Deck 12: Organization, Capital Structures, and Income Distributions of Corporations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Organization, Capital Structures, and Income Distributions of Corporations
1
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the disposal of shares by a shareholder?
A)When a shareholder sells shares to other shareholders, the corporation's capital base increases.
B)The sale of shares to other shareholders is known as a 'buy-back'.
C)The sale of shares to the corporate treasury is not allowed in the Income Tax Act.
D)The sale of shares to the corporate treasury may result in a deemed dividend and a capital gain or loss to the shareholder.
A)When a shareholder sells shares to other shareholders, the corporation's capital base increases.
B)The sale of shares to other shareholders is known as a 'buy-back'.
C)The sale of shares to the corporate treasury is not allowed in the Income Tax Act.
D)The sale of shares to the corporate treasury may result in a deemed dividend and a capital gain or loss to the shareholder.
D
2
Green Co.transferred a small piece of land to one of its shareholders as a dividend in kind.The land originally cost $50,000 and had a fair market value of $175,000 at the time of the transfer.The corporation will realize ________,and the shareholder will realize ________.
A)no tax effect; a dividend of $125,000.
B)a dividend of $125,000; no tax effect.
C)a capital gain of $125,000; a dividend of $175,000.
D)a capital gain of $50,000; a dividend of $125,000.
A)no tax effect; a dividend of $125,000.
B)a dividend of $125,000; no tax effect.
C)a capital gain of $125,000; a dividend of $175,000.
D)a capital gain of $50,000; a dividend of $125,000.
C
3
Robert Smith owns 20% of the shares of Quarks Inc.,a Canadian qualified small business corporation.He purchased the shares from a previous shareholder for $50,000.The stated paid up capital of the shares is $10,000.Two other shareholders own equal portions of the remaining shares of Quarks.
Robert has decided to sell his shares,which have a market value of $120,000.The shares are to be sold either to the two other shareholders,or back to the corporate treasury.All three shareholders used all of their capital gains deductions earlier in the year.
Robert has employment income of $185,000,a capital gain in the amount of $50,000,and property income of $20,000 for the current year.
All three shareholders are in a 50% tax bracket.The marginal rate on dividends is 43%.The corporate tax rate for Quarks is 13%.
Required:
A)Determine the tax cost for Robert is he sells his shares to:
1)the other shareholders.
2)the corporate treasury.
B)Determine the cost of the share purchase for:
1)the other shareholders,assuming that the purchase will be made using dividend income paid to the two shareholders from the corporation.
2)the corporation,assuming that the purchase will be made from business profits.
C)Which option is preferential for 1)Robert and 2)the other shareholders?
D)What is the significance of Robert's $50,000 capital gain received in the year if he were to sell his shares back to the corporate treasury?
Robert has decided to sell his shares,which have a market value of $120,000.The shares are to be sold either to the two other shareholders,or back to the corporate treasury.All three shareholders used all of their capital gains deductions earlier in the year.
Robert has employment income of $185,000,a capital gain in the amount of $50,000,and property income of $20,000 for the current year.
All three shareholders are in a 50% tax bracket.The marginal rate on dividends is 43%.The corporate tax rate for Quarks is 13%.
Required:
A)Determine the tax cost for Robert is he sells his shares to:
1)the other shareholders.
2)the corporate treasury.
B)Determine the cost of the share purchase for:
1)the other shareholders,assuming that the purchase will be made using dividend income paid to the two shareholders from the corporation.
2)the corporation,assuming that the purchase will be made from business profits.
C)Which option is preferential for 1)Robert and 2)the other shareholders?
D)What is the significance of Robert's $50,000 capital gain received in the year if he were to sell his shares back to the corporate treasury?
A)1)Sell to other shareholders:

Tax cost: $35,000 × 50% = $17,500
2)Sell back to the corporate treasury:

Tax cost: $110,000 × 43% = $47,300
 Tax saving: $20,000 × 50% tax rate = $10,000 (Robert recognized a capital gain of $50,000 during the year,so will be able to use the capital loss from the sale.)
Tax saving: $20,000 × 50% tax rate = $10,000 (Robert recognized a capital gain of $50,000 during the year,so will be able to use the capital loss from the sale.)
Total tax consequence: Tax cost of $47,300 less tax saving of $10,000 = $37,300
B)1)Cost to the other shareholders:
1x - .43x = $120,000
x = $210,526
1x - .13x = $210,526
x = $241,984 of pre-tax corporate income
2)Cost to the corporation:
1x - .13x = $120,000
x = $137,931 of pre-tax corporate income.
C)Robert would prefer to sell his shares to the other shareholders due to the lower tax cost for himself.The other shareholders would prefer that Robert sell his shares back to the corporate treasury as less business income would be required to buy his shares.
D)If Robert sells back to the corporate treasury,he will be able to recognize the $20,000 allowable capital loss against his $25,000 ($50,000 * .5)taxable capital gain.He would not otherwise be able to use the loss as his ability to convert the loss to an ABIL is not available due to the prior use of his entire capital gain deduction.

Tax cost: $35,000 × 50% = $17,500
2)Sell back to the corporate treasury:

Tax cost: $110,000 × 43% = $47,300
 Tax saving: $20,000 × 50% tax rate = $10,000 (Robert recognized a capital gain of $50,000 during the year,so will be able to use the capital loss from the sale.)
Tax saving: $20,000 × 50% tax rate = $10,000 (Robert recognized a capital gain of $50,000 during the year,so will be able to use the capital loss from the sale.)Total tax consequence: Tax cost of $47,300 less tax saving of $10,000 = $37,300
B)1)Cost to the other shareholders:
1x - .43x = $120,000
x = $210,526
1x - .13x = $210,526
x = $241,984 of pre-tax corporate income
2)Cost to the corporation:
1x - .13x = $120,000
x = $137,931 of pre-tax corporate income.
C)Robert would prefer to sell his shares to the other shareholders due to the lower tax cost for himself.The other shareholders would prefer that Robert sell his shares back to the corporate treasury as less business income would be required to buy his shares.
D)If Robert sells back to the corporate treasury,he will be able to recognize the $20,000 allowable capital loss against his $25,000 ($50,000 * .5)taxable capital gain.He would not otherwise be able to use the loss as his ability to convert the loss to an ABIL is not available due to the prior use of his entire capital gain deduction.
4
Tony Brown sold 5000 of his shares back to ABC Co.for $25,000 during the current fiscal year.He purchased these shares from Carrie White three years ago for $15,000.Carrie had originally purchased the shares from the corporate treasury for $10,000.Which of the following tax consequences will Tony recognize?
A)He will recognize a deemed dividend of $10,000 and no capital gain or loss.
B)He will recognize a deemed dividend of $15,000 and a capital loss of $5,000.
C)He will recognize a deemed dividend of $15,000 and a capital gain of $10,000.
D)He will recognize a deemed dividend of $10,000 and a capital gain of $10,000.
A)He will recognize a deemed dividend of $10,000 and no capital gain or loss.
B)He will recognize a deemed dividend of $15,000 and a capital loss of $5,000.
C)He will recognize a deemed dividend of $15,000 and a capital gain of $10,000.
D)He will recognize a deemed dividend of $10,000 and a capital gain of $10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Corporation A is a Canadian controlled private corporation and Corporation B is a public Canadian corporation.Both corporations have a paid-up capital balance of $25,000.Which of these statements is TRUE,provided the proper legal steps are followed?
A)If the private corporation makes a payment of $25,000 to its shareholders by reducing its paid-up capital, there will be no tax consequence for the shareholders.
B)If the private corporation makes a payment of $25,000 to its shareholders by reducing its paid-up capital, only 50% of the payment will be taxable.
C)If the public corporation makes a payment of $25,000 to its shareholders by reducing its paid-up capital, there will be no tax consequence for the shareholders.
D)If the public corporation makes a payment of $25,000 to its shareholders by reducing its paid-up capital, only 50% of the payment will be taxable.
A)If the private corporation makes a payment of $25,000 to its shareholders by reducing its paid-up capital, there will be no tax consequence for the shareholders.
B)If the private corporation makes a payment of $25,000 to its shareholders by reducing its paid-up capital, only 50% of the payment will be taxable.
C)If the public corporation makes a payment of $25,000 to its shareholders by reducing its paid-up capital, there will be no tax consequence for the shareholders.
D)If the public corporation makes a payment of $25,000 to its shareholders by reducing its paid-up capital, only 50% of the payment will be taxable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following scenarios would be appropriate for a section 85 rollover?
A)A shareholder of a corporation wishes to transfer his vehicle to his corporation.The vehicle originally cost $20,000 and has a market value of $12,000.
B)A corporation wishes to convert land owned by the company into a parking lot.
C)A taxpayer wishes to transfer property worth $200,000, with an ACB of $90,000, to her corporation.
D)A corporation is selling its equipment to another corporation and does not wish to own shares in the other corporation.
A)A shareholder of a corporation wishes to transfer his vehicle to his corporation.The vehicle originally cost $20,000 and has a market value of $12,000.
B)A corporation wishes to convert land owned by the company into a parking lot.
C)A taxpayer wishes to transfer property worth $200,000, with an ACB of $90,000, to her corporation.
D)A corporation is selling its equipment to another corporation and does not wish to own shares in the other corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
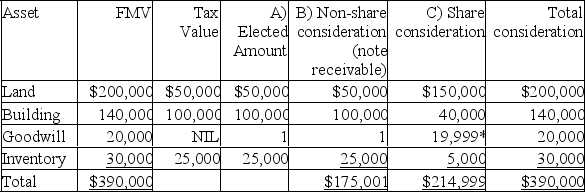
Ben is incorporating his proprietorship and would like to transfer the following capital assets to the new corporation.
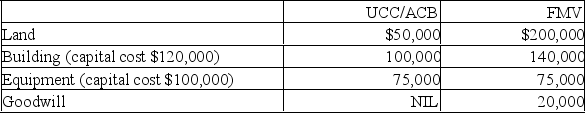 Ben will also transfer his inventory which originally cost $25,000 and has a fair market value of $30,000.
Ben will also transfer his inventory which originally cost $25,000 and has a fair market value of $30,000.
Ben wishes to defer all gains at this time so has elected to use a section 85 rollover.He will receive the maximum note receivable possible and the remainder of the transfer in preferred shares.
Required:
A)What is the elected value for each of the assets transferred under section 85?
B)What is the value of the note receivable that Ben will receive from those assets which benefit from section 85? (Show the amounts for each asset,and the total for all.)
C)What is the value of the preferred shares that Ben must receive in order to defer any income inclusions at this point in time?
 Ben will also transfer his inventory which originally cost $25,000 and has a fair market value of $30,000.
Ben will also transfer his inventory which originally cost $25,000 and has a fair market value of $30,000.Ben wishes to defer all gains at this time so has elected to use a section 85 rollover.He will receive the maximum note receivable possible and the remainder of the transfer in preferred shares.
Required:
A)What is the elected value for each of the assets transferred under section 85?
B)What is the value of the note receivable that Ben will receive from those assets which benefit from section 85? (Show the amounts for each asset,and the total for all.)
C)What is the value of the preferred shares that Ben must receive in order to defer any income inclusions at this point in time?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
There are significant differences in the tax treatment of shareholder debt and shareholder equity from the perspective of both the CCPC and the shareholders.
Required:
List one tax consequences for each of the following:
1)Return on investment - shareholder debt
2)Loss on investment - shareholder debt
3)Return of capital - shareholder debt
4)Return on investment - shareholder equity
5)Loss on investment - shareholder equity
6)Return of capital - shareholder equity
Required:
List one tax consequences for each of the following:
1)Return on investment - shareholder debt
2)Loss on investment - shareholder debt
3)Return of capital - shareholder debt
4)Return on investment - shareholder equity
5)Loss on investment - shareholder equity
6)Return of capital - shareholder equity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Anthony is the sole shareholder of Glass Co.He would like to lend $500,000 to his company by way of a shareholder loan.He is not sure whether to issue an interest free loan or a loan with an interest rate of 10%.Anthony does not pay himself a salary,but rather issues all after-tax profits to himself in the form of a dividend.
Required:
Calculate the total combined tax liability for Anthony and Glass Co.under both alternatives (an interest free loan and a loan with 10% interest).(Assume that CRA's prescribed rate of interest is 2%,Anthony's personal tax rate is 50%,his marginal tax rate on dividends is 43%,and Glass Co.has income of $200,000,subject to a 13% tax rate.)
B)Has double taxation occurred in either scenario?
Required:
Calculate the total combined tax liability for Anthony and Glass Co.under both alternatives (an interest free loan and a loan with 10% interest).(Assume that CRA's prescribed rate of interest is 2%,Anthony's personal tax rate is 50%,his marginal tax rate on dividends is 43%,and Glass Co.has income of $200,000,subject to a 13% tax rate.)
B)Has double taxation occurred in either scenario?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
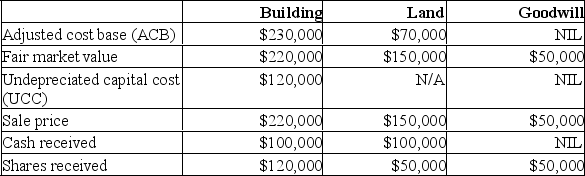
Janko Corp.has transferred the following three assets to Jumbo Corp.,a Canadian controlled private corporation,under section 85 of the Income Tax Act.
 equired:
equired:
Determine the following amounts:
A)The minimum amount that Janko may elect to transfer each asset in the rollover based on the information provided
B)Janko's income or loss for tax purposes as a result of the rollover
C)The ACB of the shares received by Janko following the rollover
D)The PUC of the shares received by Janko following the rollover
 equired:
equired:Determine the following amounts:
A)The minimum amount that Janko may elect to transfer each asset in the rollover based on the information provided
B)Janko's income or loss for tax purposes as a result of the rollover
C)The ACB of the shares received by Janko following the rollover
D)The PUC of the shares received by Janko following the rollover

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



