Deck 1: What Is Environmental Economics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/26
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: What Is Environmental Economics
1
Anthropogenic sources of carbon dioxide include volcanic activity,decaying plant matter and photosynthesis.
False
2
People make the decision to pollute or not based on the incentives that arise from the set of economic and social institutions under which they find themselves.
True
3
When considering strategies to mitigate the impact of climate change,the concept that society should consider the trade-off between the cost of preventive measures taken today versus the benefits arising from reduced future risk is known as ________.
A)adaption
B)the precautionary principle
C)benefit-cost analysis
D)climate modeling
A)adaption
B)the precautionary principle
C)benefit-cost analysis
D)climate modeling
B
4
A small coastal community with the power to control access to its scallop fishery is an example of ________.
A)common property rights
B)private property rights
C)an open access resource
D)a positive externality
A)common property rights
B)private property rights
C)an open access resource
D)a positive externality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A tax on carbon emissions,standards to improve the energy efficiency of vehicles and appliances and policies that promote solar and wind energy are all examples of ________.
A)the precautionary principle
B)adaption
C)carbon trading
D)greenhouse gas mitigation policies
A)the precautionary principle
B)adaption
C)carbon trading
D)greenhouse gas mitigation policies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Coal-fired plants are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions in the electricity sector worldwide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The ________ level of pollution can be negotiated privately based on property rights when only a few parties are involved and the source,amount and type of pollution is clearly identifiable.
A)cost-effective
B)zero-emissions
C)fair
D)socially efficient
A)cost-effective
B)zero-emissions
C)fair
D)socially efficient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A common pasture on which anyone is allowed to freely graze sheep or cattle is an example of ________.
A)private property rights
B)an open access resource
C)common property rights
D)community property rights
A)private property rights
B)an open access resource
C)common property rights
D)community property rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Only profit-motivated corporations are responsible for pollution.
Pollution is also caused by individuals,governments and states that do not necessarily operate based on the principal of profit maximization.
Pollution is also caused by individuals,governments and states that do not necessarily operate based on the principal of profit maximization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An economy that has the ability to allow the level of people's well-being to rise or at least remain constant over time is ________.
A)sustainable
B)equitable
C)self-perpetuating
D)efficient
A)sustainable
B)equitable
C)self-perpetuating
D)efficient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When you enjoy the view of your neighbour's prize-winning garden,this is an example of ________.
A)common property rights
B)a positive externality
C)a negative externality
D)a public good
A)common property rights
B)a positive externality
C)a negative externality
D)a public good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Environmental resources generally have well defined property rights.
A lack of property rights underlies many environmental problems.
A lack of property rights underlies many environmental problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When we drive our cars,we get the ________ of transportation services,while others experience the detrimental effects such as pollution and congestion which environmental economists refer to as a(n)________.
A)positive externality;negative externality
B)direct benefit;opportunity cost
C)direct benefit;negative externality
D)positive externality;opportunity cost
A)positive externality;negative externality
B)direct benefit;opportunity cost
C)direct benefit;negative externality
D)positive externality;opportunity cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Economic efficiency is the only criterion used by environmental economists to evaluate environmental policies.
In addition to economic efficiency,equity or fairness criteria are also used to assist environmental economists when choosing among policy alternatives.
In addition to economic efficiency,equity or fairness criteria are also used to assist environmental economists when choosing among policy alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the following figure,the mix of carbon-intensive goods and environmental quality given by ________ provides society with the highest possible level of well-being. 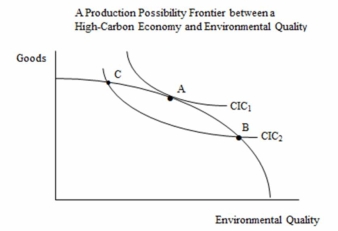
A)bundle A
B)bundle B
C)bundle C
D)none of the choices are correct

A)bundle A
B)bundle B
C)bundle C
D)none of the choices are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The number of kilometres a household drives its vehicles each year is determined by its ________ of driving.
A)opportunity cost
B)private cost
C)social cost
D)external cost
A)opportunity cost
B)private cost
C)social cost
D)external cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Any economic system will produce destructive environmental impacts if the ________ within the system are not structured to avoid them.
A)ethics
B)prices
C)property rights
D)incentives
A)ethics
B)prices
C)property rights
D)incentives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The largest source of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions globally comes from ________.
A)electricity generation and heat
B)transportation
C)agriculture
D)coal mining
A)electricity generation and heat
B)transportation
C)agriculture
D)coal mining

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A(n)________ in the economic world is something that leads people to channel their production and consumption efforts in a specific direction.
A)moral obligation
B)economic incentive
C)property right
D)ethical motive
A)moral obligation
B)economic incentive
C)property right
D)ethical motive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Forests,wetlands and oceans are referred to as ________ because of their ability to absorb CO2.
A)carbon sources
B)carbon stores
C)carbon cycles
D)carbon sinks
A)carbon sources
B)carbon stores
C)carbon cycles
D)carbon sinks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The production possibility frontier showing the trade-offs between production of high-carbon goods and environmental quality for a certain region never changes.
The PPF for a region can shift inward if the environment degrades over time or it can be shifted outward due to technological advances.
The PPF for a region can shift inward if the environment degrades over time or it can be shifted outward due to technological advances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Assume the natural environment including air,water and land can be used to produce either good A,B or C (but not all).If the value of use is $50 for good A,$60 for good B and $40 for good C,which good should be produced if the decision is based on economic efficiency?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Assume the natural environment including air,water and land can be used to produce either good X,Y or Z (but not all).If the value of use is $700 for good X,$600 for good Y and $400 for good Z,which good should be produced if the decision is based on economic efficiency?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Define the three different types of equity employed in environmental economics to help evaluate economic outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Climate change models have predicted an increase in the earth's temperature,greater climate variability and more extreme weather events in the 21st century if greenhouse gas emissions from human activity continue to be emitted at their current pace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
List three examples of policies that could be implemented to reduce emissions from household vehicle use and very briefly explain how each would result in lower emissions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 26 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



