Deck 10: Perfect Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Perfect Competition
1
Joe is self-employed in a store that has a rental value of $500 a month which he pays, but he can vacate the building without giving notice. His other expenses are $100 a month for maintenance. He makes $25,000 a year on net sales (total revenue minus the wholesale cost of the product). If he quit his job and worked the same number of hours elsewhere at a job he liked equally well, he estimates that he could make $20,000 a year. No one else can be hired to work in the store. Suppose that Joe had a long term lease which requires him to pay the rent even if he doesn't operate the store. What should Joe do?
A)Quit immediately.
B)Keep the job permanently.
C)Keep the job until the lease expires.
D)It is impossible to say with the information given in the problem.
A)Quit immediately.
B)Keep the job permanently.
C)Keep the job until the lease expires.
D)It is impossible to say with the information given in the problem.
C
2
In the graph below at a price of P*, the profit maximizing level of output is 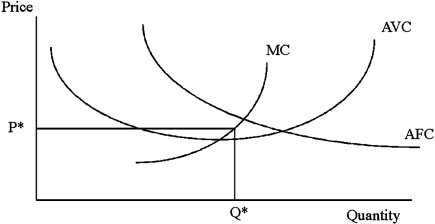
A)Q*.
B)above Q*.
C)below Q* but above zero.
D)zero.

A)Q*.
B)above Q*.
C)below Q* but above zero.
D)zero.
Q*.
3
Which statement is true of the graph shown? 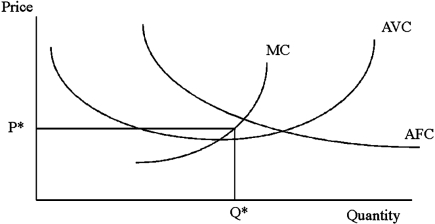
A)The marginal cost curve should not cross the AFC while it is falling.
B)If an ATC curve was drawn in the graph it would intersect the MC curve but not any other curve.
C)The shut down point of the firm would be at an output more than Q*.
D)The marginal cost curve crosses the AFC curve at the lowest point of the AFC curve.

A)The marginal cost curve should not cross the AFC while it is falling.
B)If an ATC curve was drawn in the graph it would intersect the MC curve but not any other curve.
C)The shut down point of the firm would be at an output more than Q*.
D)The marginal cost curve crosses the AFC curve at the lowest point of the AFC curve.
If an ATC curve was drawn in the graph it would intersect the MC curve but not any other curve.
4
In a decreasing cost industry, as output grows over time,
A)prices will fall.
B)prices will rise.
C)prices will stay the same.
D)prices are zero.
A)prices will fall.
B)prices will rise.
C)prices will stay the same.
D)prices are zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Say a competitive firm is producing at point where ATC = $10, AVC = $2. If the firm charges $5 for its output, then in the short-run this firm should
A)shutdown production.
B)exit the industry.
C)continue to operate.
D)try to reduce its fixed costs.
A)shutdown production.
B)exit the industry.
C)continue to operate.
D)try to reduce its fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Joe is self-employed in a store that has a rental value of $500 a month which he pays, but he can vacate the building without giving notice. His other expenses are $100 a month for maintenance. He makes $25,000 a year on net sales (total revenue minus the wholesale cost of the product). If he quit his job and worked the same number of hours elsewhere at a job he liked equally well, he estimates that he could make $20,000 a year. No one else can be hired to work in the store. Joe should
A)quit his job.
B)keep the job.
C)work part-time.
D)It is impossible to say with the information given in the problem.
A)quit his job.
B)keep the job.
C)work part-time.
D)It is impossible to say with the information given in the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
At the output where MC = ATC = P, the firm
A)should shutdown.
B)has no economic profit.
C)is profit maximizing.
D)should raise output.
A)should shutdown.
B)has no economic profit.
C)is profit maximizing.
D)should raise output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm is
A)infinitely elastic.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)downward sloping.
D)perfectly elastic.
A)infinitely elastic.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)downward sloping.
D)perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The profit maximizing output level for a perfectly competitive firm is always where
A)P = MC.
B)P = AVC.
C)MC = ATC.
D)MC = AVC.
A)P = MC.
B)P = AVC.
C)MC = ATC.
D)MC = AVC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A standardized product is a product
A)that has many perfect substitutes.
B)that is unique to one producer.
C)which is produced according to government regulations.
D)where the demand function is downward sloping for both the firm and the industry.
A)that has many perfect substitutes.
B)that is unique to one producer.
C)which is produced according to government regulations.
D)where the demand function is downward sloping for both the firm and the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The output where MC = AVC is called the
A)shutdown point.
B)break-even point.
C)profit maximizing point.
D)revenue maximizing point.
A)shutdown point.
B)break-even point.
C)profit maximizing point.
D)revenue maximizing point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In general, economists assume that firms
A)maximize accounting profit.
B)maximize economic profit.
C)maximize sales.
D)maximize revenue.
A)maximize accounting profit.
B)maximize economic profit.
C)maximize sales.
D)maximize revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the graph below at P*, the firm is making __________ economic profits. 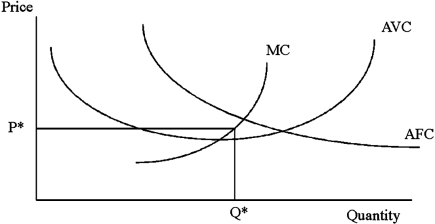
A)positive
B)negative
C)zero
D)an indeterminate level of

A)positive
B)negative
C)zero
D)an indeterminate level of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the demand curve falls below the ATC curve but lies above AVC, then the firm should
A)should shut down.
B)operate in the short run but not the long run.
C)set price = marginal cost.
D)operate in the short run and the long run.
A)should shut down.
B)operate in the short run but not the long run.
C)set price = marginal cost.
D)operate in the short run and the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the graph below if the price persists at P*, the profit maximizing firm will 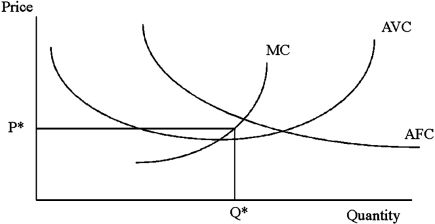
A)shut down immediately.
B)shut down in the long run.
C)operate indefinitely.
D)have a strategy that cannot be predicted without an ATC curve.

A)shut down immediately.
B)shut down in the long run.
C)operate indefinitely.
D)have a strategy that cannot be predicted without an ATC curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If firms are price takers this implies that
A)in the short-run economic profits will be zero.
B)the demand curve facing the firm is perfectly elastic.
C)the total revenue curve is horizontal.
D)the marginal revenue curve is upward sloping.
A)in the short-run economic profits will be zero.
B)the demand curve facing the firm is perfectly elastic.
C)the total revenue curve is horizontal.
D)the marginal revenue curve is upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is not a condition for perfect competition?
A)Firms take prices as given.
B)Firms sell a standardized product.
C)Firms are protected by barriers to entry.
D)Firms have perfect information.
A)Firms take prices as given.
B)Firms sell a standardized product.
C)Firms are protected by barriers to entry.
D)Firms have perfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a firm's demand curve falls below its AVC curve, then the firm should
A)shut down now.
B)operate in the short run but not the long run.
C)set price = marginal cost.
D)shutdown in the long-run.
A)shut down now.
B)operate in the short run but not the long run.
C)set price = marginal cost.
D)shutdown in the long-run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Joe is self-employed in a store that has a rental value of $500 a month which he pays, but he can vacate the building without giving notice. His other expenses are $100 a month for maintenance. He makes $25,000 a year on net sales (total revenue minus the wholesale cost of the product). If he quit his job and worked the same number of hours elsewhere at a job he liked equally well, he estimates that he could make $20,000 a year. No one else can be hired to work in the store. Suppose that the store owner gave Joe the store. Now what should he do?
A)Quit his job.
B)Keep the job.
C)Work part-time.
D)It is impossible to say with the information given in the problem.
A)Quit his job.
B)Keep the job.
C)Work part-time.
D)It is impossible to say with the information given in the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the perfectly competitive firm maximizes profits the price of its product always equals
A)average revenue.
B)marginal revenue.
C)marginal costs.
D)All of the choices are correct
A)average revenue.
B)marginal revenue.
C)marginal costs.
D)All of the choices are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a competitive industry, the industry's short-run supply curve is
A)the horizontal sum of the marginal cost curves.
B)the vertical sum of the marginal cost curves.
C)determined by the average total cost curve.
D)determined by the average variable cost curve.
A)the horizontal sum of the marginal cost curves.
B)the vertical sum of the marginal cost curves.
C)determined by the average total cost curve.
D)determined by the average variable cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the long run for a competitive firm,
A)the firm is at the bottom of its short run average cost curve.
B)the firm is at the top of its long run average cost curve.
C)the marginal cost is greater price.
D)the firm is making economic profits.
A)the firm is at the bottom of its short run average cost curve.
B)the firm is at the top of its long run average cost curve.
C)the marginal cost is greater price.
D)the firm is making economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
At point A, 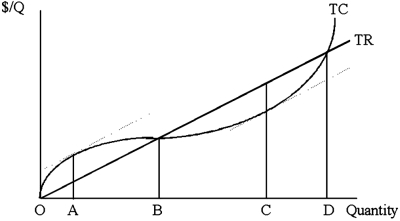
A)MC = MR.
B)The firm is making positive economic profit.
C)The firm would do worst by shutting down.
D)MC > MR.

A)MC = MR.
B)The firm is making positive economic profit.
C)The firm would do worst by shutting down.
D)MC > MR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Other things remaining the same, in the long-run as compared to the short-run
A)supply elasticity will increase.
B)supply elasticity will decrease.
C)supply elasticity will remain the same.
D)one cannot tell.
A)supply elasticity will increase.
B)supply elasticity will decrease.
C)supply elasticity will remain the same.
D)one cannot tell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Ceteris paribus, in the long run, a tax placed on a perfectly competitive industry will
A)increase the price of the good by an amount equal to the tax.
B)increase the price of the good by an amount less than the tax.
C)be borne entirely by the firm.
D)be entirely borne by the consumer.
A)increase the price of the good by an amount equal to the tax.
B)increase the price of the good by an amount less than the tax.
C)be borne entirely by the firm.
D)be entirely borne by the consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the long run, a tax placed on a perfectly competitive industry should have what effect on the entire market?
A)Increase the total amount of the good sold.
B)Decrease the total amount of the good sold.
C)Not affect the total amount of the good sold.
D)One cannot tell.
A)Increase the total amount of the good sold.
B)Decrease the total amount of the good sold.
C)Not affect the total amount of the good sold.
D)One cannot tell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the long run, 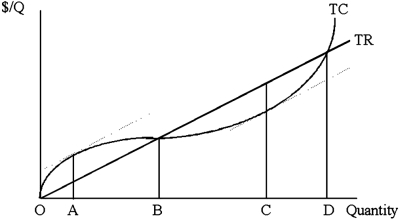
A) the firm will operate at point B.
B) the firm will operate at point C.
C) the firm will operate at point D.
D) the total revenue curve will change its slope.

A) the firm will operate at point B.
B) the firm will operate at point C.
C) the firm will operate at point D.
D) the total revenue curve will change its slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Producer surplus is given by the area
A)above the supply curve but below the price.
B)below the supply curve.
C)below the demand curve but above the price.
D)below the demand curve.
A)above the supply curve but below the price.
B)below the supply curve.
C)below the demand curve but above the price.
D)below the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If free entry and exit were not possible,
A)in the long run firms would lose money.
B)in the long run firms would make money.
C)in the long run firms would break even.
D)It is impossible to tell what would happen without more cost and revenue information.
A)in the long run firms would lose money.
B)in the long run firms would make money.
C)in the long run firms would break even.
D)It is impossible to tell what would happen without more cost and revenue information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the short run, a tax placed on a perfectly competitive industry should
A)increase the total amount of the good sold.
B)decrease the total amount of the good sold.
C)not affect the total amount of the good sold.
D)always increase the price.
A)increase the total amount of the good sold.
B)decrease the total amount of the good sold.
C)not affect the total amount of the good sold.
D)always increase the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the long run, a tax placed on a perfectly competitive industry should
A)increase the number of firms.
B)decrease the number of firms.
C)not affect the number of firms.
D)One cannot tell
A)increase the number of firms.
B)decrease the number of firms.
C)not affect the number of firms.
D)One cannot tell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the long run, the price in this market will be 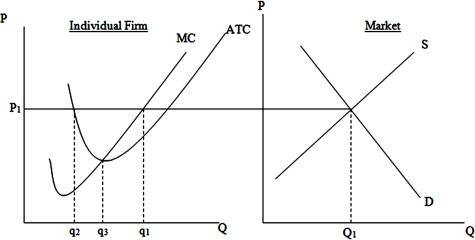
A)P1.
B)higher than P1.
C)lower than P1.
D)We need more information in order to answer

A)P1.
B)higher than P1.
C)lower than P1.
D)We need more information in order to answer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose that the supply curve is given by P = Q. What is the elasticity of supply?
A)10
B)1/10
C)1
D)Cannot be determined from these information
A)10
B)1/10
C)1
D)Cannot be determined from these information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
At point D, the firm is 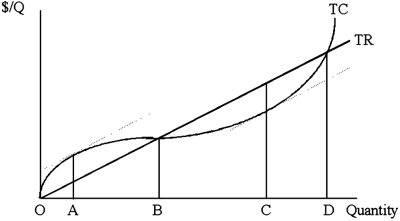
A)maximizing its profit.
B)losing money.
C)breaking even.
D)making money.

A)maximizing its profit.
B)losing money.
C)breaking even.
D)making money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the graph shown below, if the market demand were to shift right, which of the following would occur for the firm? 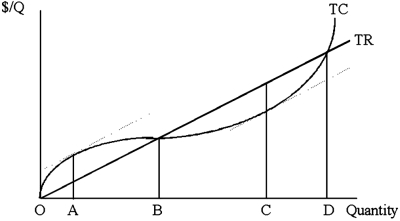
A)The total cost curve would shift downward.
B)The total revenue function would rotate upward.
C)The total revenue function would rotate downward.
D)The firm would produce less output.

A)The total cost curve would shift downward.
B)The total revenue function would rotate upward.
C)The total revenue function would rotate downward.
D)The firm would produce less output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A pecuniary diseconomy occurs when
A)supply exceeds demand.
B)an expansion of industry output increases the price of an input.
C)higher output levels results in lower unit costs.
D)higher output levels results in the same unit costs.
A)supply exceeds demand.
B)an expansion of industry output increases the price of an input.
C)higher output levels results in lower unit costs.
D)higher output levels results in the same unit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the long run, the typical firm in this market will produce a quantity equal to 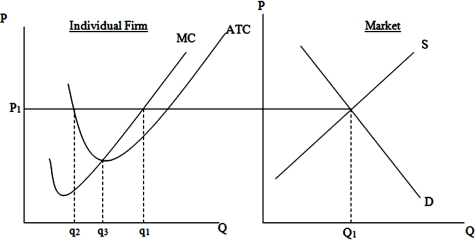
A)q1.
B)q2.
C)q3.
D)Q1.

A)q1.
B)q2.
C)q3.
D)Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the diagram below, profit is maximized at point 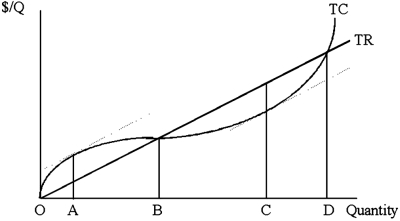
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The elasticity of supply is given by
A)
B)
C)
D)All of these are correct.
A)
B)
C)
D)All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When the price is P1, in order to maximize profits this firm must produce a quantity equal to 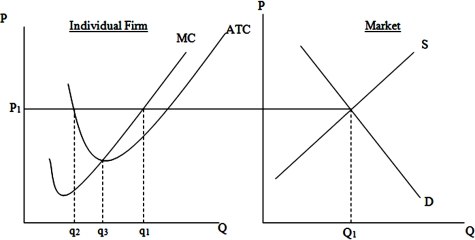
A)q1.
B)q2.
C)q3.
D)Q1.

A)q1.
B)q2.
C)q3.
D)Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the long run, any perfectly competitive firm that produces will choose a quantity such that
A)short run average cost is minimized.
B)long run total cost is minimized.
C)long run marginal cost is less than short run marginal cost.
D)price is greater marginal cost.
A)short run average cost is minimized.
B)long run total cost is minimized.
C)long run marginal cost is less than short run marginal cost.
D)price is greater marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose an industry has 100 firms, each with supply curve P = 50 + 10Q. Furthermore, suppose the market demand curve is given by P = 200 - 0.9Q. How many units of output will be produced by a firm operating in this market with a MC = 130Q?
A)2
B)5
C)0.70
D)It is impossible to answer with the information given
A)2
B)5
C)0.70
D)It is impossible to answer with the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a firm is producing where its LMC = price and the LMC is equal to LAC, then it would do better in the long run by
A)increasing output with its existing plant until LMC equals price.
B)increasing plant size until LMC and SAC are identical and equal to price.
C)decreasing plant size until LAC, SAC and price are equal.
D)changing nothing because it is already at the long run profit maximizing point.
A)increasing output with its existing plant until LMC equals price.
B)increasing plant size until LMC and SAC are identical and equal to price.
C)decreasing plant size until LAC, SAC and price are equal.
D)changing nothing because it is already at the long run profit maximizing point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
At market equilibrium, the total benefit that results from all the transactions is
A)the consumer surplus minus the producer surplus.
B)the producer surplus minus the consumer surplus.
C)the sum of the producer surplus and the consumer surplus.
D)the entire area under the demand curve up to the quantity exchanged.
A)the consumer surplus minus the producer surplus.
B)the producer surplus minus the consumer surplus.
C)the sum of the producer surplus and the consumer surplus.
D)the entire area under the demand curve up to the quantity exchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Assume a perfectly competitive economy would use an assortment of nails that weighs a total of 100 tons. However, the economy is controlled by the government and it sets a ton limit of 100 tons. When production is complete there is only one nail that weighs 100 tons. Which of the following describes what was wrong when government did the planning?
A)Producers did not follow their personal interest in planning production.
B)The wishes of consumers were not represented in the producer's actions.
C)The government miscalculated the correct tonnage that the economy needed.
D)All of these are true.
A)Producers did not follow their personal interest in planning production.
B)The wishes of consumers were not represented in the producer's actions.
C)The government miscalculated the correct tonnage that the economy needed.
D)All of these are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The expansion of the car manufacturing industry causes an improvement in the assembly line system, thus reducing costs to each firm in that industry. This is an example of
A)constant returns to scale.
B)a decreasing-cost industry.
C)a decreasing returns to scale.
D)an increasing-cost industry.
A)constant returns to scale.
B)a decreasing-cost industry.
C)a decreasing returns to scale.
D)an increasing-cost industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Suppose an industry has 100 firms, each with supply curve P = 50 + 10Q. Furthermore, suppose the market demand curve is given by P = 200 - 0.9Q. What is the industry supply curve?
A)P = 500 + Q
B)P = 50 + 0.1Q
C)P = -500 + 10P
D)P = 50 + 10 Q
A)P = 500 + Q
B)P = 50 + 0.1Q
C)P = -500 + 10P
D)P = 50 + 10 Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Some people advocate price ceilings in certain markets because they seek to
A)expand the total of consumer and producer surplus which the market generates.
B)redistribute welfare from the producer to the consumer even if overall welfare is sacrificed.
C)redistribute welfare from the consumer to the producer even if welfare is sacrificed.
D)enhance both efficiency and distribution goals with the price ceiling.
A)expand the total of consumer and producer surplus which the market generates.
B)redistribute welfare from the producer to the consumer even if overall welfare is sacrificed.
C)redistribute welfare from the consumer to the producer even if welfare is sacrificed.
D)enhance both efficiency and distribution goals with the price ceiling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In a competitive industry in the long-run, it is likely that
A)firms with the advantage of location or an especially skilled work crew will be the lone survivors in equilibrium.
B)all firms giving their best effort will have the same LAC regardless of location or the unique skills of some workers.
C)the firms with the poorest location will be the lone survivors in equilibrium because their location cost will be lowest.
D)only one large efficient firm can survive.
A)firms with the advantage of location or an especially skilled work crew will be the lone survivors in equilibrium.
B)all firms giving their best effort will have the same LAC regardless of location or the unique skills of some workers.
C)the firms with the poorest location will be the lone survivors in equilibrium because their location cost will be lowest.
D)only one large efficient firm can survive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A competitive industry consists of 100 firms. The short-run marginal cost curve for each firm is given by MC = 200 + .3Q. The demand curve faced by the industry is given as P = 400 - .1Q. How much profit is each firm making if fixed costs are $375 per firm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A firm is currently selling its product at $20 each. It estimates that its average total cost of production is $100 and its average fixed cost is $40. In the short run the firm should
A)shutdown.
B)continue production at a point where P = MC.
C)hire more employees.
D)buy more capital.
A)shutdown.
B)continue production at a point where P = MC.
C)hire more employees.
D)buy more capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
You have a small business that makes $50,000 accounting and economic profit for you. As a disabled person, you must work at home and you did not have other opportunities until your neighbor offers you a job you like equally well for $50,000 and you can do it at home. This means
A)your economic profit has gone down and your accounting profit has gone up.
B)both your accounting and economic profit have gone down.
C)both your accounting and economic profit have gone up.
D)your economic profit has gone down and your accounting profit has stayed the same.
A)your economic profit has gone down and your accounting profit has gone up.
B)both your accounting and economic profit have gone down.
C)both your accounting and economic profit have gone up.
D)your economic profit has gone down and your accounting profit has stayed the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Competitive markets result in allocative efficiency because they
A)exhaust all possibilities for mutually beneficial trade.
B)exhaust all possible benefits for the consumer.
C)generate all possible benefits for the consumers.
D)distribute resources in the most equitable way.
A)exhaust all possibilities for mutually beneficial trade.
B)exhaust all possible benefits for the consumer.
C)generate all possible benefits for the consumers.
D)distribute resources in the most equitable way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A competitive industry consists of 100 firms. The short-run marginal cost curve for each firm is given by MC = 200 + .3Q. The demand curve faced by the industry is given as P = 400 - .1Q. What is the equilibrium price and quantity produced by the industry as a whole?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A competitive industry consists of 100 firms. The short-run marginal cost curve for each firm is given by MC = 200 + .3Q. The demand curve faced by the industry is given as P = 400 - .1Q. What is the price charged by each firm and what quantity will each firm produce?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which statement is true of the market supply curve?
A)It is the vertical summation of all the individual supply curves.
B)It is the horizontal summation of the upward sloping portion of the AVC function of all firms in the industry.
C)One must know the marginal cost information of firms in order to construct a supply function.
D)In perfect competition the slope of the curve is horizontal.
A)It is the vertical summation of all the individual supply curves.
B)It is the horizontal summation of the upward sloping portion of the AVC function of all firms in the industry.
C)One must know the marginal cost information of firms in order to construct a supply function.
D)In perfect competition the slope of the curve is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Agriculture industry is often used as an example of a competitive market model. However, of the four conditions required for perfect competition, one is clearly not present in farming. Which one is the least applicable and why does it not fit the model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
I get $200 revenue from the sale of my product each day. I rent the factory that I use for $90 a day. The raw materials of the operation cost $115 a day. I do all the work myself. Both jobs are equally attractive as far as the work is concerned. Recently, a competitor offered me $30 a day to work for him. My accounting profit is ____, and my economic profit is _____.
A)-5; -35
B)-35; -35
C)25; -5
D)110; -30
A)-5; -35
B)-35; -35
C)25; -5
D)110; -30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A competitive industry consists of 100 firms. The short-run marginal cost curve for each firm is given by MC = 200 + .3Q. The demand curve faced by the industry is given as P = 400 - .1Q. What is the producer and consumer surplus in the entire market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which is not true of a perfectly competitive market?
A)The typical industry demand curve is downward sloping.
B)There is no incentive to innovate since economic profit is zero in the long-run.
C)If the long-run average total cost curve is horizontal in the relevant range of production, perfectly competitive firms can be various sizes in long-run equilibrium.
D)At long-run equilibrium, economic profit is less than accounting profit.
A)The typical industry demand curve is downward sloping.
B)There is no incentive to innovate since economic profit is zero in the long-run.
C)If the long-run average total cost curve is horizontal in the relevant range of production, perfectly competitive firms can be various sizes in long-run equilibrium.
D)At long-run equilibrium, economic profit is less than accounting profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Sketch a perfectly competitive firm operating in short-run equilibrium but making economic losses. Put in all the functions necessary to show that the firm should stay in business in the short-run despite the losses. Shade in the area of loss shown by the drawing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How can a firm stay in business if it makes no economic profit in the long run?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A competitive industry consists of 100 firms. The short-run marginal cost curve for each firm is given by MC = 200 + .3Q. The demand curve faced by the industry is given as P = 400 - .1Q. What is the producer surplus for each firm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Put yourself in the place of a blacksmith during the early years of the 20th century. Assume you and all the other blacksmiths in the town were doing as well as any alternative options that were available. Then cars began to arrive and fewer horses needed horseshoes. Describe, using terms from this chapter, the sequence of events that ultimately led to you closing your shop and hunting another job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Over the last two decades the combination of the internet, high definition TV, and the surround sound has revolutionized watching a movie at home. At the same time, advances in technology in the movie theater have raised the standard that the home entertainment alternative must achieve. Think about the effects of these technological changes on movie watching and identify another market for related goods or service where one will expand and the other will contract. Describe in detail the sequence of events as the two related items you've identified respond to the new technologies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The price of the typical cell phone has been going down in the past 10 years. What could explain this consistent drop in the price of these phones? Use the model for the long-run competitive firm to illustrate your answer (hint: you need two diagrams here: one showing the LAC for the typical firm, and another showing the long-run supply curve for the industry).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



