Deck 4: Corporate Governance Around the World
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Corporate Governance Around the World
1
The central issue of corporate governance is
A)how to protect creditors from managers and controlling shareholders.
B)how to protect outside investors from the controlling insiders.
C)how to alleviate the conflicts of interest between managers and shareholders.
D)how to alleviate the conflicts of interest between shareholders and bondholders.
A)how to protect creditors from managers and controlling shareholders.
B)how to protect outside investors from the controlling insiders.
C)how to alleviate the conflicts of interest between managers and shareholders.
D)how to alleviate the conflicts of interest between shareholders and bondholders.
B
2
Countries with strong shareholder protection tend to have more valuable stock markets and more companies listed on stock exchanges per capita than countries with weak protection.
True
3
The key strengths of the public corporation is/are
A)their capacity to allow efficient risk sharing among many investors.
B)their capacity to raise large amounts of funds at relatively low cost.
C)their capacity to consolidate decision-making.
D)all of the above
A)their capacity to allow efficient risk sharing among many investors.
B)their capacity to raise large amounts of funds at relatively low cost.
C)their capacity to consolidate decision-making.
D)all of the above
D
4
In the reality of corporate governance at the turn of this century,
A)boards of directors are often dominated by management-friendly insiders.
B)a typical board of directors often has relatively few outside directors who can independently and objectively monitor the management.
C)managers of one firm often sit on the boards of other firms, whose managers are on the board of the first firm.Due to the interlocking nature of these boards, there can exist a culture of "I'll overlook your problems if you overlook mine."
D)all of the above have been true to a greater or lesser extent in the recent past.
A)boards of directors are often dominated by management-friendly insiders.
B)a typical board of directors often has relatively few outside directors who can independently and objectively monitor the management.
C)managers of one firm often sit on the boards of other firms, whose managers are on the board of the first firm.Due to the interlocking nature of these boards, there can exist a culture of "I'll overlook your problems if you overlook mine."
D)all of the above have been true to a greater or lesser extent in the recent past.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The separation of the company's ownership and control,
A)is especially prevalent in such countries as the United States and the United Kingdom, where corporate ownership is highly diffused.
B)is especially prevalent in such countries as the Italy and Mexico, where corporate ownership is highly concentrated.
C)is a rational response to the agency problem.
D)none of the above
A)is especially prevalent in such countries as the United States and the United Kingdom, where corporate ownership is highly diffused.
B)is especially prevalent in such countries as the Italy and Mexico, where corporate ownership is highly concentrated.
C)is a rational response to the agency problem.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The key weakness of the public corporation is
A)too many shareholders, which makes it difficult to make corporate decision.
B)relatively high corporate income tax rates.
C)conflicts of interest between managers and shareholders.
D)conflicts of interests between shareholders and bondholders.
A)too many shareholders, which makes it difficult to make corporate decision.
B)relatively high corporate income tax rates.
C)conflicts of interest between managers and shareholders.
D)conflicts of interests between shareholders and bondholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In theory,
A)managers are hired by the shareholders at the annual stockholders meeting.If the managers turn in a bad year, new ones get hired.
B)shareholders hire the managers to oversee the board of directors.
C)managers are hired by the board of directors; the board is accountable to the shareholders.
D)none of the above
A)managers are hired by the shareholders at the annual stockholders meeting.If the managers turn in a bad year, new ones get hired.
B)shareholders hire the managers to oversee the board of directors.
C)managers are hired by the board of directors; the board is accountable to the shareholders.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In many countries with concentrated ownership
A)the conflicts of interest between shareholders and managers are worse than in countries with diffuse ownership of firms.
B)the conflicts of interest are greater between large controlling shareholders and small outside shareholders than between managers and shareholders.
C)the conflicts of interest are greater between managers and shareholders than between large controlling shareholders and small outside shareholders.
D)corporate forms of business organization with concentrated ownership are rare.
A)the conflicts of interest between shareholders and managers are worse than in countries with diffuse ownership of firms.
B)the conflicts of interest are greater between large controlling shareholders and small outside shareholders than between managers and shareholders.
C)the conflicts of interest are greater between managers and shareholders than between large controlling shareholders and small outside shareholders.
D)corporate forms of business organization with concentrated ownership are rare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When managerial self-dealings are excessive and left unchecked,
A)they can have serious negative effects on share values.
B)they can impede the proper functions of capital markets.
C)they can impede such measures as GDP growth.
D)all of the above
A)they can have serious negative effects on share values.
B)they can impede the proper functions of capital markets.
C)they can impede such measures as GDP growth.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When company ownership is diffuse,
A)a "free rider" problem discourages shareholder activism.
B)the large number of shareholders ensures strong monitoring of managerial behavior because with a large enough group, there's almost always someone who will to incur the costs of monitoring management.
C)few shareholders have a strong enough incentive to incur the costs of monitoring management.
D)both a) and c) are correct
A)a "free rider" problem discourages shareholder activism.
B)the large number of shareholders ensures strong monitoring of managerial behavior because with a large enough group, there's almost always someone who will to incur the costs of monitoring management.
C)few shareholders have a strong enough incentive to incur the costs of monitoring management.
D)both a) and c) are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The genius of public corporations stems from their capacity to allow efficient sharing or spreading of risk among many investors,who can buy and sell their ownership shares on liquid stock exchanges and let professional managers run the company on behalf of shareholders.This risk sharing stems from
A)the liquidity of the shares.
B)the limited liability of shareholders.
C)the limited liability of bondholders.
D)the limited ability of shareholders.
A)the liquidity of the shares.
B)the limited liability of shareholders.
C)the limited liability of bondholders.
D)the limited ability of shareholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The public corporation has a key weakness:
A)the conflicts of interest between bondholders and shareholders.
B)the conflicts of interest between managers and bondholders.
C)the conflicts of interest between stakeholders and shareholders.
D)the conflicts of interest between managers and shareholders.
A)the conflicts of interest between bondholders and shareholders.
B)the conflicts of interest between managers and bondholders.
C)the conflicts of interest between stakeholders and shareholders.
D)the conflicts of interest between managers and shareholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a public company with diffused ownership,the board of directors is entrusted with
A)monitoring the auditors and safeguarding the interests of shareholders.
B)monitoring the shareholders and safeguarding the interests of management.
C)monitoring the management and safeguarding the interests of shareholders.
D)none of the above
A)monitoring the auditors and safeguarding the interests of shareholders.
B)monitoring the shareholders and safeguarding the interests of management.
C)monitoring the management and safeguarding the interests of shareholders.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the United States,managers are bound by the "duty of loyalty" to serve the shareholders.
A)This is an ethical, not legal, obligation.
B)This is a legal obligation.
C)This is only a moral obligation; there are no penalties.
A)This is an ethical, not legal, obligation.
B)This is a legal obligation.
C)This is only a moral obligation; there are no penalties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Corporate governance structure
A)varies a great deal across countries.
B)has become homogenized following the integration of capital markets.
C)has become homogenized due to cross-listing of shares of many public corporations.
D)none of the above
A)varies a great deal across countries.
B)has become homogenized following the integration of capital markets.
C)has become homogenized due to cross-listing of shares of many public corporations.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In what country do the three largest shareholders control,on average,about 60 percent of the shares of a public company?
A)United States
B)Canada
C)Great Britain
D)Italy
A)United States
B)Canada
C)Great Britain
D)Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The public corporation
A)is jointly owned by a (potentially) large number of shareholders.
B)offers shareholders limited liability.
C)separates the ownership and control of a firm's assets.
D)all of the above
A)is jointly owned by a (potentially) large number of shareholders.
B)offers shareholders limited liability.
C)separates the ownership and control of a firm's assets.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The strongest protection for investors is provided by
A)English common law countries, such as Canada, the United States, and the U.K.
B)French civil law countries, such as Belgium, Italy, and Mexico.
C)a weak board of directors.
D)socialized firms.
A)English common law countries, such as Canada, the United States, and the U.K.
B)French civil law countries, such as Belgium, Italy, and Mexico.
C)a weak board of directors.
D)socialized firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the United States,managers are legally bound by the "duty of loyalty" to
A)the board of directors.
B)to the shareholders.
C)to the bondholders.
D)to the government.
A)the board of directors.
B)to the shareholders.
C)to the bondholders.
D)to the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Corporate governance can be defined as
A)the economic, legal, and institutional framework in which corporate control and cash flow rights are distributed among shareholders, managers and other stakeholders of the company.
B)the general framework in which company management is selected and monitored.
C)the rules and regulations adopted by boards of directors specifying how to manage companies.
D)the government-imposed rules and regulations affecting corporate management.
A)the economic, legal, and institutional framework in which corporate control and cash flow rights are distributed among shareholders, managers and other stakeholders of the company.
B)the general framework in which company management is selected and monitored.
C)the rules and regulations adopted by boards of directors specifying how to manage companies.
D)the government-imposed rules and regulations affecting corporate management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose in order to defraud the shareholders,a manager sets up an independent company that he owns sells the main company's output to this company.He would be tempted to set the transfer price
A)below market prices.
B)above market prices.
C)at the market price.
D)in accordance with GAAP.
A)below market prices.
B)above market prices.
C)at the market price.
D)in accordance with GAAP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Self-interested managers may be tempted to
A)indulge in expensive perquisites at company expense.
B)adopt antitakeover measures for their company to ensure their personal job security.
C)waste company funds by undertaking unprofitable projects that benefit themselves but not shareholders.
D)all of the above are potential abuses that self-interested managers may be tempted to visit upon shareholders.
A)indulge in expensive perquisites at company expense.
B)adopt antitakeover measures for their company to ensure their personal job security.
C)waste company funds by undertaking unprofitable projects that benefit themselves but not shareholders.
D)all of the above are potential abuses that self-interested managers may be tempted to visit upon shareholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the U.S.,the chief role of the board of directors is
A)to hire the management team.
B)to decide on the annual capital budget.
C)to design an effective incentive compatible compensation scheme for themselves.
D)none of the above
A)to hire the management team.
B)to decide on the annual capital budget.
C)to design an effective incentive compatible compensation scheme for themselves.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In high-growth industries where companies' internally generated funds fall short of profitable investment opportunities,
A)managers are less likely to waste funds in unprofitable projects.
B)managers are more likely to waste funds in unprofitable projects.
A)managers are less likely to waste funds in unprofitable projects.
B)managers are more likely to waste funds in unprofitable projects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Outside the United States and the United Kingdom,
A)concentrated ownership of the company is more the exception than the rule.
B)diffused ownership of the company is more the exception than the rule.
C)partnerships are more important than corporations.
D)none of the above
A)concentrated ownership of the company is more the exception than the rule.
B)diffused ownership of the company is more the exception than the rule.
C)partnerships are more important than corporations.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
It is important for society as a whole to solve the agency problem,since the agency problem
A)leads to waste of scarce resources.
B)hampers capital market functions.
C)retards economic growth.
D)all of the above
A)leads to waste of scarce resources.
B)hampers capital market functions.
C)retards economic growth.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Tobin's Q is
A)the ratio of the market value of company assets to the replacement costs of the assets.
B)a means to find overvalued stocks: if Q is high it means that the cost to replace a firm's assets is greater than the value of its stock.
C)The same as the price-to-book ratio.
D)Both a) and b) are correct
A)the ratio of the market value of company assets to the replacement costs of the assets.
B)a means to find overvalued stocks: if Q is high it means that the cost to replace a firm's assets is greater than the value of its stock.
C)The same as the price-to-book ratio.
D)Both a) and b) are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is true regarding leveraged buy-outs (LBOs)?
A)LBOs involve managers or buyout partners acquiring controlling interests in public companies, usually financed by heavy borrowing.
B)Concentrated ownership and high level of debt associated with LBOs are the mechanism for solving the agency problem.
C)LBOs improve a company's free cash flow and this is the mechanism by which they can solve the agency problem.
D)Both a) and b)
A)LBOs involve managers or buyout partners acquiring controlling interests in public companies, usually financed by heavy borrowing.
B)Concentrated ownership and high level of debt associated with LBOs are the mechanism for solving the agency problem.
C)LBOs improve a company's free cash flow and this is the mechanism by which they can solve the agency problem.
D)Both a) and b)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The investors supply funds to the company but are not involved in the company's daily decision making.As a result,many public companies come to have
A)strong shareholders and weak managers.
B)strong managers and weak shareholders.
C)strong managers and strong shareholders.
D)weak managers and weak shareholders.
A)strong shareholders and weak managers.
B)strong managers and weak shareholders.
C)strong managers and strong shareholders.
D)weak managers and weak shareholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The agency problem refers to the possible conflicts of interest between
A)self-interested managers as principals and shareholders of the firm who are the agents.
B)altruistic managers as agents and shareholders of the firm who are the principals.
C)self-interested managers as agents and shareholders of the firm who are the principals.
D)dutiful managers as principals and shareholders of the firm who are the agents.
A)self-interested managers as principals and shareholders of the firm who are the agents.
B)altruistic managers as agents and shareholders of the firm who are the principals.
C)self-interested managers as agents and shareholders of the firm who are the principals.
D)dutiful managers as principals and shareholders of the firm who are the agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the graph at right,X,Y,and Z represent 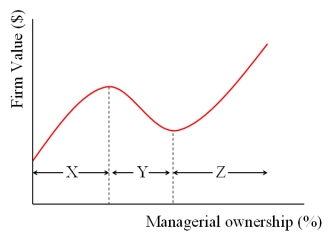
A)entrenchment, alignment, entrenchment.
B)alignment, entrenchment, alignment.
C)misalignment and alignment.
D)agency costs of debt and equity.

A)entrenchment, alignment, entrenchment.
B)alignment, entrenchment, alignment.
C)misalignment and alignment.
D)agency costs of debt and equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Free cash flow refers to
A)a firm's cash reserve in excess of tax obligation.
B)a firm's funds in excess of what's needed for undertaking all profitable projects.
C)a firm's cash reserve in excess of interest and tax payments.
D)a firm's income tax refund that is due to interest payments on borrowing.
A)a firm's cash reserve in excess of tax obligation.
B)a firm's funds in excess of what's needed for undertaking all profitable projects.
C)a firm's cash reserve in excess of interest and tax payments.
D)a firm's income tax refund that is due to interest payments on borrowing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A complete contract between shareholders and managers
A)would specify exactly what the manager will do under each of all possible future contingencies.
B)would be an expensive contract to write and a very expensive contract to monitor.
C)would eliminate any conflicts of interest (and managerial discretion).
D)all of the above
A)would specify exactly what the manager will do under each of all possible future contingencies.
B)would be an expensive contract to write and a very expensive contract to monitor.
C)would eliminate any conflicts of interest (and managerial discretion).
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The agency problem tends
A)to be more serious in firms with free cash flows.
B)to be more serious in firms with excessive amounts of excess cash.
C)to be less serious in firms with few numbers of shareholders.
D)all of the above
A)to be more serious in firms with free cash flows.
B)to be more serious in firms with excessive amounts of excess cash.
C)to be less serious in firms with few numbers of shareholders.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose in order to defraud the shareholders,a manager sets up an independent company that he owns buys one of the main company's inputs of production from this company.He would be tempted to set the transfer price
A)below market prices.
B)above market prices.
C)at the market price.
D)in accordance with GAAP.
A)below market prices.
B)above market prices.
C)at the market price.
D)in accordance with GAAP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the United Kingdom,the majority of public companies
A)voluntarily abide by the Code of Best Practice on corporate governance.
B)are compelled by law to abide by the Code of Best Practice on corporate governance.
C)do not abide by the Code of Best Practice on corporate governance.
A)voluntarily abide by the Code of Best Practice on corporate governance.
B)are compelled by law to abide by the Code of Best Practice on corporate governance.
C)do not abide by the Code of Best Practice on corporate governance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Managerial entrenchment efforts are clear signs of the agency problem.They include
A)anti-takeover defenses.
B)poison pills.
C)changes in the voting procedures to make it more difficult for the firm to be taken over.
D)all of the above
A)anti-takeover defenses.
B)poison pills.
C)changes in the voting procedures to make it more difficult for the firm to be taken over.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Why is it rational to make shareholders "weak" by giving control to the managers of the firm?
A)This may be rational when shareholders may be neither qualified nor interested in making business decisions.
B)This may be rational since many shareholders find it easier to sell their shares in an underperforming firm than to monitor the management.
C)This may be rational to the extent that managers are answerable to the board of directors.
D)All of the above are explanations for the separation of ownership and control.
A)This may be rational when shareholders may be neither qualified nor interested in making business decisions.
B)This may be rational since many shareholders find it easier to sell their shares in an underperforming firm than to monitor the management.
C)This may be rational to the extent that managers are answerable to the board of directors.
D)All of the above are explanations for the separation of ownership and control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the graph at right,for Fortune 500 companies,X,Y are 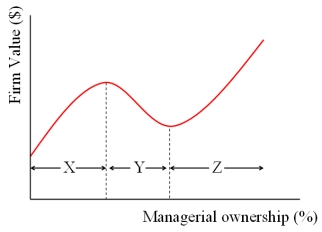
A)5% and 25%.
B)15% and 50%.
C)50% and 75%.
D)None of the above

A)5% and 25%.
B)15% and 50%.
C)50% and 75%.
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Why do managers tend to retain free cash flow?
A)Managers are in the best position to decide the best use of those funds.
B)These funds are needed for undertaking profitable projects and the issue costs are less than new issues of stocks or bonds.
C)Managers may not be acting in the shareholders best interest, and for a variety of reasons, want to use the free cash flow.
D)None of the above
A)Managers are in the best position to decide the best use of those funds.
B)These funds are needed for undertaking profitable projects and the issue costs are less than new issues of stocks or bonds.
C)Managers may not be acting in the shareholders best interest, and for a variety of reasons, want to use the free cash flow.
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the United States
A)boards of directors are legally responsible for representing the interests of the shareholders.
B)due to the diffused ownership structure of the public company, management often gets to choose board members who are likely to be friendly to management.
C)there is a correlation between underperforming firms and boards of directors who are not fully independent.
D)all of the above are true, in the United States.
A)boards of directors are legally responsible for representing the interests of the shareholders.
B)due to the diffused ownership structure of the public company, management often gets to choose board members who are likely to be friendly to management.
C)there is a correlation between underperforming firms and boards of directors who are not fully independent.
D)all of the above are true, in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When designing an incentive contract,
A)it is important for the board of directors to set up an independent compensation committee that can carefully design the contract and diligently monitor manager's actions.
B)senior executives can be trusted to not abuse incentive contracts by artificially manipulating accounting numbers since the auditors should look in to that.
C)the presence of any incentive is enough, whether it is accounting based or stock-price based.
D)the board of directors should always give the managers a "heads I win, tails you lose" type of option.
A)it is important for the board of directors to set up an independent compensation committee that can carefully design the contract and diligently monitor manager's actions.
B)senior executives can be trusted to not abuse incentive contracts by artificially manipulating accounting numbers since the auditors should look in to that.
C)the presence of any incentive is enough, whether it is accounting based or stock-price based.
D)the board of directors should always give the managers a "heads I win, tails you lose" type of option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the United States,it is not uncommon for the same person to serve as both CEO and chairman of the board.
A)This situation must not have much conflict of interest since it is common.
B)This situation has a built-in conflict of interest.
C)This is only legal if that individual owns a controlling number of shares in the firm.
D)None of the above.
A)This situation must not have much conflict of interest since it is common.
B)This situation has a built-in conflict of interest.
C)This is only legal if that individual owns a controlling number of shares in the firm.
D)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Concentrated ownership of a public company
A)is normal in the United States, following the well-publicized scandals of recent years.
B)is relatively rare in the United States and common in many other parts of the world.
C)leads to a free-rider problem with the minority shareholders relying on the majority.shareholders to assume an undue burden in monitoring the management.
D)is the norm in Great Britain.
A)is normal in the United States, following the well-publicized scandals of recent years.
B)is relatively rare in the United States and common in many other parts of the world.
C)leads to a free-rider problem with the minority shareholders relying on the majority.shareholders to assume an undue burden in monitoring the management.
D)is the norm in Great Britain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
While debt can reduce agency costs between shareholders and management,
A)excessive debt may also induce the risk-averse managers to forgo profitable but risky investment projects, causing an underinvestment problem.
B)with debt financing companies can misuse debt to finance corporate empire building.
C)both a) and b)
D)none of the above
A)excessive debt may also induce the risk-averse managers to forgo profitable but risky investment projects, causing an underinvestment problem.
B)with debt financing companies can misuse debt to finance corporate empire building.
C)both a) and b)
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the United States,it is well documented that
A)boards dominated by their chief executives are prone to trouble.
B)public scrutiny can help improve corporate governance.
C)as public firms improve their corporate governance, the stock price goes up.
D)all of the above
A)boards dominated by their chief executives are prone to trouble.
B)public scrutiny can help improve corporate governance.
C)as public firms improve their corporate governance, the stock price goes up.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For firms with free cash flows,
A)debt can be a stronger mechanism than stocks for credibly bonding managers to release cash flows to investors.
B)equity dividends can be a stronger mechanism than bonds for credibly bonding managers to release cash flows to investors.
C)preferred stock dividends can be a stronger mechanism than bonds for credibly bonding managers to release cash flows to investors.
D)none of the above
A)debt can be a stronger mechanism than stocks for credibly bonding managers to release cash flows to investors.
B)equity dividends can be a stronger mechanism than bonds for credibly bonding managers to release cash flows to investors.
C)preferred stock dividends can be a stronger mechanism than bonds for credibly bonding managers to release cash flows to investors.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Benetton,an Italian clothier,is listed on the New York Stock Exchange.
A)This decision provides their shareholders with a higher degree of protection than is available in Italy.
B)This decision can be a signal of the company's commitment to shareholder rights.
C)This may make investors both in Italy and abroad more willing to provide capital and to increase the value of the pre-existing shares.
D)All of the above
A)This decision provides their shareholders with a higher degree of protection than is available in Italy.
B)This decision can be a signal of the company's commitment to shareholder rights.
C)This may make investors both in Italy and abroad more willing to provide capital and to increase the value of the pre-existing shares.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If an incentive contract specifies certain accounting performance
A)that accounting number will likely be the focus of managers.
B)managers will set aside the accounting goal if it conflicts with the goal of maximizing shareholder wealth.
C)managers will be unable to manipulate the GAAP, so shareholders can be confident of having their wealth maximized.
A)that accounting number will likely be the focus of managers.
B)managers will set aside the accounting goal if it conflicts with the goal of maximizing shareholder wealth.
C)managers will be unable to manipulate the GAAP, so shareholders can be confident of having their wealth maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The goal of a greater accounting transparency
A)is to impose more rules and harsher penalties for their violation.
B)is to reduce the information asymmetry between corporate insiders and the public.
C)is to discourage managerial self-dealings.
D)answers b) and c)
A)is to impose more rules and harsher penalties for their violation.
B)is to reduce the information asymmetry between corporate insiders and the public.
C)is to discourage managerial self-dealings.
D)answers b) and c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In Germany the corporate board is
A)legally charged with representing the interests of shareholders exclusively.
B)legally charged with looking after the interests of stakeholders (e.g., workers, creditors, etc.) in general, not just shareholders.
C)legally charged as a supervisory board only.
D)legally charged as a management board only.
A)legally charged with representing the interests of shareholders exclusively.
B)legally charged with looking after the interests of stakeholders (e.g., workers, creditors, etc.) in general, not just shareholders.
C)legally charged as a supervisory board only.
D)legally charged as a management board only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Concentrated ownership of a public company
A)can be an effective way to alleviate the agency problem between shareholders and managers.
B)is the norm in Great Britain.
C)tends to be an ineffective way to alleviate conflicts of interest between groups of shareholders.
D)none of the above
A)can be an effective way to alleviate the agency problem between shareholders and managers.
B)is the norm in Great Britain.
C)tends to be an ineffective way to alleviate conflicts of interest between groups of shareholders.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The board of directors may grant stock options to managers.These are
A)call options.
B)put options.
C)none of the above
A)call options.
B)put options.
C)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Debt can reduce agency costs between shareholders and management,but
A)only if the firm is totally up to its eyeballs in debt.
B)only to the extent that the firm can commit all of its free cash flow.
C)excessive debt can create its own agency conflicts.
D)debt is best used as a corporate governance mechanism by young companies with limited cash reserves.
A)only if the firm is totally up to its eyeballs in debt.
B)only to the extent that the firm can commit all of its free cash flow.
C)excessive debt can create its own agency conflicts.
D)debt is best used as a corporate governance mechanism by young companies with limited cash reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Accounting Transparency
A)can only be achieved when managers commit to serving on their own audit committee.
B)occurs when the accounting department has translucent cubicles for their workers.
C)promises to reduce the information asymmetry between corporate insiders and the public.
D)none of the above
A)can only be achieved when managers commit to serving on their own audit committee.
B)occurs when the accounting department has translucent cubicles for their workers.
C)promises to reduce the information asymmetry between corporate insiders and the public.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the United States and the United Kingdom,hostile takeovers
A)are illegal.
B)can serve as a drastic corporate governance mechanism of the last resort.
C)reinforce the notion that managers can take their control of the company for granted.
D)require management approval.
A)are illegal.
B)can serve as a drastic corporate governance mechanism of the last resort.
C)reinforce the notion that managers can take their control of the company for granted.
D)require management approval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose you are the CEO of company A,and you serve on the board of company B,while the CEO of B is on your board.
A)This is a potential conflict of interest for both parties.
B)This is normal and even a desirable situation since it allows for efficient information sharing between the firms.
C)There is a potential conflict for the shareholders of the two firms.
D)All of the above are true.
A)This is a potential conflict of interest for both parties.
B)This is normal and even a desirable situation since it allows for efficient information sharing between the firms.
C)There is a potential conflict for the shareholders of the two firms.
D)All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
While debt can reduce agency costs between shareholders and management,
A)debt can create its own agency costs.
B)this only happens at extreme levels of debt.
C)this does not work for firms in mature industries with large cash reserves.
D)none of the above are true
A)debt can create its own agency costs.
B)this only happens at extreme levels of debt.
C)this does not work for firms in mature industries with large cash reserves.
D)none of the above are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Companies domiciled in countries with weak investor protection can reduce agency costs between shareholders and management
A)by moving to a better county.
B)by listing their stocks in countries with strong investor protection.
C)by voluntarily complying with the provisions of the U.S.Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
D)having a press conference and promising to be nice to their investors.
A)by moving to a better county.
B)by listing their stocks in countries with strong investor protection.
C)by voluntarily complying with the provisions of the U.S.Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
D)having a press conference and promising to be nice to their investors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The board of directors may grant stock options to managers in order to
A)save executive compensation costs.
B)use as a substitute for bonus.
C)align the interest of managers with that of shareholders.
D)none of the above
A)save executive compensation costs.
B)use as a substitute for bonus.
C)align the interest of managers with that of shareholders.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the difference between control rights and cash flow rights?
A)Since all shareholders benefit only from pro-rata cash flows, control rights and cash flow rights are the same thing.
B)Large investors may be able to derive private benefits from control, thus control rights can exceed cash flow rights.
C)Cash flow rights are more important than control rights since the only reason to invest in anything is to generate cash.
D)None of the above
A)Since all shareholders benefit only from pro-rata cash flows, control rights and cash flow rights are the same thing.
B)Large investors may be able to derive private benefits from control, thus control rights can exceed cash flow rights.
C)Cash flow rights are more important than control rights since the only reason to invest in anything is to generate cash.
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Many companies issue shares with differential voting rights,deviating from the one-share one-vote principle.
A)By accumulating superior voting shares, investors can acquire cash flow rights exceeding control rights.
B)The price of the voting shares is usually twice the price of the voting shares.
C)By accumulating superior voting shares, investors can acquire control rights exceeding cash flow rights.
D)None of the above
A)By accumulating superior voting shares, investors can acquire cash flow rights exceeding control rights.
B)The price of the voting shares is usually twice the price of the voting shares.
C)By accumulating superior voting shares, investors can acquire control rights exceeding cash flow rights.
D)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Studies show that the quality of law enforcement,as measured by the rule of law index,will tend to be
A)higher in French civil law countries than in English common law countries.
B)higher in English common law countries than in Scandinavian civil law countries.
C)highest in Scandinavian civil law countries and German civil law countries.
D)highest in English common law countries.
A)higher in French civil law countries than in English common law countries.
B)higher in English common law countries than in Scandinavian civil law countries.
C)highest in Scandinavian civil law countries and German civil law countries.
D)highest in English common law countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In a hostile takeover attempt,the bidder typically
A)makes a tender offer to the target shareholders at a price substantially less than the prevailing share price.
B)makes a tender offer to the target shareholders at the prevailing share price.
C)makes a tender offer to the target shareholders at a price substantially exceeding the prevailing share price.
D)seeks to merge with the target company with an exchange of shares.
A)makes a tender offer to the target shareholders at a price substantially less than the prevailing share price.
B)makes a tender offer to the target shareholders at the prevailing share price.
C)makes a tender offer to the target shareholders at a price substantially exceeding the prevailing share price.
D)seeks to merge with the target company with an exchange of shares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The voting premium,defined as the total vote value (value of a vote times the number of votes)as a proportion of the firm's equity market value is only about 2 percent in the United States and 36 percent in Mexico,suggesting that in Mexico,
A)dominant shareholders extract substantial private benefits of control.
B)dominant shareholders overpay and thus fail to extract substantial private benefits.
C)minority shareholders share in the private benefits of control.
D)none of the above
A)dominant shareholders extract substantial private benefits of control.
B)dominant shareholders overpay and thus fail to extract substantial private benefits.
C)minority shareholders share in the private benefits of control.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A pyramidal ownership structure is one in which
A)a shareholder controls a holding company that owns a controlling block of another company, which in turn owns controlling interests in yet another company, and so on.
B)equity cross-holdings among a group of companies, such as keiretsu and chaebols can be used to concentrate and leverage voting rights to acquire control.
C)a combination of these schemes may also be used to leverage control in a pyramidal ownership structure.
A)a shareholder controls a holding company that owns a controlling block of another company, which in turn owns controlling interests in yet another company, and so on.
B)equity cross-holdings among a group of companies, such as keiretsu and chaebols can be used to concentrate and leverage voting rights to acquire control.
C)a combination of these schemes may also be used to leverage control in a pyramidal ownership structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The key to extracting private benefits of control that are not shared by other shareholders on a pro rata basis is to
A)become a large shareholder and acquire control rights exceeding cash flow rights.
B)buy a large block of nonvoting shares.
C)sell your shares in a tender offer.
D)force the firm into bankruptcy.
A)become a large shareholder and acquire control rights exceeding cash flow rights.
B)buy a large block of nonvoting shares.
C)sell your shares in a tender offer.
D)force the firm into bankruptcy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In many countries hostile takeovers are relatively rare.This is so partly because of
A)the language barrier.
B)concentrated ownership in these countries.
C)cultural values and political environments disapproving hostile corporate takeovers.
D)both b) and c)
A)the language barrier.
B)concentrated ownership in these countries.
C)cultural values and political environments disapproving hostile corporate takeovers.
D)both b) and c)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In countries with concentrated ownership
A)hostile takeovers are quite rare.
B)hostile takeovers are quite common.
A)hostile takeovers are quite rare.
B)hostile takeovers are quite common.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose Mr.Lee and his relatives hold 30% of shares outstanding of Samsung Life,which in turn holds 20% of Samsung Electronics.What is the cash flow right of the Lee family in Samsung Electronics?
A)50 percent
B)10 percent
C)20 percent
D)6 percent
A)50 percent
B)10 percent
C)20 percent
D)6 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Several studies document the empirical link between
A)weak investor protection and GDP growth.
B)financial development and economic growth.
C)growth in GDP and concentrated ownership.
D)none of the above
A)weak investor protection and GDP growth.
B)financial development and economic growth.
C)growth in GDP and concentrated ownership.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Unless investors can derive significant private benefits of control,
A)they will pay small premiums for voting shares over nonvoting shares.
B)they will pay moderate premiums for voting shares over nonvoting shares.
C)they will pay substantial premiums for voting shares over nonvoting shares.
D)they will not pay substantial premiums for voting shares over nonvoting shares.
A)they will pay small premiums for voting shares over nonvoting shares.
B)they will pay moderate premiums for voting shares over nonvoting shares.
C)they will pay substantial premiums for voting shares over nonvoting shares.
D)they will not pay substantial premiums for voting shares over nonvoting shares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
One way to measure the value of private benefits of control
A)is to measure the difference in value between non-voting shares and voting shares.
B)is to measure the value of the "block premium" the value difference between the price per share paid for a control block of shares versus the exchange price of regular shares.
C)both a) and b)
A)is to measure the difference in value between non-voting shares and voting shares.
B)is to measure the value of the "block premium" the value difference between the price per share paid for a control block of shares versus the exchange price of regular shares.
C)both a) and b)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose the managers of a company have driven the stock price down because they have spent the investors' money on lavish perquisites like golf club memberships.
A)This situation may prompt a corporate raider to buy up the shares of the firm in a hostile takeover.
B)If the hostile takeover is successful, the managers will probably lose their jobs in the ensuing restructuring.
C)If the restructuring is successful, the corporate raider can sell his shares at a profit.
D)All of the above
A)This situation may prompt a corporate raider to buy up the shares of the firm in a hostile takeover.
B)If the hostile takeover is successful, the managers will probably lose their jobs in the ensuing restructuring.
C)If the restructuring is successful, the corporate raider can sell his shares at a profit.
D)All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Financial development can contribute to economic growth in what way(s)?
A)Financial development enhances savings.
B)Financial development channels savings toward real investments in productive capacities.
C)Financial development enhances the efficiency of investment allocation through the monitoring and signaling functions of capital markets.
D)All of the above.
A)Financial development enhances savings.
B)Financial development channels savings toward real investments in productive capacities.
C)Financial development enhances the efficiency of investment allocation through the monitoring and signaling functions of capital markets.
D)All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
After a hostile takeover
A)the existing management team is usually fired.
B)the existing management team is usually retained at a higher wage.
C)the target company usually mounts a takeover defense.
A)the existing management team is usually fired.
B)the existing management team is usually retained at a higher wage.
C)the target company usually mounts a takeover defense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Private benefits of corporate control will tend to be higher in
A)French civil law countries than in English common law countries.
B)English common law countries than in French civil law countries.
C)French civil law countries than in Scandinavian civil law countries.
D)English common law countries than in German civil law countries.
A)French civil law countries than in English common law countries.
B)English common law countries than in French civil law countries.
C)French civil law countries than in Scandinavian civil law countries.
D)English common law countries than in German civil law countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
English common law countries tend to provide a stronger protection of shareholder rights than French civil law countries because
A)the former countries tend to be more democratic than the latter.
B)the former countries tend to protect property rights better than the latter.
C)the former countries tend to have more separation of power than the latter.
D)all of the above
A)the former countries tend to be more democratic than the latter.
B)the former countries tend to protect property rights better than the latter.
C)the former countries tend to have more separation of power than the latter.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The formula to compute the value of the "block premium" is
A)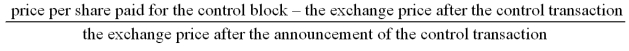
B)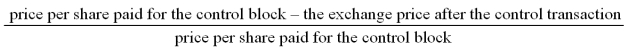
C)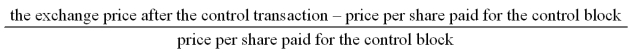
D)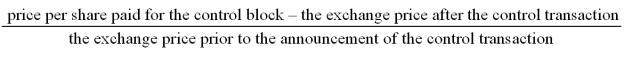
A)
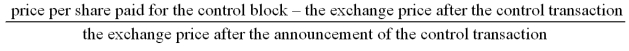
B)
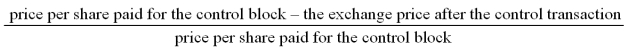
C)
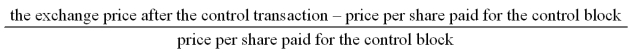
D)
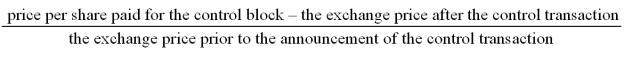

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Concentrated corporate ownership is most prevalent in
A)Italy.
B)The U.K.
C)The U.S.
D)Australia.
A)Italy.
B)The U.K.
C)The U.S.
D)Australia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



