Deck 6: A Tour of the Cell
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/96
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: A Tour of the Cell
1
Which of the following is a major cause of the size limits for certain types of cells?
A)limitation on the strength and integrity of the plasma membrane as cell size increases
B)the difference in plasma membranes between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
C)evolutionary progression in cell size; more primitive cells have smaller sizes
D)the need for a surface area of sufficient area to support the cell's metabolic needs
E)rigid cell walls that limit cell size expansion
A)limitation on the strength and integrity of the plasma membrane as cell size increases
B)the difference in plasma membranes between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
C)evolutionary progression in cell size; more primitive cells have smaller sizes
D)the need for a surface area of sufficient area to support the cell's metabolic needs
E)rigid cell walls that limit cell size expansion
D
2
When biologists wish to study the internal ultrastructure of cells, they can achieve the finest resolution by using
A)a phase-contrast light microscope.
B)a scanning electron microscope.
C)a transmission electronic microscope.
D)a confocal fluorescence microscope.
E)a super-resolution fluorescence microscope.
A)a phase-contrast light microscope.
B)a scanning electron microscope.
C)a transmission electronic microscope.
D)a confocal fluorescence microscope.
E)a super-resolution fluorescence microscope.
C
3
Which organelle or structure is absent in plant cells?
A)mitochondria
B)Golgi vesicles
C)microtubules
D)centrosomes
E)peroxisomes
A)mitochondria
B)Golgi vesicles
C)microtubules
D)centrosomes
E)peroxisomes
D
4
In the fractionation of homogenized cells using centrifugation, the primary factor that determines whether a specific cellular component ends up in the supernatant or the pellet is
A)the relative solubility of the component.
B)the size and weight of the component.
C)the percentage of carbohydrates in the component.
D)the presence or absence of nucleic acids in the component.
E)the presence or absence of lipids in the component.
A)the relative solubility of the component.
B)the size and weight of the component.
C)the percentage of carbohydrates in the component.
D)the presence or absence of nucleic acids in the component.
E)the presence or absence of lipids in the component.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If radioactive deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP)is added to a culture of rapidly growing bacterial cells, where in the cell would you expect to find the greatest concentration of radioactivity?
A)nucleus
B)cytoplasm
C)endoplasmic reticulum
D)nucleoid
E)ribosomes
A)nucleus
B)cytoplasm
C)endoplasmic reticulum
D)nucleoid
E)ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Recent evidence shows that when chromosomes decondense during interphase, their DNA molecules do not intermingle. Instead, they occupy distinct territories within the nucleus. Considering the structure and location of the following structures, which is most likely to be involved in chromosome location?
A)nuclear pores
B)the nucleolus
C)microfilaments
D)the nuclear lamina and matrix
E)the nuclear envelope
A)nuclear pores
B)the nucleolus
C)microfilaments
D)the nuclear lamina and matrix
E)the nuclear envelope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains. What are the domains?
A)Bacteria and Eukarya
B)Bacteria and Archaea
C)Archaea and Protista
D)Bacteria and Protista
E)Bacteria and Fungi
A)Bacteria and Eukarya
B)Bacteria and Archaea
C)Archaea and Protista
D)Bacteria and Protista
E)Bacteria and Fungi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A mycoplasma is an organism with a diameter between 0.1 and 1.0 µm. What does the organism's size tell you about how it might be classified?
A)It must be a single-celled protist.
B)It must be a single-celled fungus.
C)It could be almost any typical bacterium.
D)It could be a typical virus.
E)It could be a very small bacterium.
A)It must be a single-celled protist.
B)It must be a single-celled fungus.
C)It could be almost any typical bacterium.
D)It could be a typical virus.
E)It could be a very small bacterium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The volume enclosed by the plasma membrane of plant cells is often much larger than the corresponding volume in animal cells. The most reasonable explanation for this observation is that
A)plant cells are capable of having a much higher surface-to-volume ratio than animal cells.
B)plant cells have a much more highly convoluted (folded) plasma membrane than animal cells.
C)plant cells contain a large vacuole that reduces the volume of the cytoplasm.
D)animal cells are more spherical, whereas plant cells are elongated.
E)plant cells can have lower surface-to-volume ratios than animal cells because plant cells synthesize their own nutrients.
A)plant cells are capable of having a much higher surface-to-volume ratio than animal cells.
B)plant cells have a much more highly convoluted (folded) plasma membrane than animal cells.
C)plant cells contain a large vacuole that reduces the volume of the cytoplasm.
D)animal cells are more spherical, whereas plant cells are elongated.
E)plant cells can have lower surface-to-volume ratios than animal cells because plant cells synthesize their own nutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The evolution of eukaryotic cells most likely involved
A)endosymbiosis of an aerobic bacterium in a larger host cell-the endosymbiont evolved into mitochondria.
B)anaerobic archaea taking up residence inside a larger bacterial host cell to escape toxic oxygen-the anaerobic bacterium evolved into chloroplasts.
C)an endosymbiotic fungal cell evolved into the nucleus.
D)acquisition of an endomembrane system, and subsequent evolution of mitochondria from a portion of the Golgi.
A)endosymbiosis of an aerobic bacterium in a larger host cell-the endosymbiont evolved into mitochondria.
B)anaerobic archaea taking up residence inside a larger bacterial host cell to escape toxic oxygen-the anaerobic bacterium evolved into chloroplasts.
C)an endosymbiotic fungal cell evolved into the nucleus.
D)acquisition of an endomembrane system, and subsequent evolution of mitochondria from a portion of the Golgi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What technique would be most appropriate to use to observe the movements of condensed chromosomes during cell division?
A)light microscopy
B)scanning electron microscopy
C)transmission electron microscopy
D)confocal fluorescence microscopy
E)super-resolution fluorescence microscopy
A)light microscopy
B)scanning electron microscopy
C)transmission electron microscopy
D)confocal fluorescence microscopy
E)super-resolution fluorescence microscopy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The nuclear lamina is an array of filaments on the inner side of the nuclear membrane. If a method were found that could cause the lamina to fall into disarray, what would you expect to be the most likely consequence?
A)the loss of all nuclear function
B)the inability of the nucleus to divide during cell division
C)a change in the shape of the nucleus
D)failure of chromosomes to carry genetic information
E)inability of the nucleus to keep out destructive chemicals
A)the loss of all nuclear function
B)the inability of the nucleus to divide during cell division
C)a change in the shape of the nucleus
D)failure of chromosomes to carry genetic information
E)inability of the nucleus to keep out destructive chemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
All of the following are part of a prokaryotic cell except
A)DNA.
B)a cell wall.
C)a plasma membrane.
D)ribosomes.
E)an endoplasmic reticulum.
A)DNA.
B)a cell wall.
C)a plasma membrane.
D)ribosomes.
E)an endoplasmic reticulum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A primary objective of cell fractionation is to
A)view the structure of cell membranes.
B)sort cells based on their size and weight.
C)determine the size of various organelles.
D)separate the major organelles so that their particular functions can be determined.
E)separate lipid-soluble from water-soluble molecules.
A)view the structure of cell membranes.
B)sort cells based on their size and weight.
C)determine the size of various organelles.
D)separate the major organelles so that their particular functions can be determined.
E)separate lipid-soluble from water-soluble molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the reason that a modern electron microscope (TEM)can resolve biological images to the subnanometer level, as opposed to tens of nanometers achievable for the best?super-resolution light microscope?
A)The focal length of the electron microscope is significantly longer.
B)Contrast is enhanced by staining with atoms of heavy metal.
C)Electron beams have much shorter wavelengths than visible light.
D)The electron microscope has a much greater ratio of image size to real size.
E)The electron microscope cannot image whole cells at one time.
A)The focal length of the electron microscope is significantly longer.
B)Contrast is enhanced by staining with atoms of heavy metal.
C)Electron beams have much shorter wavelengths than visible light.
D)The electron microscope has a much greater ratio of image size to real size.
E)The electron microscope cannot image whole cells at one time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following correctly lists the order in which cellular components will be found in the pellet when homogenized cells are treated with increasingly rapid spins in a centrifuge?
A)ribosomes, nucleus, mitochondria
B)chloroplasts, ribosomes, vacuoles
C)nucleus, ribosomes, chloroplasts
D)vacuoles, ribosomes, nucleus
E)nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes
A)ribosomes, nucleus, mitochondria
B)chloroplasts, ribosomes, vacuoles
C)nucleus, ribosomes, chloroplasts
D)vacuoles, ribosomes, nucleus
E)nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The advantage of light microscopy over electron microscopy is that
A)light microscopy provides for higher magnification than electron microscopy.
B)light microscopy provides for higher resolving power than electron microscopy.
C)light microscopy allows one to view dynamic processes in living cells.
D)light microscopy provides higher contrast than electron microscopy.
E)specimen preparation for light microcopy does not produce artifacts.
A)light microscopy provides for higher magnification than electron microscopy.
B)light microscopy provides for higher resolving power than electron microscopy.
C)light microscopy allows one to view dynamic processes in living cells.
D)light microscopy provides higher contrast than electron microscopy.
E)specimen preparation for light microcopy does not produce artifacts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements concerning bacteria and archaea cells is correct?
A)Archaea cells contain small membrane-enclosed organelles; bacteria do not.
B)Archaea cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus; bacteria do not.
C)DNA is present in both archaea cells and bacteria cells.
D)DNA is present in the mitochondria of both bacteria and archaea cells.
A)Archaea cells contain small membrane-enclosed organelles; bacteria do not.
B)Archaea cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus; bacteria do not.
C)DNA is present in both archaea cells and bacteria cells.
D)DNA is present in the mitochondria of both bacteria and archaea cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Green fluorescent protein (GFP)can be used to fluorescently label a specific protein in cells by genetically engineering cells to synthesize the target protein fused to GFP. What is the advantage of using GFP fusions to visualize specific proteins, instead of staining cells with fluorescently labelled probes that bind to the target protein?
A)GFP fusions enable one to track changes in the location of the protein in living cells; staining usually requires preserved cells.
B)GFP fusions enable higher resolution than staining with fluorescent probes.
C)GFP permits the position of the protein in the cell more precisely than fluorescent probes.
D)GFP permits visualization of protein-protein interactions; fluorescent probes do not.
E)GFP fusions are not subject to artifacts; fluorescent probes may introduce background artifacts.
A)GFP fusions enable one to track changes in the location of the protein in living cells; staining usually requires preserved cells.
B)GFP fusions enable higher resolution than staining with fluorescent probes.
C)GFP permits the position of the protein in the cell more precisely than fluorescent probes.
D)GFP permits visualization of protein-protein interactions; fluorescent probes do not.
E)GFP fusions are not subject to artifacts; fluorescent probes may introduce background artifacts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing which of the following molecules?
A)lipids
B)glycogen
C)proteins
D)cellulose
E)nucleic acids
A)lipids
B)glycogen
C)proteins
D)cellulose
E)nucleic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following produces and modifies polysaccharides that will be secreted?
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Tay-Sachs disease is a human genetic abnormality that results in cells accumulating and becoming clogged with very large and complex lipids. Which cellular organelle must be involved in this condition?
A)the endoplasmic reticulum
B)the Golgi apparatus
C)the lysosome
D)mitochondria
E)membrane-bound ribosomes
A)the endoplasmic reticulum
B)the Golgi apparatus
C)the lysosome
D)mitochondria
E)membrane-bound ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In a plant cell, DNA may be found
A)only in the nucleus.
B)only in the nucleus and mitochondria.
C)only in the nucleus and chloroplasts.
D)in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
E)in the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes.
A)only in the nucleus.
B)only in the nucleus and mitochondria.
C)only in the nucleus and chloroplasts.
D)in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
E)in the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and peroxisomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A cell with a predominance of free ribosomes is most likely
A)producing primarily proteins for secretion.
B)producing primarily cytoplasmic proteins.
C)constructing an extensive cell wall or extracellular matrix.
D)digesting large food particles.
E)enlarging its vacuole.
A)producing primarily proteins for secretion.
B)producing primarily cytoplasmic proteins.
C)constructing an extensive cell wall or extracellular matrix.
D)digesting large food particles.
E)enlarging its vacuole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Thylakoids, DNA, and ribosomes are all components found in
A)vacuoles.
B)chloroplasts.
C)mitochondria.
D)lysosomes.
E)nuclei.
A)vacuoles.
B)chloroplasts.
C)mitochondria.
D)lysosomes.
E)nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following contains hydrolytic enzymes?
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which organelle is the primary site of ATP synthesis in eukaryotic cells?
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which plant cell organelle contains its own DNA and ribosomes?
A)glyoxysome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome
A)glyoxysome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which animal cell organelle contains enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen?
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements correctly describes some aspect of protein secretion from prokaryotic cells?
A)Prokaryotes are unlikely to be able to secrete proteins because they lack an endomembrane system.
B)The mechanism of protein secretion in prokaryotes is probably the same as that in eukaryotes.
C)Proteins that are secreted by prokaryotes are synthesized on ribosomes that are bound to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane.
D)In prokaryotes, the ribosomes that are used for the synthesis of secreted proteins are located outside of the cell.
E)Prokaryotes contain large pores in their plasma membrane that permit the movement of proteins out of the cell.
A)Prokaryotes are unlikely to be able to secrete proteins because they lack an endomembrane system.
B)The mechanism of protein secretion in prokaryotes is probably the same as that in eukaryotes.
C)Proteins that are secreted by prokaryotes are synthesized on ribosomes that are bound to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane.
D)In prokaryotes, the ribosomes that are used for the synthesis of secreted proteins are located outside of the cell.
E)Prokaryotes contain large pores in their plasma membrane that permit the movement of proteins out of the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which type of organelle or structure is primarily involved in the synthesis of oils, phospholipids, and steroids?
A)ribosome
B)lysosome
C)smooth endoplasmic reticulum
D)mitochondrion
E)contractile vacuole
A)ribosome
B)lysosome
C)smooth endoplasmic reticulum
D)mitochondrion
E)contractile vacuole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The Golgi apparatus has a polarity or sidedness to its structure and function. Which of the following statements correctly describes this polarity?
A)Transport vesicles fuse with one side of the Golgi and leave from the opposite side.
B)Proteins in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
C)Lipids in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
D)Soluble proteins in the cisternae (interior)of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
E)All of the above correctly describe polar characteristics of the Golgi function.
A)Transport vesicles fuse with one side of the Golgi and leave from the opposite side.
B)Proteins in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
C)Lipids in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
D)Soluble proteins in the cisternae (interior)of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
E)All of the above correctly describe polar characteristics of the Golgi function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which organelle often takes up much of the volume of a plant cell?
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome
A)lysosome
B)vacuole
C)mitochondrion
D)Golgi apparatus
E)peroxisome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which structure is the site of the synthesis of proteins that may be exported from the cell?
A)rough ER
B)lysosomes
C)plasmodesmata
D)Golgi vesicles
E)free cytoplasmic ribosomes
A)rough ER
B)lysosomes
C)plasmodesmata
D)Golgi vesicles
E)free cytoplasmic ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The liver is involved in detoxification of many poisons and drugs. Which of the following structures is primarily involved in this process and therefore abundant in liver cells?
A)rough ER
B)smooth ER
C)Golgi apparatus
D)nuclear envelope
E)transport vesicles
A)rough ER
B)smooth ER
C)Golgi apparatus
D)nuclear envelope
E)transport vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
One of the key innovations in the evolution of eukaryotes from a prokaryotic ancestor is the endomembrane system. What eukaryotic organelles or features might have evolved as a part of, or as an elaboration of, the endomembrane system?
A)plasma membrane
B)chloroplasts
C)mitochondria
D)nuclear envelope
E)none of these
A)plasma membrane
B)chloroplasts
C)mitochondria
D)nuclear envelope
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The fact that the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope has bound ribosomes allows one to most reliably conclude that
A)at least some of the proteins that function in the nuclear envelope are made by the ribosomes on the nuclear envelope.
B)the nuclear envelope is not part of the endomembrane system.
C)the nuclear envelope is physically separated from the endoplasmic reticulum.
D)small vesicles from the Golgi fuse with the nuclear envelope.
E)nuclear pore complexes contain proteins.
A)at least some of the proteins that function in the nuclear envelope are made by the ribosomes on the nuclear envelope.
B)the nuclear envelope is not part of the endomembrane system.
C)the nuclear envelope is physically separated from the endoplasmic reticulum.
D)small vesicles from the Golgi fuse with the nuclear envelope.
E)nuclear pore complexes contain proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Hydrolytic enzymes must be segregated and packaged to prevent general destruction of cellular components. Which of the following organelles contains these hydrolytic enzymes in animal cells?
A)chloroplast
B)lysosome
C)central vacuole
D)peroxisome
E)glyoxysome
A)chloroplast
B)lysosome
C)central vacuole
D)peroxisome
E)glyoxysome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The chemical reactions involved in respiration are virtually identical between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, ATP is synthesized primarily on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. In light of the endosymbiont theory for the evolutionary origin of mitochondria, where is most ATP synthesis likely to occur in prokaryotic cells?
A)in the cytoplasm
B)on the inner mitochondrial membrane
C)on the endoplasmic reticulum
D)on the plasma membrane
E)on the inner nuclear envelope
A)in the cytoplasm
B)on the inner mitochondrial membrane
C)on the endoplasmic reticulum
D)on the plasma membrane
E)on the inner nuclear envelope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The difference in lipid and protein composition between the membranes of the endomembrane system is largely determined by
A)the physical separation of most membranes from each other.
B)the transportation of membrane lipids among the endomembrane system by small membrane vesicles.
C)the function of the Golgi apparatus in sorting and directing membrane components.
D)the modification of the membrane components once they reach their final destination.
E)the synthesis of different lipids and proteins in each of the organelles of the endomembrane system.
A)the physical separation of most membranes from each other.
B)the transportation of membrane lipids among the endomembrane system by small membrane vesicles.
C)the function of the Golgi apparatus in sorting and directing membrane components.
D)the modification of the membrane components once they reach their final destination.
E)the synthesis of different lipids and proteins in each of the organelles of the endomembrane system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Movement of vesicles within the cell depends on what cellular structures?
A)microtubules and motor proteins
B)actin filaments and microtubules
C)actin filaments and ribosomes
D)centrioles and motor proteins
E)actin filaments and motor proteins
A)microtubules and motor proteins
B)actin filaments and microtubules
C)actin filaments and ribosomes
D)centrioles and motor proteins
E)actin filaments and motor proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When a potassium ion (K⁺)moves from the soil into the vacuole of a cell on the surface of a root, it must pass through several cellular structures. Which of the following correctly describes the order in which these structures will be encountered by the ion?
A)plasma membrane → primary cell wall → cytoplasm → vacuole
B)secondary cell wall → plasma membrane → primary cell wall → cytoplasm → vacuole
C)primary cell wall → plasma membrane → cytoplasm → vacuole
D)primary cell wall → plasma membrane → lysosome → cytoplasm → vacuole
E)primary cell wall → plasma membrane → cytoplasm → secondary cell wall → vacuole
A)plasma membrane → primary cell wall → cytoplasm → vacuole
B)secondary cell wall → plasma membrane → primary cell wall → cytoplasm → vacuole
C)primary cell wall → plasma membrane → cytoplasm → vacuole
D)primary cell wall → plasma membrane → lysosome → cytoplasm → vacuole
E)primary cell wall → plasma membrane → cytoplasm → secondary cell wall → vacuole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Motor proteins provide for molecular motion in cells by interacting with what types of cellular structures?
A)sites of energy production in cellular respiration
B)membrane proteins
C)ribosomes
D)cytoskeletal structures
E)cellulose fibres in the cell wall
A)sites of energy production in cellular respiration
B)membrane proteins
C)ribosomes
D)cytoskeletal structures
E)cellulose fibres in the cell wall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If an individual has abnormal microtubules due to a hereditary condition, in which organs or tissues would you expect dysfunction?
A)limbs, hearts, areas with a good deal of contraction
B)microvilli, alveoli, and glomeruli: cellular projections that increase surface area
C)all ducts, such as those from salivary or sebaceous glands, that transport fluids
D)sperm, larynx, and trachea: cells and tissues that contain flagella or cilia
E)phagocytic cells and white blood cells that exhibit amoeboid movement
A)limbs, hearts, areas with a good deal of contraction
B)microvilli, alveoli, and glomeruli: cellular projections that increase surface area
C)all ducts, such as those from salivary or sebaceous glands, that transport fluids
D)sperm, larynx, and trachea: cells and tissues that contain flagella or cilia
E)phagocytic cells and white blood cells that exhibit amoeboid movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and plant cells and the extracellular matrix of animal cells are all external to the plasma membrane. Which of the following is a characteristic common to all of these extracellular structures?
A)They must block water and small molecules in order to regulate the exchange of matter and energy with their environment.
B)They must permit information transfer between the cell's cytoplasm and the nucleus.
C)They must provide a rigid structure that maintains an appropriate ratio of cell surface area to volume.
D)They are constructed of polymers that are synthesized in the cytoplasm and then transported out of the cell.
E)They are composed of a mixture of lipids and carbohydrates.
A)They must block water and small molecules in order to regulate the exchange of matter and energy with their environment.
B)They must permit information transfer between the cell's cytoplasm and the nucleus.
C)They must provide a rigid structure that maintains an appropriate ratio of cell surface area to volume.
D)They are constructed of polymers that are synthesized in the cytoplasm and then transported out of the cell.
E)They are composed of a mixture of lipids and carbohydrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The smallest cell structure that would most likely be visible with a standard (not super-resolution)research-grade light microscope is
A)a mitochondrion.
B)a microtubule.
C)a ribosome.
D)a microfilament.
E)a nuclear pore.
A)a mitochondrion.
B)a microtubule.
C)a ribosome.
D)a microfilament.
E)a nuclear pore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements about the cytoskeleton is true?
A)The dynamic aspect of cytoskeletal function is made possible by the assembly and disassembly of a large variety of proteins into complex aggregates.
B)Microfilaments are structurally rigid and resist compression, whereas microtubules resist tension (stretching).
C)Movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other.
D)Chemicals that block the assembly of the cytoskeleton would cause little effect on the cell's response to external signals and stimuli.
E)Transport vesicles among the membranes of the endomembrane system produce the cytoskeleton.
A)The dynamic aspect of cytoskeletal function is made possible by the assembly and disassembly of a large variety of proteins into complex aggregates.
B)Microfilaments are structurally rigid and resist compression, whereas microtubules resist tension (stretching).
C)Movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other.
D)Chemicals that block the assembly of the cytoskeleton would cause little effect on the cell's response to external signals and stimuli.
E)Transport vesicles among the membranes of the endomembrane system produce the cytoskeleton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In a liver cell detoxifying alcohol and some other poisons, the enzymes of the peroxisome remove hydrogen from these molecules and
A)combine the hydrogen with water molecules to generate hydrogen peroxide.
B)use the hydrogen to break down hydrogen peroxide.
C)transfer the hydrogen to the mitochondria.
D)transfer the hydrogen to oxygen molecules to generate hydrogen peroxide.
A)combine the hydrogen with water molecules to generate hydrogen peroxide.
B)use the hydrogen to break down hydrogen peroxide.
C)transfer the hydrogen to the mitochondria.
D)transfer the hydrogen to oxygen molecules to generate hydrogen peroxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A cell has the following molecules and structures: enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, plasma membrane, and mitochondria. It could be a cell from
A)a bacterium.
B)an animal, but not a plant.
C)nearly any eukaryotic organism.
D)any multicellular organism, like a plant or an animal.
E)any kind of organism.
A)a bacterium.
B)an animal, but not a plant.
C)nearly any eukaryotic organism.
D)any multicellular organism, like a plant or an animal.
E)any kind of organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Cytochalasin D is a drug that prevents actin polymerization. A cell treated with cytochalasin D will still be able to
A)perform amoeboid movement.
B)form cleavage furrows.
C)contract muscle fibres.
D)extend pseudopodia.
E)move vesicles around the cell.
A)perform amoeboid movement.
B)form cleavage furrows.
C)contract muscle fibres.
D)extend pseudopodia.
E)move vesicles around the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
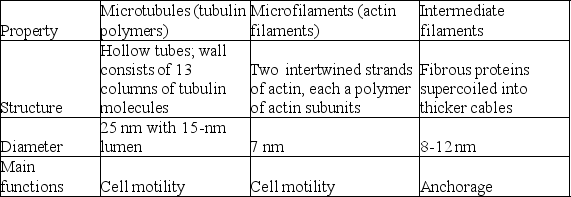
The differences among the three categories of cytoskeletal elements outlined in the table above would suggest that each of the following has specialized roles. Which of the following is a correct match? (All three elements are involved in the maintenance of cell shape.)
A)microfilaments and the nuclear lamina
B)microtubules and cleavage furrow formation
C)microfilaments and ciliary motion
D)intermediate filaments and cytoplasmic streaming
E)microtubules and chromosome movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What do the cell walls of plants and the extracellular matrix of animal cells have in common?
A)They are largely composed of phospholipids and glycoproteins.
B)Their proteins are made by free cytoplasmic ribosomes.
C)They form rigid structures that provide structural support for cells but limit their expansion.
D)They limit the passage of small molecules.
E)They have functional connections with the cytoskeleton inside the cell.
A)They are largely composed of phospholipids and glycoproteins.
B)Their proteins are made by free cytoplasmic ribosomes.
C)They form rigid structures that provide structural support for cells but limit their expansion.
D)They limit the passage of small molecules.
E)They have functional connections with the cytoskeleton inside the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Centrioles, cilia, flagella, and basal bodies have remarkably similar structural elements and arrangements. Which of the following hypotheses is most plausible in light of such structural similarities?
A)Cilia and flagella arise from the centrioles.
B)Loss of basal bodies should lead to loss of all cilia, flagella, and centrioles.
C)Motor proteins such as dynein must have evolved before any of these four kinds of structure.
D)Cilia and flagella coevolved in the same ancestral eukaryotic organism.
E)Natural selection for cell motility repeatedly selected for microtubular arrays in circular patterns in the evolution of each of these structures.
A)Cilia and flagella arise from the centrioles.
B)Loss of basal bodies should lead to loss of all cilia, flagella, and centrioles.
C)Motor proteins such as dynein must have evolved before any of these four kinds of structure.
D)Cilia and flagella coevolved in the same ancestral eukaryotic organism.
E)Natural selection for cell motility repeatedly selected for microtubular arrays in circular patterns in the evolution of each of these structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How does the cell multiply its peroxisomes?
A)They bud off from the Golgi.
B)They are brought into the cell from the environment.
C)They are built de novo from cytosol materials.
D)They split in two after they become sufficiently large.
E)The cell synthesizes hydrogen peroxide and encloses it in a membrane.
A)They bud off from the Golgi.
B)They are brought into the cell from the environment.
C)They are built de novo from cytosol materials.
D)They split in two after they become sufficiently large.
E)The cell synthesizes hydrogen peroxide and encloses it in a membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
All of the following serve an important role in determining or maintaining the structure of plant cells. Which of the following are distinct from the others in their composition?
A)microtubules
B)microfilaments
C)plant cell walls
D)intermediate filaments
E)nuclear lamina
A)microtubules
B)microfilaments
C)plant cell walls
D)intermediate filaments
E)nuclear lamina

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Cells require which of the following to form cilia or flagella?
A)centrosomes
B)laminin
C)actin
D)intermediate filaments
E)secretory vesicles
A)centrosomes
B)laminin
C)actin
D)intermediate filaments
E)secretory vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following contain the 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules, consisting of nine doublets of microtubules surrounding a pair of single microtubules?
A)both motile cilia and primary (nonmotile)cilia
B)centrioles only
C)both flagella and motile cilia
D)both basal bodies and primary (nonmotile)cilia
E)both centrioles and basal bodies
A)both motile cilia and primary (nonmotile)cilia
B)centrioles only
C)both flagella and motile cilia
D)both basal bodies and primary (nonmotile)cilia
E)both centrioles and basal bodies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which type of organelle is found in plant cells but not in animal cells?
A)ribosomes
B)mitochondria
C)nuclei
D)plastids
E)none of these
A)ribosomes
B)mitochondria
C)nuclei
D)plastids
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why isn't the mitochondrion classified as part of the endomembrane system?
A)It is a static structure.
B)Its structure is not derived from the ER or Golgi.
C)It has too many vesicles.
D)It is not involved in protein synthesis.
E)It is not attached to the outer nuclear envelope.
A)It is a static structure.
B)Its structure is not derived from the ER or Golgi.
C)It has too many vesicles.
D)It is not involved in protein synthesis.
E)It is not attached to the outer nuclear envelope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Vinblastine, a drug that inhibits microtubule polymerization, is used to treat some forms of cancer. Cancer cells given vinblastine would be unable to
A)form cleavage furrows during cell division.
B)migrate by amoeboid movement.
C)separate chromosomes during cell division.
D)extend pseudopods.
E)maintain the shape of the nucleus.
A)form cleavage furrows during cell division.
B)migrate by amoeboid movement.
C)separate chromosomes during cell division.
D)extend pseudopods.
E)maintain the shape of the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Recent evidence shows that signals from the extracellular matrix (ECM)can regulate the expression of genes in the cell nucleus. A likely mechanism is that
A)mechanical signals of the ECM can alter the cytoskeleton, which can alter intracellular signalling.
B)intracellular signals might cause changes in the fibronectin binding to the cell surface.
C)orientation of microtubules to the ECM can change gene activity.
D)integrins that receive signals from the ECM migrate to the nucleus.
E)proteoglycans in the ECM undergo endocytosis and produce intracellular signalling molecules.
A)mechanical signals of the ECM can alter the cytoskeleton, which can alter intracellular signalling.
B)intracellular signals might cause changes in the fibronectin binding to the cell surface.
C)orientation of microtubules to the ECM can change gene activity.
D)integrins that receive signals from the ECM migrate to the nucleus.
E)proteoglycans in the ECM undergo endocytosis and produce intracellular signalling molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following makes it necessary for animal cells, although they have no cell walls, to have intercellular junctions?
A)Cell membranes do not distinguish the types of ions and molecules passing through them.
B)Large molecules, such as proteins and RNA molecules, do not readily get through one, much less two, adjacent cell membranes.
C)Cell-to-cell communication requires physical attachment of one cell to another.
D)Maintenance of tissue integrity and barriers to fluid leakage requires cells to adhere tightly to one another.
E)The relative shapelessness of animal cells requires a mechanism for keeping the cells aligned.
A)Cell membranes do not distinguish the types of ions and molecules passing through them.
B)Large molecules, such as proteins and RNA molecules, do not readily get through one, much less two, adjacent cell membranes.
C)Cell-to-cell communication requires physical attachment of one cell to another.
D)Maintenance of tissue integrity and barriers to fluid leakage requires cells to adhere tightly to one another.
E)The relative shapelessness of animal cells requires a mechanism for keeping the cells aligned.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Ions can travel directly from the cytoplasm of one animal cell to the cytoplasm of an adjacent cell through
A)plasmodesmata.
B)intermediate filaments.
C)tight junctions.
D)desmosomes.
E)gap junctions.
A)plasmodesmata.
B)intermediate filaments.
C)tight junctions.
D)desmosomes.
E)gap junctions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
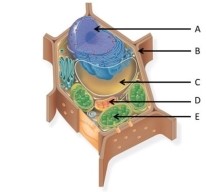
What is the function of the structure labelled A?
A)respiration
B)photosynthesis
C)maintain cell pressure
D)contain DNA
E)synthesize lipids

What is the function of the structure labelled A?
A)respiration
B)photosynthesis
C)maintain cell pressure
D)contain DNA
E)synthesize lipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
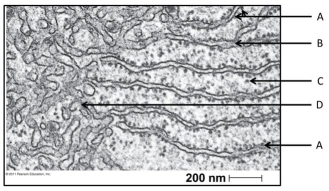
In the figure above, identify the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)The RER is not visible on this image.

In the figure above, identify the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)The RER is not visible on this image.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The minimum distance two points can be separated and still discerned as separate is the
A)resolution.
B)magnification.
C)visibility.
D)objective magnification.
E)contrast.
A)resolution.
B)magnification.
C)visibility.
D)objective magnification.
E)contrast.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Plasmodesmata in plant cells are most similar in function to which of the following structures in animal cells?
A)peroxisomes
B)desmosomes
C)gap junctions
D)extracellular matrix
E)tight junctions
A)peroxisomes
B)desmosomes
C)gap junctions
D)extracellular matrix
E)tight junctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What types of proteins are not synthesized in the rough ER?
A)endoplasmic reticulum proteins
B)extracellular matrix proteins
C)secreted proteins
D)mitochondrial proteins
E)plasma membrane proteins
A)endoplasmic reticulum proteins
B)extracellular matrix proteins
C)secreted proteins
D)mitochondrial proteins
E)plasma membrane proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A mutation that disrupts the ability of an animal cell to add polysaccharide modifications to proteins would most likely cause defects in its
A)nuclear lamina and nuclear matrix.
B)nuclear matrix and extracellular matrix.
C)mitochondria and Golgi apparatus.
D)Golgi apparatus and extracellular matrix.
E)nuclear pores and secretory vesicles.
A)nuclear lamina and nuclear matrix.
B)nuclear matrix and extracellular matrix.
C)mitochondria and Golgi apparatus.
D)Golgi apparatus and extracellular matrix.
E)nuclear pores and secretory vesicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The smallest unit of matter that can be considered alive is the/a
A)nucleic acid.
B)mitochondria.
C)virus.
D)cell.
E)organism.
A)nucleic acid.
B)mitochondria.
C)virus.
D)cell.
E)organism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.

What type of cell is pictured above?
A)Archaea
B)Bacteria
C)protist
D)plant
E)animal

What type of cell is pictured above?
A)Archaea
B)Bacteria
C)protist
D)plant
E)animal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.

The image above is a ________ image.
A)light microscope
B)phase contrast
C)scanning electron micrograph
D)transmission electron micrograph
E)confocal

The image above is a ________ image.
A)light microscope
B)phase contrast
C)scanning electron micrograph
D)transmission electron micrograph
E)confocal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.

What is the function of the structure labelled C?
A)synthesize lipids
B)make membrane proteins
C)make cytosolic proteins
D)modify protein for transport
E)package proteins for export

What is the function of the structure labelled C?
A)synthesize lipids
B)make membrane proteins
C)make cytosolic proteins
D)modify protein for transport
E)package proteins for export

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Signals between the ECM and the cytoskeleton may be transmitted by
A)fibronectin.
B)proteoglycans.
C)integrins.
D)collagen.
E)middle lamella.
A)fibronectin.
B)proteoglycans.
C)integrins.
D)collagen.
E)middle lamella.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.

Which two structures are shared by all eukaryotic cells?
A)A and C
B)A and D
C)B and D
D)B and E
E)C and E

Which two structures are shared by all eukaryotic cells?
A)A and C
B)A and D
C)B and D
D)B and E
E)C and E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The extracellular matrix is thought to participate in the regulation of animal cell behaviour by communicating information from the outside to the inside of the cell via which of the following?
A)gap junctions
B)the nucleus
C)DNA and RNA
D)integrins
E)plasmodesmata
A)gap junctions
B)the nucleus
C)DNA and RNA
D)integrins
E)plasmodesmata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.

What is the name of the structure labelled B?
A)cell wall
B)plasma membrane
C)nuclear envelope
D)cytosol
E)endoplasmic reticulum

What is the name of the structure labelled B?
A)cell wall
B)plasma membrane
C)nuclear envelope
D)cytosol
E)endoplasmic reticulum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.

What is the function of the structure labelled E?
A)respiration
B)photosynthesis
C)maintain cell pressure
D)contain DNA
E)synthesize lipids

What is the function of the structure labelled E?
A)respiration
B)photosynthesis
C)maintain cell pressure
D)contain DNA
E)synthesize lipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.

The structure labelled D functions in
A)lipid synthesis.
B)membrane production.
C)cytosolic protein production.
D)modification of proteins for transport.
E)package of proteins.

The structure labelled D functions in
A)lipid synthesis.
B)membrane production.
C)cytosolic protein production.
D)modification of proteins for transport.
E)package of proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
ECM proteins are made by ribosomes in which part of a eukaryotic cell?
A)mitochondria
B)cytoplasm
C)nuclear envelope
D)Golgi apparatus
E)rough ER
A)mitochondria
B)cytoplasm
C)nuclear envelope
D)Golgi apparatus
E)rough ER

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



