Deck 4: Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/123
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Demand
1
Draw two graphs,one directly above the other.On the upper graph,label the vertical axis Good X and label the horizontal axis Good Y.On the lower graph,label the vertical axis the Price of good Y and label the horizontal axis Good Y.In the upper graph,show the income and substitution effects of a decrease in the Price of good Y when Y is a Giffen good.Draw the corresponding demand curve for Good Y in the lower graph.
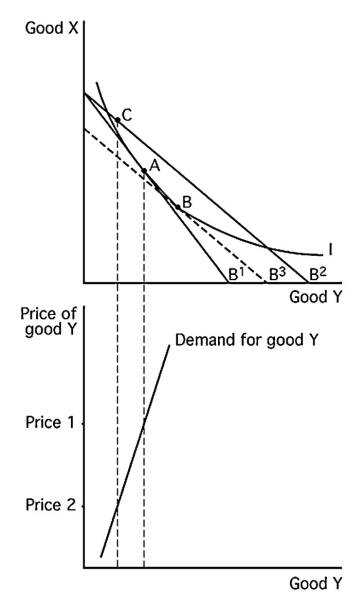 See the above figure.Point A is the original consumption point.The movement from point A to point B is the substitution effect.The movement from point B to point C is the income effect.
See the above figure.Point A is the original consumption point.The movement from point A to point B is the substitution effect.The movement from point B to point C is the income effect. 2
Use the Slutsky equation to show that a Giffen good must be an inferior good,BUT an inferior good need not be a Giffen good.
The Slutsky equation may be written as dQ/dpTotal = dQ/dpsubs - _(dQ/dI).For a Giffen good,dQ/dpTotal is positive,which implies that - _(dQ/dI)must be positive and large enough to offset dQ/dpsubs,which is always negative.For any inferior good,however,
- _(dQ/dI)is positive but not necessarily large enough to make dQ/dpTotal positive.
- _(dQ/dI)is positive but not necessarily large enough to make dQ/dpTotal positive.
3
An individual's demand curve for a good can be derived by measuring the quantities selected as
A)the price of the good changes.
B)the price of substitute goods changes.
C)income changes.
D)All of the above.
A)the price of the good changes.
B)the price of substitute goods changes.
C)income changes.
D)All of the above.
the price of the good changes.
4
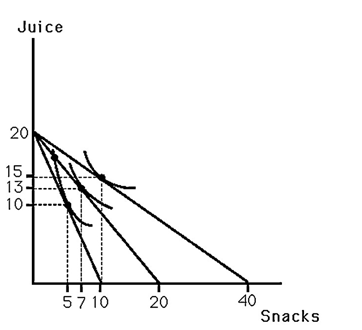
The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for juice and snacks.Also shown are three budget lines resulting from different prices for snacks assuming he has $20 to spend on these goods.Which of the following points are on Bobby's price-consumption curve?
A)10 snacks and 20 juices
B)10 snacks and 0 juices
C)10 snacks and 5 juices
D)10 snacks and 15 juices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for juice and snacks.Also shown are three budget lines resulting from different prices for snacks assuming he has $20 to spend on these goods.What is MRS for the point on Bobby's demand curve for snacks where price of snacks is $0.5?
A)-1
B)-0.5
C)-2
D)Not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the relevant price range a demand curve for a Giffen good would be
A)upward sloping.
B)downward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.
A)upward sloping.
B)downward sloping.
C)horizontal.
D)vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose the quantity of x is measured on the horizontal axis.If the price consumption curve is vertical when the price of x changes,then the demand for x is
A)perfectly elastic.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)There is not enough information to determine the price elasticity of demand for x.
A)perfectly elastic.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)unit elastic.
D)There is not enough information to determine the price elasticity of demand for x.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for juice and snacks.Also shown are three budget lines resulting from different prices for snacks.As the price of snacks rises,Bobby's utility
A)stays the same.
B)increases.
C)decreases.
D)might change,but there is not enough information to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for juice and snacks.Also shown are three budget lines resulting from different prices for snacks.As the price of snacks rises,the price for juice
A)stays the same.
B)increases.
C)decreases
D)might change,but there is not enough information to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for juice and snacks.Also shown are three budget lines resulting from different prices for snacks.Bobby's demand for snacks is
A)unit elastic.
B)elastic.
C)inelastic.
D)perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An increase in the price of a good causes
A)a change in the slope of the budget line.
B)an increase in the consumption of that good.
C)a rightward shift of the demand curve for that good.
D)a parallel rightward shift of the budget line.
A)a change in the slope of the budget line.
B)an increase in the consumption of that good.
C)a rightward shift of the demand curve for that good.
D)a parallel rightward shift of the budget line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
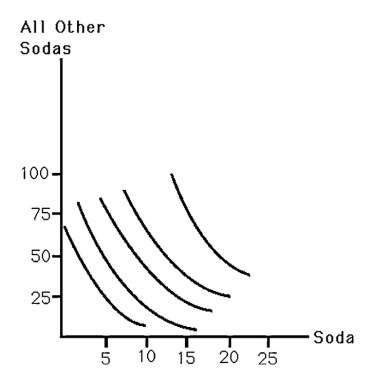
The above figure shows a consumer's indifference curves for soda and all other goods.Assuming a budget of $100,derive the consumer's demand for soda for prices of $4 and $10 per case of soda.Estimate the price elasticity of demand for soda.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As the price of a good rises,the consumer will experience
A)a desire to consume a different bundle.
B)a decrease in utility.
C)a southwesterly movement on the indifference map.
D)All of the above.
A)a desire to consume a different bundle.
B)a decrease in utility.
C)a southwesterly movement on the indifference map.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the price-consumption curve is upward sloping when the price of the good measured on the horizontal axis changes,then the demand curve for that good will be upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider a consumer with the Cobb-Douglas utility function U(q1,q2)= 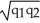
,where q1 and q2 are the quantities of goods 1 and 2 consumed,respectively.This consumer has an income denoted by Y which is devoted to goods 1 and 2.The prices of goods 1 and 2 are denoted p1 and p2.
a.What is this consumer's MRS as functions of q1 and q2?
b.Write out the Lagrangian for the consumer's utility maximization problem.
c.Using the Lagrangian method,derive the consumer's demand equations for both goods as functions of the variables p1,p2,and Y.
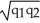
,where q1 and q2 are the quantities of goods 1 and 2 consumed,respectively.This consumer has an income denoted by Y which is devoted to goods 1 and 2.The prices of goods 1 and 2 are denoted p1 and p2.
a.What is this consumer's MRS as functions of q1 and q2?
b.Write out the Lagrangian for the consumer's utility maximization problem.
c.Using the Lagrangian method,derive the consumer's demand equations for both goods as functions of the variables p1,p2,and Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for juice and snacks.Also shown are three budget lines resulting from different prices for snacks.This information could be used to determine
A)the slope of Bobby's demand curve for juice.
B)the amount by which Bobby's demand curve for juice shifts when his income rises.
C)the amount by which Bobby's demand curve for juice shifts when the price of snacks rises.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for juice and snacks.Also shown are three budget lines resulting from different prices for snacks assuming he has $20 to spend on these goods.Which of the following points are on Bobby's demand curve for snacks?
A)p = 2,q = 10
B)p = 2,q = 13
C)p = 2,q = 5
D)p = 1,q = 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for juice and snacks.Also shown are three budget lines resulting from different prices for snacks.Bobby views snacks as a(n)
A)normal good.
B)inferior good.
C)Giffen good.
D)Not enough information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose a graph is drawn to show a consumer's preferences for football tickets and basketball tickets.The quantity of football tickets is measured on the horizontal axis.If the price-consumption curve is horizontal when the price of football tickets changes,then
A)football tickets are an inferior good.
B)the demand for football tickets is perfectly elastic.
C)the demand for football tickets is unit elastic.
D)the demand curve for football tickets will be horizontal.
A)football tickets are an inferior good.
B)the demand for football tickets is perfectly elastic.
C)the demand for football tickets is unit elastic.
D)the demand curve for football tickets will be horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for juice and snacks.Assuming income remains unchanged,when the budget line rotates out,the expenditure on snacks
A)increases.
B)decreases.
C)does not change.
D)Not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Darwin's preferences are given by U(q1,q2)= q1.5 + q2.Derive the demand equations for q1 and q2.Assume prices and income are such that both goods are consumed in strictly positive quantities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Edgar only consumes protein shakes with his income,I.The price of shakes is p.
a.What is Edgar's demand equation for shakes?
b.Can protein shakes be an inferior good for Edgar? Explain.
c.What is the price elasticity of Edgar's demand for shakes? Derive using calculus.
d.What is the income elasticity of Edgar's demand for shakes?
a.What is Edgar's demand equation for shakes?
b.Can protein shakes be an inferior good for Edgar? Explain.
c.What is the price elasticity of Edgar's demand for shakes? Derive using calculus.
d.What is the income elasticity of Edgar's demand for shakes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Jon spends all of his income on energy drinks (E)regardless of the price and his income.Derive Jon's demand equation for energy drinks,E*(p,Y).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When John's income was low,he could not afford to dine out and would respond to a pay raise by purchasing more frozen dinners.Now that his income is high,a pay raise causes him to dine out more often and buy fewer frozen dinners.Which graph in the above figure best represents John's Engel curve for dining out?
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25

When John's income was low,he could not afford to dine out and would respond to a pay raise by purchasing more frozen dinners.Now that his income is high,a pay raise causes him to dine out more often and buy fewer frozen dinners.Which graph in the above figure best represents John's Engel curve for frozen dinners?
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
After Joyce and Larry purchased their first house,they made additional home improvements in response to increases in income.After a while,their income rose so much that they could afford a larger home.Once they realized they would be moving,they reduced the amount of home improvements.Their Engel curve for home improvements on their current home is
A)negatively sloped.
B)flat.
C)positively sloped.
D)backward bending.
A)negatively sloped.
B)flat.
C)positively sloped.
D)backward bending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
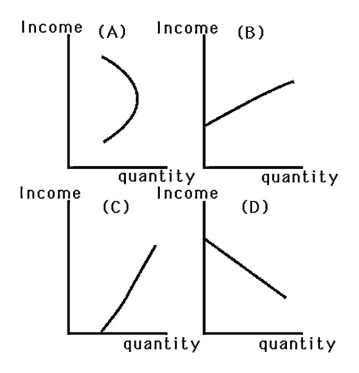
The above figure shows Larry's indifference map and budget lines for ham and pork.Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Larry's demand curve for pork shifts rightward when his income increases.
B)Larry's income elasticity of demand for pork is greater than zero.
C)Pork is a normal good.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

The above figure shows Larry's indifference map and budget lines for ham and pork.Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Pork is an inferior good.
B)Ham is an inferior good.
C)Neither pork nor ham is an inferior good.
D)Both ham and pork are inferior goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Dorothy lives in a city with high air pollution.Pollution is a bad,but she is able to avoid air pollution by wearing a face mask.Her preferences are given by
U(q1,q2)= (q1 - P)2q22
where q1 is the amount of time she spends wearing a mask,P is the amount of pollution and q2 is a composite of other goods (p2 = 1).Dorothy must decide how much to wear a mask and how much q2 to purchase.The price of masks is pM.Assume q1* > P when answering this question.
a.Derive Dorothy's demand for masks,q1*(p1,Y,P)
b.How does the quantity of pollution affect the demand for masks? That is,find q1*/P.
c.How does her income influence the quantity of masks she purchases? That is,find q1*/Y.
d.What condition must hold for the assumption q1* > P to hold?
U(q1,q2)= (q1 - P)2q22
where q1 is the amount of time she spends wearing a mask,P is the amount of pollution and q2 is a composite of other goods (p2 = 1).Dorothy must decide how much to wear a mask and how much q2 to purchase.The price of masks is pM.Assume q1* > P when answering this question.
a.Derive Dorothy's demand for masks,q1*(p1,Y,P)
b.How does the quantity of pollution affect the demand for masks? That is,find q1*/P.
c.How does her income influence the quantity of masks she purchases? That is,find q1*/Y.
d.What condition must hold for the assumption q1* > P to hold?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A consumer has the following utility function for goods X and Y:
U(X,Y)= 5XY3 + 10
The consumer faces prices of goods X and Y given by px and py and has an income given by I.
a.Write out the Lagrangian expression for the consumer's utility maximization problem.
b.Write out the first order conditions necessary for maximizing utility subject to the budget constraint.
c.Show that the first order conditions imply the budget constraint and MRS condition.Provide the economic (i.e.non-mathematical)interpretation of these conditions - specifically,why are they necessary for the consumer to be at the optimal bundle?
d.Solve for the Demand Equations,X*(px,py,I)and Y*(px,py,I)
e.Show that the demand equations are homogeneous of degree zero.That is,show
X*(cpx,cpy,cI)= X*(px,py,I)
for any positive constant,c.
U(X,Y)= 5XY3 + 10
The consumer faces prices of goods X and Y given by px and py and has an income given by I.
a.Write out the Lagrangian expression for the consumer's utility maximization problem.
b.Write out the first order conditions necessary for maximizing utility subject to the budget constraint.
c.Show that the first order conditions imply the budget constraint and MRS condition.Provide the economic (i.e.non-mathematical)interpretation of these conditions - specifically,why are they necessary for the consumer to be at the optimal bundle?
d.Solve for the Demand Equations,X*(px,py,I)and Y*(px,py,I)
e.Show that the demand equations are homogeneous of degree zero.That is,show
X*(cpx,cpy,cI)= X*(px,py,I)
for any positive constant,c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An inferior good exhibits
A)a negative income elasticity.
B)a downward-sloping Engel curve.
C)a decline in the quantity demanded as income rises.
D)All of the above.
A)a negative income elasticity.
B)a downward-sloping Engel curve.
C)a decline in the quantity demanded as income rises.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Lewis has preferences given by the Cobb-Douglas utility function U(q1,q2)= q1aq21-a,where a > 0.Show that Lewis's total amount spent on each good,does not change with the prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A movement upward along an upward-sloping Engel curve corresponds to
A)upward-sloping indifference curves.
B)crossing indifference curves.
C)a rotation in the budget constraint.
D)a parallel shift in the budget constraint.
A)upward-sloping indifference curves.
B)crossing indifference curves.
C)a rotation in the budget constraint.
D)a parallel shift in the budget constraint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Jose gets utility from the goods he consumes and also the income he earns.His utility function is given by
U(q1,q2)= q1q2Y
Derive Jose's demand equations.Does the fact that he derives utility directly from income affect his consumption in this case?
U(q1,q2)= q1q2Y
Derive Jose's demand equations.Does the fact that he derives utility directly from income affect his consumption in this case?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose the quantity of x is measured on the horizontal axis.If the income consumption curve is vertical,then the income elasticity of demand for x is
A)0.
B)1.
C)-1.
D)There is not enough information to determine the income elasticity of demand for x.
A)0.
B)1.
C)-1.
D)There is not enough information to determine the income elasticity of demand for x.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

The above figure shows Larry's indifference map and budget lines for ham and pork.Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A)Larry's Engel curve for pork will be upward sloping.
B)Larry's Engel curve for pork will be downward sloping.
C)Larry's Engel curve for pork will be backward bending.
D)Larry's Engel curve for pork cannot be derived from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Sam has preferences for weekly Video Games (V)and Sodas (S)described by the utility function U(V,S)= V2S2.Suppose the prices are denoted by pV and pS and Sam has income given by I.Assume that in Sam's optimal bundle,he consumes strictly positive quantities of both goods.
a.Write out Sam's optimization problem and the associated Lagrangian expression.
b.Compute the three critical value (first-order)conditions from the Lagrangian.
c.Using your answer to b,find the expression for the optimal bundles as functions of the prices and income.
a.Write out Sam's optimization problem and the associated Lagrangian expression.
b.Compute the three critical value (first-order)conditions from the Lagrangian.
c.Using your answer to b,find the expression for the optimal bundles as functions of the prices and income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the income elasticity of food is 0.72,then food is
A)a necessity and a normal good.
B)a normal good.
C)a necessity.
D)an inferior good.
A)a necessity and a normal good.
B)a normal good.
C)a necessity.
D)an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Jose consumes wallets (q1)and a composite of other goods (q2).The price of wallets is p1 and the price of other goods is p2 = 1.Jose's utility from wallets depends also on his income-with a higher income,he values a wallet more because he has more to put inside it! His utility is given by the equation
U(q1,q2)= q1Yq2
Derive Jose's demand for wallets.
U(q1,q2)= q1Yq2
Derive Jose's demand for wallets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When deriving an Engel curve,the prices of both goods
A)are held constant.
B)increase by the same percentage as income.
C)decrease by the same percentage as income.
D)can either decrease,increase or stay the same.
A)are held constant.
B)increase by the same percentage as income.
C)decrease by the same percentage as income.
D)can either decrease,increase or stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An increase in income (all else equal)will ALWAYS lead to a parallel shift of the budget line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the income elasticity of hamburgers is -0.8 for John,then his share of income spent on hamburgers will ________ when his income increases.
A)increase
B)decrease
C)remain the same
D)Not enough information
A)increase
B)decrease
C)remain the same
D)Not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
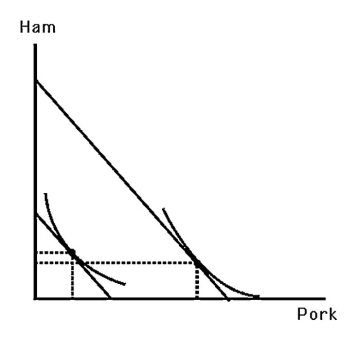
The above figure shows three different Engel curves.Rank them in terms of income elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A typical consumer spends 30% of income on housing and housing is a necessity for consumers (the income elasticity for housing is 0 < ξH < 1).What are the maximum and minimum values for the income elasticity of all other goods,ξO?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Even though Mary's income is very low,she makes sure that she purchases enough milk for her family to drink.As her income rises,she does buy more milk.Which graph in the above figure best represents Mary's Engel curve for milk?
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Jerry spends his entire income on two goods,Bran and Tea.Every month he spends half of his income on each of these goods.Jerry's income elasticity of demand for Bran is .75.What is the income elasticity of demand for Tea?
A)1.25
B).75
C)1
D)Unknown with the information provided
A)1.25
B).75
C)1
D)Unknown with the information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When John was in college and his income was low,he drank "Red Ribbon" beer.As his income increased,he purchased better-quality beer and less "Red Ribbon." Which graph in the above figure best represents John's Engel curve for "Red Ribbon" beer?
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Jill consumes nothing but soup and cola.It is possible that both soup and cola are necessities for Jill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Sylvia allocates her monthly income between Food and Housing.Her budget share spent on food in a given month is always 30%,and for Sylvia,food is a "necessity" (income elasticity between zero and one).Derive the maximum and minimum values for the income elasticity of demand for housing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Jill consumes nothing but soup and cola.If cola is a luxury good for Jill,then soup must be a necessity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Why would you expect the demand for diamond jewelry to fall faster than plastic,costume jewelry when all incomes fall?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When income increases by 1%,the quantity demanded of a good decreases by 2%.What is the income elasticity of the good? Is the good normal or inferior? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Why can't all goods be inferior?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which graph in the above figure best represents a good that is an inferior good at some income levels,and a normal good at other income levels?
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D
A)Graph A
B)Graph B
C)Graph C
D)Graph D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Draw budget constraints,indifference curves,and the income consumption curve for a good that has an income elasticity that is perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If consumer income and prices increase by the same percentage,
A)the consumer will buy more of both goods.
B)the consumer will buy more of both goods if they are both normal goods.
C)the consumer will buy less of both goods if they are both inferior goods.
D)the consumer's utility maximizing bundle stays the same.
A)the consumer will buy more of both goods.
B)the consumer will buy more of both goods if they are both normal goods.
C)the consumer will buy less of both goods if they are both inferior goods.
D)the consumer's utility maximizing bundle stays the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Alison consumes only tea and cookies and consumes them only in equal proportions.What is Alison's income elasticity of demand for tea?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Explain what the slope of the income consumption curve shows about the income elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Jerry spends his entire income on two goods,Bran and Tea.Every month he spends half of his income on each of these goods.Jerry's income elasticity of demand for Bran is -.75.What is the income elasticity of demand for Tea?
A)2.75
B)0.36
C)-2.75
D)Unknown with the information provided
A)2.75
B)0.36
C)-2.75
D)Unknown with the information provided

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
There are only two goods for John to consume: food and clothing.If clothing is an inferior good for John when his income rises to $100,000,then food is
A)also an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)Either inferior or normal could be possible.
D)Not enough information
A)also an inferior good.
B)a normal good.
C)Either inferior or normal could be possible.
D)Not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
To separate the income and substitute effects,the imaginary budget line should be
A)tangent to the new indifference curve and parallel to the new budget line.
B)tangent to the new indifference curve and parallel to the old budget line.
C)tangent to the old indifference curve and parallel to the new budget line.
D)tangent to the old indifference curve and parallel to the old budget line.
A)tangent to the new indifference curve and parallel to the new budget line.
B)tangent to the new indifference curve and parallel to the old budget line.
C)tangent to the old indifference curve and parallel to the new budget line.
D)tangent to the old indifference curve and parallel to the old budget line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The substitution effect can be measured holding ________ constant.
A)income
B)utility
C)the price of one good
D)the price of all goods
A)income
B)utility
C)the price of one good
D)the price of all goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
One characteristic of a Giffen good is that it
A)is a luxury good.
B)is an inferior good.
C)has an upward-sloping Engel curve.
D)All of the above.
A)is a luxury good.
B)is an inferior good.
C)has an upward-sloping Engel curve.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the case of a normal good,
A)demand curves always slope downward.
B)the income effect and substitution effect are in the same direction.
C)the Engel curve slopes upward.
D)All of the above.
A)demand curves always slope downward.
B)the income effect and substitution effect are in the same direction.
C)the Engel curve slopes upward.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
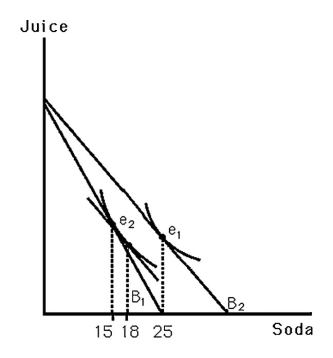
The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for soda and juice.B1 indicates his original budget line.B2 indicates his budget line resulting from a decrease in the price of soda.What change in quantity best represents his income effect?
A)3
B)10
C)15
D)7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for soda and juice.B1 indicates his original budget line.B2 indicates his budget line resulting from an increase in the price of soda.From the graph,one can conclude that
A)Bobby views soda as an inferior good.
B)Bobby's demand for soda is perfectly inelastic.
C)Bobby views soda as a normal good.
D)the income elasticity of demand for soda is one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Median household income is $50,000 per year.The typical household spends about $125 per year on milk,which has an income elasticity of about 0.07.From this information,we can conclude that
A)milk is a luxury.
B)milk is a Giffen good.
C)the income effect from a change in the price of milk is very large.
D)the income effect from a change in the price of milk is very small.
A)milk is a luxury.
B)milk is a Giffen good.
C)the income effect from a change in the price of milk is very large.
D)the income effect from a change in the price of milk is very small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When the price of a good changes,the substitution effect can be found by comparing the equilibrium quantities purchased
A)on the old budget line and the new budget line.
B)on the original indifference curve when faced with the original prices and when faced with the new prices.
C)on the new budget line and a hypothetical budget line that is a shift back to the original indifference curve parallel to the new budget line.
D)on the new indifference curve.
A)on the old budget line and the new budget line.
B)on the original indifference curve when faced with the original prices and when faced with the new prices.
C)on the new budget line and a hypothetical budget line that is a shift back to the original indifference curve parallel to the new budget line.
D)on the new indifference curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose that frozen dinners were once a normal good for John,but now frozen dinners are an inferior good for him.John's demand curve for frozen dinners
A)has become steeper as a result.
B)has become flatter as a result.
C)has not changed as a result.
D)has disappeared as a result.
A)has become steeper as a result.
B)has become flatter as a result.
C)has not changed as a result.
D)has disappeared as a result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

The above figure shows Bobby's indifference map for soda and juice.B1 indicates his original budget line.B2 indicates his budget line resulting from a decrease in the price of soda.What change in quantity best represents his substitution effect?
A)3
B)10
C)15
D)7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose that the interest rate paid to savers increases.As a result,Tom wishes to save more.This suggests that,for Tom,
A)the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
B)the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
C)utility maximization is not occurring.
D)future consumption is a luxury.
A)the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
B)the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
C)utility maximization is not occurring.
D)future consumption is a luxury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose Lisa spends all of her money on books and coffee.When the price of coffee decreases,the
A)substitution effect on coffee is positive,and the income effect on coffee is positive.
B)substitution effect on coffee is ambiguous,and the income effect on coffee is ambiguous.
C)substitution effect on coffee is positive,and the income effect on coffee is ambiguous.
D)substitution effect on coffee is ambiguous,and the income effect on coffee is positive.
A)substitution effect on coffee is positive,and the income effect on coffee is positive.
B)substitution effect on coffee is ambiguous,and the income effect on coffee is ambiguous.
C)substitution effect on coffee is positive,and the income effect on coffee is ambiguous.
D)substitution effect on coffee is ambiguous,and the income effect on coffee is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Suppose hamburger is an inferior good,but not a Giffen good,for Bob.If the price of hamburgers increases,
A)the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
B)the income effect is smaller than the substitution effect.
C)consumption of hamburger will increase.
D)We are unable to judge the change of hamburger consumption.
A)the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
B)the income effect is smaller than the substitution effect.
C)consumption of hamburger will increase.
D)We are unable to judge the change of hamburger consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A Giffen good has
A)a positive substitution effect.
B)a negative income effect.
C)a larger income effect than substitution effect.
D)All of the above.
A)a positive substitution effect.
B)a negative income effect.
C)a larger income effect than substitution effect.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When the price of a good changes,the total effect of the price change on the quantities purchased can be found by comparing the quantities purchased
A)on the old budget line and the new budget line.
B)on the original indifference curve when faced with the original prices and when faced with the new prices.
C)on the new budget line and a hypothetical budget line that is a parallel shift back to the original indifference curve.
D)on the new indifference curve.
A)on the old budget line and the new budget line.
B)on the original indifference curve when faced with the original prices and when faced with the new prices.
C)on the new budget line and a hypothetical budget line that is a parallel shift back to the original indifference curve.
D)on the new indifference curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If a good is an inferior good,then its
A)demand curve will be upward sloping.
B)income effect reinforces the substitution effect.
C)income elasticity is negative.
D)Engel curve cannot be drawn.
A)demand curve will be upward sloping.
B)income effect reinforces the substitution effect.
C)income elasticity is negative.
D)Engel curve cannot be drawn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose that the interest rate paid to savers increases.As a result,Tom wishes to save less.This suggests that,for Tom,
A)the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
B)the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
C)utility maximization is not occurring.
D)future consumption is a luxury.
A)the substitution effect is greater than the income effect.
B)the income effect is greater than the substitution effect.
C)utility maximization is not occurring.
D)future consumption is a luxury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The Slutsky equation shows that,holding the total effect constant,the income effect will be larger for goods that
A)have a smaller substitution effect.
B)make up a larger percentage of a household's budget.
C)have perfectly inelastic demand curves.
D)All of the above.
A)have a smaller substitution effect.
B)make up a larger percentage of a household's budget.
C)have perfectly inelastic demand curves.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When measuring the substitution effect,one uses the change along
A)the old indifference curve.
B)the new indifference curve.
C)either the old or the new indifference curve.
D)the budget constraint.
A)the old indifference curve.
B)the new indifference curve.
C)either the old or the new indifference curve.
D)the budget constraint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When the price of a good changes,the income effect can be found by comparing the equilibrium quantities purchased
A)on the old budget line and the new budget line.
B)on the original indifference curve when faced with the original prices and when faced with the new prices.
C)on the new budget line and a hypothetical budget line that is a shift back to the original indifference curve parallel to the new budget line.
D)on the new indifference curve.
A)on the old budget line and the new budget line.
B)on the original indifference curve when faced with the original prices and when faced with the new prices.
C)on the new budget line and a hypothetical budget line that is a shift back to the original indifference curve parallel to the new budget line.
D)on the new indifference curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



