Deck 3: Labor Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Labor Demand
1
What is an example of the scale effect?
A)Workers choose to provide more hours of labor when the wage rate decreases.
B)Hiring more labor as long as the marginal product of labor is positive.
C)The firm expands output when production costs fall.
D)The firm expands output when production costs increase.
E)The firm hires more labor when the wage falls because labor has become relatively cheaper compared to the price of other factors of production.
A)Workers choose to provide more hours of labor when the wage rate decreases.
B)Hiring more labor as long as the marginal product of labor is positive.
C)The firm expands output when production costs fall.
D)The firm expands output when production costs increase.
E)The firm hires more labor when the wage falls because labor has become relatively cheaper compared to the price of other factors of production.
C
2
The elasticity of substitutions is
A)the change in capital over the change in the price of labor.
B)the percentage change in capital over the percentage change in labor.
C)the change in the price of capital over the change in the price of labor.
D)the percentage change in the price of capital over the percentage change in the price of labor.
E)the percentage change in the capital/labor ratio resulting from a 1 percent change in the relative price of labor.
A)the change in capital over the change in the price of labor.
B)the percentage change in capital over the percentage change in labor.
C)the change in the price of capital over the change in the price of labor.
D)the percentage change in the price of capital over the percentage change in the price of labor.
E)the percentage change in the capital/labor ratio resulting from a 1 percent change in the relative price of labor.
E
3
Labor demand is more elastic
A)the greater is the supply elasticity of capital.
B)the greater is the elasticity of substitution between labor and capital.
C)the greater is the elasticity of demand for the firm's output.
D)the greater is labor's share in total costs.
E)All of the above.
A)the greater is the supply elasticity of capital.
B)the greater is the elasticity of substitution between labor and capital.
C)the greater is the elasticity of demand for the firm's output.
D)the greater is labor's share in total costs.
E)All of the above.
E
4
What is not true when thinking of the firm's objective as a cost-minimization problem rather than as a profit-maximization problem?
A)The slope at any point on any isoquant reveals the marginal rate of technical substitution.
B)The firm chooses labor and capital to minimize its costs.
C)The firm chooses a particular level of output to produce.
D)The price of the output good never enters the decision as to how much labor or capital to employ.
E)The firm will choose labor and capital inputs so that the marginal productivity of labor relative to the marginal productivity of capital equals the price of labor relative to the price of capital.
A)The slope at any point on any isoquant reveals the marginal rate of technical substitution.
B)The firm chooses labor and capital to minimize its costs.
C)The firm chooses a particular level of output to produce.
D)The price of the output good never enters the decision as to how much labor or capital to employ.
E)The firm will choose labor and capital inputs so that the marginal productivity of labor relative to the marginal productivity of capital equals the price of labor relative to the price of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the long run, a decrease in the competitive wage will be associated with which of the following?
A)A substitution effect in favor of employing more capital.
B)A scale effect in favor of employing more labor.
C)More employment if the wage decrease was a result of a decrease in the demand for labor.
D)Less employment if the wage decrease was a result of an increase in the supply of labor.
E)An increase in the output price.
A)A substitution effect in favor of employing more capital.
B)A scale effect in favor of employing more labor.
C)More employment if the wage decrease was a result of a decrease in the demand for labor.
D)Less employment if the wage decrease was a result of an increase in the supply of labor.
E)An increase in the output price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
From 1981 to 1989, the nominal federal minimum wage was unchanged.As a result:
A)The real minimum wage increased because firms paid higher wages to attract workers over time.
B)The real minimum wage decreased because firms substituted skilled labor for unskilled labor.
C)The real minimum wage increased due to higher payroll taxes.
D)The real minimum wage decreased over time due to inflation.
E)The real minimum wage was unchanged as well.
A)The real minimum wage increased because firms paid higher wages to attract workers over time.
B)The real minimum wage decreased because firms substituted skilled labor for unskilled labor.
C)The real minimum wage increased due to higher payroll taxes.
D)The real minimum wage decreased over time due to inflation.
E)The real minimum wage was unchanged as well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Labor demand is more elastic the greater the elasticity of substitution between labor and capital because
A)workers supply more labor when their wage increases.
B)the firm's output price falls when the firm produces more output.
C)a firm is less willing to pay higher labor costs if it is easy for the firm to substitute capital for labor.
D)firms always have the option of substituting capital for labor.
E)a firm's technology is slow to change.
A)workers supply more labor when their wage increases.
B)the firm's output price falls when the firm produces more output.
C)a firm is less willing to pay higher labor costs if it is easy for the firm to substitute capital for labor.
D)firms always have the option of substituting capital for labor.
E)a firm's technology is slow to change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The imposition of a minimum wage on a competitive labor market will likely
A)create additional employment opportunities because some low-skilled workers will now see their wage increase.
B)lower the wages of workers earning more than the minimum wage.
C)create unemployment as some people enter the labor market while some firms reduce the quantity of labor they are willing to employ due to the increased wage.
D)increase unemployment of high-skilled workers as firms substitute high-skilled labor for low-skilled labor.
E)lower the unemployment rate of low-income families.
A)create additional employment opportunities because some low-skilled workers will now see their wage increase.
B)lower the wages of workers earning more than the minimum wage.
C)create unemployment as some people enter the labor market while some firms reduce the quantity of labor they are willing to employ due to the increased wage.
D)increase unemployment of high-skilled workers as firms substitute high-skilled labor for low-skilled labor.
E)lower the unemployment rate of low-income families.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The production function relates
A)factor prices to output prices.
B)wages to labor employed.
C)factors of production to total output.
D)factors of production to profit.
E)the output price to factors of production.
A)factor prices to output prices.
B)wages to labor employed.
C)factors of production to total output.
D)factors of production to profit.
E)the output price to factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Marissa owns a small lunch shop.The shop's kitchen is small, so it can only accommodate one worker at any one time.The shop is only open from 11:30am - 1:30pm each day.Which of the following options is Marissa the most likely to pursue if economic pressures lower the competitive wage she pays her worker by 5 percent?
A)Borrow capital to triple the size of her kitchen.
B)Hire a second worker.
C)Extend her business hours.
D)Shut down her shop.
E)Raise her prices.
A)Borrow capital to triple the size of her kitchen.
B)Hire a second worker.
C)Extend her business hours.
D)Shut down her shop.
E)Raise her prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
At a wage of $25 per hour, the firm employs 50,000 hours of labor per week.If the wage would increase to $27 per hour, the firm would employ 45,000 hours of labor per week.What is the elasticity of labor demand?
A)-2.50.
B)-1.50.
C)-1.25.
D)-0.50.
E)-0.25.
A)-2.50.
B)-1.50.
C)-1.25.
D)-0.50.
E)-0.25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How would imposing a minimum wage above the market clearing wage affect employment in a competitive labor market?
A)Employment would increase as previously unemployed workers would be more encouraged to find a job.
B)Employment would increase because a higher minimum wage would create more jobs for low-skilled workers.
C)Employment would increase as firms would illegally hire workers below the original competitive wage.
D)Employment would be unchanged as workers are non-responsive to low wages.
E)Employment would decrease as some workers who are willing to work at the lower competitive wage would no longer be able to find work.
A)Employment would increase as previously unemployed workers would be more encouraged to find a job.
B)Employment would increase because a higher minimum wage would create more jobs for low-skilled workers.
C)Employment would increase as firms would illegally hire workers below the original competitive wage.
D)Employment would be unchanged as workers are non-responsive to low wages.
E)Employment would decrease as some workers who are willing to work at the lower competitive wage would no longer be able to find work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If unskilled labor and capital are substitutes,
A)demand for unskilled labor increases when the price of capital decreases.
B)the cross-elasticity between unskilled labor and capital is positive.
C)the price of unskilled labor decreases when the price of capital increases.
D)the price of capital is increasing.
E)the demand curve for capital is upward-sloping.
A)demand for unskilled labor increases when the price of capital decreases.
B)the cross-elasticity between unskilled labor and capital is positive.
C)the price of unskilled labor decreases when the price of capital increases.
D)the price of capital is increasing.
E)the demand curve for capital is upward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is an example of the substitution effect?
A)Workers choose to provide more hours of labor when the wage rate decreases.
B)Hiring more labor as long as the marginal product of labor is positive.
C)The firm expands output when production costs fall.
D)The firm expands output when production costs increase.
E)The firm hires more labor when the wage falls because labor has become relatively cheaper compared to the price of other factors of production.
A)Workers choose to provide more hours of labor when the wage rate decreases.
B)Hiring more labor as long as the marginal product of labor is positive.
C)The firm expands output when production costs fall.
D)The firm expands output when production costs increase.
E)The firm hires more labor when the wage falls because labor has become relatively cheaper compared to the price of other factors of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
At what point should a firm stop hiring workers?
A)When the wage per worker starts to increase.
B)When the price of capital starts to decrease.
C)When the firm's marginal gain from hiring an additional worker is zero.
D)When the firm's marginal profit from hiring an additional worker equals the cost of hiring that worker.
E)When the firm's value of marginal product equals zero.
A)When the wage per worker starts to increase.
B)When the price of capital starts to decrease.
C)When the firm's marginal gain from hiring an additional worker is zero.
D)When the firm's marginal profit from hiring an additional worker equals the cost of hiring that worker.
E)When the firm's value of marginal product equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The slope of the production function while holding capital fixed is
A)the marginal product of labor.
B)the marginal product of capital.
C)the average product of labor.
D)the labor-capital ratio.
E)the capital-labor ratio.
A)the marginal product of labor.
B)the marginal product of capital.
C)the average product of labor.
D)the labor-capital ratio.
E)the capital-labor ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How does a profit-maximizing firm that is operating in a competitive labor market respond to an increase in the wage rate?
A)The firm will demand less capital due to the substitution effect.
B)The firm will demand more labor due to the substitution effect.
C)The firm will produce less output due to the scale effect.
D)The firm will demand more capital due to the scale effect.
E)The firm will demand more labor due to the scale effect.
A)The firm will demand less capital due to the substitution effect.
B)The firm will demand more labor due to the substitution effect.
C)The firm will produce less output due to the scale effect.
D)The firm will demand more capital due to the scale effect.
E)The firm will demand more labor due to the scale effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Labor demand is more elastic the greater the elasticity of demand for the firm's output because
A)the firm would see its quantity demanded fall substantially if the firm tried to pass increased labor costs through to the consumer by increasing the price of the output good.
B)the firm's output price falls when the firm produces less output.
C)a firm that operates in a competitive output market cannot lower its price.
D)capital is usually price elastic.
E)the firm will want to hire fewer workers when the wage rate increases.
A)the firm would see its quantity demanded fall substantially if the firm tried to pass increased labor costs through to the consumer by increasing the price of the output good.
B)the firm's output price falls when the firm produces less output.
C)a firm that operates in a competitive output market cannot lower its price.
D)capital is usually price elastic.
E)the firm will want to hire fewer workers when the wage rate increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Ally owns a shoe store.The market wage is $10 per hour, and the cost of capital is $2 per week for every $1,000 of capital borrowed.Consider the isocost line associated with spending $8,000 per week, and let the y-axis be the amount of capital borrowed in $1,000s.Which of the following is not true?
A)If Ally borrows no capital, she can employ 800 hours of work.
B)If Ally employs no workers, she can borrow $4 million of capital.
C)If Ally employs 600 hours of work, she can borrow $1 million of capital.
D)If Ally employs 400 hours of work, she can borrow $3 million of capital.
E)The slope of the isocost line is -5.
A)If Ally borrows no capital, she can employ 800 hours of work.
B)If Ally employs no workers, she can borrow $4 million of capital.
C)If Ally employs 600 hours of work, she can borrow $1 million of capital.
D)If Ally employs 400 hours of work, she can borrow $3 million of capital.
E)The slope of the isocost line is -5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the United States, the federal minimum wage is legislated in nominal terms.This means that
A)the federal minimum wage is indexed for inflation.
B)the federal minimum wage historically decreases in value during stretches when the minimum wage is not increased.
C)employers do not have to pay payroll taxes on wages paid to minimum wage workers.
D)unemployed workers collect government assistance equal to the minimum wage.
E)the government pays the minimum wage to all local, state, and federal workers.
A)the federal minimum wage is indexed for inflation.
B)the federal minimum wage historically decreases in value during stretches when the minimum wage is not increased.
C)employers do not have to pay payroll taxes on wages paid to minimum wage workers.
D)unemployed workers collect government assistance equal to the minimum wage.
E)the government pays the minimum wage to all local, state, and federal workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is the most accurate description of the value of a worker to the firm?
A)The wage.
B)The firm's total output when holding capital fixed.
C)The firm's average product when holding capital fixed.
D)The dollar value of the worker's output.
E)The dollar value of the average worker's output.
A)The wage.
B)The firm's total output when holding capital fixed.
C)The firm's average product when holding capital fixed.
D)The dollar value of the worker's output.
E)The dollar value of the average worker's output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For which reason is increasing the federal minimum wage not a good anti-poverty program?
A)It is very costly for the government.
B)Roughly two-thirds of minimum wage earners are not the primary worker in their household.
C)Increasing the federal minimum wage will likely increase employment opportunities.
D)The minimum wage discriminates against minorities.
E)The minimum wage discriminates against the young.
A)It is very costly for the government.
B)Roughly two-thirds of minimum wage earners are not the primary worker in their household.
C)Increasing the federal minimum wage will likely increase employment opportunities.
D)The minimum wage discriminates against minorities.
E)The minimum wage discriminates against the young.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Why is the short-run labor demand curve less elastic relative to the long-run labor demand curve?
A)Because firms care about changes in wages in the short-run but not in the long-run.
B)Because firms are better able to substitute capital for labor in the long run compared to the short run.
C)Because labor is a normal good.
D)Because a perfectly competitive firm can always pay lower wages in the long run.
E)Because isocost curves get shallower when the wage increases.
A)Because firms care about changes in wages in the short-run but not in the long-run.
B)Because firms are better able to substitute capital for labor in the long run compared to the short run.
C)Because labor is a normal good.
D)Because a perfectly competitive firm can always pay lower wages in the long run.
E)Because isocost curves get shallower when the wage increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consider the following hypothetical difference-in-differences results concerning the average of hours worked in "big-box stores" between North and South Dakota before and after North Dakota increased its minimum wage.The minimum wage increase is associated with average hours of working decreasing by how much per week in North Dakota relative to South Dakota? 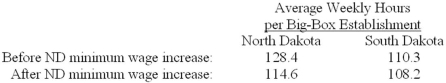
A)2.1 hours
B)11.7 hours
C)13.8 hours
D)15.9 hours
E)20.2 hours
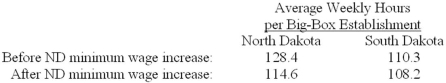
A)2.1 hours
B)11.7 hours
C)13.8 hours
D)15.9 hours
E)20.2 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the U.S.labor market, it is typically the case that:
A)If job creation is high, then job destruction is low.
B)If job creation is low, then job destruction is high.
C)There is relatively little job destruction during economic up-turns.
D)There is relatively little job creation during economic down-turns.
E)There is a large amount of job creation and job destruction happening at the same time, during both expansions and contractions.
A)If job creation is high, then job destruction is low.
B)If job creation is low, then job destruction is high.
C)There is relatively little job destruction during economic up-turns.
D)There is relatively little job creation during economic down-turns.
E)There is a large amount of job creation and job destruction happening at the same time, during both expansions and contractions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Adjustment costs are those costs
A)incurred by a firm as it transports its product from the factory to the marketplace.
B)incurred by a firm when it pays its workers overtime.
C)incurred by a firm as it changes the size of its workforce.
D)saved by a firm as it takes advantage of tax credits offered by the government.
E)saved by the firm when it fires a worker.
A)incurred by a firm as it transports its product from the factory to the marketplace.
B)incurred by a firm when it pays its workers overtime.
C)incurred by a firm as it changes the size of its workforce.
D)saved by a firm as it takes advantage of tax credits offered by the government.
E)saved by the firm when it fires a worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The marginal rate of technical substitution at any particular labor-capital bundle is
A)the slope of the isoquant.
B)the average product of labor relative to the average product of capital.
C)the wage relative to the cost of capital.
D)the slope of the indifference curve.
E)the ratio of labor to capital.
A)the slope of the isoquant.
B)the average product of labor relative to the average product of capital.
C)the wage relative to the cost of capital.
D)the slope of the indifference curve.
E)the ratio of labor to capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the minimum wage applies to one sector (the covered sector) but not another sector (the uncovered sector), an increase in the minimum wage in the covered sector is likely to result in which of the following?
A)Greater employment in the covered sector.
B)Less employment in the uncovered sector.
C)A lower wage in the covered sector.
D)A lower wage in the uncovered sector.
E)Workers willingly leaving the covered sector for the uncovered sector in search of higher wages.
A)Greater employment in the covered sector.
B)Less employment in the uncovered sector.
C)A lower wage in the covered sector.
D)A lower wage in the uncovered sector.
E)Workers willingly leaving the covered sector for the uncovered sector in search of higher wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The cross-elasticity of labor with respect to capital is
A)the change in labor relative to a change in capital.
B)the change in wages relative to a change in the price of capital.
C)the percent change in labor relative to a percent change in capital.
D)the percent change in wages relative to a percent change in the price of capital.
E)the percent change in labor relative to a percent change in the price of capital.
A)the change in labor relative to a change in capital.
B)the change in wages relative to a change in the price of capital.
C)the percent change in labor relative to a percent change in capital.
D)the percent change in wages relative to a percent change in the price of capital.
E)the percent change in labor relative to a percent change in the price of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Firms usually face asymmetric variable adjustment costs because
A)hiring costs are typically high.
B)firing workers is relatively easy.
C)firing workers can be difficult and costly for legal reasons.
D)workers are reluctant to change jobs during a recession.
E)firms vary in size.
A)hiring costs are typically high.
B)firing workers is relatively easy.
C)firing workers can be difficult and costly for legal reasons.
D)workers are reluctant to change jobs during a recession.
E)firms vary in size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



