Deck 2: Chemical Basis of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/107
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Chemical Basis of Life
1
Sodium ions and calcium ions are examples of
A) cations.
B) uncharged particles.
C) anions.
D) salts.
A) cations.
B) uncharged particles.
C) anions.
D) salts.
A
2
Matter is composed of elements, which are composed of _____.
A) atoms
B) inorganic molecules
C) organic molecules
D) chemicals
A) atoms
B) inorganic molecules
C) organic molecules
D) chemicals
A
3
When cations and anions meet, they
A) repel.
B) form ionic bonds.
C) form covalent bonds.
D) form individual molecules.
A) repel.
B) form ionic bonds.
C) form covalent bonds.
D) form individual molecules.
B
4
Radioactive isotopes have stable nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The atomic number of an atom equals the number of ______ and the atomic weight equals the ____.
A) neutrons; number of protons
B) protons; weight of all the electrons
C) neutrons; number of protons plus electrons
D) protons; number of protons plus neutrons
A) neutrons; number of protons
B) protons; weight of all the electrons
C) neutrons; number of protons plus electrons
D) protons; number of protons plus neutrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Exposure to ionizing radiation may
A) cloud the lens of the eye.
B) cause cancer.
C) interfere with normal growth.
D) all of the above.
A) cloud the lens of the eye.
B) cause cancer.
C) interfere with normal growth.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The isotope most likely to be used to study the thyroid gland is
A) iodine-131.
B) iron-59.
C) thallium-201.
D) cobalt-60.
A) iodine-131.
B) iron-59.
C) thallium-201.
D) cobalt-60.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Carbon can form ___ covalent bonds.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The number of protons in an atom of an element always equals its atomic weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Water causes ionically-bonded atoms to
A) bond more strongly.
B) dissociate.
C) bond covalently.
D) decompose.
A) bond more strongly.
B) dissociate.
C) bond covalently.
D) decompose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Sodium and chloride atoms combine readily because they both lose electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
PET imaging follows the emission of
A) positrons.
B) electrons.
C) neutrons.
D) protons.
A) positrons.
B) electrons.
C) neutrons.
D) protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a covalent bond
A) one atom loses and another atom gains electrons.
B) atoms share a pair or more of electrons.
C) oppositely charged atoms attract.
D) like-charged atoms repel.
A) one atom loses and another atom gains electrons.
B) atoms share a pair or more of electrons.
C) oppositely charged atoms attract.
D) like-charged atoms repel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A CT scan differs from a conventional X-ray image because it is
A) two-dimensional.
B) three-dimensional.
C) four-dimensional.
D) safer.
A) two-dimensional.
B) three-dimensional.
C) four-dimensional.
D) safer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Atomic radiation is useful for treating cancer because
A) radiation affects cancer cells but not normal cells.
B) radiation protects normal cells against the effects of cancer.
C) radiation harms cancer cells more readily than it does most non-cancer cells.
D) normal cells are not affected by radiation.
A) radiation affects cancer cells but not normal cells.
B) radiation protects normal cells against the effects of cancer.
C) radiation harms cancer cells more readily than it does most non-cancer cells.
D) normal cells are not affected by radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In an ionic bond
A) each atom gains electrons.
B) atoms share a pair or more of electrons.
C) oppositely charged atoms attract.
D) like-charged atoms repel.
A) each atom gains electrons.
B) atoms share a pair or more of electrons.
C) oppositely charged atoms attract.
D) like-charged atoms repel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The ______ uses iodine in a synthesis reaction.
A) spleen
B) liver
C) thymus
D) thyroid gland
A) spleen
B) liver
C) thymus
D) thyroid gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The symbol Na+ represents a sodium atom that has lost an electron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following isotopes has the longest half-life?
A) Iodine-131
B) Iron-59
C) Phosphorus-32
D) Cobalt-60
A) Iodine-131
B) Iron-59
C) Phosphorus-32
D) Cobalt-60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not a source of ionizing radiation?
A) Cosmic rays from outer space
B) Cholesterol and triglycerides
C) Atomic and nuclear weapons
D) Smoke detectors
A) Cosmic rays from outer space
B) Cholesterol and triglycerides
C) Atomic and nuclear weapons
D) Smoke detectors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following substances is an element?
A) Iron
B) Water
C) Sodium chloride
D) Glucose
A) Iron
B) Water
C) Sodium chloride
D) Glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Isotopes of an element have
A) the same atomic number and same atomic weight.
B) the same atomic number but different atomic weights.
C) different atomic numbers but the same atomic weight.
D) different atomic numbers and different atomic weights.
A) the same atomic number and same atomic weight.
B) the same atomic number but different atomic weights.
C) different atomic numbers but the same atomic weight.
D) different atomic numbers and different atomic weights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Deep Check
A decomposition reaction can be symbolized by
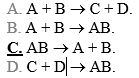
A decomposition reaction can be symbolized by
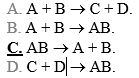

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is(are) ionizing radiation?
A) Cosmic radiation only
B) Gamma radiation only
C) Both cosmic radiation and gamma radiation
D) Neither cosmic nor gamma radiation
A) Cosmic radiation only
B) Gamma radiation only
C) Both cosmic radiation and gamma radiation
D) Neither cosmic nor gamma radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The type of chemical bond formed when ions with opposite electrical charges attract is a(n) ________ bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following groups of elements accounts for more than 95% of the human body by weight?
A) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
B) Calcium, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
C) Carbon, phosphorus, oxygen, hydrogen
D) Calcium, phosphorus, hydrogen, nitrogen
A) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
B) Calcium, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
C) Carbon, phosphorus, oxygen, hydrogen
D) Calcium, phosphorus, hydrogen, nitrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The type of subatomic particle that does not have an electrical charge is a(n) ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The atoms of the isotopes of a particular element vary in the number of
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) neutrons.
D) nuclei.
A) electrons.
B) protons.
C) neutrons.
D) nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The atomic weight of an element whose atoms contain 8 protons, 8 electrons, and 8 neutrons is
A) 8.
B) 16.
C) 24.
D) 32.
A) 8.
B) 16.
C) 24.
D) 32.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Chemistry deals with
A) the composition and changes of substances that make up living as well as non-living matter.
B) the composition and changes of substances found in organisms only.
C) the composition of and changes of substances that make up non-living matter only.
D) the location of organs in body cavities.
A) the composition and changes of substances that make up living as well as non-living matter.
B) the composition and changes of substances found in organisms only.
C) the composition of and changes of substances that make up non-living matter only.
D) the location of organs in body cavities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The parts of an atom that carry single negative electrical charges are called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The atoms of different elements have
A) the same atomic number and same atomic weight.
B) the same atomic number but different atomic weights.
C) different atomic numbers.
D) different atomic numbers but the same number of electrons.
A) the same atomic number and same atomic weight.
B) the same atomic number but different atomic weights.
C) different atomic numbers.
D) different atomic numbers but the same number of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A water solution that contains equal numbers of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions is
A) acidic.
B) basic.
C) alkaline.
D) neutral.
A) acidic.
B) basic.
C) alkaline.
D) neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Water is an example of a compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The formula H2O refers to
A) Two hydrogen molecules and one oxygen molecule.
B) One hydrogen molecule and two oxygen molecules.
C) A molecule that contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
D) A molecule that contains one hydrogen atom and two oxygen atoms.
A) Two hydrogen molecules and one oxygen molecule.
B) One hydrogen molecule and two oxygen molecules.
C) A molecule that contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
D) A molecule that contains one hydrogen atom and two oxygen atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When forming a bond, an atom that has 3 electrons in its second shell and a filled first shell will
A) lose 3 electrons from its second shell.
B) lose all of the electrons from its first shell.
C) lose all of the electrons from both its first and second shells.
D) gain 5 electrons in its second shell.
A) lose 3 electrons from its second shell.
B) lose all of the electrons from its first shell.
C) lose all of the electrons from both its first and second shells.
D) gain 5 electrons in its second shell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Chemistry is important to the study of physiology because
A) the foods that we eat are chemicals.
B) body functions depend on cellular functions that reflect chemical changes.
C) chemical reactions enable our bodies to extract energy from nutrients.
D) all of the above.
A) the foods that we eat are chemicals.
B) body functions depend on cellular functions that reflect chemical changes.
C) chemical reactions enable our bodies to extract energy from nutrients.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An atom with 10 protons and which has lost 2 electrons is electrically neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The first electron shell of an atom can hold a maximum of
A) 1 electron.
B) 2 electrons.
C) 4 electrons.
D) 8 electrons.
A) 1 electron.
B) 2 electrons.
C) 4 electrons.
D) 8 electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Two or more atoms bonding form a ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Proteins denature when
A) bonds between carbon and oxygen break.
B) hydrogen bonds break.
C) peptide bonds break.
D) peptide bonds form.
A) bonds between carbon and oxygen break.
B) hydrogen bonds break.
C) peptide bonds break.
D) peptide bonds form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is the most abundant inorganic substance in the body?
A) Carbohydrate
B) Water
C) Lipid
D) Protein
A) Carbohydrate
B) Water
C) Lipid
D) Protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider the following list of commonly found items and their pH values: 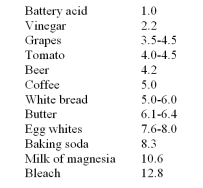 Which of the following choices includes all acids?
Which of the following choices includes all acids?
A) Egg whites, baking soda, milk of magnesia, and bleach
B) Tomatoes, egg whites, and baking soda
C) Vinegar, grapes, tomatoes, and coffee
D) Beer, butter, and baking soda
 Which of the following choices includes all acids?
Which of the following choices includes all acids?A) Egg whites, baking soda, milk of magnesia, and bleach
B) Tomatoes, egg whites, and baking soda
C) Vinegar, grapes, tomatoes, and coffee
D) Beer, butter, and baking soda

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Electrolytes that release hydrogen ions in water are
A) bases.
B) nucleotides.
C) acids.
D) electrons.
A) bases.
B) nucleotides.
C) acids.
D) electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The difference in hydrogen ion concentration between solutions with pH 4 and pH 5 is
A) twofold.
B) fivefold.
C) tenfold.
D) twentyfold.
A) twofold.
B) fivefold.
C) tenfold.
D) twentyfold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the body, oxygen
A) reacts with water to form carbonic acid.
B) is used during cellular respiration.
C) is a major electrolyte.
D) is produced by cells.
A) reacts with water to form carbonic acid.
B) is used during cellular respiration.
C) is a major electrolyte.
D) is produced by cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A chemical reaction in which parts of different molecules trade positions is a(n)
A) decomposition reaction.
B) exchange reaction.
C) reversible reaction.
D) synthesis reaction.
A) decomposition reaction.
B) exchange reaction.
C) reversible reaction.
D) synthesis reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is characteristic of carbohydrates?
A) They contain C, H, O, with twice as many hydrogen as oxygen atoms.
B) They provide much of the energy that the cell requires.
C) They include sugars and starches.
D) all of the above.
A) They contain C, H, O, with twice as many hydrogen as oxygen atoms.
B) They provide much of the energy that the cell requires.
C) They include sugars and starches.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An acid reacting with a base is
A) a synthesis reaction.
B) hydrolysis.
C) a decomposition reaction.
D) an exchange reaction.
A) a synthesis reaction.
B) hydrolysis.
C) a decomposition reaction.
D) an exchange reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A simple carbohydrate
A) has a molecular formula of C6H12O6.
B) is a building block of protein.
C) consists of several joined chains.
D) has only one nucleotide.
A) has a molecular formula of C6H12O6.
B) is a building block of protein.
C) consists of several joined chains.
D) has only one nucleotide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A person has alkalosis if the blood pH
A) is above 7.0.
B) is below 7.0.
C) rises above 7.5.
D) drops below 7.3.
A) is above 7.0.
B) is below 7.0.
C) rises above 7.5.
D) drops below 7.3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not organic?
A) Sodium chloride
B) Lipids
C) Nucleic acids
D) Enzymes
A) Sodium chloride
B) Lipids
C) Nucleic acids
D) Enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Lipids
A) are insoluble in water.
B) include phospholipids, cholesterol, and fats.
C) contain C, H, and O, but with proportionately less oxygen than in carbohydrates.
D) all of the above.
A) are insoluble in water.
B) include phospholipids, cholesterol, and fats.
C) contain C, H, and O, but with proportionately less oxygen than in carbohydrates.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Electrolytes are substances that
A) form covalent bonds with water.
B) ionize in water.
C) cannot conduct electricity in solution.
D) form bonds that are stable in water.
A) form covalent bonds with water.
B) ionize in water.
C) cannot conduct electricity in solution.
D) form bonds that are stable in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The secondary structure of a protein molecule is the result of
A) oxygen double bonds.
B) covalent bonds.
C) ionic bonds.
D) hydrogen bonds.
A) oxygen double bonds.
B) covalent bonds.
C) ionic bonds.
D) hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The pH scale measures the
A) concentration of hydrogen ions in solution.
B) number of molecules of salts dissolved in water.
C) number of hydroxide ions in water.
D) strength of an electrical current that a solution carries.
A) concentration of hydrogen ions in solution.
B) number of molecules of salts dissolved in water.
C) number of hydroxide ions in water.
D) strength of an electrical current that a solution carries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Synthesis reactions are particularly important in the body for
A) release of energy.
B) digestion of food products.
C) growth of body parts.
D) neutralization of acids by buffers.
A) release of energy.
B) digestion of food products.
C) growth of body parts.
D) neutralization of acids by buffers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A complete atom is electrically neutral because
A) the number of protons equals the number of neutrons.
B) the number of electrons equals the number of neutrons.
C) the number of electrons equals the number of protons.
D) electrons is greater than the number of protons.
A) the number of protons equals the number of neutrons.
B) the number of electrons equals the number of neutrons.
C) the number of electrons equals the number of protons.
D) electrons is greater than the number of protons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
On the pH scale
A) a tenfold difference in hydrogen ion concentration separates each whole number.
B) the lower the whole number on the scale, the greater the H+ concentration.
C) pH values above 7 are basic (alkaline).
D) all of the above.
A) a tenfold difference in hydrogen ion concentration separates each whole number.
B) the lower the whole number on the scale, the greater the H+ concentration.
C) pH values above 7 are basic (alkaline).
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Bases reacting with acids form ________ and water.
A) buffers
B) salts
C) new elements
D) proteins
A) buffers
B) salts
C) new elements
D) proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Glycogen is stored in the liver and ______.
A) spleen
B) skeletal muscles
C) pancreas
D) heart
A) spleen
B) skeletal muscles
C) pancreas
D) heart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A biomarker is
A) a gene that encodes a particular protein.
B) always a protein.
C) a body chemical associated with a particular disease or exposure to a toxin.
D) any chemical in the body.
A) a gene that encodes a particular protein.
B) always a protein.
C) a body chemical associated with a particular disease or exposure to a toxin.
D) any chemical in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An organic compound always contains
A) carbon and hydrogen.
B) oxygen and nitrogen.
C) carbon and oxygen.
D) nitrogen and hydrogen.
A) carbon and hydrogen.
B) oxygen and nitrogen.
C) carbon and oxygen.
D) nitrogen and hydrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The parts of a protein that change when it denatures are
A) the primary and secondary structures.
B) the secondary and tertiary structures.
C) the amino acid sequence and the secondary structure.
D) the tertiary and quaternary structures.
A) the primary and secondary structures.
B) the secondary and tertiary structures.
C) the amino acid sequence and the secondary structure.
D) the tertiary and quaternary structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A triglyceride consists of
A) 3 glycerols and 1 fatty acid.
B) 3 glucose molecules.
C) 3 fatty acids and 3 phosphate groups.
D) 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol.
A) 3 glycerols and 1 fatty acid.
B) 3 glucose molecules.
C) 3 fatty acids and 3 phosphate groups.
D) 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following groups of compounds is hydrophobic?
A) Carbohydrates
B) Lipids
C) Proteins
D) Nucleic Acids
A) Carbohydrates
B) Lipids
C) Proteins
D) Nucleic Acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
DNA
A) is a protein.
B) plays no role in the synthesis of fats.
C) stores genetic information, including instructions for enzymes that synthesize fats and carbohydrates.
D) is routinely broken down to provide cellular energy.
A) is a protein.
B) plays no role in the synthesis of fats.
C) stores genetic information, including instructions for enzymes that synthesize fats and carbohydrates.
D) is routinely broken down to provide cellular energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In phenylketonuria, an individual cannot break down the amino acid phenylalanine. Molecules that include phenylalanine build up in the blood, which causes intellectual disability and other symptoms. This inherited disease can be controlled by following a diet that is very low in
A) carbohydrates.
B) cholesterol.
C) protein.
D) nucleic acids.
A) carbohydrates.
B) cholesterol.
C) protein.
D) nucleic acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Nucleic acids are
A) very small, simple molecules.
B) structural molecules that have no function other than support.
C) composed of building blocks called nucleotides.
D) primary sources of cellular energy.
A) very small, simple molecules.
B) structural molecules that have no function other than support.
C) composed of building blocks called nucleotides.
D) primary sources of cellular energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following molecules does not have a polar region?
A) Water
B) Triglyceride
C) Water-soluble amino acid
D) Glucose
A) Water
B) Triglyceride
C) Water-soluble amino acid
D) Glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
DNA and RNA differ in that
A) RNA has deoxyribose and DNA has ribose.
B) RNA is double-stranded and DNA is single-stranded.
C) DNA holds genetic information and RNA uses that information to synthesize protein.
D) RNA is found only in the nucleus and DNA is found only in the cytoplasm.
A) RNA has deoxyribose and DNA has ribose.
B) RNA is double-stranded and DNA is single-stranded.
C) DNA holds genetic information and RNA uses that information to synthesize protein.
D) RNA is found only in the nucleus and DNA is found only in the cytoplasm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Saturated fats _______ than unsaturated fats.
A) contain more water
B) have more glycerol
C) have more single carbon-carbon bonds
D) have fewer hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atoms
A) contain more water
B) have more glycerol
C) have more single carbon-carbon bonds
D) have fewer hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atoms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Conformation is
A) the three-dimensional shape of a molecule, such as a protein.
B) the energy held in the bonds of an organic molecule, such as a protein.
C) the ability of DNA to copy itself.
D) the amino acid sequence (primary structure) of a protein.
A) the three-dimensional shape of a molecule, such as a protein.
B) the energy held in the bonds of an organic molecule, such as a protein.
C) the ability of DNA to copy itself.
D) the amino acid sequence (primary structure) of a protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Nucleic acids include
A) proteins and DNA.
B) RNA and DNA.
C) enzymes and RNA.
D) steroids and triglycerides.
A) proteins and DNA.
B) RNA and DNA.
C) enzymes and RNA.
D) steroids and triglycerides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Table sugar breaking down into glucose and fructose is a(n) _______ reaction.
A) synthesis
B) hydrolysis
C) acid-base
D) exchange reaction
A) synthesis
B) hydrolysis
C) acid-base
D) exchange reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The informational content of DNA and RNA is in the nitrogenous bases because
A) the bases are of several types and therefore can form a code sequence.
B) they all contain nitrogen.
C) the sugars and phosphates vary.
D) the bases are also parts of amino acids.
A) the bases are of several types and therefore can form a code sequence.
B) they all contain nitrogen.
C) the sugars and phosphates vary.
D) the bases are also parts of amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The type of organic molecule that can replicate is a
A) protein.
B) lipid.
C) carbohydrate.
D) nucleic acid.
A) protein.
B) lipid.
C) carbohydrate.
D) nucleic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of these is not a monosaccharide?
A) Glucose
B) Ribose
C) 6-carbon sugar
D) Sucrose
A) Glucose
B) Ribose
C) 6-carbon sugar
D) Sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Proteins
A) are structural materials.
B) can function as enzymes.
C) contain C, H, O, and N, and sometimes S.
D) all of the above.
A) are structural materials.
B) can function as enzymes.
C) contain C, H, O, and N, and sometimes S.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An enzyme is a ____.
A) protein that speeds up chemical reactions without being changed or depleted
B) protein that functions as a hormone
C) protein that inhibits chemical reactions by being changed or depleted
D) fibrous protein that is part of certain tissues in the body
A) protein that speeds up chemical reactions without being changed or depleted
B) protein that functions as a hormone
C) protein that inhibits chemical reactions by being changed or depleted
D) fibrous protein that is part of certain tissues in the body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



