Deck 21: Understanding the Business Environment: The Economics of Regulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Understanding the Business Environment: The Economics of Regulation
1
In the 1980s, "voluntary restrictions" on automobile imports raised prices of Japanese cars $1,000, European cars by $2,000 and American cars by $500. During the period following these restrictions, both Japanese and European automakers opened parts and assembly plants in the US. Why did this happen? How is it related to regulation?
The threat of government regulation led foreign car manufactures to restrict the number of cars they imported in order to prevent even stricter import quotas or large tariffs. The opening of new auto plants in the US by Japanese and European automakers allows these firms to produce cars that would not be affected by trade barriers. The opening of these plants within the United States may also increase political support for these companies' preferred policies including lower trade barriers for imported cars.
2
The transactions costs of writing and enforcing contracts are higher in:
A) countries with poorly-enforced property rights.
B) countries with strongly-enforced property rights.
C) all counties with good court systems.
D) countries without political risks of property confiscation.
A) countries with poorly-enforced property rights.
B) countries with strongly-enforced property rights.
C) all counties with good court systems.
D) countries without political risks of property confiscation.
A
3
Draw a profit/price tradeoff curve that results from moving from a competitive to a monopoly industry organization. Show the equilibrium position for the regulator with a political support function (PS curve). What can we say about prices and profits of the regulated industry if it started as a monopoly?
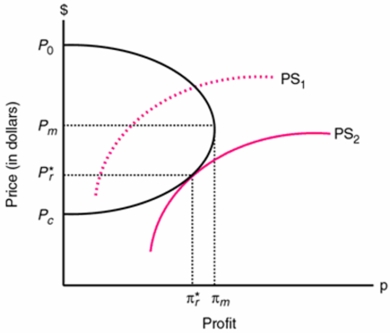 The above diagram shows the equilibrium position for the regulator with a political support function (PS curve). The dark curve shows the relationship between price, which a regulator can limit, and profits of the industry. This political equilibrium results in a price greater than the price under a perfectly competitive market structure, but lower than the price under a monopoly market structure. If this industry was originally an unregulated monopoly, then prices and industry profits will be lower under regulation.
The above diagram shows the equilibrium position for the regulator with a political support function (PS curve). The dark curve shows the relationship between price, which a regulator can limit, and profits of the industry. This political equilibrium results in a price greater than the price under a perfectly competitive market structure, but lower than the price under a monopoly market structure. If this industry was originally an unregulated monopoly, then prices and industry profits will be lower under regulation. 4
In parts of Eastern Europe, companies maintain special guards to protect payday funds, to help move products to market, and to enforce immediate payment for products sold to retailers. All of these features indicate:
A) that property rights are respected and transactions costs are low.
B) that property rights are weak and transactions costs are low.
C) that property rights are weak and transactions costs are high.
D) that property rights are respected and transactions costs are high
A) that property rights are respected and transactions costs are low.
B) that property rights are weak and transactions costs are low.
C) that property rights are weak and transactions costs are high.
D) that property rights are respected and transactions costs are high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
OSHA is charged with enforcing workplace safety regulations in the United States. Employees are not allowed to waive these safety rights or to trade them off for higher salaries. That means the safety standards are:
A) alienable.
B) inalienable.
C) negotiable.
D) transferable.
A) alienable.
B) inalienable.
C) negotiable.
D) transferable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The case study in the chapter uses World Motors Corporation (WM). This company, headquartered in Atlanta, is faced with two major regulatory thrusts. One - emission standards - catches WM with its major competitor having an efficient patented emission control device. The second - miles-per-gallon standards - finds WM in the same position as its competitors. Where would WM put its lobbying effort, assuming that conservation groups are currently lobbying strongly for higher emission standards?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If property rights are enforced and contracts in trade are legally respected, it is usually assumed that:
A) output will begin to fall.
B) investment will be encouraged.
C) transactions costs will rise.
D) government is unnecessary.
A) output will begin to fall.
B) investment will be encouraged.
C) transactions costs will rise.
D) government is unnecessary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If property rights are very hard to assign and transactions costs are particularly high, then, given the Coase Theorem, externalities:
A) may reduce the efficiency of resource allocation.
B) would leave resource efficiency unchanged.
C) allow resource allocations to remain efficient.
D) have not relationship to efficiency.
A) may reduce the efficiency of resource allocation.
B) would leave resource efficiency unchanged.
C) allow resource allocations to remain efficient.
D) have not relationship to efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Draw a profit/price tradeoff curve that is the result of moving from a competitive to a monopoly industry organization. Show the equilibrium position for the regulator with a political support function (PS curve). What can we say about prices and profits of the regulated industry if it started as a competitive industry?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Most governments enforce patents, copyrights, and trademarks. While these are clear restrictions on free trade, it is believed that inventors and investors:
A) generally oppose these restrictions as monopolistic.
B) favor these restrictions since they promote inventive activities.
C) are indifference since they have no impact on business.
D) prefer low prices to patents.
A) generally oppose these restrictions as monopolistic.
B) favor these restrictions since they promote inventive activities.
C) are indifference since they have no impact on business.
D) prefer low prices to patents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The FDIC insures each deposit up to $100,000 in the banking system. If you are a manager of a bank and if your bonus is tied to the number of loans you generate, will you care about the nature of the loans and their risk?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In 2003, conservation groups paid western cattlemen to move their herds away from wild buffalo herds so that the buffalo would have more feed and not have to compete with the cattle. What has this got to do with regulation and the Coase Theorem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Informational deficits of producers or consumers, plus problems of externalities, can:
A) cause market failure.
B) always be solved by alternative dispute resolution (ADR).
C) improve free trade.
D) restrict the use of property rights in a market economy.
A) cause market failure.
B) always be solved by alternative dispute resolution (ADR).
C) improve free trade.
D) restrict the use of property rights in a market economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Regulating political campaign contributions is a big issue in Washington and many times we hear politicians making headlines by speaking against it, and trying to move legislation to prevent lobbying and in trying to gain more accountability in the system. But political campaign contributions and lobbying are at an all time high, with no end in sight. Why are the political pundits not successful in their actions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The enforcement of contracts and the adjudication of contract disputes through the court system:
A) is a major source of business inefficiency in the United States.
B) is not common in most of Europe.
C) is an important way to reduce transactions costs.
D) weakens the system of property rights.
A) is a major source of business inefficiency in the United States.
B) is not common in most of Europe.
C) is an important way to reduce transactions costs.
D) weakens the system of property rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The idea that resource allocation can remain efficient, even in the presence of externalities, as long as property rights are clearly assigned and transactions costs are low is referred to as the:
A) Law of Demand.
B) Black/Schloes Formula.
C) Coase Theorem.
D) Law of Diminishing Returns.
A) Law of Demand.
B) Black/Schloes Formula.
C) Coase Theorem.
D) Law of Diminishing Returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations tend to go through many stages of review and approval before they are implemented. Not only do many regulators have to approve a new regulation, but comments and reviews from industry and conservation organizations are typical. Explain these complicated procedures in light of the theories of supply and demand for regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Describe the lemons problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) is used to:
A) eliminate the need for a court system.
B) solve problems with public goods.
C) stop frivolous suits.
D) reduce the high cost commercial litigation.
A) eliminate the need for a court system.
B) solve problems with public goods.
C) stop frivolous suits.
D) reduce the high cost commercial litigation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Explain how Coase's theorem is implemented by the EPA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In some industries, pollution rights are sold from one company that does not need them to another that does. In recent years, conservation groups have purchased pollution rights so they cannot be exercised. Companies in need of pollution rights would find that:
A) the supply of pollution rights had increased.
B) the prices of pollution rights had fallen.
C) the relative costs of pollution control equipment had gone up.
D) the supply of pollution rights had declined.
A) the supply of pollution rights had increased.
B) the prices of pollution rights had fallen.
C) the relative costs of pollution control equipment had gone up.
D) the supply of pollution rights had declined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The economic theory of regulation treats politicians as:
A) publicly spirited individuals who work for the public welfare.
B) corrupt individuals who sell contracts to the highest bidders.
C) self-interested individuals who benefit themselves by supplying legislation.
D) people who only represent the small segment of the population that elects them.
A) publicly spirited individuals who work for the public welfare.
B) corrupt individuals who sell contracts to the highest bidders.
C) self-interested individuals who benefit themselves by supplying legislation.
D) people who only represent the small segment of the population that elects them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Between 1971 and 1991, more than _________ federal lawsuits were filed.
A) 10 million
B) 6 million
C) 3 million
D) 4 million
A) 10 million
B) 6 million
C) 3 million
D) 4 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For politician or regulator of an industry, there is a clear trade-off between:
A) supply and demand.
B) profits and costs of the regulated company.
C) prices charged consumers and profits earned by producers.
D) publicly spirited and self-interested individuals,
A) supply and demand.
B) profits and costs of the regulated company.
C) prices charged consumers and profits earned by producers.
D) publicly spirited and self-interested individuals,

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Public Goods:
A) are goods for a few, by a few and of a few.
B) are goods whose consumption by a few reduces the amount for the rest.
C) are goods whose consumption by one reduces the amount for others.
D) are goods whose consumption by one does not diminish the amount for others.
A) are goods for a few, by a few and of a few.
B) are goods whose consumption by a few reduces the amount for the rest.
C) are goods whose consumption by one reduces the amount for others.
D) are goods whose consumption by one does not diminish the amount for others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Average wealth loss per firms from litigation amounts to about ___________.
A) 200 million
B) 20 billion
C) 2 billion
D) 21 million
A) 200 million
B) 20 billion
C) 2 billion
D) 21 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A monopolist sets the price where marginal costs equal marginal revenue and the price is higher than the competitive level. Since there are some consumers who are willing to pay more than the marginal cost of production, then:
A) there are gains to be made from more trade.
B) all gains from trade are exhausted.
C) it is clear that monopolists do not maximize profits.
D) it is clear that monopolists do make profits.
A) there are gains to be made from more trade.
B) all gains from trade are exhausted.
C) it is clear that monopolists do not maximize profits.
D) it is clear that monopolists do make profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The problem with public goods is:
A) self-selection.
B) adverse selection.
C) moral hazard.
D) free-riding.
A) self-selection.
B) adverse selection.
C) moral hazard.
D) free-riding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A jury ordered McDonald's to pay $2.7 million to Stella Liebeck, a drive-through customer who burned herself with hot coffee after placing the cup between her legs to remove the top and add cream: she claimed that the coffee was too hot. This tells us the our legal system can:
A) promote efficiency by making property rights secure.
B) promote efficiency by lowering transactions costs.
C) lower costs by creating incentives to litigate frivolous suits.
D) raise costs by creating incentives to litigate frivolous suits.
A) promote efficiency by making property rights secure.
B) promote efficiency by lowering transactions costs.
C) lower costs by creating incentives to litigate frivolous suits.
D) raise costs by creating incentives to litigate frivolous suits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The 1890 Sherman Act was legislated by the:
A) SEC.
B) EPA.
C) FDA.
D) FTC.
A) SEC.
B) EPA.
C) FDA.
D) FTC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In some industries, pollution rights are sold from one company that does not need them to another that does. In recent years, conservation groups have purchased pollution rights so they cannot be exercised. Companies in need of pollution rights would find that:
A) the supply of pollution rights had increased.
B) the prices of pollution rights had fallen.
C) the relative costs of pollution control equipment had gone up.
D) the prices of pollution rights had gone up.
A) the supply of pollution rights had increased.
B) the prices of pollution rights had fallen.
C) the relative costs of pollution control equipment had gone up.
D) the prices of pollution rights had gone up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In some industries, pollution rights are sold from one company that does not need them to another that does. In recent years, conservation groups have purchased pollution rights so they cannot be exercised. Companies in need of pollution rights would find that:
A) the supply of pollution rights had increased.
B) the prices of pollution rights had fallen.
C) the relative costs of pollution control equipment had gone up.
D) the relative costs of pollution control equipment had fallen.
A) the supply of pollution rights had increased.
B) the prices of pollution rights had fallen.
C) the relative costs of pollution control equipment had gone up.
D) the relative costs of pollution control equipment had fallen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following regulatory procedures transfers wealth from consumers to producers?
A) Import quotas and tariffs.
B) Efficiency wages.
C) Transactions costs.
D) Deadweight loss.
A) Import quotas and tariffs.
B) Efficiency wages.
C) Transactions costs.
D) Deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
As an industry moves from competitive to monopolistic prices:
A) and profits fall.
B) fall and profits rise.
C) rise and profits fall.
D) and profits rise.
A) and profits fall.
B) fall and profits rise.
C) rise and profits fall.
D) and profits rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following regulatory procedures transfers wealth from consumers to producers?
A) Property rights.
B) Transactions costs.
C) Zoning restrictions.
D) Banning guns.
A) Property rights.
B) Transactions costs.
C) Zoning restrictions.
D) Banning guns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following regulatory procedures transfers wealth from consumers to producers?
A) Efficiency wages.
B) Licensing of doctors and dentists.
C) Deadweight loss.
D) Transactions cost.
A) Efficiency wages.
B) Licensing of doctors and dentists.
C) Deadweight loss.
D) Transactions cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Many people believe that the supply and demand for regulation will result in the most powerful coalition group controlling the regulatory body. That powerful group is often made up of the companies that are supposed to be regulated. This theory is called:
A) the capture theory.
B) adverse selection theory.
C) the law of demand.
D) market failure theory.
A) the capture theory.
B) adverse selection theory.
C) the law of demand.
D) market failure theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A person buys a used 1998 Honda Civic and finds that there is a problem in the drive train so that the whole set of axles must be replaced. However, the state has a lemon law that protects the buyer from these kinds of discoveries for 30 days. These lemon laws attempt to correct for the problem of:
A) monopoly power.
B) adverse selection.
C) risk premiums.
D) ratification before implementation.
A) monopoly power.
B) adverse selection.
C) risk premiums.
D) ratification before implementation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Special interest groups, in the theory of regulation, may be defined as:
A) publicly spirited individuals who will benefits from regulation.
B) self-interested individuals who benefit from regulation.
C) self-interested individuals who will suffer from regulation.
D) publicly spirited individuals who will suffer from regulation.
A) publicly spirited individuals who will benefits from regulation.
B) self-interested individuals who benefit from regulation.
C) self-interested individuals who will suffer from regulation.
D) publicly spirited individuals who will suffer from regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In a regulatory environment, the number of regulated companies is small and the payoff to successful lobbying is large, and the:
A) number of consumers is also small, but their payoff to success is also small for each person.
B) number of consumers is large, and the payoff to success is small for each person.
C) number of regulators is small and corrupt.
D) supply of regulation is usually tied to another industry's success.
A) number of consumers is also small, but their payoff to success is also small for each person.
B) number of consumers is large, and the payoff to success is small for each person.
C) number of regulators is small and corrupt.
D) supply of regulation is usually tied to another industry's success.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



