Deck 4: Public Goods
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Public Goods
1
Pure private goods are nonrival in consumption.
True
2
When asked to reveal their true preferences people
A)always tell the truth.
B)never tell the truth.
C)sometimes tell the truth.
D)generally don't know what preferences are.
A)always tell the truth.
B)never tell the truth.
C)sometimes tell the truth.
D)generally don't know what preferences are.
sometimes tell the truth.
3
The MRT is
A)the marginal ring tone.
B)the minimal rate of time.
C)the maximum rate of transformation.
D)none of the above.
A)the marginal ring tone.
B)the minimal rate of time.
C)the maximum rate of transformation.
D)none of the above.
none of the above.
4
Summing demand curves horizontally sends market ______________ to individuals,while summing vertically sends market ______________ to individuals.
A)price;price
B)quantity;quantity
C)quantity;price
D)price;quantity
A)price;price
B)quantity;quantity
C)quantity;price
D)price;quantity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Charging individual prices that are based on consumers' willingness to pay is
A)government price supports.
B)will pricing.
C)second tier pricing.
D)price discrimination.
A)government price supports.
B)will pricing.
C)second tier pricing.
D)price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is a public good?
A)public defense
B)public television
C)a library
D)schools
E)all of the above
A)public defense
B)public television
C)a library
D)schools
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The free rider problem causes less than optimal production of a public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A ________ is a person who wants to enjoy the benefits of a public good without contributing his or her marginal benefit to the cost of financing the amount made.
A)free rider
B)politician
C)price maker
D)price optimizer
A)free rider
B)politician
C)price maker
D)price optimizer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Equilibrium for public goods is characterized by
A)MSB = MSB.
B)( MRS = MRT).
C)MRS1 = MRS2 = MRS3=…= MRSn = MRT.
D)MC = MB.
E)MRS - MRT = MSB.
A)MSB = MSB.
B)( MRS = MRT).
C)MRS1 = MRS2 = MRS3=…= MRSn = MRT.
D)MC = MB.
E)MRS - MRT = MSB.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When those that do not contribute to the costs of a public good are denied use,this is a case of
A)exclusion.
B)being nonrival.
C)price discrimination.
D)infeasibility.
A)exclusion.
B)being nonrival.
C)price discrimination.
D)infeasibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Public goods can be
A)provided privately.
B)provided publicly.
C)subject to free rider problems.
D)all of the above.
A)provided privately.
B)provided publicly.
C)subject to free rider problems.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
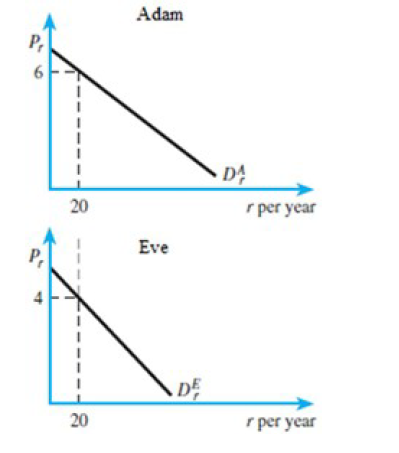
Figure 4.3
From Figure 4.3 ,the market price of rockets is
A)10.
B)4.
C)6.
D)20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Market mechanisms are unlikely to provide
A)prices.
B)nonrival goods efficiently.
C)supply and demand.
D)none of the above.
A)prices.
B)nonrival goods efficiently.
C)supply and demand.
D)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A private good is
A)nonrival in consumption.
B)subject to free rider problems.
C)not subject to exclusion.
D)subject to exclusion.
A)nonrival in consumption.
B)subject to free rider problems.
C)not subject to exclusion.
D)subject to exclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Commodity egalitarianism refers to commodities that
A)are important for most consumers.
B)are too dangerous for most consumers.
C)should be made available to all consumers.
D)are good ideas but never produced.
A)are important for most consumers.
B)are too dangerous for most consumers.
C)should be made available to all consumers.
D)are good ideas but never produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Congestible public goods
A)are nonrival in consumption.
B)cannot be priced in the market.
C)are rival in consumption.
D)are never provided by the private sector.
A)are nonrival in consumption.
B)cannot be priced in the market.
C)are rival in consumption.
D)are never provided by the private sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A pure private good is
A)nonrival in consumption and subject to exclusion.
B)rival in consumption and subject to exclusion.
C)rival in consumption and not subject to exclusion.
D)all of the above.
A)nonrival in consumption and subject to exclusion.
B)rival in consumption and subject to exclusion.
C)rival in consumption and not subject to exclusion.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
School vouchers are
A)provided by the government.
B)provided by private organizations.
C)public funds to be used for private tuition.
D)all of the above.
A)provided by the government.
B)provided by private organizations.
C)public funds to be used for private tuition.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Vertical summation of demand curves yield results equivalent to those of horizontal summation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Public goods are characterized by
A)nonrivalness.
B)excludability.
C)the sum of the MRSs equaling MRT.
D)all of the above.
A)nonrivalness.
B)excludability.
C)the sum of the MRSs equaling MRT.
D)all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Increasing the quantity of a pure public good can be done at zero cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Private goods are always provided by the private sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose there is a public good that has market supply characterized by the equation X = (P/3)- (32/3).Suppose further that market demand for this good can be characterized by the equation X = 25 -P.Find the equilibrium quantity of the public good that will be supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Demand curves for pure public goods satisfy the law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Discuss and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of public highways versus toll roads.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to "Discussion Questions" number 11 in your text.How does your answer change if the marginal cost of building each additional lighthouse increases to $150?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Pure public goods involve positive externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Some economists believe that public schools would improve if they were subjected to competition.Discuss the pros and cons of this idea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Use the answer you found when adding market demand curves vertically in Question 18 above to find the market equilibrium quantity if the market supply is constant at 4 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose you are given the following demand curves: Q = 32 - P and Q = 16 - (P/2).Add these two demand curves vertically and find the market demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose there are two individuals with identical demand curves characterized by the equation P = 2 - Q.What is market demand if these demand curves are added horizontally? Vertically?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Global Positioning System (GPS)is an example of a good that is both non-rival and excludable good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Some people do not engage in free riding,even when there is no cost or chance or reprisal.Discuss why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
You have read that the free rider problem affects equilibrium in a public good context.Explain how this situation can be modeled as a prisoner's dilemma game.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 34 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



