Deck 16: Our Galaxy: The Milky Way
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Our Galaxy: The Milky Way
1
Neutral hydrogen atoms are found only inside dense clouds where they are shielded from stellar radiation.
True
2
There is a 109 M black hole at the center of the Milky Way that is rapidly accreting stars and gas.
False
3
Cosmic rays come mostly from extragalactic sources and contribute little to the overall energy balance in the Milky Way disk.
False
4
Our galaxy is a typical barred spiral galaxy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Stars in the Milky Way that are 12 to 13 billion years old are only found in globular clusters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The coldest molecular clouds in our galaxy have temperatures of approximately 1000 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Every open star cluster in the Milky Way is younger than even the youngest globular cluster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The chemical abundance of a main-sequence star usually reflects how much nuclear burning has gone on inside it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Milky Way has two major spiral arms that emanate from the ends of its bar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
There are many more individual stars residing in the Milky Way stellar halo than inside globular clusters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Stars forming in molecular clouds tend to form first in the low-density periphery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Open clusters are only found in the disk of the Milky Way; globular clusters are only found in the halo of the Milky Way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The dust in the interstellar medium comes primarily from stellar winds of main-sequence stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The only effect of interstellar dust is that it makes objects appear redder than they really are.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
We observe molecular hydrogen gas (H2)using 21-cm emission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Our galaxy is classified as an Sd galaxy in the Hubble sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The average density of the interstellar medium is many times less dense than the best vacuum on Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Halo stars formed before gas in the Milky Way collapsed to form the disk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Globular clusters have much higher stellar densities than the local solar neighborhood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The lowest-density gas in the interstellar medium is also the coldest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Cosmic rays are:
A) photons with even higher energy than gamma rays
B) high-velocity particles produced in novae
C) primarily protons with very high energies
D) synchrotron emission from strong magnetic fields
A) photons with even higher energy than gamma rays
B) high-velocity particles produced in novae
C) primarily protons with very high energies
D) synchrotron emission from strong magnetic fields

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Warm ionized gas in the interstellar medium appears __________ when imaged in the optical region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
A) red
B) yellow
C) blue
D) dark
A) red
B) yellow
C) blue
D) dark

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Dust that is heated to 30 K will emit a blackbody spectrum that peaks at:
A) 1 m
B) 30 m
C) 50 m
D) 100 m
A) 1 m
B) 30 m
C) 50 m
D) 100 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why is 21-cm radiation the best way to map the spiral arms in the Milky Way?
A) The molecular hydrogen gas that produces this emission is concentrated in the spiral arms.
B) These photons,which are produced by neutral hydrogen,penetrate the dense clouds of gas and dust in the disk.
C) This synchrotron emission is produced by supernovae,which are concentrated in the spiral arms.
D) Radio telescopes are easier to operate than optical telescopes and observations can be made even during the daytime.
A) The molecular hydrogen gas that produces this emission is concentrated in the spiral arms.
B) These photons,which are produced by neutral hydrogen,penetrate the dense clouds of gas and dust in the disk.
C) This synchrotron emission is produced by supernovae,which are concentrated in the spiral arms.
D) Radio telescopes are easier to operate than optical telescopes and observations can be made even during the daytime.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An H II region signals the presence of:
A) newly formed stars
B) young stars
C) O- and B-type stars
D) all of the above
A) newly formed stars
B) young stars
C) O- and B-type stars
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Molecular cloud cores are places where you might find:
A) protostars
B) Herbig-Haro objects
C) carbon monoxide
D) all of the above
A) protostars
B) Herbig-Haro objects
C) carbon monoxide
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A typical molecular cloud has a temperature of approximately:
A) 0.3 K
B) 10 K
C) 300 K
D) 1000 K
A) 0.3 K
B) 10 K
C) 300 K
D) 1000 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Cosmic rays in the Milky Way are important because:
A) these energetic photons easily penetrate the Earth's atmosphere
B) they can be collected and used to generate electricity
C) they have about the same energy as that contained in the radiation and the kinetic energy of gas clouds
D) they carry information about AGN in external galaxies
A) these energetic photons easily penetrate the Earth's atmosphere
B) they can be collected and used to generate electricity
C) they have about the same energy as that contained in the radiation and the kinetic energy of gas clouds
D) they carry information about AGN in external galaxies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
We detect neutral gas in the interstellar medium by looking for radiation at 21 cm that arises when:
A) an electron moves from the n = 1 to n = 2 state in a hydrogen atom
B) an electron is ionized from a hydrogen atom
C) carbon monoxide (CO)gas is excited by stellar radiation
D) the spin of an electron flips and aligns with the spin of a proton in a hydrogen atom
A) an electron moves from the n = 1 to n = 2 state in a hydrogen atom
B) an electron is ionized from a hydrogen atom
C) carbon monoxide (CO)gas is excited by stellar radiation
D) the spin of an electron flips and aligns with the spin of a proton in a hydrogen atom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Sitting in a 100°F hot tub feels much hotter than standing outside on a 100°F day.This analogy illustrates why:
A) interstellar dust is dark at optical wavelengths but bright in the infrared
B) supernovae can heat their shells to such high temperatures
C) an astronaut would feel cold in the 106 K intercloud gas
D) the Solar System is immersed in a hot bubble of gas
A) interstellar dust is dark at optical wavelengths but bright in the infrared
B) supernovae can heat their shells to such high temperatures
C) an astronaut would feel cold in the 106 K intercloud gas
D) the Solar System is immersed in a hot bubble of gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Dust appears dark in __________ wavelengths and bright in __________ wavelengths.
A) optical; ultraviolet
B) infrared; radio
C) radio; ultraviolet
D) optical; infrared
A) optical; ultraviolet
B) infrared; radio
C) radio; ultraviolet
D) optical; infrared

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If you wanted to study regions where star formation is currently happening you could use:
A) Hydrogen emission to look for O and B stars
B) a radio telescope to search for molecular cloud cores
C) infrared emission to identify T Tauri stars
D) all of the above
A) Hydrogen emission to look for O and B stars
B) a radio telescope to search for molecular cloud cores
C) infrared emission to identify T Tauri stars
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Interstellar clouds are:
A) hydrogen gas,condensed out of the interstellar medium,like water clouds in the Earth's atmosphere
B) regions where hydrogen tends to be denser than the surrounding gas
C) regions where water condenses out of the interstellar medium
D) oxygen gas,condensed out of the interstellar medium,like water clouds in the Earth's atmosphere
A) hydrogen gas,condensed out of the interstellar medium,like water clouds in the Earth's atmosphere
B) regions where hydrogen tends to be denser than the surrounding gas
C) regions where water condenses out of the interstellar medium
D) oxygen gas,condensed out of the interstellar medium,like water clouds in the Earth's atmosphere

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is responsible for heating the bulk of the very hot intercloud gas?
A) High-energy radiation from stars
B) Supernovae
C) Young O and B stars
D) The heating is an even mix of all three sources.
A) High-energy radiation from stars
B) Supernovae
C) Young O and B stars
D) The heating is an even mix of all three sources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The AVERAGE density of the interstellar medium is:
A) 1 atom/cm3
B) 1,000 atoms/cm3
C) 106 atoms/cm3
D) 1012 atoms/cm3
A) 1 atom/cm3
B) 1,000 atoms/cm3
C) 106 atoms/cm3
D) 1012 atoms/cm3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When radiation from an object passes through the interstellar medium:
A) the object appears dimmer
B) the object appears bluer
C) the object appears redder and dimmer
D) the object's apparent velocity changes
A) the object appears dimmer
B) the object appears bluer
C) the object appears redder and dimmer
D) the object's apparent velocity changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the interstellar medium,molecules survive only in regions with:
A) low temperatures
B) high densities
C) lots of dust
D) all of the above
A) low temperatures
B) high densities
C) lots of dust
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Magnetic fields in the Milky Way are concentrated in the disk because:
A) halo stars are incapable of producing strong magnetic fields
B) the fields are tied to the charged particles in dense molecular clouds
C) gravity forces them to sink to the center of the disk
D) supernovae explosions continually force them toward the middle of the disk
A) halo stars are incapable of producing strong magnetic fields
B) the fields are tied to the charged particles in dense molecular clouds
C) gravity forces them to sink to the center of the disk
D) supernovae explosions continually force them toward the middle of the disk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Molecular clouds are best observed at __________ wavelengths.
A) ultraviolet
B) optical
C) infrared
D) radio
A) ultraviolet
B) optical
C) infrared
D) radio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Dust reddens starlight because:
A) it re-emits the light it absorbs at red wavelengths
B) it emits mostly in the infrared due to its cold temperature
C) it is made mostly of hydrogen,which produces the red Halpha emission line
D) it preferentially affects light at optical and shorter wavelengths
A) it re-emits the light it absorbs at red wavelengths
B) it emits mostly in the infrared due to its cold temperature
C) it is made mostly of hydrogen,which produces the red Halpha emission line
D) it preferentially affects light at optical and shorter wavelengths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Open star clusters primarily inhabit which part of spiral galaxies?
A) Disk
B) Halo
C) Bulge
D) Nucleus
A) Disk
B) Halo
C) Bulge
D) Nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the main observational difficulty in observing the shape of the Milky Way?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Because of the ages of globular clusters in the Milky Way,we think our galaxy's early formation history was characterized by:
A) one single cloud of gas gently collapsing and star formation proceeding slowly within it
B) one single cloud of gas that rapidly collapsed and turned most of its gas into stars
C) violent merging of protogalactic fragments that stimulated a high rate of star formation
D) slow merging of protogalactic fragments after they had already turned most of their gas into stars
A) one single cloud of gas gently collapsing and star formation proceeding slowly within it
B) one single cloud of gas that rapidly collapsed and turned most of its gas into stars
C) violent merging of protogalactic fragments that stimulated a high rate of star formation
D) slow merging of protogalactic fragments after they had already turned most of their gas into stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the Large Magellanic Cloud is orbiting the Milky Way in a circular orbit with a speed of 175 km/s and a distance of 165,000 light-years from the center,how long would it take for the Large Magellanic Cloud to complete one orbit around the Milky Way?
A) 600 million years
B) 1.8 billion years
C) 3.5 billion years
D) 17 billion years
A) 600 million years
B) 1.8 billion years
C) 3.5 billion years
D) 17 billion years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What observed property of the Milky Way suggests that it contains a large amount of matter not in the form of stars?
A) The rotation curve
B) The velocities of the open star clusters
C) The number and shape of the spiral arms
D) The thickness of the disk
A) The rotation curve
B) The velocities of the open star clusters
C) The number and shape of the spiral arms
D) The thickness of the disk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In which part of the Milky Way would you find little or no neutral hydrogen,no current star formation,and stars that are older than 10 billion years?
A) The halo
B) The disk
C) The galactic center
D) The solar neighborhood
A) The halo
B) The disk
C) The galactic center
D) The solar neighborhood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Where are the most metal-rich stars found in the Milky Way?
A) In the disk near the Sun
B) At the center
C) In the halo
D) In globular clusters
A) In the disk near the Sun
B) At the center
C) In the halo
D) In globular clusters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Globular clusters,when compared to open clusters,generally:
A) are located closer to the center of the Milky Way
B) are younger in age
C) have fewer amounts of heavy elements
D) all of the above
A) are located closer to the center of the Milky Way
B) are younger in age
C) have fewer amounts of heavy elements
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is ripping apart the Sagittarius dwarf spheroidal galaxy?
A) A supermassive black hole at its center
B) The energetic decay of a WIMP
C) A violent episode of star formation
D) The gravitational tidal force of the Milky Way
A) A supermassive black hole at its center
B) The energetic decay of a WIMP
C) A violent episode of star formation
D) The gravitational tidal force of the Milky Way

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Milky Way is classified as an __________ galaxy. 
A) Sa
B) SBbc
C) Sd
D) SBc

A) Sa
B) SBbc
C) Sd
D) SBc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Milky Way Galaxy is a(n)__________ galaxy.
A) irregular
B) elliptical
C) spiral
D) lenticular
A) irregular
B) elliptical
C) spiral
D) lenticular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The chemical composition of a star's atmosphere tells us:
A) how much nuclear burning has gone on in the star
B) the star's evolutionary stage
C) the chemical composition of the cloud from which the star formed
D) all of the above
A) how much nuclear burning has gone on in the star
B) the star's evolutionary stage
C) the chemical composition of the cloud from which the star formed
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Why do we know that at least one generation of stars formed and died before the Milky Way's globular clusters formed?
A) All globular clusters reside in the disk of the Milky Way.
B) No globular cluster has zero heavy elements.
C) Globular clusters are 9-10 billion years old.
D) No globular cluster is older than 12 billion years.
A) All globular clusters reside in the disk of the Milky Way.
B) No globular cluster has zero heavy elements.
C) Globular clusters are 9-10 billion years old.
D) No globular cluster is older than 12 billion years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Studying standard candles in globular clusters offered the first conclusive proof that our galaxy was much __________ than originally believed.
A) smaller
B) rounder
C) larger
D) flatter
A) smaller
B) rounder
C) larger
D) flatter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Sagittarius A*,the radio source located at the center of our galaxy,is believed to be:
A) a massive star cluster
B) a supernova remnant
C) a quasar
D) a supermassive black hole
A) a massive star cluster
B) a supernova remnant
C) a quasar
D) a supermassive black hole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How have astronomers measured the mass of the black hole at the center of our galaxy?
A) Using the rotation curve derived from 21-cm emission
B) By observing the motions of stars near the center of the galaxy
C) By measuring the brightness of the quasar
D) By measuring the Doppler shift of Sagittarius A*
A) Using the rotation curve derived from 21-cm emission
B) By observing the motions of stars near the center of the galaxy
C) By measuring the brightness of the quasar
D) By measuring the Doppler shift of Sagittarius A*

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In a star that has a chemical abundance similar to the Sun,what percentage of its mass is made of heavy elements?
A) 0.02 percent
B) 0.2 percent
C) 2 percent
D) 20 percent
A) 0.02 percent
B) 0.2 percent
C) 2 percent
D) 20 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following are NOT found in our galaxy's halo?
A) Globular clusters
B) Planetary nebulae
C) RR Lyrae stars
D) Clouds emitting 21-cm emission
A) Globular clusters
B) Planetary nebulae
C) RR Lyrae stars
D) Clouds emitting 21-cm emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Most of the mass in our galaxy is in the form of:
A) stars
B) gas
C) dust
D) dark matter
A) stars
B) gas
C) dust
D) dark matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What type of standard candle is used to determine distances to globular clusters?
A) RR Lyrae stars
B) Cepheid variable stars
C) T Tauri stars
D) Type Ia supernovae
A) RR Lyrae stars
B) Cepheid variable stars
C) T Tauri stars
D) Type Ia supernovae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe the basic scenario that describes the formation and evolution of the Milky Way,including a description of how the halo and disk formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why do stars form most often within molecular clouds?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the figure below,the spectrum of a star is given without being obscured by dust and also being obscured by dust.Explain how the dust affects the light arriving from the star.
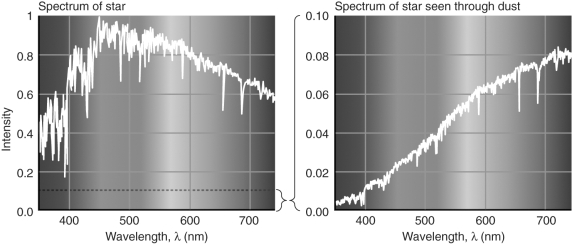


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Describe the structure of the disk of the Milky Way (figure below).



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Explain how a standard candle allows you to determine the distance to an object.What is it that you have to measure or know about the standard candle to derive its distance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If you wanted to study the properties of nearby stars that were some of the first stars to form in the Milky Way,but were NOT members of a globular cluster,how could you go about finding them?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Examine the figure below.How does the H-R diagram of the globular star cluster M92 show that its age is very old?
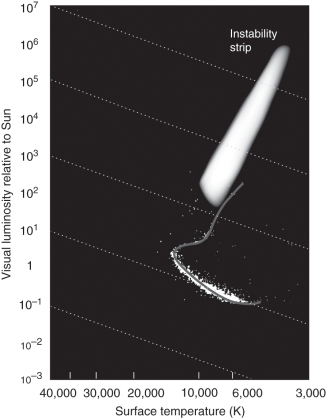


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Examine the figure below.How does the H-R diagram of open star cluster NGC 6530 show that its age is very young?
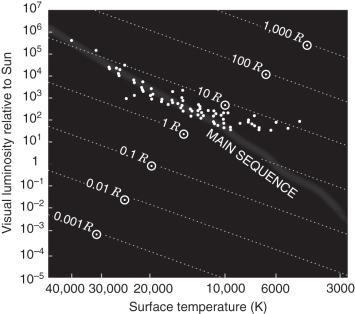


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
At what wavelength are H II regions most clearly visible,and why do H II regions mark the regions where new stars are currently being formed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Where would we find the stars with the richest abundance of massive elements? Where would we find those with the smallest amounts of massive elements? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Describe the differences between the ages and chemical abundances of globular and open star clusters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Why can the observed chemical abundance of a star tell you something about its age?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
How do we know that globular cluster stars were not the first stars that formed in our galaxy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Label the parts of the Milky Way on the figure below.
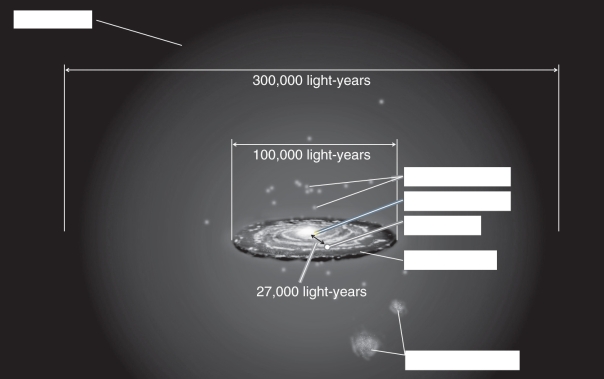


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
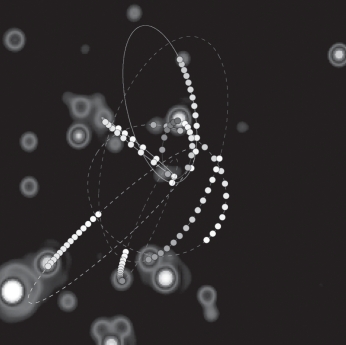
The figure below shows the orbits of several stars very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy.How do astronomers know that these stars orbit a supermassive black hole?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Describe a scale model of the disk of the Milky Way using a scale in which 1 cm = 1,000 light-years.Note that the diameter of the disk is approximately 100,000 light-years,the thickness of young stars is 500 light-years,and the thickness of the older stars is 4,000 light-years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Describe the population of globular star clusters in the Milky Way: how many are there,where do they reside in the Milky Way,and how do their ages and chemical abundances compare to the Sun?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Why is the supermassive black hole in the center of our galaxy not an AGN right now? Could it be active in the future? Why or why not?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A typical globular cluster (image below)is composed of 500,000 stars in a sphere whose radius is approximately 15 light-years.The distance between stars in a globular cluster is given approximately by d r/N1/3,where r is the radius and N is the number of stars in the cluster.Calculate this distance,and determine how many times smaller it is than the typical distance between stars in the solar neighborhood,which is 3 light-years.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Why can we see dust in the interstellar medium better at far-infrared wavelengths than we can at optical wavelengths?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



