Deck 9: Short-Term Profit Planning: Cost-Volume-Profit Cvp Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Short-Term Profit Planning: Cost-Volume-Profit Cvp Analysis
1
The breakeven point is:
A)The sales volume at which revenues equal total cost plus an operating profit of zero.
B)The sales volume at which revenues equal variable cost and profit is zero.
C)The sales volume at which revenues equal fixed cost and profit is zero.
D)The point at which revenues meet the budget target.
E)The sales volume at which the total contribution margin exceeds total variable costs.
A)The sales volume at which revenues equal total cost plus an operating profit of zero.
B)The sales volume at which revenues equal variable cost and profit is zero.
C)The sales volume at which revenues equal fixed cost and profit is zero.
D)The point at which revenues meet the budget target.
E)The sales volume at which the total contribution margin exceeds total variable costs.
A
2
The contribution margin per unit multiplied by the number of units sold is the:
A)Segment margin.
B)Total contribution margin (CM).
C)Contribution margin ratio.
D)Margin of safety (MOS).
E)Breakeven point.
A)Segment margin.
B)Total contribution margin (CM).
C)Contribution margin ratio.
D)Margin of safety (MOS).
E)Breakeven point.
B
3
Calculating the margin of safety (MOS) measure will help a firm answer which of the following questions?
A)Will we break even?
B)Are we using our debt wisely?
C)How much will profits change if sales change?
D)How much profit will we earn?
E)How much revenue can we lose before we drop below the breakeven point?
A)Will we break even?
B)Are we using our debt wisely?
C)How much will profits change if sales change?
D)How much profit will we earn?
E)How much revenue can we lose before we drop below the breakeven point?
E
4
CVP analysis with multiple products assumes that sales will continue at the same mix of products, expressed in either sales units or sales dollars. This assumption is essential, because a change in the product mix will probably change:
A)The average sales price per unit.
B)The average variable cost per unit.
C)The weighted-average contribution margin (per unit or ratio).
D)The total fixed cost.
E)The average contribution margin (per unit or ratio).
A)The average sales price per unit.
B)The average variable cost per unit.
C)The weighted-average contribution margin (per unit or ratio).
D)The total fixed cost.
E)The average contribution margin (per unit or ratio).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which one of the following is the most useful measure for comparing the risk of two alternative products?
A)Contribution margin ratio.
B)Margin of safety ratio (MOS%).
C)Financial leverage.
D)Breakeven point.
E)Regression analysis.
A)Contribution margin ratio.
B)Margin of safety ratio (MOS%).
C)Financial leverage.
D)Breakeven point.
E)Regression analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In measuring the variable cost per unit, CVP analysis includes:
A)Only variable production costs.
B)Only variable distribution and selling costs.
C)Both variable production and variable selling/distribution costs.
D)Only variable and semi-variable production costs.
A)Only variable production costs.
B)Only variable distribution and selling costs.
C)Both variable production and variable selling/distribution costs.
D)Only variable and semi-variable production costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A relatively low margin of safety ratio (MOS%) for a product is usually an indication that the product:
A)Is losing money.
B)Has a high contribution margin.
C)Is riskier than a product with a higher margin of safety ratio.
D)Is less risky than a product with a higher margin of safety ratio.
E)Requires heavy fixed cost to produce or sell.
A)Is losing money.
B)Has a high contribution margin.
C)Is riskier than a product with a higher margin of safety ratio.
D)Is less risky than a product with a higher margin of safety ratio.
E)Requires heavy fixed cost to produce or sell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
High operating leverage represents increased risk associated with relatively:
A)High variable costs in the firm's cost structure.
B)High fixed cost in the firm's cost structure.
C)High sales revenue combined with high variable costs.
D)High asset turnover.
E)High levels of unit-level (i.e., volume-related) costs.
A)High variable costs in the firm's cost structure.
B)High fixed cost in the firm's cost structure.
C)High sales revenue combined with high variable costs.
D)High asset turnover.
E)High levels of unit-level (i.e., volume-related) costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The annual breakeven point in dollar sales is calculated to be:
A)$504,000.
B)$576,000.
C)$468,000.
D)$612,000.
E)$540,000.
A)$504,000.
B)$576,000.
C)$468,000.
D)$612,000.
E)$540,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which one of the following is defined, at any given sales volume, as the ratio of the total contribution margin to operating profit at that sales volume?
A)Contribution margin ratio.
B)Margin of safety ratio (MOS%).
C)Degree of operating leverage (DOL).
D)Breakeven point.
E)Margin of safety (MOS).
A)Contribution margin ratio.
B)Margin of safety ratio (MOS%).
C)Degree of operating leverage (DOL).
D)Breakeven point.
E)Margin of safety (MOS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The difference between sales price per unit and variable cost per unit is the:
A)Contribution margin per unit (cm).
B)Total contribution margin (CM).
C)Contribution margin ratio.
D)Margin of safety (MOS).
E)Breakeven point.
A)Contribution margin per unit (cm).
B)Total contribution margin (CM).
C)Contribution margin ratio.
D)Margin of safety (MOS).
E)Breakeven point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The CVP profit-planning model assumes that over the relevant range of activity:
A)Only revenues are linear.
B)Only revenues and fixed costs are linear.
C)Only revenues and variable costs are linear.
D)Variable cost per unit decreases because of increases in productivity.
E)Both revenues and total costs are linear.
A)Only revenues are linear.
B)Only revenues and fixed costs are linear.
C)Only revenues and variable costs are linear.
D)Variable cost per unit decreases because of increases in productivity.
E)Both revenues and total costs are linear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
CVP analysis for revenue and cost planning has the primary objective of:
A)Maximizing revenue.
B)Minimizing costs.
C)Both revenue maximization and cost minimization.
D)Achieving a desired level of sales and profits.
E)Consistently producing sales above the breakeven level.
A)Maximizing revenue.
B)Minimizing costs.
C)Both revenue maximization and cost minimization.
D)Achieving a desired level of sales and profits.
E)Consistently producing sales above the breakeven level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
CVP analysis using activity-based costs will tend to shift some costs from fixed to variable classifications, resulting in:
A)Lower breakeven sales.
B)Higher breakeven sales.
C)Higher or lower breakeven sales, depending on batch size.
D)A higher contribution margin per unit.
E)A lower contribution margin per unit.
A)Lower breakeven sales.
B)Higher breakeven sales.
C)Higher or lower breakeven sales, depending on batch size.
D)A higher contribution margin per unit.
E)A lower contribution margin per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which one of the following is not included as a factor in CVP analysis?
A)Total fixed costs.
B)Variable cost per unit.
C)Desired (targeted) profit.
D)Selling price per unit.
E)Expected production level.
A)Total fixed costs.
B)Variable cost per unit.
C)Desired (targeted) profit.
D)Selling price per unit.
E)Expected production level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In performing short-term CVP analysis for a new product or service, the decision-maker would:
A)Include all current and future fixed costs.
B)Include only current fixed costs.
C)Include only future fixed costs.
D)Include only incremental fixed costs.
E)Include only allocated fixed costs.
A)Include all current and future fixed costs.
B)Include only current fixed costs.
C)Include only future fixed costs.
D)Include only incremental fixed costs.
E)Include only allocated fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The annual breakeven point in unit sales is calculated to be:
A)15,000 units.
B)14,000 units.
C)16,000 units.
D)13,000 units.
E)17,000 units.
A)15,000 units.
B)14,000 units.
C)16,000 units.
D)13,000 units.
E)17,000 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The contribution income statement would require a firm to:
A)Separate costs into fixed and variable categories.
B)Separate revenue into different categories.
C)Round off amounts to the nearest dollar.
D)Ignore some estimated fixed expenses, such as depreciation, that don't involve a cash outlay.
E)Restructure its accounting system to accommodate activity-based costing
A)Separate costs into fixed and variable categories.
B)Separate revenue into different categories.
C)Round off amounts to the nearest dollar.
D)Ignore some estimated fixed expenses, such as depreciation, that don't involve a cash outlay.
E)Restructure its accounting system to accommodate activity-based costing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
From a strategic management perspective, the primary reason a firm performs CVP analysis is to find the level of sales that:
A)Produces a desired (or targeted) level of profit for the firm.
B)Will allow the firm to compete in a market place.
C)Will just cover all fixed costs.
D)Promises a satisfactory growth in revenue.
E)Reduces the threat of bankruptcy.
A)Produces a desired (or targeted) level of profit for the firm.
B)Will allow the firm to compete in a market place.
C)Will just cover all fixed costs.
D)Promises a satisfactory growth in revenue.
E)Reduces the threat of bankruptcy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not an underlying assumption of a conventional CVP analysis?
A)Learning-curve effects (i.e., productivity gains with experience)
B)Fixed costs, in total, do not change as sales mix or total sales volume change.
C)Selling price per unit is unrelated to assumed sales volume.
D)Inputs to the profit-planning model are known with certainty.
E)Variable costs per unit are unrelated to changes in volume.
A)Learning-curve effects (i.e., productivity gains with experience)
B)Fixed costs, in total, do not change as sales mix or total sales volume change.
C)Selling price per unit is unrelated to assumed sales volume.
D)Inputs to the profit-planning model are known with certainty.
E)Variable costs per unit are unrelated to changes in volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The annual breakeven point, in dollar sales, is calculated to be:
A)$4,800,000.
B)$4,500,000.
C)$4,100,000.
D)$4,600,000.
E)$4,300,000.
A)$4,800,000.
B)$4,500,000.
C)$4,100,000.
D)$4,600,000.
E)$4,300,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The annual breakeven point in sales dollars for X Company is:
A)$102,857.
B)$90,000.
C)$63,000.
D)$110,769.
E)$91,657.
A)$102,857.
B)$90,000.
C)$63,000.
D)$110,769.
E)$91,657.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
X Company's degree of operating leverage (DOL) at the current sales volume level is calculated to be:
A)4.00
B)5.00
C)7.00
D)6.00
E)3.00
A)4.00
B)5.00
C)7.00
D)6.00
E)3.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
X Company's margin of safety ratio (MOS%) is calculated to be:
A)7.69%.
B)14.29%.
C)23.62%.
D)47.50%.
E)25.00%.
A)7.69%.
B)14.29%.
C)23.62%.
D)47.50%.
E)25.00%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The annual breakeven point, in unit sales, is:
A)15,000 units.
B)24,000 units.
C)36,000 units.
D)13,000 units.
E)19,000 units.
A)15,000 units.
B)24,000 units.
C)36,000 units.
D)13,000 units.
E)19,000 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Becker Sofa Company's margin of safety (MOS) in sales dollars is:
A)$36,200,000.
B)$42,600,000.
C)$33,300,000.
D)$46,700,000.
E)$39,100,000.
A)$36,200,000.
B)$42,600,000.
C)$33,300,000.
D)$46,700,000.
E)$39,100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Staley Co.'s operating income is calculated to be:
A)$19,800.
B)$21,800.
C)$24,800.
D)$23,800.
E)$20,800.
A)$19,800.
B)$21,800.
C)$24,800.
D)$23,800.
E)$20,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Power Cords Corp.'s margin of safety (MOS) in units is:
A)48,800.
B)39,000.
C)40,900.
D)36,100.
E)32,500.
A)48,800.
B)39,000.
C)40,900.
D)36,100.
E)32,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Power Cord Corp.'s margin of safety ratio (MOS%) is (rounded to two decimal points):
A)91.59%.
B)97.38%.
C)90.71%.
D)99.47%.
E)93.15%.
A)91.59%.
B)97.38%.
C)90.71%.
D)99.47%.
E)93.15%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
OutlyTech's margin of safety (MOS) in units is (rounded up to nearest whole number):
A)18,270.
B)17,100.
C)20,880.
D)16,970.
E)22,190.
A)18,270.
B)17,100.
C)20,880.
D)16,970.
E)22,190.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If 24,000 hats were sold, Grant's operating income would be:
A)$100,800.
B)$115,200.
C)$93,600.
D)$108,000.
E)$122,400.
A)$100,800.
B)$115,200.
C)$93,600.
D)$108,000.
E)$122,400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is Staley Co.'s margin of safety (MOS), in units, if 600 units are sold and all costs and revenues are as budgeted? (Round intermediate calculation up to nearest whole number of units.)
A)123.
B)242.
C)128.
D)141.
E)214.1. Break-even point, in units = Fixed costs ÷ contribution margin per unit = $80,000 (given) ÷ $168/unit (given) = 477 units (rounded up)
A)123.
B)242.
C)128.
D)141.
E)214.1. Break-even point, in units = Fixed costs ÷ contribution margin per unit = $80,000 (given) ÷ $168/unit (given) = 477 units (rounded up)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
OutlyTech's margin of safety ratio (MOS%) is:
A)71.25%.
B)87.00%.
C)70.25%.
D)92.50%.
E)76.15%.
A)71.25%.
B)87.00%.
C)70.25%.
D)92.50%.
E)76.15%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The annual breakeven point in unit sales is calculated to be:
A)1,600 units.
B)2,000 units.
C)3,400 units.
D)1,300 units.
E)2,600 units.
A)1,600 units.
B)2,000 units.
C)3,400 units.
D)1,300 units.
E)2,600 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
OutlyTech's margin of safety (MOS) in sales dollars is:
A)$76,577,000.
B)$87,517,000.
C)$82,044,000.
D)$54,720,000.
E)$66,900,000.
A)$76,577,000.
B)$87,517,000.
C)$82,044,000.
D)$54,720,000.
E)$66,900,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The annual breakeven point in dollar sales is calculated to be:
A)$1,300,000.
B)$1,500,000.
C)$1,100,000.
D)$1,600,000.
E)$1,800,000.
A)$1,300,000.
B)$1,500,000.
C)$1,100,000.
D)$1,600,000.
E)$1,800,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Staley Co.'s margin of safety ratio (MOS%) if 600 units are sold, is calculated to be:
A)33.4%.
B)17.7%.
C)20.5%.
D)19.5%.
E)79.5%.
A)33.4%.
B)17.7%.
C)20.5%.
D)19.5%.
E)79.5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If 4,000 bed frames were sold, Premium Bed's operating income would be:
A)$1,240,000.
B)$1,280,000.
C)$1,200,000.
D)$1,340,000.
E)$1,120,000.
A)$1,240,000.
B)$1,280,000.
C)$1,200,000.
D)$1,340,000.
E)$1,120,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If an $18,000 increase in the advertising budget would increase monthly sales by $60,000, the new level of operating income for Staley Co. would be:
A)$19,800.
B)$21,800.
C)$24,800.
D)$23,800.
E)$20,800.
A)$19,800.
B)$21,800.
C)$24,800.
D)$23,800.
E)$20,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If 40,000 office chairs were sold, Stylish Sitting's operating income would be:
A)$240,000.
B)$280,000.
C)$210,000.
D)$340,000.
E)$120,000.
A)$240,000.
B)$280,000.
C)$210,000.
D)$340,000.
E)$120,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The sales dollars required for Kelvin Co. to make a before-tax profit of $10,000 are:
A)$300,000.
B)$309,000.
C)$276,000.
D)$306,000.
E)$312,000.
A)$300,000.
B)$309,000.
C)$276,000.
D)$306,000.
E)$312,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Assuming that sales mix remains constant in dollars, what is the breakeven point in dollars? (Round intermediate calculations to 4 decimal places and final answer up to the nearest whole number.)
A)$244,765.
B)$306,513.
C)$118,365.
D)$945,667.
E)$288,735.
A)$244,765.
B)$306,513.
C)$118,365.
D)$945,667.
E)$288,735.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When using cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis, the following information helps to show how decisions affect operating income except:
A)Variable costs.
B)Fixed costs.
C)Output level.
D)Gross margin.
E)Sales volume.
A)Variable costs.
B)Fixed costs.
C)Output level.
D)Gross margin.
E)Sales volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is Staley Co.'s degree of operating leverage (DOL) at this sales volume? (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
A)5.118.
B)4.405.
C)5.630.
D)5.000.
E)4.846.
A)5.118.
B)4.405.
C)5.630.
D)5.000.
E)4.846.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The sales dollars required to make an after-tax profit for Kelvin Co. of $15,000, given an income tax rate of 40%, are calculated to be:
A)$336,000.
B)$339,000.
C)$342,000.
D)$360,000.
E)$345,000.
A)$336,000.
B)$339,000.
C)$342,000.
D)$360,000.
E)$345,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The sales units required by Framing House to make a before-tax profit of $15,000 are calculated to be:
A)16,850 units.
B)11,625 units.
C)20,675 units.
D)28,350 units.
E)18,125 units.
A)16,850 units.
B)11,625 units.
C)20,675 units.
D)28,350 units.
E)18,125 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The sales dollars required by Framing House to make an after-tax profit of $10,000, given an income tax rate of 20 percent, are calculated to be (round intermediate calculation(s) to nearest whole number):
A)$436,500
B)$439,000
C)$442,750
D)$460,000
E)$445,325
A)$436,500
B)$439,000
C)$442,750
D)$460,000
E)$445,325

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is not an assumption of conventional cost/volume/profit (CVP) analysis?
A)The variable cost per unit varies over the relevant range of activity.
B)The sales mix is unchanged over the relevant range of activity.
C)Total fixed cost is constant over the relevant range of activity.
D)Total variable cost changes in direct proportion to changes in the level of activity over the relevant range.
E)The total revenue function is linear within the relevant range.
A)The variable cost per unit varies over the relevant range of activity.
B)The sales mix is unchanged over the relevant range of activity.
C)Total fixed cost is constant over the relevant range of activity.
D)Total variable cost changes in direct proportion to changes in the level of activity over the relevant range.
E)The total revenue function is linear within the relevant range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The sales in units required by Framing House to make an after-tax profit of $10,000, given an income tax rate, t, of 20%, are calculated to be (round up to nearest whole unit):
A)17,734 units.
B)16,583 units.
C)17,813 units.
D)17,049 units.
E)16,366 units.
A)17,734 units.
B)16,583 units.
C)17,813 units.
D)17,049 units.
E)16,366 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following equations is correct for determining the required sales in units to generate a targeted amount of pre-tax income under the equation method (where Q= sales in units, F = total fixed costs, πB = pre-tax profit, v = variable cost per unit, and p = selling price per unit)?
A)vQ + F + πB - pQ = 0.
B)vQ - F + πB - pQ = 0.
C)F - πB - vQ - pQ = 0.
D)pQ + vQ + F + πB = 0.
E)πB = F × (p - c)Q.
A)vQ + F + πB - pQ = 0.
B)vQ - F + πB - pQ = 0.
C)F - πB - vQ - pQ = 0.
D)pQ + vQ + F + πB = 0.
E)πB = F × (p - c)Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Cost-volume-profit (CVP) relationships that are curvilinear may be analyzed linearly by considering only:
A)Fixed and semi-variable costs.
B)Relevant fixed costs.
C)Relevant variable costs.
D)A relevant range of volume.
E)The multi-product/multi-service context.
A)Fixed and semi-variable costs.
B)Relevant fixed costs.
C)Relevant variable costs.
D)A relevant range of volume.
E)The multi-product/multi-service context.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Assuming that sales mix remains constant in units, what is the breakeven point in total units? (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places and final answer to the nearest whole number.)
A)687.
B)711.
C)805.
D)945.
E)1,006.
A)687.
B)711.
C)805.
D)945.
E)1,006.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The sales units required for Kelvin Co. to make an after-tax profit of $15,000, given an income tax rate of 40%, are:
A)47,500 units.
B)56,500 units.
C)65,661 units.
D)60,000 units.
E)57,500 units.
A)47,500 units.
B)56,500 units.
C)65,661 units.
D)60,000 units.
E)57,500 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following factors is not involved in studying cost/volume/profit (CVP) relationships?
A)Desired profit, expressed on an after-tax basis.
B)Variable cost per unit.
C)Total fixed costs.
D)Product (or service) mix.
E)Actual sales volume.
A)Desired profit, expressed on an after-tax basis.
B)Variable cost per unit.
C)Total fixed costs.
D)Product (or service) mix.
E)Actual sales volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
At the breakeven point, total fixed cost is:
A)Less than the total contribution margin.
B)Equal to the total contribution margin.
C)More than the total contribution margin.
D)Equal to the contribution margin per unit.
E)Equal to the contribution margin divided by operating income.
A)Less than the total contribution margin.
B)Equal to the total contribution margin.
C)More than the total contribution margin.
D)Equal to the contribution margin per unit.
E)Equal to the contribution margin divided by operating income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The sales dollars required to make a before-tax profit of $20,000 for Framing House are calculated to be:
A)$445,650.
B)$468,750.
C)$476,350.
D)$406,150.
E)$412,050.
A)$445,650.
B)$468,750.
C)$476,350.
D)$406,150.
E)$412,050.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The sales units required for Kelvin Co. to make a before-tax profit of $12,000 are:
A)46,000 units.
B)51,500 units.
C)50,000 units.
D)51,000 units.
E)52,000 units.
A)46,000 units.
B)51,500 units.
C)50,000 units.
D)51,000 units.
E)52,000 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The following information pertains to Korning Corp:  How many total units must be sold to obtain an after-tax profit of $47,775?
How many total units must be sold to obtain an after-tax profit of $47,775?
A)780 units.
B)894 units.
C)955 units.
D)1,021 units.
 How many total units must be sold to obtain an after-tax profit of $47,775?
How many total units must be sold to obtain an after-tax profit of $47,775?A)780 units.
B)894 units.
C)955 units.
D)1,021 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Nantucket Company has the following cost-volume-profit (CVP) relationships:  What is the variable cost per unit?
What is the variable cost per unit?
A)$515.00.
B)$562.50.
C)$625.00.
D)$655.25.
E)$62.50.
 What is the variable cost per unit?
What is the variable cost per unit?A)$515.00.
B)$562.50.
C)$625.00.
D)$655.25.
E)$62.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Cost/volume/profit (CVP) analysis is a technique available to management to understand better the interrelationships of several factors that combine to determine a firm's profit. As with many such techniques, the accountant oversimplifies the real world by making assumptions. Which of the following is not a major assumption underlying CVP analysis?
A)All costs incurred by a firm can be separated into their fixed and variable components.
B)The product selling price per unit is affected by changes in volume levels.
C)Operating efficiency and employee productivity are constant at all volume levels.
D)In multi-product situations, the sales mix changes as volume changes.
E)Total costs vary only with changes in sales volume.
A)All costs incurred by a firm can be separated into their fixed and variable components.
B)The product selling price per unit is affected by changes in volume levels.
C)Operating efficiency and employee productivity are constant at all volume levels.
D)In multi-product situations, the sales mix changes as volume changes.
E)Total costs vary only with changes in sales volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Cleaning Care's margin of safety ratio (MOS%) is:
A)20%.
B)40%.
C)80%.
D)85%.
E)90%
A)20%.
B)40%.
C)80%.
D)85%.
E)90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
EZ Carry Corp. is the maker of high quality golf bags. They currently have three different lines of bags, which they sell to sporting goods and golf shops throughout the world. EZ Carry sells a constant mix of 4 small bags for each medium-sized bag and 5 medium bags for each large-sized bag. Total fixed costs for the year are expected to be $2,027,562. (Note: round all decimals to three decimal places.) 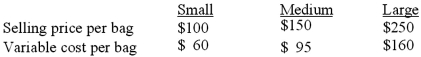 The breakeven point in units (for the year) would be:
The breakeven point in units (for the year) would be:
A)32,400 small, 8,100 medium, 1,620 large.
B)34,808 small, 8,700 medium, 1,740 large.
C)37,010 small, 9250 medium, 1,850 large.
D)38,505 small, 9,625 medium, 1,925 large.
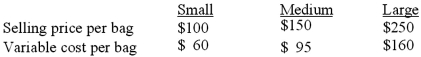 The breakeven point in units (for the year) would be:
The breakeven point in units (for the year) would be:A)32,400 small, 8,100 medium, 1,620 large.
B)34,808 small, 8,700 medium, 1,740 large.
C)37,010 small, 9250 medium, 1,850 large.
D)38,505 small, 9,625 medium, 1,925 large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Calculating the margin of safety (MOS) measure will help a firm answer which of the following questions?
A)Will we break even?
B)Are we using our debt wisely?
C)How much will profits change if sales change?
D)How much profit will we earn?
E)How much revenue can we lose before we drop below the breakeven point?
A)Will we break even?
B)Are we using our debt wisely?
C)How much will profits change if sales change?
D)How much profit will we earn?
E)How much revenue can we lose before we drop below the breakeven point?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Cleaning Care's margin of safety (MOS) in sales dollars is:
A)$12,000.
B)$24,000.
C)$48,000.
D)$50,000.
E)$96,000.
A)$12,000.
B)$24,000.
C)$48,000.
D)$50,000.
E)$96,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The form of the income statement that is used in CVP analysis is referred to as:
A)An activity-based cost (ABC) income statement.
B)A contribution income statement.
C)An absorption costing income statement.
D)A flexible-budget income statement.
E)A segment profitability report.
A)An activity-based cost (ABC) income statement.
B)A contribution income statement.
C)An absorption costing income statement.
D)A flexible-budget income statement.
E)A segment profitability report.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Cathy's Towels sells three items (which it purchases from a supplier): bath towels, hand towels, and washcloths in a 4:3:2 mix (thus, a batch of 9 towels has 4 bath towels, 3 hand towels, and 2 washcloths). Each bath towel sells for $10 and costs $4, each hand towel sells for $5 and costs $2; and each washcloth sells for $2.50 and costs $1. The shop's annual fixed expenses are $324,000, and the income tax rate is 40%. How many bath towels must the firm sell at the breakeven point?
A)20,000.
B)36,000.
C)44,000.
D)51,000.
E)81,000.
A)20,000.
B)36,000.
C)44,000.
D)51,000.
E)81,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The calculation of an amount given different levels of a factor that influences that amount is called:
A)Sales-value analysis.
B)What-if analysis.
C)Factor analysis.
D)Cost analysis.
E)Profit Analysis.
A)Sales-value analysis.
B)What-if analysis.
C)Factor analysis.
D)Cost analysis.
E)Profit Analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The following information pertains to MacKenzie Corp: 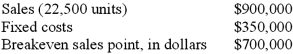 If the sales price per unit were to decrease by 5% and variable expenses were to increase by $2.00 per unit, which of the following is true?
If the sales price per unit were to decrease by 5% and variable expenses were to increase by $2.00 per unit, which of the following is true?
A)The new selling price is $36 per unit.
B)The new breakeven point is $831,250.
C)The new variable expenses are $18 per unit.
D)The new breakeven point is 21,750 units.
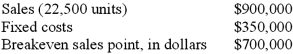 If the sales price per unit were to decrease by 5% and variable expenses were to increase by $2.00 per unit, which of the following is true?
If the sales price per unit were to decrease by 5% and variable expenses were to increase by $2.00 per unit, which of the following is true?A)The new selling price is $36 per unit.
B)The new breakeven point is $831,250.
C)The new variable expenses are $18 per unit.
D)The new breakeven point is 21,750 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The equation method for CVP analysis:
A)Can be used to determine the breakeven point in units sold but not in sales dollars.
B)Can be used to determine the breakeven point in sales dollars but not in units sold.
C)Cannot be used to determine the breakeven point in units sold.
D)Cannot be used to determine the breakeven point in sales dollars.
E)Can be used to determine the breakeven point in units sold or sales dollars.
A)Can be used to determine the breakeven point in units sold but not in sales dollars.
B)Can be used to determine the breakeven point in sales dollars but not in units sold.
C)Cannot be used to determine the breakeven point in units sold.
D)Cannot be used to determine the breakeven point in sales dollars.
E)Can be used to determine the breakeven point in units sold or sales dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Hart Company sold 5,000 units for a price of $50 per unit and had the following information: 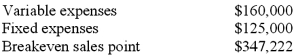 If the sales price per unit were to increase by 10%, variable expenses were to increase by 12.5% and fixed expenses were to increase by 20%, what would be the new contribution margin per unit?
If the sales price per unit were to increase by 10%, variable expenses were to increase by 12.5% and fixed expenses were to increase by 20%, what would be the new contribution margin per unit?
A)$19.
B)$21.
C)$23.
D)$25.
E)$32.
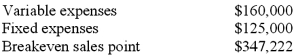 If the sales price per unit were to increase by 10%, variable expenses were to increase by 12.5% and fixed expenses were to increase by 20%, what would be the new contribution margin per unit?
If the sales price per unit were to increase by 10%, variable expenses were to increase by 12.5% and fixed expenses were to increase by 20%, what would be the new contribution margin per unit?A)$19.
B)$21.
C)$23.
D)$25.
E)$32.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The degree of operating leverage (DOL), at any sales volume, is equal to:
A)(Operating profit - fixed expenses) ÷ sales.
B)(Sales - variable expenses) ÷ operating profit.
C)Operating profit ÷ (fixed expenses - variable expenses).
D)Sales ÷ (fixed expenses - operating profit).
E)Fixed costs ÷ Total contribution margin.
A)(Operating profit - fixed expenses) ÷ sales.
B)(Sales - variable expenses) ÷ operating profit.
C)Operating profit ÷ (fixed expenses - variable expenses).
D)Sales ÷ (fixed expenses - operating profit).
E)Fixed costs ÷ Total contribution margin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Gralyn Corp. compares two products' margin of safety ratios (MOS%). Product A has a ratio of 0.13 and product B has a ratio of 0.31. Based on this information, what should the managers at Gralyn Corp. do and why?
A) They should choose Product A because it will cost less than half as much to produce.
B) They should choose Product A because it is less risky and might require less management attention than Product B.
C) They should choose Product B because it will produce more than double the profit of Product A.
D) They should choose Product B because it is less risky and might require less management attention than Product A.
A) They should choose Product A because it will cost less than half as much to produce.
B) They should choose Product A because it is less risky and might require less management attention than Product B.
C) They should choose Product B because it will produce more than double the profit of Product A.
D) They should choose Product B because it is less risky and might require less management attention than Product A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
JCH Sports plans to market a new product for the upcoming college season. Costs associated with the new product, at two different volume ranges, are as follows: 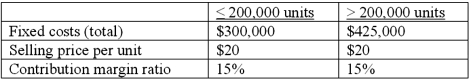 How many units must be sold in order to reach a before-tax income on the product of $400,000?
How many units must be sold in order to reach a before-tax income on the product of $400,000?
A)148,333.
B)385,000.
C)313,000.
D)275,000.
E)233,333.
 How many units must be sold in order to reach a before-tax income on the product of $400,000?
How many units must be sold in order to reach a before-tax income on the product of $400,000?A)148,333.
B)385,000.
C)313,000.
D)275,000.
E)233,333.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Label Corp. recorded sales of $2,235,245. The company's breakeven sales point (in dollars) is $1,650,000 and its margin of safety ratio (MOS%) at the current sales level is 27%. What sales are needed to increase the company's margin of safety ratio (MOS%) to 38%?
A)$2,277,000.
B)$2,661,290.
C)$2,932,640.
D)$3,024,050.
A)$2,277,000.
B)$2,661,290.
C)$2,932,640.
D)$3,024,050.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Effective use of the CVP (cost-volume-profit) model requires an understanding of all of the following concepts, except:
A)Contribution margin per unit.
B)Contribution margin ratio.
C)Contribution income statement.
D)Total cost of goods sold (CGS)
E)Variable versus fixed cost behavior patterns.
A)Contribution margin per unit.
B)Contribution margin ratio.
C)Contribution income statement.
D)Total cost of goods sold (CGS)
E)Variable versus fixed cost behavior patterns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following can use cost/volume/profit (CVP) analysis?
A)Not-for-profit organizations, but not service firms.
B)Service firms, but not organizations that are not-for-profit.
C)Not-for-profit organizations, service firms, and manufacturers.
D)Manufacturing firms, but not service firms.
A)Not-for-profit organizations, but not service firms.
B)Service firms, but not organizations that are not-for-profit.
C)Not-for-profit organizations, service firms, and manufacturers.
D)Manufacturing firms, but not service firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The name for a variety of methods used to examine how an amount will change if factors involved in predicting that amount change is:
A)Sensitivity analysis.
B)Contribution margin analysis.
C)Factor analysis.
D)Cost analysis.
E)Cost-volume-profit analysis.
A)Sensitivity analysis.
B)Contribution margin analysis.
C)Factor analysis.
D)Cost analysis.
E)Cost-volume-profit analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following illustrates how the level of operating profit changes over different levels of output/sales volume?
A)Revenue-volume graph.
B)Cost-revenue chart.
C)Revenue-cost graph.
D)Profit-volume graph.
E)Profit-cost graph.
A)Revenue-volume graph.
B)Cost-revenue chart.
C)Revenue-cost graph.
D)Profit-volume graph.
E)Profit-cost graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In measuring variable cost per unit for cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis purposes:
A)Only variable production costs are included.
B)Only variable selling/distribution costs are included.
C)Both variable production and variable selling/distribution costs are included.
D)Only variable and semi-variable production costs are included.
E)The amount assumed is a function of anticipated output volume.
A)Only variable production costs are included.
B)Only variable selling/distribution costs are included.
C)Both variable production and variable selling/distribution costs are included.
D)Only variable and semi-variable production costs are included.
E)The amount assumed is a function of anticipated output volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Cleaning Care's margin of safety (MOS) in units is:
A)1,000.
B)2,000.
C)4,000.
D)8,000.
E)9,000.
A)1,000.
B)2,000.
C)4,000.
D)8,000.
E)9,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



