Deck 13: Pests and Pest Control
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/91
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Pests and Pest Control
1
Weeds are types of
A)pathogens that spread disease to humans or between plants.
B)animals or plants that can cause disease.
C)plants that can rapidly spread through lightly airborne seeds.
D)pests that may threaten our health or compete with our food.
A)pathogens that spread disease to humans or between plants.
B)animals or plants that can cause disease.
C)plants that can rapidly spread through lightly airborne seeds.
D)pests that may threaten our health or compete with our food.
pests that may threaten our health or compete with our food.
2
A man discovers that he has a fungus attacking the roots of flowers in his garden.If he uses a broad-spectrum fungicide to kill the pests,he may risk
A)poisoning his children
B)killing beneficial pollinating insects
C)killing beneficial decomposer fungi and mycorrhizae
D)killing many of the flowers he is trying to protect.
A)poisoning his children
B)killing beneficial pollinating insects
C)killing beneficial decomposer fungi and mycorrhizae
D)killing many of the flowers he is trying to protect.
killing beneficial decomposer fungi and mycorrhizae
3
DDT quickly became widely used because it
A)was toxic to many types of insects.
B)seemed nontoxic to humans.
C)was inexpensive.
D)All of the choices are correct.
A)was toxic to many types of insects.
B)seemed nontoxic to humans.
C)was inexpensive.
D)All of the choices are correct.
All of the choices are correct.
4
Analysis of bedbug control options has revealed that
A)a single pesticide can give effective control.
B)infestations do not respond to any type of control.
C)adequate control will pose serious health risks to people.
D)a combination of several methods will be needed to have effective control.
A)a single pesticide can give effective control.
B)infestations do not respond to any type of control.
C)adequate control will pose serious health risks to people.
D)a combination of several methods will be needed to have effective control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suffering the impact of swarms of locusts,a farmer uses an airplane to spray an insecticide over 1,500 acres of his corn field.This farmer is trying to address this pest problem by using
A)a chemical treatment.
B)an agricultural treatment.
C)an ecological control.
D)integrated pest management.
A)a chemical treatment.
B)an agricultural treatment.
C)an ecological control.
D)integrated pest management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The current crisis in controlling bedbugs has encountered difficulties because
A)bedbugs are vectors for serious human diseases and require powerful chemical pesticides.
B)home applications of effective pesticides can endanger children.
C)the only way to get any control is to burn infested bedding.
D)bedbugs are internal parasites that require long doses of antibiotics to eliminate.
A)bedbugs are vectors for serious human diseases and require powerful chemical pesticides.
B)home applications of effective pesticides can endanger children.
C)the only way to get any control is to burn infested bedding.
D)bedbugs are internal parasites that require long doses of antibiotics to eliminate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Despite widespread use of insecticides and herbicides,infestations of insects,plant pathogens,and weeds currently cause a loss of about
A)5% of potential agricultural production in the United States.
B)35% of potential agricultural production in the United States.
C)50% of potential agricultural production in the United States.
D)95% of potential agricultural production in the United States.
A)5% of potential agricultural production in the United States.
B)35% of potential agricultural production in the United States.
C)50% of potential agricultural production in the United States.
D)95% of potential agricultural production in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Herbicides would be most useful in combating
A)mosquitoes that spread malaria in tropical rainforests.
B)weeds that infect our agricultural fields.
C)bacteria,such as Salmonella,which sometimes contaminate meat.
D)fungi that attack plant roots.
A)mosquitoes that spread malaria in tropical rainforests.
B)weeds that infect our agricultural fields.
C)bacteria,such as Salmonella,which sometimes contaminate meat.
D)fungi that attack plant roots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The effectiveness of DDT in agriculture allowed growers to
A)raise less resistant but more productive crops.
B)raise crops through the winter months.
C)raise vegetables without the need for pollinators.
D)eliminate irrigation in fields where it had been used previously.
A)raise less resistant but more productive crops.
B)raise crops through the winter months.
C)raise vegetables without the need for pollinators.
D)eliminate irrigation in fields where it had been used previously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Insecticides would be most useful in combating
A)mosquitoes that spread malaria.
B)weeds that infect our agricultural fields.
C)bacteria,such as Salmonella,which sometimes contaminate meat.
D)fungi that contribute to molds and mildew that lead to respiratory infections.
A)mosquitoes that spread malaria.
B)weeds that infect our agricultural fields.
C)bacteria,such as Salmonella,which sometimes contaminate meat.
D)fungi that contribute to molds and mildew that lead to respiratory infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Weeds are commonly defined as any
A)monocot that has flowers,grows closely to the ground,and consumes nutrients in the soil.
B)dicot that blooms for more than one month of the year and competes with turf grasses for sunlight.
C)plant that competes with crops,forests,or forage grasses for sunlight and nutrients.
D)plant that is found growing outside of its native ecosystem.
A)monocot that has flowers,grows closely to the ground,and consumes nutrients in the soil.
B)dicot that blooms for more than one month of the year and competes with turf grasses for sunlight.
C)plant that competes with crops,forests,or forage grasses for sunlight and nutrients.
D)plant that is found growing outside of its native ecosystem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Chlorinated hydrocarbon pesticides,like DDT,are synthetic versions of
A)heavy metals.
B)non-biodegradable,persistent molecules.
C)ions and salts.
D)vitamins and minerals.
A)heavy metals.
B)non-biodegradable,persistent molecules.
C)ions and salts.
D)vitamins and minerals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Control of bedbugs is difficult because their habitat is
A)lawns and gardens frequented by people and pets.
B)initially cats and dogs and then transfers to human hosts.
C)human bedding,cracks in bed frames and nearby household objects.
D)widely dispersed in forested and brushy environments.
A)lawns and gardens frequented by people and pets.
B)initially cats and dogs and then transfers to human hosts.
C)human bedding,cracks in bed frames and nearby household objects.
D)widely dispersed in forested and brushy environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The local health department is trying to limit the spread of West Nile virus in a suburban community.West Nile Virus is spread by mosquitoes as they feed.In newspapers and on the radio,people in the region are told to drain standing water from any places where mosquitoes might breed.In addition,the health department announces that in a week,they will begin spraying a fog of mosquito poison in the early evening,as soon as the sun sets and mosquitoes become most active.The approach taken by this health department best represents
A)chemical treatment.
B)agricultural treatment.
C)ecological control.
D)integrated pest management.
A)chemical treatment.
B)agricultural treatment.
C)ecological control.
D)integrated pest management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Pesticide resistant insects would
A)have evolved more slowly if the pesticides were used in just a few regions.
B)not have evolved if even more pesticide had been used.
C)have evolved if a different type of pesticide was used each year.
D)have evolved if an herbicide had been used instead of a pesticide.
A)have evolved more slowly if the pesticides were used in just a few regions.
B)not have evolved if even more pesticide had been used.
C)have evolved if a different type of pesticide was used each year.
D)have evolved if an herbicide had been used instead of a pesticide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

The insects infesting this bag of rice are
A)stored product pests that can live on almost no water and are resistant to pesticides.
B)is a rare species occasionally caught in U.S.grain imports over the past decade.
C)highly diet-specific,eating only certain strains of rice.
D)unsightly,but of no economic or health significance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
DDT was widely used,and remains in use today in some countries,to fight malaria by
A)killing the parasite that causes malaria.
B)fouling the water used by mosquitoes for reproduction.
C)killing the virus that causes malaria.
D)killing mosquitoes that are the major malarial vector.
A)killing the parasite that causes malaria.
B)fouling the water used by mosquitoes for reproduction.
C)killing the virus that causes malaria.
D)killing mosquitoes that are the major malarial vector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Pesticide resistant insects develop from the widespread use of insecticides because
A)pesticides cause mutations in the insects that make them resistant.
B)pesticides increase the biotic potential of some insects.
C)insects learn to avoid the places where insecticides have been applied.
D)over many generations,the naturally resistant pests survive and increase in number.
A)pesticides cause mutations in the insects that make them resistant.
B)pesticides increase the biotic potential of some insects.
C)insects learn to avoid the places where insecticides have been applied.
D)over many generations,the naturally resistant pests survive and increase in number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The common definition of pest
A)is based on the negative impacts of an organism on human activities.
B)varies depending upon whether the organism is an herbivore or carnivore.
C)varies widely in the world depending upon the particular culture.
D)is limited to organisms that are plants.
A)is based on the negative impacts of an organism on human activities.
B)varies depending upon whether the organism is an herbivore or carnivore.
C)varies widely in the world depending upon the particular culture.
D)is limited to organisms that are plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A garden is suffering from a quickly growing mold.The most effective treatment for this problem would be the application of
A)an herbicide.
B)a fungicide.
C)a pesticide.
D)a rodenticide.
A)an herbicide.
B)a fungicide.
C)a pesticide.
D)a rodenticide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Non-persistent pesticides like organophosphates and carbamates
A)will be far less likely to cause biomagnification and bioamplification than persistent pesticides.
B)will produce fatal toxic effects in all producers and low-level consumers that are exposed.
C)target only the pest species;there are no non-target kills.
D)produce resistance in pest predators but not in the pests themselves.
A)will be far less likely to cause biomagnification and bioamplification than persistent pesticides.
B)will produce fatal toxic effects in all producers and low-level consumers that are exposed.
C)target only the pest species;there are no non-target kills.
D)produce resistance in pest predators but not in the pests themselves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program
A)will test pesticides for their ability to cause cancer.
B)will examine all disease causing aspects of pesticides.
C)is being developed by the EPA and will screen chemicals for potential endocrine disruption.
D)has already identified and banned more than 300 pesticides that disrupt the endocrine system.
A)will test pesticides for their ability to cause cancer.
B)will examine all disease causing aspects of pesticides.
C)is being developed by the EPA and will screen chemicals for potential endocrine disruption.
D)has already identified and banned more than 300 pesticides that disrupt the endocrine system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The levels of mercury are low in the fish eaten almost daily by people living near an ocean.For these people,bioaccumulation means that
A)people eliminate most of the mercury they consume after a single day.
B)mercury builds up in the fish and not the people.
C)mercury has been accumulating in their bodies for many years.
D)mercury and other heavy metals accumulate in the bottom of the ocean and not in the fish they eat.
A)people eliminate most of the mercury they consume after a single day.
B)mercury builds up in the fish and not the people.
C)mercury has been accumulating in their bodies for many years.
D)mercury and other heavy metals accumulate in the bottom of the ocean and not in the fish they eat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Pesticide resistance against one pesticide
A)is permanently restricted to that one kind of pesticide.
B)can become resistance to many if many are used.
C)can provide protection against herbivores.
D)often harms insects by decreasing their ability to reproduce.
A)is permanently restricted to that one kind of pesticide.
B)can become resistance to many if many are used.
C)can provide protection against herbivores.
D)often harms insects by decreasing their ability to reproduce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a food chain consisting of toxic soil,toxic grasses,rabbits that eat the toxic grass,and hawks that eat the rabbits,the highest concentrations of toxins would occur in the
A)tissues of the grasses.
B)tissues of the rabbits.
C)tissues of the hawks.
D)soils.
A)tissues of the grasses.
B)tissues of the rabbits.
C)tissues of the hawks.
D)soils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
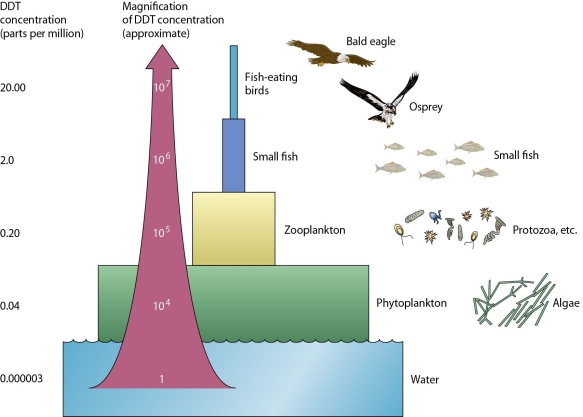
In the processes of biomagnification and bioaccumulation described in the figure,
A)the pesticide has to be non-biodegradable (persistent)for the processes to occur.
B)the greatest levels of mortality are in the producers and first level consumers.
C)the concentrations may not be fatal if the top consumers are very small.
D)consumers at the top of the food chain will develop rapid pesticide resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A woman has a large garden and decides this year she will not let the pests get beyond control.At the earliest sign of insect pests,she applies an organic insecticide and continues to apply it every month throughout the growing season.The next year the woman decides not to use any insecticides,thinking that she must have eliminated the pests with the prior year's treatments.Unfortunately,the pests reappear in numbers greater than she has ever seen before,and her crops are destroyed.Investigating this phenomenon,she learns that she has just experienced a phenomenon known as
A)resurgence.
B)pesticide resistance.
C)natural selection.
D)emergence.
A)resurgence.
B)pesticide resistance.
C)natural selection.
D)emergence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The evolution of pesticide resistance,resurgence,and secondary-pest outbreaks are only some of the problems that result from reliance on
A)crop rotation and biological controls,which disrupt the natural dynamics of ecosystems.
B)pesticides,creating the need to alternate between a pesticide and an herbicide every other year.
C)rodenticides to kill weeds and insect pests and prevent the spread of viral diseases.
D)pesticides,creating a never-ending pesticide treadmill requiring new pest-fighting strategies.
A)crop rotation and biological controls,which disrupt the natural dynamics of ecosystems.
B)pesticides,creating the need to alternate between a pesticide and an herbicide every other year.
C)rodenticides to kill weeds and insect pests and prevent the spread of viral diseases.
D)pesticides,creating a never-ending pesticide treadmill requiring new pest-fighting strategies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Our experience with herbicides and insecticides indicate that
A)both are capable of selecting for natural resistance by evolution.
B)herbicides but not insecticides are capable of selecting for natural resistance by evolution.
C)insecticides but not herbicides are capable of selecting for natural resistance by evolution.
D)neither are capable of selecting for natural resistance by evolution.
A)both are capable of selecting for natural resistance by evolution.
B)herbicides but not insecticides are capable of selecting for natural resistance by evolution.
C)insecticides but not herbicides are capable of selecting for natural resistance by evolution.
D)neither are capable of selecting for natural resistance by evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The pesticides that also function as endocrine disruptors cause disease by
A)causing excessive secretion of stomach acids.
B)mimicking the effects of estrogenic hormones.
C)causing muscle spasms and cramping in major muscle groups.
D)greatly reducing the ability of the intestines to absorb nutrients.
A)causing excessive secretion of stomach acids.
B)mimicking the effects of estrogenic hormones.
C)causing muscle spasms and cramping in major muscle groups.
D)greatly reducing the ability of the intestines to absorb nutrients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If glyphosate-resistant weeds become widespread in the future,we can expect farmers to
A)kill these weeds by applying more glyphosate to their fields.
B)switch to a pesticide that is more effective for this problem.
C)return to traditional tillage,leading to increased soil erosion.
D)switch to raising these "weeds" as a new type of crop.
A)kill these weeds by applying more glyphosate to their fields.
B)switch to a pesticide that is more effective for this problem.
C)return to traditional tillage,leading to increased soil erosion.
D)switch to raising these "weeds" as a new type of crop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a food chain,biomagnification is the result of
A)bioaccumulation up the trophic levels.
B)bioaccumulation down the trophic levels.
C)higher levels of toxins than in the organisms living in that region.
D)the elimination of toxic wastes from the body.
A)bioaccumulation up the trophic levels.
B)bioaccumulation down the trophic levels.
C)higher levels of toxins than in the organisms living in that region.
D)the elimination of toxic wastes from the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A gardener applied heavy doses of the same insecticide to her garden for two consecutive years to kill squash bugs.During the third year,although the squash bugs were reduced,the woman called in an expert to explain why she had an abundance of new pests that were destroying her garden.The expert explained that the abundant new pests were largely due to her previous use of an insecticide in a phenomenon known as
A)pesticide resistance.
B)secondary-pest outbreak.
C)triennial pest emergence.
D)bounce back resurgence.
A)pesticide resistance.
B)secondary-pest outbreak.
C)triennial pest emergence.
D)bounce back resurgence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Widely applying pesticides may lead to resurgence and secondary-pest outbreaks because
A)the insecticide also killed the natural competitors and predators of the pests.
B)the plants have now lost their ability to fight the pests.
C)pesticides typically harm plants in ways that take several years to appear.
D)new species that are more resistant to insecticides have evolved.
A)the insecticide also killed the natural competitors and predators of the pests.
B)the plants have now lost their ability to fight the pests.
C)pesticides typically harm plants in ways that take several years to appear.
D)new species that are more resistant to insecticides have evolved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Pesticide exposure has been shown to cause diseases of the
A)endocrine and immune systems.
B)muscular and skeletal systems.
C)pancreas and kidneys.
D)ears and eyes.
A)endocrine and immune systems.
B)muscular and skeletal systems.
C)pancreas and kidneys.
D)ears and eyes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The best way to avoid the evolution of pesticide resistance is to
A)use more of the pesticide anytime resistance appears.
B)use crop rotation and biological controls instead of pesticides.
C)develop new forms of pesticides.
D)apply pesticides to the soil before planting and after harvesting a crop.
A)use more of the pesticide anytime resistance appears.
B)use crop rotation and biological controls instead of pesticides.
C)develop new forms of pesticides.
D)apply pesticides to the soil before planting and after harvesting a crop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Many synthetic organic chemicals are concentrated in the fat of carnivores because
A)the chemicals are non-biodegradable or persistent and highly soluble in lipids.
B)the chemicals are highly soluble in water.
C)these animals eliminate toxins from the body by storing them in fat.
D)fat is able to break down toxins more effectively than the liver.
A)the chemicals are non-biodegradable or persistent and highly soluble in lipids.
B)the chemicals are highly soluble in water.
C)these animals eliminate toxins from the body by storing them in fat.
D)fat is able to break down toxins more effectively than the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The highest amounts of pesticides or their breakdown products would be found in a cougar in its
A)saliva.
B)muscles.
C)kidneys.
D)body fat.
A)saliva.
B)muscles.
C)kidneys.
D)body fat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Most organisms accumulate synthetic organic chemicals in their bodies because these chemicals
A)are easily converted into molecules that are used to build parts of cells.
B)are a concentrated source of minerals,needed for cellular metabolism.
C)cannot be broken down by the natural metabolic mechanisms.
D)are a major source of calories when food is not available.
A)are easily converted into molecules that are used to build parts of cells.
B)are a concentrated source of minerals,needed for cellular metabolism.
C)cannot be broken down by the natural metabolic mechanisms.
D)are a major source of calories when food is not available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Chronic pesticide exposure has been clearly linked to
A)malaria and bubonic plague.
B)viral outbreaks.
C)cancer,neurological disorders,and infertility.
D)heart disease and strokes.
A)malaria and bubonic plague.
B)viral outbreaks.
C)cancer,neurological disorders,and infertility.
D)heart disease and strokes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A foundation wishes to promote sustainable agriculture and organic farming.A consultant suggests that the foundation may want to give money to researchers investigating ecological control of pests.As the foundation reviews grant proposals,they should give the most money to researchers wanting to learn more about
A)the natural relationships between pests,their host plants,and the general environment.
B)the specific nutritional requirements of the desired crops.
C)differences between persistent and nonpersistent pesticides previously used in the region.
D)biomagnification of pesticides used to control the pests.
A)the natural relationships between pests,their host plants,and the general environment.
B)the specific nutritional requirements of the desired crops.
C)differences between persistent and nonpersistent pesticides previously used in the region.
D)biomagnification of pesticides used to control the pests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Developing a new form of ecological pest control,researchers engineer crops to produce the pheromones of the pest.The crops now produce the pest pheromone,overwhelming the fields and causing the male pests to fail to find a mate.This new form of ecological pest control combines
A)natural enemies and cultural control.
B)cultural and natural enemies control.
C)genetic and cultural control.
D)genetic and natural chemical control.
A)natural enemies and cultural control.
B)cultural and natural enemies control.
C)genetic and cultural control.
D)genetic and natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The dangers of widespread DDT use are largely due to two main characteristics of DDT,its
A)bioremediation and nonpersistence.
B)degradation and nonpersistence.
C)biomagnification and persistence.
D)bioremediation and persistence.
A)bioremediation and nonpersistence.
B)degradation and nonpersistence.
C)biomagnification and persistence.
D)bioremediation and persistence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Most of the wheat,rice,and corn raised in the world has resulted from genetic engineering of one sort or another,either by crossing certain varieties or deliberately transferring genes using transgenic techniques.These methods select for plants that produce their own defenses against pests with chemicals or physical barriers.Helping to feed the world,this represents an example of
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Researchers genetically engineer a crop to produce chemicals that attract the natural enemies of a pest.This approach combines
A)natural enemies and cultural control.
B)cultural and genetic control.
C)genetic and natural enemies control.
D)cultural control and natural chemical control.
A)natural enemies and cultural control.
B)cultural and genetic control.
C)genetic and natural enemies control.
D)cultural control and natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In any food web,biomagnification will result in the highest concentrations of toxins in the
A)lowest trophic level.
B)highest trophic level.
C)highest photosynthetic trophic level.
D)herbivores of the systems.
A)lowest trophic level.
B)highest trophic level.
C)highest photosynthetic trophic level.
D)herbivores of the systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Raising young children who crawl about the floor,Mom does not want to spray chemicals of any sort in or around the home.However,she is well aware of West Nile virus spread by mosquitoes and Lyme disease spread by ticks.Therefore,Mom decides to take a different strategy.Carefully examining and repairing the window screens,window enclosures,and doorways,she closes up any cracks or tears where bugs might get in.This loving mother is protecting her children by using
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Compared to persistent pesticides,nonpersistent pesticides are
A)less likely to cause resurgences,secondary-pest outbreaks,or promote pesticide resistance.
B)more likely to cause biomagnification and bioamplification.
C)equally as likely to cause resurgences,secondary-pest outbreaks,or promote pesticide resistance.
D)more likely to cause resurgences and secondary-pest outbreaks but less likely to promote pesticide resistance.
A)less likely to cause resurgences,secondary-pest outbreaks,or promote pesticide resistance.
B)more likely to cause biomagnification and bioamplification.
C)equally as likely to cause resurgences,secondary-pest outbreaks,or promote pesticide resistance.
D)more likely to cause resurgences and secondary-pest outbreaks but less likely to promote pesticide resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In many freshwater toxicology studies,investigators rely upon knowledge of biomagnification to guide their investigations.If the researchers were looking for evidence of mercury contamination from a nearby power plant,they would most likely find the highest levels in the blood of
A)herbivorous ducks living near the power plant.
B)rabbits that live near the power plant.
C)tadpoles in water near the power plant.
D)snapping turtles in water near the power plant.
A)herbivorous ducks living near the power plant.
B)rabbits that live near the power plant.
C)tadpoles in water near the power plant.
D)snapping turtles in water near the power plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Because of biomagnification,the most toxic organisms in any ecosystem will be the
A)producers.
B)primary consumers.
C)secondary consumers.
D)soils.
A)producers.
B)primary consumers.
C)secondary consumers.
D)soils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
According to recent EPA studies,70% of pesticide poisonings in humans come from
A)heavy metals such as arsenic and lead.
B)persistent chemicals like DDT.
C)non-persistent organophosphates.
D)eating meat tainted with persistent pesticides.
A)heavy metals such as arsenic and lead.
B)persistent chemicals like DDT.
C)non-persistent organophosphates.
D)eating meat tainted with persistent pesticides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
a)
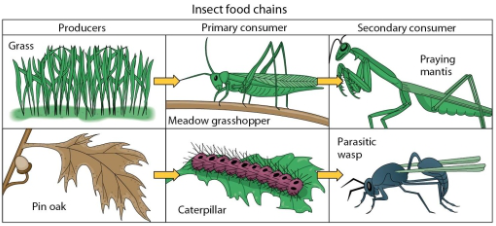
b)

Two insect food chains are illustrated in this figure.If a persistent insecticide were applied to the plants in these systems,where would we expect to find the high concentrations due to biomagnification?
A)the grasshopper and caterpillar
B)the praying mantis and caterpillar
C)the caterpillar and parasitic wasp
D)the praying mantis and parasitic wasp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Colony collapse disorder
A)affects honey bees colonies leaving most of the workers dead in the hive.
B)has been traced to poisoning by organophosphate pesticides.
C)is thought to be caused by a combination of pesticides,pathogens,hive pests or other synergistic toxic chemicals.
D)is not a threat to U.S.crops because other unaffected pollinators will replace honey bees.
A)affects honey bees colonies leaving most of the workers dead in the hive.
B)has been traced to poisoning by organophosphate pesticides.
C)is thought to be caused by a combination of pesticides,pathogens,hive pests or other synergistic toxic chemicals.
D)is not a threat to U.S.crops because other unaffected pollinators will replace honey bees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When college students first learn about the invasion of zebra mussels into the Great Lakes about 25 years ago,they frequently ask what controls zebra mussel populations in their native regions.If introducing natural zebra mussel predators into the Great Lakes would not cause new problems,this approach might work as an example of
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Farmers in the Midwestern United States routinely rotate between soybean and corn crops.Sometimes it is said that they do this because the soybeans introduce nitrogen into the soil.Although this is true,farmers also rotate their corn and soybean crops as a form of
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Synergistic effects involving pesticides occur when
A)nonpersistent pesticides are transformed into persistent pesticides.
B)pesticide toxicity interacts with other environmental or chemical factors to produce an unexpected outcome.
C)one pesticide is used to control numerous different pests.
D)beneficial insects or other wildlife become non-target casualties of pesticides.
A)nonpersistent pesticides are transformed into persistent pesticides.
B)pesticide toxicity interacts with other environmental or chemical factors to produce an unexpected outcome.
C)one pesticide is used to control numerous different pests.
D)beneficial insects or other wildlife become non-target casualties of pesticides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Today the best approach to fighting malaria in developing countries primarily relies on the
A)widespread application of DDT.
B)use of mosquito nets and DDT.
C)use of mosquito nets but not DDT.
D)antimalarial drugs.
A)widespread application of DDT.
B)use of mosquito nets and DDT.
C)use of mosquito nets but not DDT.
D)antimalarial drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
First published in 1962,the book Silent Spring helped to establish
A)the modern civil rights movement.
B)modern environmental movement.
C)the Food and Drug Administration.
D)the National Wildlife Federation.
A)the modern civil rights movement.
B)modern environmental movement.
C)the Food and Drug Administration.
D)the National Wildlife Federation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59

The bird in this figure is a fish-eating osprey with its chicks.What commonly used pesticide nearly caused the extinction of this and other large predatory bird species in the 1970s?
A)malathion
B)Round Up
C)DDT
D)pyrethroids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Nonpersistent pesticides can be more dangerous than persistent pesticides because they usually
A)are more toxic.
B)last longer in the environment.
C)are radioactive.
D)are broken down into nontoxic products within a few weeks of application.
A)are more toxic.
B)last longer in the environment.
C)are radioactive.
D)are broken down into nontoxic products within a few weeks of application.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The primary job of APHIS is to
A)intercept pests arriving through international or interstate commerce.
B)monitor and evaluate pest control using IPM methods.
C)develop new biological pest control methods.
D)monitor biofouling organisms and their damage to ships,docks and dams.
A)intercept pests arriving through international or interstate commerce.
B)monitor and evaluate pest control using IPM methods.
C)develop new biological pest control methods.
D)monitor biofouling organisms and their damage to ships,docks and dams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
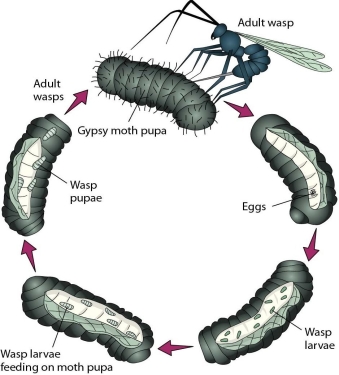
The parasitic relationship illustrated in this figure represents a type of
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
You are tired of watching your crops die in the field from several pest species.You decide that next year you are going to use every type of ecological pest control you can find to address your problem.Over the winter you get ready,ordering pheromones that interfere with the reproduction of the pests,sterile male flies that will try to reproduce with some of the pest flies that you have,and wasps that lay their eggs in the larvae of another of your pests.It is expensive,but you think this should work well.Which of the following forms of control are you not using?
A)cultural control
B)natural enemies control
C)genetic control
D)natural chemical control
A)cultural control
B)natural enemies control
C)genetic control
D)natural chemical control

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A promising alternative to toxic pesticides to reduce the billions of dollars damage done by marine biofouling organisms is
A)marine predatory insects that eat the sessile biofoulers.
B)polymers that make it difficult for the organisms to attach to a substrate.
C)attracting fish to fouled sites to eat the fouling organisms.
D)electrified ship hulls,intake pipes and docks to electrocute the pests.
A)marine predatory insects that eat the sessile biofoulers.
B)polymers that make it difficult for the organisms to attach to a substrate.
C)attracting fish to fouled sites to eat the fouling organisms.
D)electrified ship hulls,intake pipes and docks to electrocute the pests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The spread of Integrated Pest Management (IPM)continues because
A)traditional methods using pesticides are being outlawed.
B)IPM eliminates pests completely and does not create pesticide resistance.
C)the benefits of IPM are many and the costs are greatly reduced.
D)government regulations worldwide are mandating these techniques.
A)traditional methods using pesticides are being outlawed.
B)IPM eliminates pests completely and does not create pesticide resistance.
C)the benefits of IPM are many and the costs are greatly reduced.
D)government regulations worldwide are mandating these techniques.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Struggling with various pests attacking the garden every year,a neighbor suggests that next year they might plant a row of marigold flowers completely around the outside edge of the garden.Sure enough,the next year they did this and had fewer pests and better crops.This strategy represents
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
To meet current USDA organic food standards,100% organic certified foods may be
A)genetically engineered.
B)irradiated.
C)fertilized with sewage sludge.
D)meat,grains,or vegetables.
A)genetically engineered.
B)irradiated.
C)fertilized with sewage sludge.
D)meat,grains,or vegetables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Organically grown foods are typically
A)free of all pesticide residues.
B)usually less expensive than non-organic foods.
C)grown with traditional methods,diverse crops,soil conservation and based in local economies.
D)grown on farms that are typically larger than non-organic food farms.
A)free of all pesticide residues.
B)usually less expensive than non-organic foods.
C)grown with traditional methods,diverse crops,soil conservation and based in local economies.
D)grown on farms that are typically larger than non-organic food farms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69

The sick tomato plant in this figure is devastated by tomato wilt,a type of fungus that infects the soil with spores and returns every year to attack more tomato plants.One effective way to combat this fungus using ecological/cultural pest control is to
A)keep dead tomato plants from the prior year around to try to divert the fungus to the dead plants.
B)spray a broad-spectrum insecticide over your garden before and after the crops come up.
C)plant something other than tomatoes in this part of the garden next year.
D)rake the soil before planting next year's tomatoes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In using control by natural enemies of pests,from the ecological perspective it is best to
A)import enemies from abroad or from distant ecosystems to have the highest kill rate.
B)select enemies that have a very broad range of pest prey or hosts.
C)couple this method with intensive broad-spectrum pesticide spraying.
D)select enemies that are local and have a narrow specificity for the pest in question.
A)import enemies from abroad or from distant ecosystems to have the highest kill rate.
B)select enemies that have a very broad range of pest prey or hosts.
C)couple this method with intensive broad-spectrum pesticide spraying.
D)select enemies that are local and have a narrow specificity for the pest in question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Integrated pest management focuses on
A)eliminating crop damage by using preventative techniques.
B)eliminating crop damage by using only cultural techniques.
C)maintaining crop damage below the economic threshold using preventative techniques.
D)maintaining crop damage below the economic threshold using broad-spectrum pesticides.
A)eliminating crop damage by using preventative techniques.
B)eliminating crop damage by using only cultural techniques.
C)maintaining crop damage below the economic threshold using preventative techniques.
D)maintaining crop damage below the economic threshold using broad-spectrum pesticides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Farmers who regularly experience pests that cause catastrophic damage once infestation occurs,may benefit from insurance spraying,in which
A)the insurance company pays for the spraying and in turn does not pay for damaged crops.
B)just a small percentage of pesticide is released to warn the pests that more is to come.
C)the crops are sprayed with a pesticide before there is evidence of crop damage.
D)a chemical treatment for one pest is applied,but no broad-spectrum pesticides are used.
A)the insurance company pays for the spraying and in turn does not pay for damaged crops.
B)just a small percentage of pesticide is released to warn the pests that more is to come.
C)the crops are sprayed with a pesticide before there is evidence of crop damage.
D)a chemical treatment for one pest is applied,but no broad-spectrum pesticides are used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The use of pesticides crosses the economic threshold when the cost of
A)crop damage is more than the cost of the pesticide.
B)pesticide is more than the cost of the crop damage.
C)harvesting the crop is more than the cost of raising the crop.
D)cost of raising the crop is more than the cost of the crop damage.
A)crop damage is more than the cost of the pesticide.
B)pesticide is more than the cost of the crop damage.
C)harvesting the crop is more than the cost of raising the crop.
D)cost of raising the crop is more than the cost of the crop damage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Flies are destroying your crop despite years of investing in pesticides.Investigating an ecological pest control approach,you learn that the female flies that are killing your crop mate only once,lay their eggs,and then die.In fact,you can purchase sterile male flies to release around your crop to keep these flies from reproducing.Such a strategy represents
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Bt crops
A)are GM plants that incorporate the gene for producing a potent bacterially produced insecticide.
B)produce chemicals that interfere with the molting of insect pests.
C)should always be planted in pure stands to reduce the chance of Bt resistant pests.
D)produce chemicals that are similar to insect pheromones,interrupting pest mating cycles.
A)are GM plants that incorporate the gene for producing a potent bacterially produced insecticide.
B)produce chemicals that interfere with the molting of insect pests.
C)should always be planted in pure stands to reduce the chance of Bt resistant pests.
D)produce chemicals that are similar to insect pheromones,interrupting pest mating cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Using a broad spectrum chemical pesticide would be counterproductive if you were relying on
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The cassava is an important food crop for people living in sub-Saharan Africa.In the 1970s,mealybug infestations destroyed harvests and people starved.A researcher who studied the mealybug in its native environment discovered a parasitoid wasp that was a natural predator.After extensive testing to determine safety,the parasitoid wasp was introduced into the sub-Saharan region with tremendous effect controlling the mealybug throughout most of Africa.This approach represented a form of
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.
A)cultural control.
B)natural enemies control.
C)genetic control.
D)natural chemical control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Because it does not affect the crop yield or nutritional value,a local grower advertises that in his orchard he does not use
A)cosmetic spraying.
B)insurance spraying.
C)crop rotation.
D)natural predators.
A)cosmetic spraying.
B)insurance spraying.
C)crop rotation.
D)natural predators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Deciding to use a natural enemies approach to control the mites that infect her crops,a farmer purchases 10,000 ladybugs in the spring and spreads them over her 100 acre fields.This represents the use of natural
A)predators.
B)parasitoids.
C)pathogens.
D)plant-eaters.
A)predators.
B)parasitoids.
C)pathogens.
D)plant-eaters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Indonesia has become a model for other rice growing nations because
A)they switched from heavy pesticide spraying to IPM with help from the FAO.
B)they have planted exclusively the improved GM golden rice.
C)they have brokered cheap prices for importing U.S.made pesticides.
D)rice is planted and grown in undisturbed ecosystems.
A)they switched from heavy pesticide spraying to IPM with help from the FAO.
B)they have planted exclusively the improved GM golden rice.
C)they have brokered cheap prices for importing U.S.made pesticides.
D)rice is planted and grown in undisturbed ecosystems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 91 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



