Deck 12: Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/61
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Monopoly
1
If the demand curve for a single price monopolist always is a downward sloping straight line, then marginal revenue
A)Will be a straight line with a negative slope of twice the demand curve slope
B)Will be a straight line with a negative slope of one-half the demand curve slope
C)Will be identical to the demand curve
D)Will be a horizontal line
A)Will be a straight line with a negative slope of twice the demand curve slope
B)Will be a straight line with a negative slope of one-half the demand curve slope
C)Will be identical to the demand curve
D)Will be a horizontal line
A
2
If a profit maximizing monopolist faces a linear demand curve and has zero marginal cost, it will produce where demand elasticity is __________________ if it will produce at all.
A)Inelastic
B)Elastic
C)1
D)Information is inadequate to answer the question
A)Inelastic
B)Elastic
C)1
D)Information is inadequate to answer the question
C
3
A monopolist has a marginal revenue curve given by MR = 102 - Q, and a total cost curve given by TC = Q2+ 16.The monopolist's profit maximizing price and quantity are ___, _____ respectively.
A)85,34
B)52,50
C)100,2
D)77,50
A)85,34
B)52,50
C)100,2
D)77,50
A
4
The demand equation for a single price monopolist is P = 50 - Q.The marginal revenue equation for this monopolist is
A)25 - Q
B)50 - 2Q
C)50 - Q
D)100 - Q
A)25 - Q
B)50 - 2Q
C)50 - Q
D)100 - Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a firm could perfectly price discriminate
A)The marginal revenue curve would be the same as the demand curve
B)The marginal revenue curve would lie below the demand curve
C)The marginal revenue curve would lie above the demand curve
D)There would be no marginal revenue function
A)The marginal revenue curve would be the same as the demand curve
B)The marginal revenue curve would lie below the demand curve
C)The marginal revenue curve would lie above the demand curve
D)There would be no marginal revenue function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The profit maximizing markup (over MC) is given by
A)1/elasticity
B)Elasticity
C)Elasticity2
D)Elasticity + 1
A)1/elasticity
B)Elasticity
C)Elasticity2
D)Elasticity + 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a profit maximizing monopolist faces a linear demand curve and has zero marginal cost, it will produce at:
A.lowest point of marginal revenue curve
B.elasticity of demand equals 1
C.lowest point of marginal profit curve
D.all of the choices are correct
A.lowest point of marginal revenue curve
B.elasticity of demand equals 1
C.lowest point of marginal profit curve
D.all of the choices are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not a source of monopoly power?
A)Exclusive control over inputs
B)Economies of scale
C)Patents
D)Rapid low cost technological change in the industry
A)Exclusive control over inputs
B)Economies of scale
C)Patents
D)Rapid low cost technological change in the industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which statement is true for a profit maximizing monopolist?
A)It always faces a downward sloping demand curve
B)It can avoid diminishing returns to production
C)It will not produce where marginal cost equals marginal revenue
D)It can charge whatever price it wants
A)It always faces a downward sloping demand curve
B)It can avoid diminishing returns to production
C)It will not produce where marginal cost equals marginal revenue
D)It can charge whatever price it wants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If a profit maximizing monopolist sells its output for $100, then we know that its marginal revenue is
A)More than $100 if it is a perfect price discriminator
B)Less than $100 if it is a single price monopolist
C)Equal to $100 in all cases
D)Less than $100 if it is a perfect price discriminator
A)More than $100 if it is a perfect price discriminator
B)Less than $100 if it is a single price monopolist
C)Equal to $100 in all cases
D)Less than $100 if it is a perfect price discriminator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the above diagram the profit maximizing firm is
A)Making positive economic profit
B)Making zero economic profit
C)Making negative economic profit
D)One cannot tell
A)Making positive economic profit
B)Making zero economic profit
C)Making negative economic profit
D)One cannot tell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the long-run, profit maximizing monopolists
A)Price where MC and price are equal
B)Never make positive economic profits
C)Produce where average total costs are minimized
D)Will produce with the same size operation as a perfectly competitive firm would use in the long run
A)Price where MC and price are equal
B)Never make positive economic profits
C)Produce where average total costs are minimized
D)Will produce with the same size operation as a perfectly competitive firm would use in the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The marginal revenue curve of a single price monopolist
A)Lies above the demand curve
B)Lies below the demand curve
C)Lies along the demand curve
D)Is a horizontal line
A)Lies above the demand curve
B)Lies below the demand curve
C)Lies along the demand curve
D)Is a horizontal line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The total revenue curve for a firm is given by TR = 2Q.
A)The firm is definitely a monopolist
B)The firm is definitely not a monopolist
C)The firm may be a monopolist or a perfectly competitive firm
D)One can not tell from the equation what market form applies
A)The firm is definitely a monopolist
B)The firm is definitely not a monopolist
C)The firm may be a monopolist or a perfectly competitive firm
D)One can not tell from the equation what market form applies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The demand equation for a single price monopolist is P = 120 - 3Q.The marginal revenue curve for this monopolist is
A)120 - 1.5Q
B)60 - 3Q
C)60 - 6Q
D)120 - 6Q
A)120 - 1.5Q
B)60 - 3Q
C)60 - 6Q
D)120 - 6Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A natural monopoly always has
A)A downward sloping long run average cost curve
B)A downward sloping marginal cost curve
C)Its profit maximization point where price = marginal cost
D)Patent rights
A)A downward sloping long run average cost curve
B)A downward sloping marginal cost curve
C)Its profit maximization point where price = marginal cost
D)Patent rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the above diagram the profit maximizing output level is
A)OA
B)OB
C)OC
D)It is impossible to say
A)OA
B)OB
C)OC
D)It is impossible to say

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the diagram above, the profit maximizing price level is
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Monopoly is characterized by
A)Many close substitutes
B)No barriers to entry
C)A downward sloping demand curve
D)A horizontal demand curve
A)Many close substitutes
B)No barriers to entry
C)A downward sloping demand curve
D)A horizontal demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the owner of the firm, shown above is a profit maximizer, the firm should ______ in the short run.
A)Continue to operate at the existing output
B)Shutdown
C)Expand output to lower costs
D)More data is needed to say definitively what the firm should do
A)Continue to operate at the existing output
B)Shutdown
C)Expand output to lower costs
D)More data is needed to say definitively what the firm should do

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The profit maximizing quantity of output in market A would be:
A)46
B)23
C)21
D)5
A)46
B)23
C)21
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In long-run equilibrium for a single-price monopolist
A)The plant size is always the one at the bottom of the long-run ATC curve
B)Output is at the level where short-run and long-run marginal cost are the same
C)Marginal cost equals ATC
D)Marginal revenue equals price
A)The plant size is always the one at the bottom of the long-run ATC curve
B)Output is at the level where short-run and long-run marginal cost are the same
C)Marginal cost equals ATC
D)Marginal revenue equals price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A profit maximizing monopolist faces the following information: P = $10, MR = $5, ATC = $6, MC = $5.The firm should
A)Shut down
B)Decrease output
C)Increase output
D)Stay at its current level of output
A)Shut down
B)Decrease output
C)Increase output
D)Stay at its current level of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For the output maximizing monopolist whose stockholders demand a normal economic return on equity, economic profit
A)Is positive
B)Is negative
C)Is zero
D)May be positive or zero
A)Is positive
B)Is negative
C)Is zero
D)May be positive or zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following could not be considered price discrimination?
A)The issuing of discount tickets to week-end travelers
B)Airlines offering super-saver fares to everyone
C)Movies offering cheap matinees
D)Senior citizen's discounts
A)The issuing of discount tickets to week-end travelers
B)Airlines offering super-saver fares to everyone
C)Movies offering cheap matinees
D)Senior citizen's discounts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Under rate of return regulation
A)P = MC
B)P = ATC
C)P = AVC
D)P > ATC
A)P = MC
B)P = ATC
C)P = AVC
D)P > ATC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A single price monopoly that faces the demand curve P = 10 - Q and profit maximizes by reducing price from $6 to $5 must have a marginal cost of
A)1
B)5
C)6
D)10
A)1
B)5
C)6
D)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For the output maximizing monopolist
A)Average total cost must be falling
B)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
C)Long-run marginal cost equals demand
D)Price equals average total cost
A)Average total cost must be falling
B)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
C)Long-run marginal cost equals demand
D)Price equals average total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the long run equilibrium for a monopolist
A)The short-run average cost curve is at its lowest point
B)The long-run average cost curve is at its lowest point
C)A and b
D)None of the above is necessarily true
A)The short-run average cost curve is at its lowest point
B)The long-run average cost curve is at its lowest point
C)A and b
D)None of the above is necessarily true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A profit maximizing monopolist faces the following information: P = $4, MR = $2, MC = $1.50.The firm should
A)Shut down
B)Decrease output
C)Increase output
D)Stay at its current level of output
A)Shut down
B)Decrease output
C)Increase output
D)Stay at its current level of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
According to the text, the most important of the four factors which give rise to monopoly is
A)Exclusive control over important inputs
B)Economies of scale
C)Patents
D)Government licenses
A)Exclusive control over important inputs
B)Economies of scale
C)Patents
D)Government licenses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Price discrimination is possible only if
A)Economies of scale exist
B)Markets can be segregated
C)Each person in the market has the same elasticity of demand
D)Prices are kept secret so those paying the high price do not know that others paid less
A)Economies of scale exist
B)Markets can be segregated
C)Each person in the market has the same elasticity of demand
D)Prices are kept secret so those paying the high price do not know that others paid less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Under rate of return regulation
A)Firms earn positive economic profits
B)Firms earn negative economic profits
C)Firms earn zero economic profits
D)Firms earn zero accounting profits
A)Firms earn positive economic profits
B)Firms earn negative economic profits
C)Firms earn zero economic profits
D)Firms earn zero accounting profits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The supply curve for a monopolist
A)Is upward sloping
B)Is vertical
C)Does not exist
D)Is downward sloping
A)Is upward sloping
B)Is vertical
C)Does not exist
D)Is downward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is not true for a profit maximizing single-price monopolist in the long run?
A)It will make profit or break even
B)Price is greater than marginal revenue
C)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
D)Demand is inelastic
A)It will make profit or break even
B)Price is greater than marginal revenue
C)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
D)Demand is inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In first-degree price discrimination
A)The monopolist knows the equilibrium price
B)The monopolist segments the market
C)The monopolist charges only two different prices
D)The monopolist gets less of the consumer surplus than would be taken if 2nd degree price discrimination was practiced
A)The monopolist knows the equilibrium price
B)The monopolist segments the market
C)The monopolist charges only two different prices
D)The monopolist gets less of the consumer surplus than would be taken if 2nd degree price discrimination was practiced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In second-degree price discrimination it is true that
A)People who buy a lot pay a lower price
B)People who buy relatively little pay a lower price
C)The monopolist cannot earn economic profits
D)The market need not be segmented
A)People who buy a lot pay a lower price
B)People who buy relatively little pay a lower price
C)The monopolist cannot earn economic profits
D)The market need not be segmented

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A single-price monopolist with a positive marginal cost will maximize profit by producing where
A)Demand is price elastic
B)Demand is price inelastic
C)Demand is unit elastic
D)Any of the above may apply
A)Demand is price elastic
B)Demand is price inelastic
C)Demand is unit elastic
D)Any of the above may apply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The monopolist would charge a price of _______ in market B in order to maximize profits:
A)29
B)8
C)8.
D)0
A)29
B)8
C)8.
D)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Say a monopolist knew that at the current price for its product demand is inelastic. If marginal costs for this firm are zero, then in order to maximize profits this monopolists should:
A)increase output
B)reduce output
C)keep output at the same level
D)decrease its price
A)increase output
B)reduce output
C)keep output at the same level
D)decrease its price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the firm facing the demand curve P = 10 - Q still has zero marginal costs and is now a perfect price discriminator instead of a single price monopolist, what will profits be if fixed costs are 12?
A)10
B)12
C)13
D)38
A)10
B)12
C)13
D)38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Explain why price discrimination solves the welfare loss problem of monopoly, but then describe the downside of solving the welfare loss problem this way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A single price monopolist has a demand curve: P = 500 - 50Q.It has the total cost curve: TC = 1000 + 100Q.If the firm is a profit maximizer or loss minimizer, what output and price should it plan for ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If a monopolist had no costs, its best possible price would be where demand is
A)Infinitely elastic
B)Relatively (but not perfectly) elastic
C)Unit elastic
D)Relatively (but not completely) inelastic
A)Infinitely elastic
B)Relatively (but not perfectly) elastic
C)Unit elastic
D)Relatively (but not completely) inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When the monopolists maximizes profits the price elasticity of demand for widgets is:
A)9
B)36
C)0.5
D)0.02
A)9
B)36
C)0.5
D)0.02

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the firm in question 44 can perfectly price discriminate and each unit of output is infinitely divisible, what quantity would it produce and what would its profit (loss) situation then be?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All of the following are true about a monopolist except:
A)Average and marginal revenues are not the same
B)Marginal revenue is greater than price
C)Marginal revenue decreases with increases in output
D)Marginal revenue can be negative
A)Average and marginal revenues are not the same
B)Marginal revenue is greater than price
C)Marginal revenue decreases with increases in output
D)Marginal revenue can be negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The following is a difference between a monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm:
A)output is maximized when MR =MC
B)at some point there will always be diminishing returns to the marginal input.
C)the marginal cost curve is usually U-shaped
D)at equilibrium price is usually higher than marginal cost
A)output is maximized when MR =MC
B)at some point there will always be diminishing returns to the marginal input.
C)the marginal cost curve is usually U-shaped
D)at equilibrium price is usually higher than marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A firm with a demand curve P = 10 - Q is a perfect price discriminating monopolist with zero marginal costs and fixed costs of 12.Consider the following two statements comparing the price discriminating case with a single price monopolist.1) In this case consumers are better off as a group because more of the product is produced.2) Producers are better off because they have higher profits.Which of the following comments about these statements is true?
A)Both statements are true
B)Only the first statement is true
C)Only the second statement is true
D)Both statements are false
A)Both statements are true
B)Only the first statement is true
C)Only the second statement is true
D)Both statements are false

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Show graphically why economists refer to single-price monopoly market structure as inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the monopolist facing the demand curve P = 10 - Q is a perfectly discriminating monopolist and marginal cost is constant at $4, how much will the firm sell if it profit maximizes?
A)6
B)5
C)4
D)10
A)6
B)5
C)4
D)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which is true of a single price monopoly firm?
A)Its supply curve is equal to its marginal cost function
B)It can not pass along all its cost increases directly to the customer
C)Its shutdown point is where ATC = price
D)An increased profits tax will lower the quantity the firm will produce
A)Its supply curve is equal to its marginal cost function
B)It can not pass along all its cost increases directly to the customer
C)Its shutdown point is where ATC = price
D)An increased profits tax will lower the quantity the firm will produce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following explains why theater prices for popcorn are three or four times higher than the popcorn price in the grocery store.
A)The grocery store sells a much higher volume and gets its profits that way
B)The cost of popping the popcorn is high
C)Grocery stores are satisfied with normal profit while theaters seek economic profit
D)The demand curve for popcorn in a theater is more inelastic than the demand for popcorn at the grocery store
A)The grocery store sells a much higher volume and gets its profits that way
B)The cost of popping the popcorn is high
C)Grocery stores are satisfied with normal profit while theaters seek economic profit
D)The demand curve for popcorn in a theater is more inelastic than the demand for popcorn at the grocery store

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the marginal costs are constant and zero for a single price monopolist facing the demand curve P = 10 - Q, what will profits be if fixed costs are 12?
A)10
B)12
C)13
D)38
A)10
B)12
C)13
D)38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a monopoly generally brings a loss of economic efficiency and consumer surplus, why would a local government give only one utility company (such as a cable television company) a license to enter its market? Should local governments continue this practice?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Many college bookstores give faculty a discount that students do not receive.Show with a sketch graph why this practice is most likely a profit maximizing strategy instead of a college perk given to the faculty at college expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is not true?
A)A monopolist typically seeks to maximize profits
B)A monopolist can set price at arbitrarily high levels
C)A monopolist may engage in advertising
D)Monopolists price on the elastic portion of their demand curves
A)A monopolist typically seeks to maximize profits
B)A monopolist can set price at arbitrarily high levels
C)A monopolist may engage in advertising
D)Monopolists price on the elastic portion of their demand curves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A single price profit maximizing monopolist is inefficient because
A)It produces too much output
B)It perfectly price discriminates when it can
C)The sum of consumer and producer surplus is less than it could be
D)It produces where price equals marginal cost rather than where marginal cost equals marginal revenue
A)It produces too much output
B)It perfectly price discriminates when it can
C)The sum of consumer and producer surplus is less than it could be
D)It produces where price equals marginal cost rather than where marginal cost equals marginal revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose you own a firm that produces widgets and is a monopoly.The market demand is given by the equation P = 50 - 0.08Q, where P is the price of gadgets and Q is the quantity of gadgets sold per week.The marginal costs for the firm are 0.08Q
A.Draw the firm's demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves.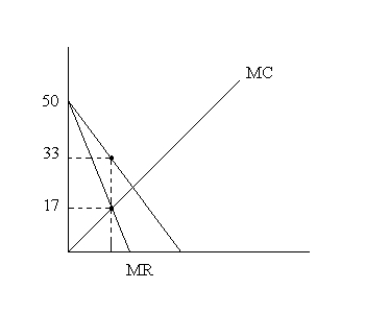
B.Find the profit-maximizing level of output for this firm.Will the firm earn positive or negative profits?
MR = 50 - 0.66Q
A.Draw the firm's demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves.

B.Find the profit-maximizing level of output for this firm.Will the firm earn positive or negative profits?
MR = 50 - 0.66Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the profit (loss) of the firm in question 44 above?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Sketch graph a natural monopoly with the typical ATC, MC, and demand and MR functions
a.Label the profit maximizing monopoly price with a P1.b.Label the typical public utility commission regulated price which requires no subsidy as P2 c.Label the socially efficient price as P3 d.Shade in the area of the subsidy required in one of the cases above e.Explain why a subsidy is often used for public transportation but not for municipal water supply
a.Label the profit maximizing monopoly price with a P1.b.Label the typical public utility commission regulated price which requires no subsidy as P2 c.Label the socially efficient price as P3 d.Shade in the area of the subsidy required in one of the cases above e.Explain why a subsidy is often used for public transportation but not for municipal water supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



