that there are two countries,Home and Far Far Away,and that residents of each own only one asset,domestic land yielding an annual harvest of mangoes.Assume that the yield on the land is uncertain.Half the time,Home's land yields a harvest of 5,000 tons of mangoes at the same time as Far Far Away's land yields a harvest of 2,500 tons.The other half of the time the outcomes are reversed.The average for each country mango harvest is
A)2500.
B)2750.
C)3500.
D)3750.
E)3000.
A)2500.
B)2750.
C)3500.
D)3750.
E)3000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What are the three types of transactions between the residents of different countries?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Using international asset trade,countries can
A)never really eliminate all risk.
B)eliminate all risk.
C)actually increase their risk in some cases.
D)eliminate all their risk except for emerging markets.
E)never really diversify their holdings.
A)never really eliminate all risk.
B)eliminate all risk.
C)actually increase their risk in some cases.
D)eliminate all their risk except for emerging markets.
E)never really diversify their holdings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Describe three types of gains from trades?
A)trades of exchange rates for goods or services,trades of goods or services for property,and trades of gold for textiles
B)trades of goods or services for goods or services,trades of goods or services for assets,and trades of assets for assets
C)trades of imports for exports,trades of exports for imports,and trades of natural resources for financial assets
D)trades of services for goods,trades of currency for services,and trades of one type of currency for another
E)trades of current goods for future services,trades of currency for gold,and trades of one type of currency for another
A)trades of exchange rates for goods or services,trades of goods or services for property,and trades of gold for textiles
B)trades of goods or services for goods or services,trades of goods or services for assets,and trades of assets for assets
C)trades of imports for exports,trades of exports for imports,and trades of natural resources for financial assets
D)trades of services for goods,trades of currency for services,and trades of one type of currency for another
E)trades of current goods for future services,trades of currency for gold,and trades of one type of currency for another

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The idea of risk aversion
A)is at odds with the idea of insurance.
B)help explain the profitability of insurance companies.
C)has nothing to do with insurance companies.
D)help explain the losses suffers by the insurance industry.
E)help explain why insurance companies in the long run are zero profit companies.
A)is at odds with the idea of insurance.
B)help explain the profitability of insurance companies.
C)has nothing to do with insurance companies.
D)help explain the losses suffers by the insurance industry.
E)help explain why insurance companies in the long run are zero profit companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Risk averse people
A)will never hold bonds denominated in several different currencies because of transaction costs.
B)will always hold bonds denominated in several different currencies because of transaction costs.
C)may hold bonds denominated in several different currencies.
D)may hold bonds denominated in several different currencies only if satisfying the well known interest party condition.
E)will hold only domestic bonds because of the home bias effect.
A)will never hold bonds denominated in several different currencies because of transaction costs.
B)will always hold bonds denominated in several different currencies because of transaction costs.
C)may hold bonds denominated in several different currencies.
D)may hold bonds denominated in several different currencies only if satisfying the well known interest party condition.
E)will hold only domestic bonds because of the home bias effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For the following questions assume the following facts: (1)Balance of Payments = 0 prior to the transactions.
(2)Person A (who lives in the United States)purchases an airplane from British Airways for $150,000.
(3)Person A pays with a check from his account at First Union Bank in the United States.
(4)British airways,since it will need dollars in 1 month,deposits the check at the Bank of England.
(5)Bank of England deposits the $150,000 at Commonwealth bank,which is located in the United States.
Due to the transactions above,what are the effects on the reserve at the Fed?
A)Fact 2 is a decrease of $150,000,fact 5 is a decrease of $150,000,a net effect of -$300,000.
B)Fact 3 is a decrease of $150,000,fact 5 is an increase of $150,000,a net effect of 0.
C)Fact 3 is an increase of $150,000,fact 5 is a decrease of $150,000,a net effect of 0.
D)Both fact 3 and fact 5 result in increases of $150,000,a net effect of +$300,000.
E)Both fact 3 and fact 5 result in decrease of $150,000,a net effect of -$300,000.
(2)Person A (who lives in the United States)purchases an airplane from British Airways for $150,000.
(3)Person A pays with a check from his account at First Union Bank in the United States.
(4)British airways,since it will need dollars in 1 month,deposits the check at the Bank of England.
(5)Bank of England deposits the $150,000 at Commonwealth bank,which is located in the United States.
Due to the transactions above,what are the effects on the reserve at the Fed?
A)Fact 2 is a decrease of $150,000,fact 5 is a decrease of $150,000,a net effect of -$300,000.
B)Fact 3 is a decrease of $150,000,fact 5 is an increase of $150,000,a net effect of 0.
C)Fact 3 is an increase of $150,000,fact 5 is a decrease of $150,000,a net effect of 0.
D)Both fact 3 and fact 5 result in increases of $150,000,a net effect of +$300,000.
E)Both fact 3 and fact 5 result in decrease of $150,000,a net effect of -$300,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the basic motive for asset trade?
A)the belief that large risks will lead to large returns
B)restoration of the balance of payments
C)portfolio unification
D)economic stability
E)increase expected returns and reduced risk
A)the belief that large risks will lead to large returns
B)restoration of the balance of payments
C)portfolio unification
D)economic stability
E)increase expected returns and reduced risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose that trade in asset is not allowed but the two countries sign a treaty that guarantee the sending of 25 tons of kiwi in good time by the high output country in that season.What will the outcome of such a treaty? Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Why is the foreign exchange market so vital?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Calculate the expected payoff for the following cases,where q1 and q2 are the probabilities of state 1 and 2,respectively. 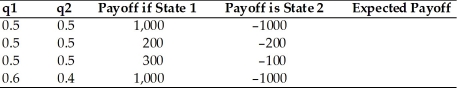


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Complete the following table. 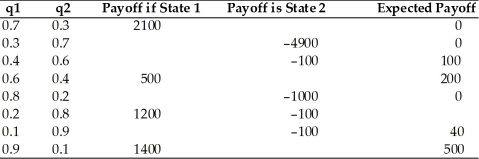


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How international trade in assets can make both countries better off?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why is portfolio diversification so important in international trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Complete the following table. 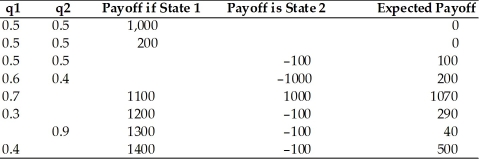


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Explain Tobin's idea of "Don't put all your eggs in one basket."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Calculate the expected payoff for the following cases with the formula: (P1)* (payoff if state 1)+ (P2)* (payoff if state 2),where P1 and P2 are the probabilities of state 1 and 2,respectively. 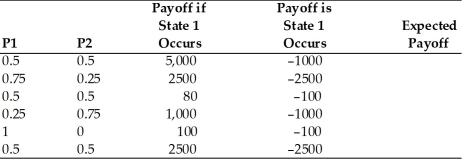


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose the two countries can trade shares in the ownership of their perspective assets without any restrictions.Assume that the consumers in both countries would like to totally smooth their consumption.Describe the outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Define risk aversion and give an example of a risk-averse person?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose the two countries can trade shares in the ownership of their perspective assets.Further,assume that a Home owner of a 10 percent share in Foreign land.He will receive 10 percent share in Foreign land,and thus receives 10 percent of the annual Foreign kiwi fruit harvest.Further assume that a Foreign owner of a 10 percent share in Home land is permitted.In this case,a Foreigner is entitled to 10 percent of the Home harvest.Calculate the expected value of kiwi fruit for each investor.Is the investor better off?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the difference between equity instruments and debt instruments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Why is it useful to make a distinction between debt and equity instruments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose you are offered a gamble in which you win $1,000 half the time but lose $1,000 half the time.If you are risk averter will you take the gamble?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose the two countries can trade shares in the ownership of their perspective assets.Further assume that a Home owner of a 25 percent share in Foreign land.He will receive 25 percent share in Foreign land and thus receives 25 percent of the annual Foreign kiwi fruit harvest.Further assume that also that a Foreign owner of a 25 percent share in Home land is permitted.In this case,a Foreigner is entitled to 25 percent of the Home harvest.Calculate the expected value of kiwi fruit for each investor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose you are offered a gamble in which you win $1,000 1/3 half the time but lose $800 2/3 half the time.If you are risk lover will you take the gamble? What will your expected payoff be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The following simple two-country question illustrates how countries are made better off by trade in assets.Imagine that there are two countries,Home and Foreign,and that residents of each own only one asset,domestic land yielding an annual harvest of kiwi fruit.Assume that the yield on the land is uncertain.Half the time,Home's land yields a harvest of 100 tons of kiwi fruit at the same time as Foreign's land yields a harvest of 50 tons.The other half of the time the outcomes are reversed.The Foreign's harvest is 100 tons,but the Home harvest is only 50.
Calculate the average,for each country of kiwi harvest.
Calculate the average,for each country of kiwi harvest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What are the three types of gains from international transactions between the residents of different countries?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Calculate the expected payoff for the following cases,where q1 and q2 are the probabilities of state 1 and 2,respectively. 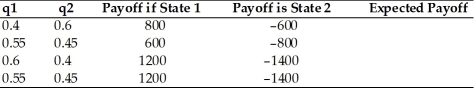


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What are the types of institution banks used to conduct foreign business?
A)corporations
B)central banks
C)commercial banks
D)agency offices,subsidiary banks,and foreign branches
E)state-owned enterprises
A)corporations
B)central banks
C)commercial banks
D)agency offices,subsidiary banks,and foreign branches
E)state-owned enterprises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Credit Suisse,Goldman Sachs,and Lazard Freres are examples of
A)commercial banks.
B)corporations.
C)non-bank financial institutions,such as insurance companies,pension funds,and mutual funds.This includes investment banks,which specialize in underwriting sales of stocks and bonds by corporations and in some cases governments.
D)central banks and other government agencies.
E)non-profit organizations.
A)commercial banks.
B)corporations.
C)non-bank financial institutions,such as insurance companies,pension funds,and mutual funds.This includes investment banks,which specialize in underwriting sales of stocks and bonds by corporations and in some cases governments.
D)central banks and other government agencies.
E)non-profit organizations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
After Bretton Woods period,countries chose to control
A)fixed exchange rate only.
B)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals only.
C)freedom of international capital movements only.
D)fixed exchange rate and freedom of international capital movements.
E)fixed exchange rate and monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals.
A)fixed exchange rate only.
B)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals only.
C)freedom of international capital movements only.
D)fixed exchange rate and freedom of international capital movements.
E)fixed exchange rate and monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
As a country begins to liberalize its capital account,what would you expect to happen to the difference between the interest rates for similar assets in this country and another country with open capital markets?
A)get larger
B)get smaller
C)stay the same
D)it depends on the existing exchange rate.
E)exponential divergence
A)get larger
B)get smaller
C)stay the same
D)it depends on the existing exchange rate.
E)exponential divergence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which type of main institution in the international capital market most often is involved in foreign exchange intervention?
A)central banks
B)non-bank financial institutions
C)insurance companies
D)corporations
E)commercial banks
A)central banks
B)non-bank financial institutions
C)insurance companies
D)corporations
E)commercial banks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Eurodollars are
A)dollar deposits located in the United States.
B)dollar deposits located in Europe.
C)dollar deposits located outside Europe.
D)dollar deposits located outside the United States.
E)dollar deposits located outside both Europe and the United States.
A)dollar deposits located in the United States.
B)dollar deposits located in Europe.
C)dollar deposits located outside Europe.
D)dollar deposits located outside the United States.
E)dollar deposits located outside both Europe and the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A country can control
A)its flexible exchange rate.
B)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals.
C)international capital movements.
D)foreign inflationary policies.
E)and avoid risks in international trade.
A)its flexible exchange rate.
B)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals.
C)international capital movements.
D)foreign inflationary policies.
E)and avoid risks in international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which one of the following possibilities is TRUE?
A)Much of eurocurrency trading occurs in Europe.
B)Much of eurocurrency trading occurs in the United States.
C)Eurocurrencies trading occurs everywhere except the United States.
D)Eurocurrencies trading occurs everywhere except Europe.
E)Eurocurrencies trading occurs everywhere except China.
A)Much of eurocurrency trading occurs in Europe.
B)Much of eurocurrency trading occurs in the United States.
C)Eurocurrencies trading occurs everywhere except the United States.
D)Eurocurrencies trading occurs everywhere except Europe.
E)Eurocurrencies trading occurs everywhere except China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Under a gold standard,countries control
A)its flexible exchange rate.
B)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals.
C)international capital movements.
D)foreign inflationary policies.
E)and avoid risks in international trade.
A)its flexible exchange rate.
B)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals.
C)international capital movements.
D)foreign inflationary policies.
E)and avoid risks in international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Rising inflationary pressure caused the U.S.to tighten its monetary policy at the end of the 1960s.As a result,market interest rates rose above the Regulation Q ceiling and American banks found it impossible to attract time deposits for re-lending.How did the banks get around this problem?
A)by setting their own interest rates and then using better business as compensation for government regulations
B)by borrowing funds from European branches,which faced no restriction on the interest they could pay on Eurodollar deposits
C)by pushing through new legislation that nullified Regulation Q
D)by creating subsidiary branches in foreign countries
E)by waiting to trade time deposits until Regulation Q no longer applied
A)by setting their own interest rates and then using better business as compensation for government regulations
B)by borrowing funds from European branches,which faced no restriction on the interest they could pay on Eurodollar deposits
C)by pushing through new legislation that nullified Regulation Q
D)by creating subsidiary branches in foreign countries
E)by waiting to trade time deposits until Regulation Q no longer applied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The leading center of Eurocurrency trading is
A)New York City.
B)Chicago.
C)London.
D)Paris.
E)Frankfurt.
A)New York City.
B)Chicago.
C)London.
D)Paris.
E)Frankfurt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What structures make up the international capital markets?
A)stock market,IFM,and the World bank
B)bond market,foreign exchange rates,IFM,and the World bank
C)commercial banks,corporations,non-bank financial institutions,the central banks,and other government agencies
D)commercial banks and corporations
E)the central banks and non-bank financial institutions
A)stock market,IFM,and the World bank
B)bond market,foreign exchange rates,IFM,and the World bank
C)commercial banks,corporations,non-bank financial institutions,the central banks,and other government agencies
D)commercial banks and corporations
E)the central banks and non-bank financial institutions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Besides world trade growth,what can explain the growth of international banking since the 1960s?
A)war in the Middle East
B)government focus on banking regulation.
C)an increase in world travel.
D)the emergence of developing countries like China.
E)desire of depositors to hold currencies outside the jurisdiction of the countries that issue them
A)war in the Middle East
B)government focus on banking regulation.
C)an increase in world travel.
D)the emergence of developing countries like China.
E)desire of depositors to hold currencies outside the jurisdiction of the countries that issue them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Under the unified Euro regime,the European countries control
A)fixed exchange rate only.
B)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals only.
C)freedom of international capital movements only.
D)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals and freedom of international capital movements.
E)fixed exchange rate and freedom of international capital movements.
A)fixed exchange rate only.
B)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals only.
C)freedom of international capital movements only.
D)monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals and freedom of international capital movements.
E)fixed exchange rate and freedom of international capital movements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Investment banks in the U.S.are
A)regular banks specializing in investment projects.
B)not banks at all but institutions which specialize in underwriting sales of stocks and bonds.
C)special arm of the U.S.government for U.S.banks operating outside the U.S.
D)regular banks specializing in investment projects,but allowed to offer limited domestic transactions.
E)international banks that are heavily invest in the U.S.
A)regular banks specializing in investment projects.
B)not banks at all but institutions which specialize in underwriting sales of stocks and bonds.
C)special arm of the U.S.government for U.S.banks operating outside the U.S.
D)regular banks specializing in investment projects,but allowed to offer limited domestic transactions.
E)international banks that are heavily invest in the U.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Eurobanks are
A)all European Banks.
B)all non American banks.
C)banks that accept deposits denominated in Eurocurrencies excluding Eurodollars.
D)banks that accept deposits denominated in Eurocurrencies including Eurodollars.
E)banks that do not take U.S.dollars.
A)all European Banks.
B)all non American banks.
C)banks that accept deposits denominated in Eurocurrencies excluding Eurodollars.
D)banks that accept deposits denominated in Eurocurrencies including Eurodollars.
E)banks that do not take U.S.dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Fed's Regulation Q
A)placed a ceiling on the interest rates U.S.banks could pay on time deposits to foreigners.
B)placed a ceiling on the interest rates U.S.banks could pay on time deposits.
C)placed a ceiling on the amount U.S.residents can deposits in Euro banks.
D)placed a ceiling on the amount foreign residents can deposits in domestic American banks.
E)placed a ceiling on the amount foreign banks can pay on time deposits.
A)placed a ceiling on the interest rates U.S.banks could pay on time deposits to foreigners.
B)placed a ceiling on the interest rates U.S.banks could pay on time deposits.
C)placed a ceiling on the amount U.S.residents can deposits in Euro banks.
D)placed a ceiling on the amount foreign residents can deposits in domestic American banks.
E)placed a ceiling on the amount foreign banks can pay on time deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The difference between an agency office located abroad and a subsidiary bank located abroad is
A)an agency office is just a home bank in another country while a subsidiary bank is controlled by a foreign bank and subject to the same regulations as local banks.
B)an agency office is just a home bank in another country while a subsidiary bank arranges loans and transfers funds but does not accept deposits.
C)an agency office arranges loans and transfers funds but does not accept deposits while a subsidiary bank is controlled by a foreign bank and subject to the same regulations as local banks.
D)an agency office arranges loans and transfers funds but does not accept deposits while a subsidiary bank is just a home bank in a foreign country.
E)an agency office is controlled by a foreign bank and subject to the same regulations as local banks while a subsidiary bank arranges loans and transfers funds but does not accept deposits.
A)an agency office is just a home bank in another country while a subsidiary bank is controlled by a foreign bank and subject to the same regulations as local banks.
B)an agency office is just a home bank in another country while a subsidiary bank arranges loans and transfers funds but does not accept deposits.
C)an agency office arranges loans and transfers funds but does not accept deposits while a subsidiary bank is controlled by a foreign bank and subject to the same regulations as local banks.
D)an agency office arranges loans and transfers funds but does not accept deposits while a subsidiary bank is just a home bank in a foreign country.
E)an agency office is controlled by a foreign bank and subject to the same regulations as local banks while a subsidiary bank arranges loans and transfers funds but does not accept deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The Eurodollar market's early growth was stimulated by the Cold War between the United States and U.S.S.R.Why?
A)Soviets feared the U.S.might confiscate dollars place in American banks if conditions of Cold War were to worsen.
B)The United States didn't feel safe holding as many dollars in American banks.
C)The Cold War did not stimulate the Eurodollar market's early growth.
D)Developing technologies required larger money transfers than central banks could handle.
E)Soviets developed a new banking system with new allies developed during the tension.
A)Soviets feared the U.S.might confiscate dollars place in American banks if conditions of Cold War were to worsen.
B)The United States didn't feel safe holding as many dollars in American banks.
C)The Cold War did not stimulate the Eurodollar market's early growth.
D)Developing technologies required larger money transfers than central banks could handle.
E)Soviets developed a new banking system with new allies developed during the tension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Complete the following table with the formula (P1)* (payoff if state 1)+ (P2)* (payoff if state 2),where P1 and P2 are the probabilities of state 1 and 2,respectively. 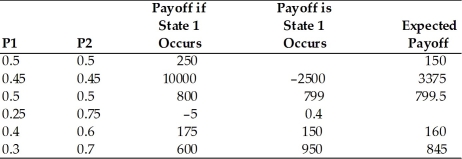


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Who are the main actors in the international capital market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A business's use of a bank located outside of the home country is called
A)Swiss banking.
B)offshore banking.
C)international banking.
D)domestic banking.
E)international swapping.
A)Swiss banking.
B)offshore banking.
C)international banking.
D)domestic banking.
E)international swapping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The fact that assets of the political opponents of the U.S.were frozen in U.S.banks
A)was challenged as unconstitutional.
B)lead to an increased amount of funds being placed in Eurobanks.
C)lead to a violation of the Law of One Price.
D)lead to the Cold War.
E)lead to a violation of Regulation Q.
A)was challenged as unconstitutional.
B)lead to an increased amount of funds being placed in Eurobanks.
C)lead to a violation of the Law of One Price.
D)lead to the Cold War.
E)lead to a violation of Regulation Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Offshore banking can take place at which institution?
A)agency office only
B)subsidiary bank only
C)foreign bank only
D)subsidiary bank and foreign bank
E)agency office,subsidiary bank,and foreign bank
A)agency office only
B)subsidiary bank only
C)foreign bank only
D)subsidiary bank and foreign bank
E)agency office,subsidiary bank,and foreign bank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Regulatory asymmetries can explain why the following places have become main Eurocurrency centers
A)the United States.
B)Germany.
C)Zurich,Somalia,and Mozambique.
D)London,Luxembourg,and The United States.
E)London,Luxembourg,and Hong Kong.
A)the United States.
B)Germany.
C)Zurich,Somalia,and Mozambique.
D)London,Luxembourg,and The United States.
E)London,Luxembourg,and Hong Kong.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following statements is TRUE for the U.S.?
A)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against losses up to $250,000.
B)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against losses up to $100,000.
C)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against losses up to $10,000.
D)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against natural disaster up to $100,000.
E)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against floods up to $100,000.
A)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against losses up to $250,000.
B)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against losses up to $100,000.
C)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against losses up to $10,000.
D)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against natural disaster up to $100,000.
E)The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)insures bank deposits against floods up to $100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Bank failure is limited to banks that have mismanaged their assets.
B)Bank failure is limited to banks that have invested in real estate.
C)Bank failure is limited to banks that have invested in government bonds.
D)Bank failure is limited to a few banks.
E)Bank failure is NOT limited to banks that have mismanaged their assets.
A)Bank failure is limited to banks that have mismanaged their assets.
B)Bank failure is limited to banks that have invested in real estate.
C)Bank failure is limited to banks that have invested in government bonds.
D)Bank failure is limited to a few banks.
E)Bank failure is NOT limited to banks that have mismanaged their assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a country chooses to have a monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals and the freedom of international capital movements,then
A)it can have a fixed exchange rate.
B)it cannot have a fixed exchange rate.
C)it cannot balance its current account.
D)it cannot have a fiscal policy oriented toward domestic goals.
E)it cannot control money supply growth.
A)it can have a fixed exchange rate.
B)it cannot have a fixed exchange rate.
C)it cannot balance its current account.
D)it cannot have a fiscal policy oriented toward domestic goals.
E)it cannot control money supply growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The scale of transactions in the international capital market has
A)grown more quickly than world GDP since the early 1970s.
B)grown less quickly than world GDP since the early 1970s.
C)grown about the same rate as the world GDP since the early 1970s.
D)been fixed by international regulations.
E)decreased more quickly than world GDP since the early 1970s.
A)grown more quickly than world GDP since the early 1970s.
B)grown less quickly than world GDP since the early 1970s.
C)grown about the same rate as the world GDP since the early 1970s.
D)been fixed by international regulations.
E)decreased more quickly than world GDP since the early 1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
For the following question,assume the following facts: (1)Chase (which is located in the United States)has a 20% reserve requirement imposed by the government.
(2)Bank of Germany has no reserve requirements.
(3)Both banks may invest at an 8% interest rate.
(4)Both banks have fixed costs of $3 per deposit made.
What is the difference between the minimum interest rates each bank can offer and still make a profit if the deposit is $500 for 1 year?
A)0 - Both banks can offer the same rate.
B)1%
C)1.6%
D)0.4%
E)20%
(2)Bank of Germany has no reserve requirements.
(3)Both banks may invest at an 8% interest rate.
(4)Both banks have fixed costs of $3 per deposit made.
What is the difference between the minimum interest rates each bank can offer and still make a profit if the deposit is $500 for 1 year?
A)0 - Both banks can offer the same rate.
B)1%
C)1.6%
D)0.4%
E)20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Explain what Eurocurrencies are and why they are significant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements is TRUE for the U.S.?
A)Federally chartered banks are required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank
Deposits insurance.
B)Federally chartered banks are not required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank deposits insurance.
C)The States are not required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank deposits insurance for banks with their main branch in that State.
D)The States are required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank deposits insurance for banks with their main branch in that State.
E)The specific municipality where the main branch of the bank is located is required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank deposits insurance.
A)Federally chartered banks are required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank
Deposits insurance.
B)Federally chartered banks are not required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank deposits insurance.
C)The States are not required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank deposits insurance for banks with their main branch in that State.
D)The States are required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank deposits insurance for banks with their main branch in that State.
E)The specific municipality where the main branch of the bank is located is required to make contributions to the FDIC to cover the cost of bank deposits insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If a country chooses to have a monetary policy oriented toward domestic goals and a fixed exchange rate,then
A)it can have the freedom of international capital movements.
B)it cannot have the freedom of international capital movements.
C)it cannot balance its current account.
D)it cannot have fiscal policy oriented toward domestic goals.
E)it cannot control money supply growth.
A)it can have the freedom of international capital movements.
B)it cannot have the freedom of international capital movements.
C)it cannot balance its current account.
D)it cannot have fiscal policy oriented toward domestic goals.
E)it cannot control money supply growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following statements is TRUE for the U.S.?
A)The FDIC does not provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations.
B)The FDIC does provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations,but only up to $50,000.
C)The FDIC does provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations up to $250,000.
D)The FDIC does provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations up to $150,000.
E)The FDIC does provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations up to $100,000.
A)The FDIC does not provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations.
B)The FDIC does provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations,but only up to $50,000.
C)The FDIC does provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations up to $250,000.
D)The FDIC does provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations up to $150,000.
E)The FDIC does provide insurance for deposits for Savings and Loans (S&L)associations up to $100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What do you expect would be the effects of 9/11 on the size of the Eurocurrency markets?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Bank failures inflict serious financial harm on individual depositors.
B)Bank failures do not inflict serious financial harm on individual depositors.
C)Bank failures inflict not only serious financial harm on individual depositors,but also harm the macroeconomic stability of the economy.
D)Bank failures inflict serious financial harm on individual depositors,but fortunately do not harm the macroeconomic stability of the economy.
E)Bank failures only inflict serious financial harm on the macroeconomic stability of the economy.
A)Bank failures inflict serious financial harm on individual depositors.
B)Bank failures do not inflict serious financial harm on individual depositors.
C)Bank failures inflict not only serious financial harm on individual depositors,but also harm the macroeconomic stability of the economy.
D)Bank failures inflict serious financial harm on individual depositors,but fortunately do not harm the macroeconomic stability of the economy.
E)Bank failures only inflict serious financial harm on the macroeconomic stability of the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Describe how the Eurodollar market's early growth was spawned by the Cold War between the United States and the U.S.S.R.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Explain how Eurobanks played a role in the Iranian Hostage Crisis in 1979.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Explain why a London Eurobank has a competitive advantage over a bank in New York in attracting dollar deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Describe the role of offshore banking and of offshore currency (eurocurrencies)trading

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



