Deck 18: Personal Taxation and Behavior
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/31
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Personal Taxation and Behavior
1
The Laffer curve is
A)never referred to in modern day discussions of public finance.
B)a curve that describes the relationship between tax rates and tax revenues.
C)used to describe the relationship between consumption and hours worked.
D)a curve that refers to the endowment of time.
A)never referred to in modern day discussions of public finance.
B)a curve that describes the relationship between tax rates and tax revenues.
C)used to describe the relationship between consumption and hours worked.
D)a curve that refers to the endowment of time.
a curve that describes the relationship between tax rates and tax revenues.
2
An intertemporal budget constraint
A)requires an endowment point.
B)requires time to remain constant.
C)has no endowment point.
D)requires time to move in a loop.
A)requires an endowment point.
B)requires time to remain constant.
C)has no endowment point.
D)requires time to move in a loop.
requires an endowment point.
3
A compensation package offered by employers often includes
A)wages.
B)health benefits.
C)vacations.
D)pensions.
E)all of the above.
A)wages.
B)health benefits.
C)vacations.
D)pensions.
E)all of the above.
all of the above.
4
An individual's consumption and saving behavior during a given year,as a result of a planning process that considers his or her lifetime economic situations,is known as the
A)lifetime model.
B)consumption model.
C)life-cycle model.
D)income model.
A)lifetime model.
B)consumption model.
C)life-cycle model.
D)income model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An decrease in the interest rate will cause the intertemporal budget constraint to _______________ through the endowment point.
A)pivot clockwise
B)pivot counter-clockwise
C)shift clockwise
D)shift counter-clockwise
A)pivot clockwise
B)pivot counter-clockwise
C)shift clockwise
D)shift counter-clockwise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Real rates of return are
A)not taxed.
B)not adjusted for inflation.
C)adjusted for inflation.
D)used in individual financing and not corporate financing.
A)not taxed.
B)not adjusted for inflation.
C)adjusted for inflation.
D)used in individual financing and not corporate financing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The personal income tax excludes the imputed rent from owner-occupied housing from taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Human capital is
A)how firms use more humans than machines in the production process.
B)the accumulation of investments that make people more productive.
C)more costly than other forms of capital.
D)none of the above.
A)how firms use more humans than machines in the production process.
B)the accumulation of investments that make people more productive.
C)more costly than other forms of capital.
D)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An income effect
A)is measured as the change in prices over time.
B)is not possible when people are unemployed.
C)requires interest rates to remain constant.
D)is the change in the quantity demand due to the fact that real income changes when prices change.
A)is measured as the change in prices over time.
B)is not possible when people are unemployed.
C)requires interest rates to remain constant.
D)is the change in the quantity demand due to the fact that real income changes when prices change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the leisure-income model,taxing income causes
A)the budget constraint to kink.
B)males to work to change their work habits dramatically.
C)utility to increase.
D)all of the above.
A)the budget constraint to kink.
B)males to work to change their work habits dramatically.
C)utility to increase.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Social savings is
A)just another way of defining security.
B)the sum of government and private savings.
C)government savings only.
D)defined by higher rates of interest for the government.
A)just another way of defining security.
B)the sum of government and private savings.
C)government savings only.
D)defined by higher rates of interest for the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
On the Laffer curve,an increase in tax rates causes tax revenue to increase if the starting point is
A)to the right of the top.
B)exactly at the top.
C)to the left of the top.
D)to the farthest point to the right.
A)to the right of the top.
B)exactly at the top.
C)to the left of the top.
D)to the farthest point to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The consumption bundle that is available,if there are no exchanges with the market,is known as the
A)federal system.
B)endowment point.
C)Ramsey Rule.
D)Gross Replacement Rate.
A)federal system.
B)endowment point.
C)Ramsey Rule.
D)Gross Replacement Rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An example of a tax-preferred savings account would be
A)an IRA.
B)an interest bearing savings account.
C)a noninterest bearing checking account.
D)cash.
A)an IRA.
B)an interest bearing savings account.
C)a noninterest bearing checking account.
D)cash.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Residential housing consumption is not affected by U.S.personal income taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In 2009,President Obama proposed limiting the value of deductions for high-earners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
No profession in the United States has what is known as a "backward bending" supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The theoretical effects of taxation on portfolio composition are ambiguous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Full loss offset allows individuals to
A)claim children as dependents.
B)deduct mortgage interest from taxes.
C)deduct savings interest from taxes.
D)deduct capital losses from taxable income.
A)claim children as dependents.
B)deduct mortgage interest from taxes.
C)deduct savings interest from taxes.
D)deduct capital losses from taxable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
To accurately draw a labor supply curve,there should be a relationship between _______ and __________.
A)the wage rate;utility
B)total expenditures;the wage rate
C)the wage rate;hours worked
D)taxes;utility
A)the wage rate;utility
B)total expenditures;the wage rate
C)the wage rate;hours worked
D)taxes;utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the textbook,there was a discussion of the average numbers of hours worked in the US being around 34 hours per week.As you enter the work force,do you expect this number to increase or decrease?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Sometimes increases in the wage rate will cause individuals to work more hours.It is also the case that this same increase could cause people to work fewer hours.What is happening to cause this variance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Big Boi earns $4,000 and she wants to save it for retirement,which is 10 years away.She can either save it in a taxable account or put it into a Roth IRA.Suppose that Big Boi can receive an annual rate of return of 8 percent and her marginal tax rate is 25 percent.By the time she reaches retirement,how much money would she have in either option?
NOTE: Big Boi has to pay tax on the $4,000,so she cannot put the full amount into either the taxable account or the Roth IRA.
NOTE: Big Boi has to pay tax on the $4,000,so she cannot put the full amount into either the taxable account or the Roth IRA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Jennifer lives in two periods.In the first period,her income is fixed at $72,000;in the second,she is gets a 4% raise in her income.She can borrow and save at the market interest rate of 5 percent.
(A)Sketch her intertemporal budget constraint.
(B)Suppose that Jennifer is unable to lend at any rate of interest,although she can still borrow at 5 percent.Sketch her new intertemporal budget constraint.
(A)Sketch her intertemporal budget constraint.
(B)Suppose that Jennifer is unable to lend at any rate of interest,although she can still borrow at 5 percent.Sketch her new intertemporal budget constraint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A capital shortage results from insufficient capital to meet our national "needs."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose the labor supply equation is L = (W/3)- (4/3).The wage rate is initially 5.What is the amount of producer surplus here?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to Figure 18.7 in your textbook.The intercept point N is actually found by I1 + I0(1 + r).The intercept point M is calculated by I0 + I1/(1 + r).Show that the slope of the budget constraint is indeed 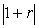
.
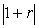
.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Refer to Figure 18.1 in your textbook.If the total number of hours (T)per week is 168 and the wage rate is $10,how much consumption is possible if the number of hours worked is 35? How does your answer change if the wage rate decreases to $8.50 but number of hours worked also increases to 40?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The analysis of a progressive tax is very similar to that of a proportional tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Returns to investments in human capital can be calculated with great accuracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The tax code in the United States allows for the deductibility of mortgage interest,but not for interest on credit cards.Why is this difference allowed to exist?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



