Deck 9: Management of Economic Exposure
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Management of Economic Exposure
1
The exposure coefficient b = 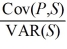 in the regression P = a + b × S + e informs
in the regression P = a + b × S + e informs
A)how much of a foreign currency to sell forward.
B)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate.
C)captures the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)how many call options to write.
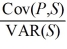 in the regression P = a + b × S + e informs
in the regression P = a + b × S + e informsA)how much of a foreign currency to sell forward.
B)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate.
C)captures the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)how many call options to write.
A
2
When exchange rates change,
A)U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers will be unaffected.
B)U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers can be affected if they compete against imports.
C)U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers will be affected,but only if they borrow in foreign currency to finance their domestic operations.
D)U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers will be unaffected,and U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers can be affected if they compete against imports.
A)U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers will be unaffected.
B)U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers can be affected if they compete against imports.
C)U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers will be affected,but only if they borrow in foreign currency to finance their domestic operations.
D)U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers will be unaffected,and U.S.firms that produce domestically and sell only to domestic customers can be affected if they compete against imports.
B
3
In recent years,the U.S.dollar has depreciated substantially against most major currencies of the world,especially against the euro.
A)The stronger euro has made many European products more expensive in dollar terms,hurting sales of these products in the United States.
B)The stronger euro has made many American products less expensive in euro terms,boosting sales of U.S.products in Europe.
C)The stronger euro has made many European products more expensive in dollar terms,hurting sales of these products in the United States.Additionally,the stronger euro has made many American products less expensive in euro terms,boosting sales of U.S.products in Europe.
D)none of the options
A)The stronger euro has made many European products more expensive in dollar terms,hurting sales of these products in the United States.
B)The stronger euro has made many American products less expensive in euro terms,boosting sales of U.S.products in Europe.
C)The stronger euro has made many European products more expensive in dollar terms,hurting sales of these products in the United States.Additionally,the stronger euro has made many American products less expensive in euro terms,boosting sales of U.S.products in Europe.
D)none of the options
C
4
When exchange rates change,
A)this can alter the operating cash flow of a domestic firm.
B)this can alter the competitive position of a domestic firm.
C)this can alter the home currency values of a multinational firm's assets and liabilities.
D)all of the options
A)this can alter the operating cash flow of a domestic firm.
B)this can alter the competitive position of a domestic firm.
C)this can alter the home currency values of a multinational firm's assets and liabilities.
D)all of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
It is conventional to classify foreign currency exposures into the following types:
A)economic exposure,transaction exposure,and translation exposure.
B)economic exposure,noneconomic exposure,and political exposure.
C)national exposure,international exposure,and trade exposure.
D)conversion exposure,and exchange exposure.
A)economic exposure,transaction exposure,and translation exposure.
B)economic exposure,noneconomic exposure,and political exposure.
C)national exposure,international exposure,and trade exposure.
D)conversion exposure,and exchange exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The exposure coefficient in the regression P = a + b × S + e is given by
A)b =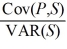
B)P = a + b × S + e
C)b =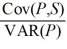
D)none of the options
A)b =
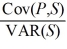
B)P = a + b × S + e
C)b =
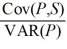
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose a U.S.-based MNC maintains a vacation home for employees in the British countryside and the local price of this property is always moving together with the pound price of the U.S.dollar.As a result,
A)whenever the pound depreciates against the dollar,the local currency price of this property goes up by the same proportion.
B)the firm is not exposed to currency risk even if the pound-dollar exchange rate fluctuates randomly.
C)whenever the pound depreciates against the dollar,the local currency price of this property goes up by the same proportion.Additionally,the firm is not exposed to currency risk even if the pound-dollar exchange rate fluctuates randomly.
D)none of the options
A)whenever the pound depreciates against the dollar,the local currency price of this property goes up by the same proportion.
B)the firm is not exposed to currency risk even if the pound-dollar exchange rate fluctuates randomly.
C)whenever the pound depreciates against the dollar,the local currency price of this property goes up by the same proportion.Additionally,the firm is not exposed to currency risk even if the pound-dollar exchange rate fluctuates randomly.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A purely domestic firm that sources and sells only domestically,
A)faces exchange rate risk to the extent that it has international competitors in the domestic market.
B)faces no exchange rate risk.
C)should never hedge since this could actually increase its currency exposure.
D)faces no exchange rate risk and should never hedge since this could actually increase its currency exposure.
A)faces exchange rate risk to the extent that it has international competitors in the domestic market.
B)faces no exchange rate risk.
C)should never hedge since this could actually increase its currency exposure.
D)faces no exchange rate risk and should never hedge since this could actually increase its currency exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The link between a firm's future operating cash flows and exchange rate fluctuations is
A)asset exposure.
B)operating exposure.
C)asset exposure and operating exposure.
D)none of the options
A)asset exposure.
B)operating exposure.
C)asset exposure and operating exposure.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The exposure coefficient b = 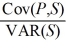 in the regression P = a + b × S + e is
in the regression P = a + b × S + e is
A)a measure of how a change in the exchange rate affects the dollar value of a firm's assets.
B)a value of zero if the value of the firm's assets is perfectly correlated with changes in the exchange rate.
C)a measure of how a change in the exchange rate affects the dollar value of a firm's assets,and has a value of zero if the value of the firm's assets is perfectly correlated with changes in the exchange rate.
D)none of the options
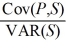 in the regression P = a + b × S + e is
in the regression P = a + b × S + e isA)a measure of how a change in the exchange rate affects the dollar value of a firm's assets.
B)a value of zero if the value of the firm's assets is perfectly correlated with changes in the exchange rate.
C)a measure of how a change in the exchange rate affects the dollar value of a firm's assets,and has a value of zero if the value of the firm's assets is perfectly correlated with changes in the exchange rate.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Exposure to currency risk can be measured by the sensitivities of
A)the future home currency values of the firm's assets and liabilities.
B)the firm's operating cash flows to random changes in exchange rates.
C)the future home currency values of the firm's assets and liabilities,as well as the firm's operating cash flows to random changes in exchange rates.
D)none of the options
A)the future home currency values of the firm's assets and liabilities.
B)the firm's operating cash flows to random changes in exchange rates.
C)the future home currency values of the firm's assets and liabilities,as well as the firm's operating cash flows to random changes in exchange rates.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Before you can use the hedging strategies such as a forward market hedge,options market hedge,and so on,you should consider running a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e .When reviewing the output,you should initially focus on
A)the intercept a.
B)the slope coefficient b.
C)mean square error,MSE.
D)R2.
A)the intercept a.
B)the slope coefficient b.
C)mean square error,MSE.
D)R2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Economic exposure refers to
A)the sensitivity of realized domestic currency values of the firm's contractual cash flows denominated in foreign currencies to unexpected exchange rate changes.
B)the extent to which the value of the firm would be affected by unanticipated changes in exchange rate.
C)the potential that the firm's consolidated financial statement can be affected by changes in exchange rates.
D)ex post and ex ante currency exposures.
A)the sensitivity of realized domestic currency values of the firm's contractual cash flows denominated in foreign currencies to unexpected exchange rate changes.
B)the extent to which the value of the firm would be affected by unanticipated changes in exchange rate.
C)the potential that the firm's consolidated financial statement can be affected by changes in exchange rates.
D)ex post and ex ante currency exposures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Two studies found a link between exchange rates and the stock prices of U.S.firms;
A)this suggests that exchange rate changes can systematically affect the value of the firm by influencing its operating cash flows.
B)this suggests that exchange rate changes can systematically affect the value of the firm by influencing the domestic currency values of its assets and liabilities.
C)this suggests that exchange rate changes can systematically affect the value of the firm by influencing its operating cash flows,as well influencing the domestic currency values of its assets and liabilities.
D)none of the options
A)this suggests that exchange rate changes can systematically affect the value of the firm by influencing its operating cash flows.
B)this suggests that exchange rate changes can systematically affect the value of the firm by influencing the domestic currency values of its assets and liabilities.
C)this suggests that exchange rate changes can systematically affect the value of the firm by influencing its operating cash flows,as well influencing the domestic currency values of its assets and liabilities.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The link between the home currency value of a firm's assets and liabilities and exchange rate fluctuations is
A)asset exposure.
B)operating exposure.
C)asset exposure and operating exposure.
D)none of the options
A)asset exposure.
B)operating exposure.
C)asset exposure and operating exposure.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When the Mexican peso collapsed in 1994,declining by 37 percent,
A)U.S.firms that exported to Mexico and priced in peso were adversely affected.
B)U.S.firms that exported to Mexico and priced in dollars were adversely affected.
C)U.S.firms were unaffected by the peso collapse,since Mexico is such a small market.
D)U.S.firms that exported to Mexico and priced in peso were adversely affected,and U.S.firms that exported to Mexico and priced in dollars were adversely affected.
A)U.S.firms that exported to Mexico and priced in peso were adversely affected.
B)U.S.firms that exported to Mexico and priced in dollars were adversely affected.
C)U.S.firms were unaffected by the peso collapse,since Mexico is such a small market.
D)U.S.firms that exported to Mexico and priced in peso were adversely affected,and U.S.firms that exported to Mexico and priced in dollars were adversely affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose the U.S.dollar substantially depreciates against the Japanese yen.The change in exchange rate
A)will tend to weaken the competitive position of import-competing U.S.car makers.
B)will tend to strengthen the competitive position of import-competing U.S.car makers.
C)will tend to strengthen the competitive position of Japanese car makers at the expense of U.S.makers.
D)none of the options
A)will tend to weaken the competitive position of import-competing U.S.car makers.
B)will tend to strengthen the competitive position of import-competing U.S.car makers.
C)will tend to strengthen the competitive position of Japanese car makers at the expense of U.S.makers.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Currency risk
A)is the same as currency exposure.
B)represents random changes in exchange rates.
C)measure "what the firm has at risk."
D)is the same as currency exposure and represents random changes in exchange rates.
A)is the same as currency exposure.
B)represents random changes in exchange rates.
C)measure "what the firm has at risk."
D)is the same as currency exposure and represents random changes in exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Operating exposure measures
A)the extent to which the foreign currency value of the firm's assets is affected by unanticipated changes in exchange rates.
B)the extent to which the firm's operating cash flows will be affected by unexpected changes in exchange rates.
C)the effect of changes in exchange rates will have on the consolidated financial reports of a MNC.
D)the effect of unanticipated changes in exchange rates on the dollar value of contractual obligations denominated in a foreign currency.
A)the extent to which the foreign currency value of the firm's assets is affected by unanticipated changes in exchange rates.
B)the extent to which the firm's operating cash flows will be affected by unexpected changes in exchange rates.
C)the effect of changes in exchange rates will have on the consolidated financial reports of a MNC.
D)the effect of unanticipated changes in exchange rates on the dollar value of contractual obligations denominated in a foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose the U.S.dollar substantially depreciates against the Japanese yen.The change in exchange rate
A)can have significant economic consequences for U.S.firms.
B)can have significant economic consequences for Japanese firms.
C)can have significant economic consequences for both U.S.and Japanese firms.
D)none of the options
A)can have significant economic consequences for U.S.firms.
B)can have significant economic consequences for Japanese firms.
C)can have significant economic consequences for both U.S.and Japanese firms.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider a U.S.MNC who owns a foreign asset.If the foreign currency value of the asset is inversely related to changes in the dollar-foreign currency exchange rate,
A)the company has a built-in hedge.
B)the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
C)the company has a built-in hedge and the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)none of the options
A)the company has a built-in hedge.
B)the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
C)the company has a built-in hedge and the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
On the basis of regression equation P = a + b × S + e,we can decompose the variability of the dollar value of the asset,VAR(P),into two separate components:
A)Cov(P,S)= b2 × VAR(P)+ VAR(S)
B)VAR(P)= b2 × VAR(S)+ VAR(e)
C)Cov(P,S)= b2 × Cov(S,P)+ Cov(S,e)
D)VAR(P)= b2 × VAR(S)
A)Cov(P,S)= b2 × VAR(P)+ VAR(S)
B)VAR(P)= b2 × VAR(S)+ VAR(e)
C)Cov(P,S)= b2 × Cov(S,P)+ Cov(S,e)
D)VAR(P)= b2 × VAR(S)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What does it mean to have redenominated an asset in terms of the dollar?
A)You have undertaken a hedging strategy that gives the asset a constant dollar value.
B)Multiply the foreign currency value of the asset by the spot exchange rate.
C)You have undertaken accounting changes to eliminate translation exposure.
D)none of the options
A)You have undertaken a hedging strategy that gives the asset a constant dollar value.
B)Multiply the foreign currency value of the asset by the spot exchange rate.
C)You have undertaken accounting changes to eliminate translation exposure.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following are identified by your text as a strategy for managing operating exposure? (i)Selecting low-cost production sites
(ii)Flexible sourcing policy
(iii)Diversification of the market
(iv)Product differentiation and R&D efforts
(v)Financial Hedging
A)(i),(iii),and (v)only
B)(ii)and (iv)only
C)(i),(iv),and (v)only
D)all of the options
(ii)Flexible sourcing policy
(iii)Diversification of the market
(iv)Product differentiation and R&D efforts
(v)Financial Hedging
A)(i),(iii),and (v)only
B)(ii)and (iv)only
C)(i),(iv),and (v)only
D)all of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: 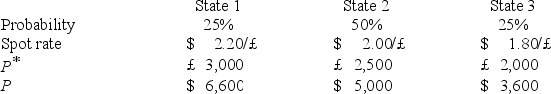 where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The variance of the exchange rate is
A)0.0200
B)0.10
C)0.002
D)none of the options
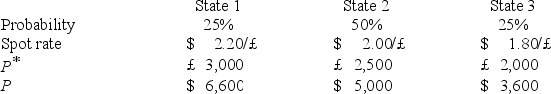 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The variance of the exchange rate is
A)0.0200
B)0.10
C)0.002
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A firm with a highly elastic demand for its products
A)will be unable to pass increased costs following unfavorable changes in the exchange rate without significantly lowering the quantity sold.
B)will be able to raise prices following unfavorable changes in the exchange rate without significantly lowering the quantity sold.
C)can easily pass increased costs on to consumers.
D)will sell about the same amount of product regardless of price.
A)will be unable to pass increased costs following unfavorable changes in the exchange rate without significantly lowering the quantity sold.
B)will be able to raise prices following unfavorable changes in the exchange rate without significantly lowering the quantity sold.
C)can easily pass increased costs on to consumers.
D)will sell about the same amount of product regardless of price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
With regard to operational hedging versus financial hedging,
A)operational hedging provides a more stable long-term approach than does financial hedging.
B)financial hedging,when instituted on a rollover basis,is a superior long-term approach to operational hedging.
C)since they both have the same goal,stabilizing the firm's cash flows in domestic currency,they are fungible in use.
D)none of the options
A)operational hedging provides a more stable long-term approach than does financial hedging.
B)financial hedging,when instituted on a rollover basis,is a superior long-term approach to operational hedging.
C)since they both have the same goal,stabilizing the firm's cash flows in domestic currency,they are fungible in use.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In recent years,
A)the U.S.dollar has appreciated substantially against most major currencies of the world,especially against the euro.
B)the U.S.dollar has depreciated substantially against most major currencies of the world,especially against the euro.
C)the U.S.dollar has maintained its value against most major currencies of the world,especially against the euro.
D)none of the options
A)the U.S.dollar has appreciated substantially against most major currencies of the world,especially against the euro.
B)the U.S.dollar has depreciated substantially against most major currencies of the world,especially against the euro.
C)the U.S.dollar has maintained its value against most major currencies of the world,especially against the euro.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario:  where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The variance of the exchange rate is:
A)0.0200
B)0.10
C)0.002
D)none of the options
 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The variance of the exchange rate is:
A)0.0200
B)0.10
C)0.002
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario:  where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is
A)$4,950.
B)$3,700.
C)$2,112.50.
D)none of the options
 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is
A)$4,950.
B)$3,700.
C)$2,112.50.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
From the perspective of the U.S.firm that owns an asset in Britain,the exposure that can be measured by the coefficient b in regressing the dollar value P of the British asset on the dollar-pound exchange rate S using regression equation P = a + b × S + e is
A)asset exposure.
B)operating exposure.
C)accounting exposure.
D)none of the options
A)asset exposure.
B)operating exposure.
C)accounting exposure.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario:  where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following would be an effective hedge?
A)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell £25,000 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
D)none of the options
 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following would be an effective hedge?
A)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell £25,000 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario:  P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The "exposure" (i.e.the regression coefficient beta)is
Hint: Calculate the expression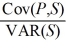 .
.
A)−25,000
B)2,500
C)−2,500
D)none of the options
 P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firmP = Dollar price of the same asset
The "exposure" (i.e.the regression coefficient beta)is
Hint: Calculate the expression
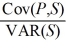 .
.A)−25,000
B)2,500
C)−2,500
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Operating exposure can be defined as
A)the link between the future home currency values of the firm's assets and liabilities and exchange rate fluctuations.
B)the extent to which the firm's operating cash flows would be affected by random changes in exchange rates.
C)the sensitivity of realized domestic currency values of the firm's contractual cash flows denominated in foreign currencies to unexpected exchange rate changes.
D)the potential that the firm's consolidated financial statement can be affected by changes in exchange rates.
A)the link between the future home currency values of the firm's assets and liabilities and exchange rate fluctuations.
B)the extent to which the firm's operating cash flows would be affected by random changes in exchange rates.
C)the sensitivity of realized domestic currency values of the firm's contractual cash flows denominated in foreign currencies to unexpected exchange rate changes.
D)the potential that the firm's consolidated financial statement can be affected by changes in exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The extent to which the firm's operating cash flows would be affected by random changes in exchange rates is called
A)asset exposure.
B)operating exposure.
C)asset exposure or operating exposure.
D)none of the options
A)asset exposure.
B)operating exposure.
C)asset exposure or operating exposure.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
On the basis of regression equation P = a + b × S + e,we can decompose the variability of the dollar value of the asset,VAR(P),into two separate components: VAR(P)= b2 × VAR(S)+ VAR(e).The second term in the right-hand side of the equation,VAR(e)represents
A)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate.
B)the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
C)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate,as well as the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)none of the options
A)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate.
B)the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
C)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate,as well as the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: 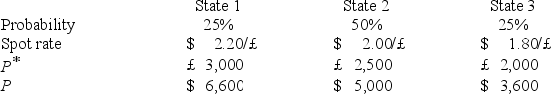 where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is
A)$5,050
B)$3,700
C)$2,112.50
D)none of the options
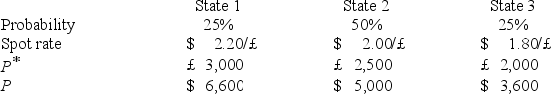 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is
A)$5,050
B)$3,700
C)$2,112.50
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The variability of the dollar value of an asset (invested overseas)depends on
A)the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate.
B)the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
C)the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate,as well as the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)none of the options
A)the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate.
B)the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
C)the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate,as well as the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: ![<strong>A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: where, P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset Which of the following conclusions are correct?</strong> A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f148_1110_926a_371e38935296_TB2600_00.jpg) where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following conclusions are correct?
A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.
D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.
![<strong>A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: where, P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset Which of the following conclusions are correct?</strong> A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f148_1110_926a_371e38935296_TB2600_00.jpg) where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following conclusions are correct?
A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.
D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
On the basis of regression equation P = a + b × S + e,we can decompose the variability of the dollar value of the asset,VAR(P),into two separate components: VAR(P)= b2 × VAR(S)+ VAR(e).The first term in the right-hand side of the equation,b2 × VAR(S)represents
A)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate.
B)the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
C)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate,as well as the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)none of the options
A)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate.
B)the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
C)the part of the variability of the dollar value of the asset that is related to random changes in the exchange rate,as well as the residual part of the dollar value variability that is independent of exchange rate movements.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Israel and faces the following scenario:  where,
where,
P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The variance of the exchange rate is:
A)0.001901
B)0.002969
C)0.0039
D)0.0049
 where,
where,P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The variance of the exchange rate is:
A)0.001901
B)0.002969
C)0.0039
D)0.0049

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: ![<strong>A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: where, P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset Which of the following conclusions are correct?</strong> A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 1,125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 2,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f148_fb76_926a_553db31d614f_TB2600_00.jpg) where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following conclusions are correct?
A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 1,125,000 ($)2 and 2,500 ($)2 respectively.
B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.
D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.
![<strong>A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: where, P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset Which of the following conclusions are correct?</strong> A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 1,125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 2,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f148_fb76_926a_553db31d614f_TB2600_00.jpg) where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following conclusions are correct?
A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 1,125,000 ($)2 and 2,500 ($)2 respectively.
B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.
D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: 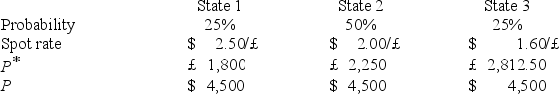 where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following would be an effective hedge?
A)Sell £2,278.13 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell £25,000 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
D)none of the options
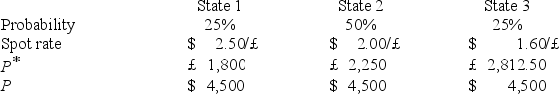 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following would be an effective hedge?
A)Sell £2,278.13 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell £25,000 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose a U.S.firm has an asset in Britain whose local currency price is random.For simplicity,suppose there are only three states of the world and each state is equally likely to occur.The future local currency price of this British asset (P*)as well as the future exchange rate (S)will be determined,depending on the realized state of the world. 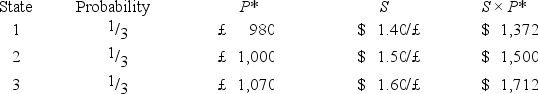 Which of the following statements is most correct?
Which of the following statements is most correct?
A)The firm faces no exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are negatively correlated.
B)The firm faces substantial exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are positively correlated.
C)The firm's exchange rate exposure can be completely hedged with derivatives written on the British pound.
D)Since randomness is involved,no hedging is possible.
 Which of the following statements is most correct?
Which of the following statements is most correct?A)The firm faces no exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are negatively correlated.
B)The firm faces substantial exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are positively correlated.
C)The firm's exchange rate exposure can be completely hedged with derivatives written on the British pound.
D)Since randomness is involved,no hedging is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose a U.S.firm has an asset in Britain whose local currency price is random.For simplicity,suppose there are only three states of the world and each state is equally likely to occur.The future local currency price of this British asset (P*)as well as the future exchange rate (S)will be determined,depending on the realized state of the world. 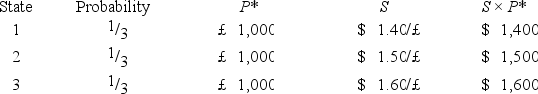 Which of the following statements is most correct?
Which of the following statements is most correct?
A)The firm faces no exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are negatively correlated.
B)The firm faces substantial exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are positively correlated.
C)The firm's exchange rate exposure can be completely hedged with derivatives written on the British pound.
D)Since randomness is involved,no hedging is possible.
 Which of the following statements is most correct?
Which of the following statements is most correct?A)The firm faces no exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are negatively correlated.
B)The firm faces substantial exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are positively correlated.
C)The firm's exchange rate exposure can be completely hedged with derivatives written on the British pound.
D)Since randomness is involved,no hedging is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Israel and faces the following scenario:  where,
where,
P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The "exposure" (i.e.,the regression coefficient beta)is
Hint: Calculate the expression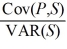 .
.
A)−52.6316
B)1,289.80
C)12,898.00
D)none of the options
 where,
where,P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The "exposure" (i.e.,the regression coefficient beta)is
Hint: Calculate the expression
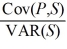 .
.A)−52.6316
B)1,289.80
C)12,898.00
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: 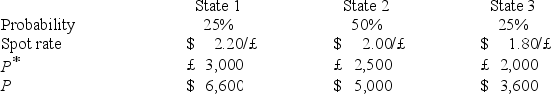 where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The "exposure" (i.e.the regression coefficient beta)is
Hint: Calculate the expression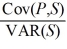 .
.
A)7,500
B)2,500
C)−2,500
D)none of the options
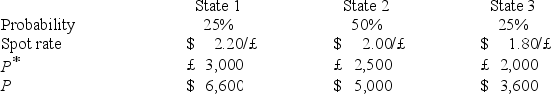 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The "exposure" (i.e.the regression coefficient beta)is
Hint: Calculate the expression
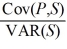 .
.A)7,500
B)2,500
C)−2,500
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Israel and faces the following scenario:  where,
where,
P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following would be an effective hedge?
A)Sell 53 Israeli shekels forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/IS),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy 53 Israeli shekels forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/IS),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell 12,898 Israeli shekels forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/IS),that prevails at time zero.
D)none of the options
 where,
where,P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following would be an effective hedge?
A)Sell 53 Israeli shekels forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/IS),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy 53 Israeli shekels forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/IS),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell 12,898 Israeli shekels forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/IS),that prevails at time zero.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: 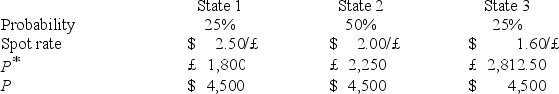 where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The variance of the exchange rate is
A)0.0200
B)0.1019
C)0.0020
D)none of the options
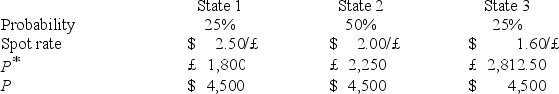 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The variance of the exchange rate is
A)0.0200
B)0.1019
C)0.0020
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Italy and faces the following scenario:  Where
Where
P* = Euro price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
The CFO decides to hedge his exposure by selling forward the expected value of the euro denominated cash flow at F1($/£)= $1.50/€.As a result,
A)the firm's exposure to the exchange rate is made worse.
B)he has a nearly perfect hedge.
C)he has a perfect hedge.
D)none of the options
 Where
WhereP* = Euro price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
The CFO decides to hedge his exposure by selling forward the expected value of the euro denominated cash flow at F1($/£)= $1.50/€.As a result,
A)the firm's exposure to the exchange rate is made worse.
B)he has a nearly perfect hedge.
C)he has a perfect hedge.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Israel and faces the following scenario: ![<strong>A U.S.firm holds an asset in Israel and faces the following scenario: where, P<sup>*</sup> = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset Which of the following conclusions are correct?</strong> A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 8.22 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 59,211 ($)<sup>2</sup>,respectively. D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 8.22 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 59,211 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14a_f752_926a_b5a11098ed53_TB2600_00.jpg) where,
where,
P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following conclusions are correct?
A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 8.22 ($)2 and 59,211 ($)2,respectively.
D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 8.22 ($)2 and 59,211 ($)2 respectively.
![<strong>A U.S.firm holds an asset in Israel and faces the following scenario: where, P<sup>*</sup> = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset Which of the following conclusions are correct?</strong> A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 493,751 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 8.22 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 59,211 ($)<sup>2</sup>,respectively. D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 8.22 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 59,211 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14a_f752_926a_b5a11098ed53_TB2600_00.jpg) where,
where,P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following conclusions are correct?
A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
B)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 236,717 ($)2 and 493,751 ($)2 respectively.
C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 8.22 ($)2 and 59,211 ($)2,respectively.
D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the Israeli asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[Var(S)] and VAR(e)are 8.22 ($)2 and 59,211 ($)2 respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_08ca_926a_0df9d220200c_TB2600_00.jpg) P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e
The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b =![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fdb_926a_3f707cdc8405_TB2600_11.jpg) Where
Where
Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50
Cov(P,S)= 150
B =![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fdc_926a_fd4419d8f35c_TB2600_11.jpg) = 7,500
= 7,500
The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as
E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80
= $.55 + $1 + $.45
= $2.00
VAR(S)= 0.25![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fdd_926a_355f2320a425_TB2600_11.jpg) + 0.50
+ 0.50 ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fde_926a_d9a8d3c29456_TB2600_11.jpg) + 0.25
+ 0.25 ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fdf_926a_c1ced75100b8_TB2600_11.jpg) = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01
= 0.01 + 0 + 0.01
= 0.02
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is:
E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050
Suppose that you implement your hedge at F1($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be
A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100.
B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100.
C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000.
D)none of the options
![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_08ca_926a_0df9d220200c_TB2600_00.jpg) P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firmP = Dollar price of the same asset
The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e
The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b =
![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fdb_926a_3f707cdc8405_TB2600_11.jpg) Where
WhereCov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50
Cov(P,S)= 150
B =
![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fdc_926a_fd4419d8f35c_TB2600_11.jpg) = 7,500
= 7,500The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as
E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80
= $.55 + $1 + $.45
= $2.00
VAR(S)= 0.25
![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fdd_926a_355f2320a425_TB2600_11.jpg) + 0.50
+ 0.50 ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fde_926a_d9a8d3c29456_TB2600_11.jpg) + 0.25
+ 0.25 ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Suppose that you implement your hedge at F<sub>1</sub>($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be</strong> A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100. B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100. C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000. D)none of the options](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14c_2fdf_926a_c1ced75100b8_TB2600_11.jpg) = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01
= 0.01 + 0 + 0.01= 0.02
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is:
E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050
Suppose that you implement your hedge at F1($/£)= $2/£.Your cash flows in state 1,2,and 3 respectively will be
A)$5,100,$5,000,$5,100.
B)$5,100,$5,100,$5,100.
C)$5,000,$5,000,$5,000.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Israel and faces the following scenario:  where,
where,
P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is:
A)$2,083.33
B)$762.50
C)$6,250.00
D)$6,562.50
 where,
where,P* = Israeli shekel (IS)price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is:
A)$2,083.33
B)$762.50
C)$6,250.00
D)$6,562.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: ![<strong>A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: where, P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset Which of the following conclusions are correct?</strong> A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 0 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 0 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. B)None of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 0 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 0 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f149_e5dc_926a_abbca78bc1ce_TB2600_00.jpg) where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following conclusions are correct?
A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 0 ($)2 and 0 ($)2 respectively.
B)None of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 0 ($)2 and 0 ($)2 respectively.
C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.
D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.
![<strong>A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: where, P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset Which of the following conclusions are correct?</strong> A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 0 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 0 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. B)None of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 0 ($)<sup>2</sup> and 0 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively. D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b<sup>2</sup>[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)<sup>2</sup> and −127,500 ($)<sup>2</sup> respectively.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f149_e5dc_926a_abbca78bc1ce_TB2600_00.jpg) where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following conclusions are correct?
A)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 0 ($)2 and 0 ($)2 respectively.
B)None of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 0 ($)2 and 0 ($)2 respectively.
C)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset cannot be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.
D)Most of the volatility of the dollar value of the British asset can be removed by hedging exchange risk because b2[VAR(S)] and VAR(e)are 125,000 ($)2 and −127,500 ($)2 respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: 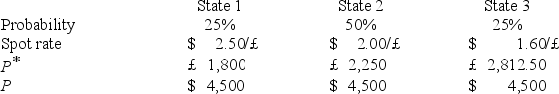 where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The "exposure" (i.e.the regression coefficient beta)is
Hint: Calculate the expression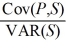 .
.
A)7,500
B)2,500
C)−2,500
D)none of the options
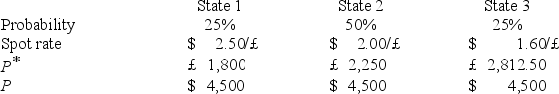 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The "exposure" (i.e.the regression coefficient beta)is
Hint: Calculate the expression
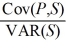 .
.A)7,500
B)2,500
C)−2,500
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: 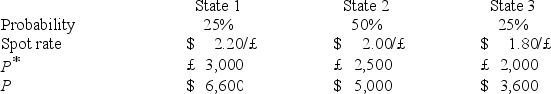 where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following would be an effective hedge?
A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell £25,000 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
D)none of the options
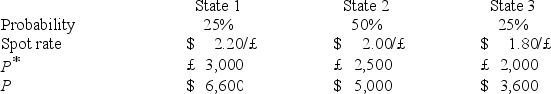 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
Which of the following would be an effective hedge?
A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell £25,000 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose a U.S.firm has an asset in Britain whose local currency price is random.For simplicity,suppose there are only three states of the world and each state is equally likely to occur.The future local currency price of this British asset (P*)as well as the future exchange rate (S)will be determined,depending on the realized state of the world. 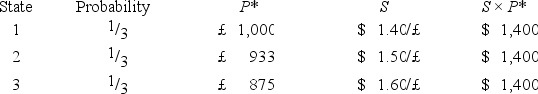 Which of the following statements is most correct?
Which of the following statements is most correct?
A)The firm faces no exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are negatively correlated.
B)The firm faces substantial exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are positively correlated.
C)The firm's exchange rate exposure can be completely hedged with derivatives written on the British pound.
D)Since randomness is involved,no hedging is possible.
 Which of the following statements is most correct?
Which of the following statements is most correct?A)The firm faces no exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are negatively correlated.
B)The firm faces substantial exchange rate risk since the local currency price of the asset and the exchange rate are positively correlated.
C)The firm's exchange rate exposure can be completely hedged with derivatives written on the British pound.
D)Since randomness is involved,no hedging is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: 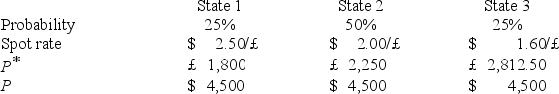 where,
where,
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is:
A)$5,050
B)$4,500
C)$2,112.50
D)none of the options
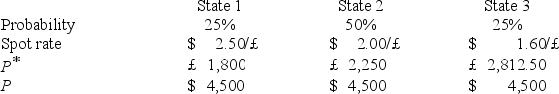 where,
where,P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is:
A)$5,050
B)$4,500
C)$2,112.50
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_6c84_926a_d51f69f7681a_TB2600_00.jpg) P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P = Dollar price of the same asset
The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e
The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b =![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_6c85_926a_7b08c5967131_TB2600_11.jpg) Where
Where
Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50
Cov(P,S)= 150
B =![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_9396_926a_ff511986a7bd_TB2600_11.jpg) = 7,500
= 7,500
The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as
E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80
= $.55 + $1 + $.45
= $2.00
VAR(S)= 0.25![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_9397_926a_fdf8135afc6d_TB2600_11.jpg) + 0.50
+ 0.50 ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_9398_926a_251e2b93ce1d_TB2600_11.jpg) + 0.25
+ 0.25 ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_baa9_926a_e920fb4bbc91_TB2600_11.jpg) = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01
= 0.01 + 0 + 0.01
= 0.02
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is:
E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050
Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?
A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500
![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_6c84_926a_d51f69f7681a_TB2600_00.jpg) P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firmP = Dollar price of the same asset
The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e
The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b =
![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_6c85_926a_7b08c5967131_TB2600_11.jpg) Where
WhereCov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50
Cov(P,S)= 150
B =
![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_9396_926a_ff511986a7bd_TB2600_11.jpg) = 7,500
= 7,500The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as
E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80
= $.55 + $1 + $.45
= $2.00
VAR(S)= 0.25
![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_9397_926a_fdf8135afc6d_TB2600_11.jpg) + 0.50
+ 0.50 ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_9398_926a_251e2b93ce1d_TB2600_11.jpg) + 0.25
+ 0.25 ![<strong>Find an effective hedge financial hedge if a U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: P<sup>*</sup> = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm P = Dollar price of the same asset The CFO runs a regression of the form P = a + b × S + e The regression coefficient beta is calculated as b = Where Cov(P,S)= 0.25 × ($6,600 - $5,050)× ($2.20 - $2.00)+ 0.50 × ($5,000 - $5,050)× ($2.00 - $2.00)+ 0.25 × ($3,600 - $5,050)× ($1.80 - $2.00)Cov(P,S)= 77.50 + 0 + 72.50 Cov(P,S)= 150 B = = 7,500 The variance of the exchange rate is calculated as E(S)= 0.25 × $2.20 + 0.50 × $2.00 + 0.25 × $1.80 = $.55 + $1 + $.45 = $2.00 VAR(S)= 0.25 + 0.50 + 0.25 = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01 = 0.02 The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is: E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050 Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?</strong> A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F<sub>1</sub>($/£),that prevails at time zero. D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2600/11ea727a_f14b_baa9_926a_e920fb4bbc91_TB2600_11.jpg) = 0.01 + 0 + 0.01
= 0.01 + 0 + 0.01= 0.02
The expected value of the investment in U.S.dollars is:
E[P] = 0.25 × $6,600 + 0.50 × $5,000 + 0.25 × $3,600 = $5,050
Which of the following is the most effective hedge financial hedge?
A)Sell £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
B)Buy £7,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
C)Sell £2,500 forward at the 1-year forward rate,F1($/£),that prevails at time zero.
D)0.25 × £3,000 + 0.50 × £2,500 + 0.25 × £2,000 = £2,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A U.S.firm holds an asset in Great Britain and faces the following scenario: 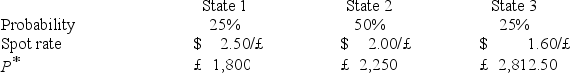 Where
Where
P* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
The CFO decides to hedge his exposure by selling forward the expected value of the pound denominated cash flow at F1($/£)= $2/£.As a result,
A)the firm's exposure to the exchange rate is made worse.
B)he has a nearly perfect hedge.
C)he has a perfect hedge.
D)none of the options
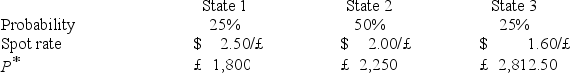 Where
WhereP* = Pound sterling price of the asset held by the U.S.firm
The CFO decides to hedge his exposure by selling forward the expected value of the pound denominated cash flow at F1($/£)= $2/£.As a result,
A)the firm's exposure to the exchange rate is made worse.
B)he has a nearly perfect hedge.
C)he has a perfect hedge.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the objective of managing operating exposure?
A)Stabilize cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.
B)Selecting low cost production sites.
C)Increase the variability of cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.
D)Stabilize cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates,and increase the variability of cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.
A)Stabilize cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.
B)Selecting low cost production sites.
C)Increase the variability of cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.
D)Stabilize cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates,and increase the variability of cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Consider a U.S.-based MNC with a wholly-owned Italian subsidiary.Following a depreciation of the dollar against the euro,which of the following describes the competitive effect of the depreciation?
A)The cash flow in euro could be altered due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)A given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
C)The cash flow in euro could be altered due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace,and a given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
D)none of the options
A)The cash flow in euro could be altered due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)A given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
C)The cash flow in euro could be altered due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace,and a given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Generally speaking,when both a firm's costs and its price are sensitive to exchange rate changes,
A)the firm is not subject to high degrees of operating exposure.
B)the firm is subject to high degrees of operating exposure.
C)the firm should hedge.
D)none of the options
A)the firm is not subject to high degrees of operating exposure.
B)the firm is subject to high degrees of operating exposure.
C)the firm should hedge.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The firm may not be able to pass through changes in the exchange rate
A)in markets with low product differentiation.
B)in markets with high price elasticities.
C)in markets with low product differentiation or in markets with high price elasticities.
D)none of the options
A)in markets with low product differentiation.
B)in markets with high price elasticities.
C)in markets with low product differentiation or in markets with high price elasticities.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A firm's operating exposure is
A)defined as the extent to which the firm's operating cash flows would be affected by the random changes in exchange rates.
B)determined by the structure of the markets in which the firm sources its inputs,such as labor and materials,and sells its products.
C)determined by the firm's ability to mitigate the effect of exchange rate changes by adjusting its markets,product mix,and sourcing.
D)all of the options
A)defined as the extent to which the firm's operating cash flows would be affected by the random changes in exchange rates.
B)determined by the structure of the markets in which the firm sources its inputs,such as labor and materials,and sells its products.
C)determined by the firm's ability to mitigate the effect of exchange rate changes by adjusting its markets,product mix,and sourcing.
D)all of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose a U.S.firm has an asset in Italy whose local currency price is random.For simplicity,suppose there are only three states of the world and each state is equally likely to occur.The future local currency price of this asset (P*)as well as the future exchange rate (S)will be determined,depending on the realized state of the world. 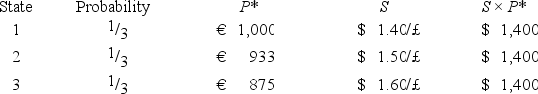 Assume that you choose to "hedge" this asset by selling forward the expected value of the euro denominated cash flow at F1($/£)= $1.50/€.Calculate your cash flows in each of the possible states.
Assume that you choose to "hedge" this asset by selling forward the expected value of the euro denominated cash flow at F1($/£)= $1.50/€.Calculate your cash flows in each of the possible states.
A)$1,400,$1,400,$1,400
B)$1,496.6,$1,400,$1,306.40
C)$1,404,$1,404.$1,404
D)none of the options
 Assume that you choose to "hedge" this asset by selling forward the expected value of the euro denominated cash flow at F1($/£)= $1.50/€.Calculate your cash flows in each of the possible states.
Assume that you choose to "hedge" this asset by selling forward the expected value of the euro denominated cash flow at F1($/£)= $1.50/€.Calculate your cash flows in each of the possible states.A)$1,400,$1,400,$1,400
B)$1,496.6,$1,400,$1,306.40
C)$1,404,$1,404.$1,404
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following can a company use to manage operating exposure?
A)Selecting low-cost production sites,diversifying the market.
B)Low cost production sites,but not financial hedging.
C)Pursuing a flexible sourcing policy,product differentiation,R&D efforts.
D)Selecting low-cost production sites,diversifying the market,as well as pursuing a flexible sourcing policy,product differentiation,R&D efforts.
A)Selecting low-cost production sites,diversifying the market.
B)Low cost production sites,but not financial hedging.
C)Pursuing a flexible sourcing policy,product differentiation,R&D efforts.
D)Selecting low-cost production sites,diversifying the market,as well as pursuing a flexible sourcing policy,product differentiation,R&D efforts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The firm may not be able to pass through changes in the exchange rate
A)in markets with mainly domestic (foreign to the firm)competitors.
B)in markets with low price elasticities.
C)in markets with mainly domestic (foreign to the firm)competitors or in markets with low price elasticities.
D)none of the options
A)in markets with mainly domestic (foreign to the firm)competitors.
B)in markets with low price elasticities.
C)in markets with mainly domestic (foreign to the firm)competitors or in markets with low price elasticities.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The firm may not be subject to high degrees of operating exposure
A)when changes in real exchange rates are exactly offset by the inflation differential.
B)when changes in nominal exchange rates are exactly matched by the inflation differential.
C)when changes in nominal exchange rates are exactly offset by the inflation differential.
D)none of the options
A)when changes in real exchange rates are exactly offset by the inflation differential.
B)when changes in nominal exchange rates are exactly matched by the inflation differential.
C)when changes in nominal exchange rates are exactly offset by the inflation differential.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Generally speaking,a firm is subject to high degrees of operating exposure
A)when its costs are sensitive to exchange rate changes.
B)when its prices are sensitive to exchange rate changes.
C)when either its cost or its price is sensitive to exchange rate changes.
D)none of the options
A)when its costs are sensitive to exchange rate changes.
B)when its prices are sensitive to exchange rate changes.
C)when either its cost or its price is sensitive to exchange rate changes.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Consider a U.S.-based MNC with a wholly-owned French subsidiary.Following a depreciation of the dollar against the euro,which of the following best describes the mechanism of any effect of the depreciation?
A)The change in the cash flow in euro due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace is in part a function of the elasticity of demand for the firm's product.
B)A given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow regardless of the firm's hedging program.
C)The change in the cash flow in euro due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace is in part a function of the elasticity of demand for the firm's product,and a given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow regardless of the firm's hedging program.
D)none of the options
A)The change in the cash flow in euro due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace is in part a function of the elasticity of demand for the firm's product.
B)A given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow regardless of the firm's hedging program.
C)The change in the cash flow in euro due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace is in part a function of the elasticity of demand for the firm's product,and a given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow regardless of the firm's hedging program.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Consider a U.S.-based MNC with a wholly-owned European subsidiary selling a product sourced in euro and priced in euro with inelastic demand.Following a depreciation of the dollar against the euro,which of the following is the truest?
A)Since they have inelastic demand,the U.S.firm can just pass through the impact of the exchange rate change.
B)Since they have elastic demand,the U.S.firm cannot just pass through the impact of the exchange rate change.
C)Since the exchange rate movement was favorable to the U.S.firm,there is no impact on the firm's position.
D)none of the options.
A)Since they have inelastic demand,the U.S.firm can just pass through the impact of the exchange rate change.
B)Since they have elastic demand,the U.S.firm cannot just pass through the impact of the exchange rate change.
C)Since the exchange rate movement was favorable to the U.S.firm,there is no impact on the firm's position.
D)none of the options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Managing operating exposure
A)is a short-term tactical issue.
B)is a long-term issue,like selecting a site for a factory.
C)is relatively unimportant,since most MNCs have a built-in hedge.
D)none of the options
A)is a short-term tactical issue.
B)is a long-term issue,like selecting a site for a factory.
C)is relatively unimportant,since most MNCs have a built-in hedge.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Consider a U.S.MNC with operations in Great Britain.Which of the following are potential risks following a strengthening of the dollar?
A)A pound sterling depreciation may affect operating cash flow in pounds by altering the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)A given operating cash flow in pounds will be converted into a lower dollar amount after the pound depreciation.
C)A pound sterling depreciation may affect operating cash flow in pounds by altering the firm's competitive position in the marketplace,and a given operating cash flow in pounds will be converted into a lower dollar amount after the pound depreciation.
D)none of the options
A)A pound sterling depreciation may affect operating cash flow in pounds by altering the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)A given operating cash flow in pounds will be converted into a lower dollar amount after the pound depreciation.
C)A pound sterling depreciation may affect operating cash flow in pounds by altering the firm's competitive position in the marketplace,and a given operating cash flow in pounds will be converted into a lower dollar amount after the pound depreciation.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is false?
A)The competitive effect is that a depreciation may affect operating cash flow in the foreign currency by altering the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)The conversion effect is defined as a given operating cash flow in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after a currency depreciation.
C)The competitive effect is defined as a given operating cash flow in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after a currency depreciation.
D)none of the options
A)The competitive effect is that a depreciation may affect operating cash flow in the foreign currency by altering the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)The conversion effect is defined as a given operating cash flow in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after a currency depreciation.
C)The competitive effect is defined as a given operating cash flow in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after a currency depreciation.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the objective of managing operating exposure?
A)Stabilize accounting results in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.
B)Selecting low cost production sites.
C)Increase the variability of cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.
D)none of the options
A)Stabilize accounting results in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.
B)Selecting low cost production sites.
C)Increase the variability of cash flows in the face of fluctuating exchange rates.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Consider a U.S.-based MNC with a wholly-owned German subsidiary.Following a depreciation of the dollar against the euro,which of the following describes the conversion effect of the depreciation?
A)The cash flow in euro could be altered due a change in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)A given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
C)The cash flow in euro could be altered due a change in the firm's competitive position in the market place,and a given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
D)none of the options
A)The cash flow in euro could be altered due a change in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)A given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
C)The cash flow in euro could be altered due a change in the firm's competitive position in the market place,and a given operating cash flow in euro will be translated to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Consider a U.S.-based MNC with a wholly-owned Italian subsidiary.Following a depreciation of the dollar against the euro,which of the following conclusions are correct?
A)The cash flow in euro could be altered due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)A given operating cash flow in euro will be converted to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
C)The cash flow in euro could be altered due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace,and a given operating cash flow in euro will be converted to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
D)none of the options
A)The cash flow in euro could be altered due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)A given operating cash flow in euro will be converted to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
C)The cash flow in euro could be altered due an alteration in the firm's competitive position in the marketplace,and a given operating cash flow in euro will be converted to a higher U.S.dollar cash flow.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Generally speaking,a firm is subject to high degrees of operating exposure when
A)either its cost or its price is sensitive to exchange rate changes.
B)both the cost and the price are sensitive to exchange rate changes.
C)both the cost and the price are insensitive to exchange rate changes.
D)none of the options
A)either its cost or its price is sensitive to exchange rate changes.
B)both the cost and the price are sensitive to exchange rate changes.
C)both the cost and the price are insensitive to exchange rate changes.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is true?
A)The competitive effect is that a currency depreciation may affect operating cash flow in the foreign currency by altering the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)The conversion effect is defined as a given accounting cash value in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after currency depreciation.
C)The competitive effect is defined as a given operating cash flow in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after a currency depreciation.
D)none of the options
A)The competitive effect is that a currency depreciation may affect operating cash flow in the foreign currency by altering the firm's competitive position in the marketplace.
B)The conversion effect is defined as a given accounting cash value in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after currency depreciation.
C)The competitive effect is defined as a given operating cash flow in a foreign currency will be converted into a lower dollar amount after a currency depreciation.
D)none of the options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



