Deck 13: Imperfect Competition: a Game-Theoretic Approach
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Imperfect Competition: a Game-Theoretic Approach
1
If two tit-for-tat players interact together over a long period of time, the result will be
A)Cooperation
B)Defection
C)Marginal cost pricing
D)A leader will emerge as in the Stackelberg model
A)Cooperation
B)Defection
C)Marginal cost pricing
D)A leader will emerge as in the Stackelberg model
A
2
Excess capacity for a firm in an oligopoly situation
A)Can not contribute to long run profit for a firm
B)Encourages competitors to enter the market and build at optimal capacity
C)Is a deterrent to entry in the market by potential competitors
D)Will be temporary if the planning was done right
A)Can not contribute to long run profit for a firm
B)Encourages competitors to enter the market and build at optimal capacity
C)Is a deterrent to entry in the market by potential competitors
D)Will be temporary if the planning was done right
C
3
One difficulty is that tit-for-tat's effectiveness depends on the existence of
A)Perfect information about another's actions
B)Only two players in the game
C)An infinite number of players in the game
D)An industry that is not growing
A)Perfect information about another's actions
B)Only two players in the game
C)An infinite number of players in the game
D)An industry that is not growing
B
4
In a prisoner's dilemma game a dominant strategy would mean that one of the players
A)Follows the moves of the opponent no matter what the opponent does
B)Knows the payoff matrix outcomes while the other does not
C)Is sure to come out with the most preferred outcome no matter what the other does
D)Will benefit most from one particular move no matter what the opponent does
A)Follows the moves of the opponent no matter what the opponent does
B)Knows the payoff matrix outcomes while the other does not
C)Is sure to come out with the most preferred outcome no matter what the other does
D)Will benefit most from one particular move no matter what the opponent does

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a battle of Boeing and Airbus a Nash equilibrium will exist if
A)They both have agreed to a monopoly pricing structure
B)They are presently operating at a point where neither one would benefit by unilaterally changing strategies
C)Boeing has the power to drive Airbus out of business with a predatory pricing strategy
D)Both pass up profit opportunities because they fear retaliation
A)They both have agreed to a monopoly pricing structure
B)They are presently operating at a point where neither one would benefit by unilaterally changing strategies
C)Boeing has the power to drive Airbus out of business with a predatory pricing strategy
D)Both pass up profit opportunities because they fear retaliation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the Bertrand model
A)Each firm takes the quantities produced by its rivals as given
B)Each firm takes the prices charged by its rivals as given
C)One firm plays a leadership role and its rivals merely follow
D)Prices are higher and quantities are slightly less than we would see if the firms colluded to achieve the monopoly outcome
A)Each firm takes the quantities produced by its rivals as given
B)Each firm takes the prices charged by its rivals as given
C)One firm plays a leadership role and its rivals merely follow
D)Prices are higher and quantities are slightly less than we would see if the firms colluded to achieve the monopoly outcome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following markets can most accurately be described as monopolistically competitive?
A)Toothpaste
B)Milk
C)Electricity
D)Apples
A)Toothpaste
B)Milk
C)Electricity
D)Apples

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When each company follows its dominant strategy the profits for each of the firms are equal to:
A)$2,499
B)$2,500
C)$2,000
D)$4,998
A)$2,499
B)$2,500
C)$2,000
D)$4,998

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the Cournot model
A)Each firm takes the quantities produced by its rivals as given
B)Each firm takes the prices charged by its rivals as given
C)One firm plays a leadership role and its rivals merely follow
D)Prices are higher and quantities are slightly less than we would see if the firms colluded
A)Each firm takes the quantities produced by its rivals as given
B)Each firm takes the prices charged by its rivals as given
C)One firm plays a leadership role and its rivals merely follow
D)Prices are higher and quantities are slightly less than we would see if the firms colluded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the payoff matrix above the Nash equilibrium for the game is
A)for both players to follow strategy A
B)for both players to follow strategy B
C)for player 2 to follow strategy A and for player 2 to follow strategy B
D)there is no Nash equilibrium in this game
A)for both players to follow strategy A
B)for both players to follow strategy B
C)for player 2 to follow strategy A and for player 2 to follow strategy B
D)there is no Nash equilibrium in this game

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The unraveling problem in interdependent relationships arises from a situation in which
A)There is a known, finite number of future interactions
B)There is not a known, finite number of future interactions
C)Interactions suddenly and surprisingly cease
D)A recession hits an industry
A)There is a known, finite number of future interactions
B)There is not a known, finite number of future interactions
C)Interactions suddenly and surprisingly cease
D)A recession hits an industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
You are given the four payout option show below for a coin toss.If you are using a maximum strategy, which option do you choose?
A)Heads you win $500, tails you lose $100
B)Heads you win $1,000, tails you lose $110
C)Heads you win $50, tails you lose $25
D)Heads you win $5, tails you lose $0
A)Heads you win $500, tails you lose $100
B)Heads you win $1,000, tails you lose $110
C)Heads you win $50, tails you lose $25
D)Heads you win $5, tails you lose $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In game theory, a player follows its maximum strategy is the option that
A)makes the lowest possible payoff as large as possible
B)gives the highest possible payoff.
C)makes the highest possible payoff as large as possible
D)allow the player to maximize his/her losses.
A)makes the lowest possible payoff as large as possible
B)gives the highest possible payoff.
C)makes the highest possible payoff as large as possible
D)allow the player to maximize his/her losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A tit for tat strategy has the best chance of working if
A)A transaction is a one time event
B)The interaction between participants is frequent and open-ended
C)The interaction is frequent, but has a specific end date
D)Neither side in the interaction trusts the other's commitment to the strategy
A)A transaction is a one time event
B)The interaction between participants is frequent and open-ended
C)The interaction is frequent, but has a specific end date
D)Neither side in the interaction trusts the other's commitment to the strategy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If one company defects the agreement and the other one doesn't, then the defecting company would make profits equal to:
A)$4,998
B)$2,500
C)$2000
D)$0
A)$4,998
B)$2,500
C)$2000
D)$0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In sequential game strategies, each player could avoid the worst case outcomes by
A)Assuming that the other player will always rationally avoid its worst case outcome
B)Pursuing a strategy that leads toward the highest end point gains possible
C)Pursuing a strategy that leads in the direction of the worst case scenario
D)The strategies listed in both a and b will definitely keep one from the worst case scenario
A)Assuming that the other player will always rationally avoid its worst case outcome
B)Pursuing a strategy that leads toward the highest end point gains possible
C)Pursuing a strategy that leads in the direction of the worst case scenario
D)The strategies listed in both a and b will definitely keep one from the worst case scenario

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The model of monopolistic competition differs from the model of perfect competition in which of the following assumptions?
A)Free entry and exit
B)Product homogeneity
C)Large number of firms
D)Perfect information
A)Free entry and exit
B)Product homogeneity
C)Large number of firms
D)Perfect information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The strategy of tit-for-tat is
A)To cooperate for the first interaction, and to defect for each subsequent interaction
B)To cooperate for the first interaction, and to imitate your rival's behavior in each subsequent interaction
C)To defect for the first interaction, and to cooperate for each subsequent interaction
D)To always be the first one to defect
A)To cooperate for the first interaction, and to defect for each subsequent interaction
B)To cooperate for the first interaction, and to imitate your rival's behavior in each subsequent interaction
C)To defect for the first interaction, and to cooperate for each subsequent interaction
D)To always be the first one to defect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Oligopoly is a market structure in which
A)Firms are price takers
B)There exist many firms, each producing a product that is a close, but imperfect, substitute for the products of other firms
C)There are only a few sellers
D)There is only one seller
A)Firms are price takers
B)There exist many firms, each producing a product that is a close, but imperfect, substitute for the products of other firms
C)There are only a few sellers
D)There is only one seller

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The conditions discussed by Axelrod help to explain
A)Only when people are most likely to defect
B)Only when people cooperate
C)When people cooperate and also when they are most likely not to cooperate
D)Why there is never mutual restraint in trench warfare
A)Only when people are most likely to defect
B)Only when people cooperate
C)When people cooperate and also when they are most likely not to cooperate
D)Why there is never mutual restraint in trench warfare

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When marginal cost is constant and zero, the interdependence between Cournot duopolists causes
A)Price to be 1/3 higher and quantity to be 1/3 lower than the corresponding values in the monopoly case
B)Price to be 1/3 lower and quantity to be 1/3 higher than the corresponding values in the monopoly case
C)Prices and quantities to be the same as they would be in the monopoly case
D)Prices and quantities to be the same as they would be in the perfectly competitive case
A)Price to be 1/3 higher and quantity to be 1/3 lower than the corresponding values in the monopoly case
B)Price to be 1/3 lower and quantity to be 1/3 higher than the corresponding values in the monopoly case
C)Prices and quantities to be the same as they would be in the monopoly case
D)Prices and quantities to be the same as they would be in the perfectly competitive case

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The strategy for the Stackelberg Leader is
A)To sell a marginally higher quantity of goods than the rival
B)To sell at a marginally lower price than the rival
C)Collusion
D)To take account of the effect of its own behavior on the rival firm's quantity choice
A)To sell a marginally higher quantity of goods than the rival
B)To sell at a marginally lower price than the rival
C)Collusion
D)To take account of the effect of its own behavior on the rival firm's quantity choice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the above diagram the profit-maximizing price is at
A)02
B)03
C)04
D)05
A)02
B)03
C)04
D)05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The strategy for the shared monopoly is
A)To sell a marginally higher quantity of goods than the rival
B)To sell at a marginally lower price than the rival
C)Collusion
D)To take account of the effect of its own behavior on the rival firm's quantity choice
A)To sell a marginally higher quantity of goods than the rival
B)To sell at a marginally lower price than the rival
C)Collusion
D)To take account of the effect of its own behavior on the rival firm's quantity choice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The demand curve shown below has four points depicting possible total market oligopoly outcomes of quantity and price.For the given demand and price coordinates labeled A-D, pick the matching oligopoly models that lead to these comparative outcomes. 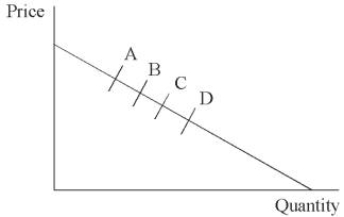
A)A = Bertrand: B = Cournot: C = Stackelberg: D = Shared Monopoly
B)A = Cournot: B = Bertrand: C = Stackelberg: D = Shared Monopoly
C)A = Shared Monopoly: B = Cournot: C = Bertrand: D = Stackelberg
D)A = Shared Monopoly: B = Cournot: C = Stackelberg: D = Bertrand

A)A = Bertrand: B = Cournot: C = Stackelberg: D = Shared Monopoly
B)A = Cournot: B = Bertrand: C = Stackelberg: D = Shared Monopoly
C)A = Shared Monopoly: B = Cournot: C = Bertrand: D = Stackelberg
D)A = Shared Monopoly: B = Cournot: C = Stackelberg: D = Bertrand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the above graph the profit maximization level of output for a monopolistically competitive firm is
A)OA
B)OB
C)OC
D)OD
A)OA
B)OB
C)OC
D)OD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the duopoly models has the lowest overall combined profit level?
A)The Cournot model
B)The Bertrand model
C)The Stackelberg Leader-Follower model
D)The shared monopoly model
A)The Cournot model
B)The Bertrand model
C)The Stackelberg Leader-Follower model
D)The shared monopoly model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the duopoly models has the highest overall combined profit level?
A)The Cournot model
B)The Bertrand model
C)The Stackelberg Leader-Follower model
D)The shared monopoly model
A)The Cournot model
B)The Bertrand model
C)The Stackelberg Leader-Follower model
D)The shared monopoly model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The basic idea of the theory of contestable markets is that when the cost of entry and exit is very low, the threat of entry can be sufficient to produce an allocation similar to the one we see under
A)Monopoly
B)Monopolistic competition
C)Perfect competition
D)Oligopoly
A)Monopoly
B)Monopolistic competition
C)Perfect competition
D)Oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The basic problem of a shared monopoly from the point of view of those involved is that
A)Profits are lower than in the other oligopoly models
B)The shared output is too high for the high price to be maintained
C)Collusive agreements are difficult to sustain
D)Revenue is lower than in the other oligopoly models
A)Profits are lower than in the other oligopoly models
B)The shared output is too high for the high price to be maintained
C)Collusive agreements are difficult to sustain
D)Revenue is lower than in the other oligopoly models

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the graph above if additional firms enter the market we would expect
A)The DD curve to shift right
B)Each individual firm to be worse off
C)The dd curve to become steeper
D)The MC and ATC curves to shift downward
A)The DD curve to shift right
B)Each individual firm to be worse off
C)The dd curve to become steeper
D)The MC and ATC curves to shift downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The oligopoly model in which each firm assumes that rivals will continue to produce at their current output levels is called the:
A)Cournot model
B)Bertrand model
C)Stackelberg model
D)Chamberlin model
A)Cournot model
B)Bertrand model
C)Stackelberg model
D)Chamberlin model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Prices in the Bertrand model are
A)The same as prices under a shared monopoly
B)Slightly higher than prices would be under a shared monopoly
C)The same as prices would be in the perfectly competitive case
D)Slightly higher than prices would be in the perfectly competitive case
A)The same as prices under a shared monopoly
B)Slightly higher than prices would be under a shared monopoly
C)The same as prices would be in the perfectly competitive case
D)Slightly higher than prices would be in the perfectly competitive case

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the graph above at the profit maximizing price and output the firm is making
A)Positive economic profit
B)Negative economic profit
C)Zero economic profit
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given
A)Positive economic profit
B)Negative economic profit
C)Zero economic profit
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The strategy for the Bertrand model is
A)To sell a marginally higher quantity of goods than the rival
B)To sell at a marginally lower price than the rival but not below marginal cost
C)Collusion
D)To take account of the effect of its own behavior on the rival firm's quantity choice
A)To sell a marginally higher quantity of goods than the rival
B)To sell at a marginally lower price than the rival but not below marginal cost
C)Collusion
D)To take account of the effect of its own behavior on the rival firm's quantity choice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the Stackelberg model
A)Each firm takes the quantities produced by its rivals as given
B)Each firm takes the prices charged by its rivals as given
C)One firm plays a leadership role and its rivals merely react to the leader's quantity
D)Prices are higher and quantities are slightly less than we would see if the firms colluded to achieve the monopoly outcome
A)Each firm takes the quantities produced by its rivals as given
B)Each firm takes the prices charged by its rivals as given
C)One firm plays a leadership role and its rivals merely react to the leader's quantity
D)Prices are higher and quantities are slightly less than we would see if the firms colluded to achieve the monopoly outcome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Cournot duopolists face a market demand curve given by P = 90 - Q where Q is total market demand.Each firm can produce output at a constant marginal cost of 30 per unit.The equilibrium price and quantity for the total market will be
A)Q = 30, P = 60
B)Q = 60, P = 30
C)Q = 40, P = 50
D)Q = 45, P = 45
A)Q = 30, P = 60
B)Q = 60, P = 30
C)Q = 40, P = 50
D)Q = 45, P = 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the duopolists in Problem 17 behave according to the Stackelberg Leader-Follower model, the equilibrium price and total quantity for the market will be
A)Q = 30, P = 60
B)Q = 60, P = 30
C)Q = 40, P = 50
D)Q = 45, P = 45
A)Q = 30, P = 60
B)Q = 60, P = 30
C)Q = 40, P = 50
D)Q = 45, P = 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the duopolists in Problem 17 behave as a shared monopoly, the equilibrium price and total quantity of output will be
A)Q = 30, P = 60
B)Q = 60, P = 30
C)Q = 40, P = 50
D)Q = 45, P = 45
A)Q = 30, P = 60
B)Q = 60, P = 30
C)Q = 40, P = 50
D)Q = 45, P = 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the duopolists in problem 17 behave, instead, according to the Bertrand model, the equilibrium price and quantity for the total market will be
A)Q = 30, P = 60
B)Q = 60, P = 30
C)Q = 40, P = 50
D)Q = 45, P = 45
A)Q = 30, P = 60
B)Q = 60, P = 30
C)Q = 40, P = 50
D)Q = 45, P = 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In an example of restaurant location on an island, if the number of people on the island doubled, the number of restaurants
A)Would stay the same
B)Would double
C)Would halve
D)Would increase by a factor of
A)Would stay the same
B)Would double
C)Would halve
D)Would increase by a factor of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the distance around the island is 50 miles and there are two restaurants equally spaced on the island and each of 100 people are equally spaced around the island and eat a meal a day at a restaurant, what will be the average distance traveled to and from restaurants in a day's time.
A)25 miles
B)50 miles
C)12.5 miles
D)125 miles
A)25 miles
B)50 miles
C)12.5 miles
D)125 miles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What will industry output be at equilibrium in this model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the Bertrand model is assumed to be the appropriate one for analysis, what will the price of the product and the quantity sold be in this duopoly market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In game theory, a dominant strategy is one
A)In which the firm gains the greatest competitive advantage
B)In which the same strategy is chosen by one firm regardless of the anticipated action
C)of the other firm
D)That produces the greatest comparative advantage
E)That both firms agree on independently
A)In which the firm gains the greatest competitive advantage
B)In which the same strategy is chosen by one firm regardless of the anticipated action
C)of the other firm
D)That produces the greatest comparative advantage
E)That both firms agree on independently

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose that two firms are producers of spring water, which can be obtained at zero cost.The market demand curve for their combined output is p = 100 - Q where p is the price and Q is the amount of spring water sold by both together.If the two producers act in accord with the Cournot model, their combined output will be
A)33.33
B)66.66
C)50
D)0
A)33.33
B)66.66
C)50
D)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose there are two firms in a market: firm A and firm
A)Greater than firm B
B)Further, assume that they produce a homogenous product at a constant marginal cost of $10.In the Bertrand model solution, firm A will charge a price:
B)Smaller than firm B
C)Equal to $10
D)Greater than $10
A)Greater than firm B
B)Further, assume that they produce a homogenous product at a constant marginal cost of $10.In the Bertrand model solution, firm A will charge a price:
B)Smaller than firm B
C)Equal to $10
D)Greater than $10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
As the firm's fixed costs increase
A)The number of firms will rise in the long run
B)The number of firms will fall in the long run
C)The number of firms will stay the same in the long run
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given
A)The number of firms will rise in the long run
B)The number of firms will fall in the long run
C)The number of firms will stay the same in the long run
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the graph above the dd curve is based on the assumption
A)That firms all follow each other when any one of them changes price
B)That market demand is more elastic than the demand for any one firm
C)That firms can gain market share by lowering their price below the price of the competition
D)That firms will follow any price increases of their competitors
A)That firms all follow each other when any one of them changes price
B)That market demand is more elastic than the demand for any one firm
C)That firms can gain market share by lowering their price below the price of the competition
D)That firms will follow any price increases of their competitors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm acting according to the Chamberlin model
A)Will operate at the minimum point of the average cost curve
B)Will not operate at the minimum point of the average cost curve
C)Will earn positive economic profits
D)Will operate at the minimum point of the marginal cost curve
A)Will operate at the minimum point of the average cost curve
B)Will not operate at the minimum point of the average cost curve
C)Will earn positive economic profits
D)Will operate at the minimum point of the marginal cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In sequential games
A)Players move at the same time
B)The order of moves matter
C)The order of the moves is irrelevant
D)There is always two Nash equilibriums
A)Players move at the same time
B)The order of moves matter
C)The order of the moves is irrelevant
D)There is always two Nash equilibriums

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
As the number of customers increase
A)The number of firms will rise in the long run
B)The number of firms will fall in the long run
C)The number of firms will stay the same in the long run
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given
A)The number of firms will rise in the long run
B)The number of firms will fall in the long run
C)The number of firms will stay the same in the long run
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If a monopolistically competitive firm is making positive economic profits we would expect
A)Entry of other firms
B)The firm to continue making the positive economic profits
C)The firm to expand market share and the industry to move toward an oligopoly structure
D)The firm to hire more labor
A)Entry of other firms
B)The firm to continue making the positive economic profits
C)The firm to expand market share and the industry to move toward an oligopoly structure
D)The firm to hire more labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Given the payoff table above, in Nash Equilibrium Player's 2 payoff is:
A)3
B)-3
C)0
D)There is no Nash equilibrium in this game
A)3
B)-3
C)0
D)There is no Nash equilibrium in this game

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is an application of the Hoteling model of monopolistic competition.
A)Politicians tend toward positions more extreme than what they actually believe
B)Stores of similar types tend to cluster
C)Efficiency requires that stores are spread equidistant from each other in a given space
D)As space increases between firms, each firm produces less
A)Politicians tend toward positions more extreme than what they actually believe
B)Stores of similar types tend to cluster
C)Efficiency requires that stores are spread equidistant from each other in a given space
D)As space increases between firms, each firm produces less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The variety that monopolistic competition provides is paid primarily by
A)The producer whose ability to pass on costs is limited by his demand curve
B)All consumers whether they desire variety or not
C)Those customers who desire the variety
D)No one because variety costs no more to produce than uniform products cost to produce
A)The producer whose ability to pass on costs is limited by his demand curve
B)All consumers whether they desire variety or not
C)Those customers who desire the variety
D)No one because variety costs no more to produce than uniform products cost to produce

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Derive the reaction curve for a Cournot duopolist where the industry demand curve is as stated above and the MC of production is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
As the firm's variable costs rise,
A)The number of firms will rise in the long run
B)The number of firms will fall in the long run
C)The number of firms will stay the same in the long run
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given
A)The number of firms will rise in the long run
B)The number of firms will fall in the long run
C)The number of firms will stay the same in the long run
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the graph above one would expect the demand curve facing a monopolistically competitive firm to be
A)More elastic than a monopoly in the same industry
B)Less elastic than a monopoly in the same industry
C)More elastic than a perfectly competitive firm in the same industry
D)As elastic as a monopoly in the same industry
A)More elastic than a monopoly in the same industry
B)Less elastic than a monopoly in the same industry
C)More elastic than a perfectly competitive firm in the same industry
D)As elastic as a monopoly in the same industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
As transportation costs on the island rise,
A)The number of firms will rise in the long run
B)The number of firms will fall in the long run
C)The number of firms will stay the same in the long run
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given
A)The number of firms will rise in the long run
B)The number of firms will fall in the long run
C)The number of firms will stay the same in the long run
D)It is impossible to tell from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Compare the models analyzed here with reference to the consumer and economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If the town was one restaurant below its optimal number when you are brought in as a consultant to help decide some planning issues, and the city fathers want to know how much the town could save overall if it built another restaurant, what would you tell them?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What is the rate at which transportation costs are falling when the optimal number of restaurants is reached?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the town projected a total population of 180 by the end of the decade, how many restaurants would the city planners project as optimal for the end of the decade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If the lower right cell has 85's for each company instead of 70's, would either have a dominant strategy then?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Sketch graph two total cost curves as functions of the number of restaurants.The first one is the total cost of meals per day and the second is the total cost of transportation per day.Plot five points for each curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Does either airline have a dominant strategy? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If firm 1 is a Stackelberg leader and firm 2 is a follower, what will each firm produce?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Beginning from the initial population of 81, how high would the cost per mile have to go before the optimal number of restaurants would be one more than it was with transportation costs at $10 per mile?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
On your graph, vertically sum the two total cost curves and show what the optimal number of restaurants should be.Use the five points calculated to sum the total cost curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Is there a Nash equilibrium?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What price will the two Stackelberg firms charge?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Calculate the optimal number of restaurants without using the graph.Show your work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Gasoline comes in octane levels from 87 to 93.Supposedly, higher octane leads to less engine repair, but it costs more to produce.Sketch a total cost function for each of these two factors and a vertically summed total for both costs.On your sketch graph, show the appropriate octane level that will be produced.(Do not use numerical values on the graph except for the octane levels.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What will be the price and quantity of this duopoly market if the duopolists act as shared monopolists?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



