Deck 8: Benefit-Cost Analysis: Costs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Benefit-Cost Analysis: Costs
1
Suppose the government imposes a tax of $8 per unit of Good B.What is the incidence of this tax on consumers and producers?
In order to answer this question,we need to determine the changes in consumer and producer surplus that result from the imposition of the tax.Without the tax,the competitive equilibrium output can be found by equating demand and supply:
180 - 2Q = 40 + 2Q
Q = 140/4 = 35
Producers and consumers both pay the same price P = $110.The consumer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 70 and width 35 which is $1,225.The producer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 70 and width 35 which is equal to $1,225.With the tax,the consumer price will equal the producer price plus $8.We find the tax equilibrium output by setting PC = PP + 8:
180 - 2Q = 40 + 2Q + 8
Q = 132/4 = 33
Now consumers pay PC = $114 and producers pay PP = $106 (notice the difference between the two price levels is equal to the per unit tax).The consumer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 66 and width 33 which equals $1,089.Producer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 66 and width 33 which is $1,089.The tax affects consumers by increasing the price they pay from $110 to $114 resulting in a loss of consumer surplus of $136.The tax affects producers by decreasing the price they receive from $110 to $106 resulting in a loss of producer surplus of $136.
In order to answer this question,we need to determine the changes in consumer and producer surplus that result from the imposition of the tax.Without the tax,the competitive equilibrium output can be found by equating demand and supply:
180 - 2Q = 40 + 2Q
Q = 140/4 = 35
Producers and consumers both pay the same price P = $110.The consumer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 70 and width 35 which is $1,225.The producer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 70 and width 35 which is equal to $1,225.With the tax,the consumer price will equal the producer price plus $8.We find the tax equilibrium output by setting PC = PP + 8:
180 - 2Q = 40 + 2Q + 8
Q = 132/4 = 33
Now consumers pay PC = $114 and producers pay PP = $106 (notice the difference between the two price levels is equal to the per unit tax).The consumer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 66 and width 33 which equals $1,089.Producer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 66 and width 33 which is $1,089.The tax affects consumers by increasing the price they pay from $110 to $114 resulting in a loss of consumer surplus of $136.The tax affects producers by decreasing the price they receive from $110 to $106 resulting in a loss of producer surplus of $136.
In order to answer this question,we need to determine the changes in consumer and producer surplus that result from the imposition of the tax.Without the tax,the competitive equilibrium output can be found by equating demand and supply:
180 - 2Q = 40 + 2Q
Q = 140/4 = 35
Producers and consumers both pay the same price P = $110.The consumer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 70 and width 35 which is $1,225.The producer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 70 and width 35 which is equal to $1,225.With the tax,the consumer price will equal the producer price plus $8.We find the tax equilibrium output by setting PC = PP + 8:
180 - 2Q = 40 + 2Q + 8
Q = 132/4 = 33
Now consumers pay PC = $114 and producers pay PP = $106 (notice the difference between the two price levels is equal to the per unit tax).The consumer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 66 and width 33 which equals $1,089.Producer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 66 and width 33 which is $1,089.The tax affects consumers by increasing the price they pay from $110 to $114 resulting in a loss of consumer surplus of $136.The tax affects producers by decreasing the price they receive from $110 to $106 resulting in a loss of producer surplus of $136.
180 - 2Q = 40 + 2Q
Q = 140/4 = 35
Producers and consumers both pay the same price P = $110.The consumer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 70 and width 35 which is $1,225.The producer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 70 and width 35 which is equal to $1,225.With the tax,the consumer price will equal the producer price plus $8.We find the tax equilibrium output by setting PC = PP + 8:
180 - 2Q = 40 + 2Q + 8
Q = 132/4 = 33
Now consumers pay PC = $114 and producers pay PP = $106 (notice the difference between the two price levels is equal to the per unit tax).The consumer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 66 and width 33 which equals $1,089.Producer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 66 and width 33 which is $1,089.The tax affects consumers by increasing the price they pay from $110 to $114 resulting in a loss of consumer surplus of $136.The tax affects producers by decreasing the price they receive from $110 to $106 resulting in a loss of producer surplus of $136.
2
Resources devoted to monitoring the behaviour of firms,agencies,and individuals subject to environmental regulations are called ________.
A)abatement costs
B)enforcement costs
C)private costs
D)environmental costs
A)abatement costs
B)enforcement costs
C)private costs
D)environmental costs
B
3
Suppose an industry facing an inverse demand equation equal to P = 120 - 4Q faces a new pollution control law that shifts its constant marginal cost of production from C1 = 50 to C2 = 68.Compute the social costs of regulation in this industry.
The social cost will be equal to the changes in consumer and producer surplus resulting from the regulation.Before regulation,the market price will be $50 and output will be equal to 17.5 units.There is no producer surplus because the marginal cost is constant,but the consumer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 70 and width 17.5 which is $612.50.After regulation,the market price will be $68 and the output will be 13 units.Again producer surplus is zero,but the consumer surplus is the area of triangle with height 52 and width 13 which is $338.The loss in consumer surplus resulting from the regulation is equal to $274.50 which is equal to the social cost of the pollution control law.
4
Illegal roadside dumping resulting from the introduction of waste disposal charges is one example of the ________ of an environmental policy.
A)pollution control cost
B)enforcement cost
C)unintended consequences
D)before/after result
A)pollution control cost
B)enforcement cost
C)unintended consequences
D)before/after result

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Suppose the government imposes a tax of $12 per unit of Good A.What is the incidence of this tax on consumers and producers?
HYPERLINK "" Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.
In order to answer this question,we need to determine the changes in consumer and producer surplus that result from the imposition of the tax.Without the tax,the competitive equilibrium output can be found by equating demand and supply:
80 - ½ Q = 14 + Q
Q = 66/1.5 = 44
Producers and consumers both pay the same price P = $58.The consumer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 22 and width 44 which is $484.The producer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 44 and width 44 which is equal to $968.With the tax,the consumer price will equal the producer price plus $12.We find the tax equilibrium output by setting PC = PP + 12:
80 - ½ Q = 14 + Q + 12
Q = 54/1.5 = 36
Now consumers pay PC = $62 and producers pay PP = $50 (notice the difference between the two price levels is equal to the per unit tax).The consumer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 18 and width 36 which equals $324.Producer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 36 and width 36 which is $648.The tax affects consumers by increasing the price they pay from $58 to $62 resulting in a loss of consumer surplus of $160.The tax affects producers by decreasing the price they receive from $58 to $50 resulting in a loss of producer surplus of $320.
HYPERLINK "" Error! Hyperlink reference not valid.
In order to answer this question,we need to determine the changes in consumer and producer surplus that result from the imposition of the tax.Without the tax,the competitive equilibrium output can be found by equating demand and supply:
80 - ½ Q = 14 + Q
Q = 66/1.5 = 44
Producers and consumers both pay the same price P = $58.The consumer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 22 and width 44 which is $484.The producer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 44 and width 44 which is equal to $968.With the tax,the consumer price will equal the producer price plus $12.We find the tax equilibrium output by setting PC = PP + 12:
80 - ½ Q = 14 + Q + 12
Q = 54/1.5 = 36
Now consumers pay PC = $62 and producers pay PP = $50 (notice the difference between the two price levels is equal to the per unit tax).The consumer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 18 and width 36 which equals $324.Producer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 36 and width 36 which is $648.The tax affects consumers by increasing the price they pay from $58 to $62 resulting in a loss of consumer surplus of $160.The tax affects producers by decreasing the price they receive from $58 to $50 resulting in a loss of producer surplus of $320.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When environmental regulation of an entire industry results in output adjustments,the social cost of the regulation can be measured by the changes in consumer and producer surpluses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the following figure,the social opportunity cost of reducing 40 units of emissions is equal to ________. 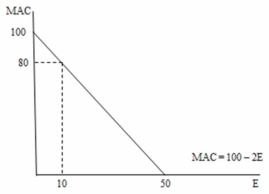
A)$100
B)$800
C)$900
D)$1,600

A)$100
B)$800
C)$900
D)$1,600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider the following illustrative numbers,applying to a manufacturing firm for which a pollution-control regulation has been proposed:

Determine the before/after costs of the regulation and the with/without costs of the regulation.Which of these two costs best reflects the true cost of the regulation?

Determine the before/after costs of the regulation and the with/without costs of the regulation.Which of these two costs best reflects the true cost of the regulation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose an industry facing an inverse demand equation equal to P = 400 - 0.5Q faces a new pollution control law that shifts its constant marginal cost of production from C1 = 80 to C2 = 100.Compute the social costs of regulation in this industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose an industry facing an inverse demand equation equal to P = 250 - 2.5Q faces a new pollution control law that shifts its constant marginal cost of production from C1 = 25 to C2 = 50.Compute the social costs of regulation in this industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose a manufacturing firm that is about to be regulated faces the following actual and potential production costs: 1)$500 before regulation;2)$630 in the future without the regulation;and 3)$700 in the future with the regulation.The true cost of the proposed regulation is $200.
$200 represents the before/after costs of the regulation while the true cost is better reflected by the with/without costs of the regulation which in this example would be $70.
$200 represents the before/after costs of the regulation while the true cost is better reflected by the with/without costs of the regulation which in this example would be $70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose a manufacturing firm that is about to be regulated faces the following actual and potential production costs: 1)$2,500 before regulation;2)$2,925 in the future without the regulation;and 3)$3,240 in the future with the regulation.The before/after cost of the regulation is ________ and the with/without cost of the regulation is ________.
A)$425;$740
B)$425;$315
C)$740;$315
D)$315;$425
A)$425;$740
B)$425;$315
C)$740;$315
D)$315;$425

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose the government imposes a tax of $6 per unit of Good A.What is the incidence of this tax on consumers and producers?
In order to answer this question,we need to determine the changes in consumer and producer surplus that result from the imposition of the tax.Without the tax,the competitive equilibrium output can be found by equating demand and supply:
80 - ½ Q = 14 + Q
Q = 66/1.5 = 44
Producers and consumers both pay the same price P = $58.The consumer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 22 and width 44 which is $484.The producer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 44 and width 44 which is equal to $968.With the tax,the consumer price will equal the producer price plus $6.We find the tax equilibrium output by setting PC = PP + 6:
80 - ½ Q = 14 + Q + 6
Q = 60/1.5 = 40
Now consumers pay PC = $60 and producers pay PP = $54 (notice the difference between the two price levels is equal to the per unit tax).The consumer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 20 and width 40 which equals $400.Producer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 40 and width 40 which is $800.The tax affects consumers by increasing the price they pay from $58 to $60 resulting in a loss of consumer surplus of $84.The tax affects producers by decreasing the price they receive from $58 to $54 resulting in a loss of producer surplus of $168.
In order to answer this question,we need to determine the changes in consumer and producer surplus that result from the imposition of the tax.Without the tax,the competitive equilibrium output can be found by equating demand and supply:
80 - ½ Q = 14 + Q
Q = 66/1.5 = 44
Producers and consumers both pay the same price P = $58.The consumer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 22 and width 44 which is $484.The producer surplus is equal to the area of a triangle with height 44 and width 44 which is equal to $968.With the tax,the consumer price will equal the producer price plus $6.We find the tax equilibrium output by setting PC = PP + 6:
80 - ½ Q = 14 + Q + 6
Q = 60/1.5 = 40
Now consumers pay PC = $60 and producers pay PP = $54 (notice the difference between the two price levels is equal to the per unit tax).The consumer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 20 and width 40 which equals $400.Producer surplus is now equal to the area of a triangle with height 40 and width 40 which is $800.The tax affects consumers by increasing the price they pay from $58 to $60 resulting in a loss of consumer surplus of $84.The tax affects producers by decreasing the price they receive from $58 to $54 resulting in a loss of producer surplus of $168.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The social opportunity cost of a new environmental regulation should include the cost of enforcement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A region is considering two sites on which to locate a new wastewater treatment plant.
Site A has been owned by the region for five years and the region initially paid $200,000 for the land.The current market value of the site is $400,000.Site B is land the region would have to purchase for $300,000.What is the social opportunity cost of each site? Based on this,which site should they choose?
Site A has been owned by the region for five years and the region initially paid $200,000 for the land.The current market value of the site is $400,000.Site B is land the region would have to purchase for $300,000.What is the social opportunity cost of each site? Based on this,which site should they choose?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose a manufacturing firm that is about to be regulated faces the following actual and potential production costs: 1)$4,000 before regulation;2)$4,550 in the future without the regulation;and 3)$5,200 in the future with the regulation.The true cost of the proposed regulation is ________.
A)$550
B)$1,200
C)$650
D)impossible to determine from the information provideD.
A)$550
B)$1,200
C)$650
D)impossible to determine from the information provideD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When supply and demand are linear curves,the incidence of the tax depends on the slopes of the demand and supply curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a firm goes out of business because an environmental regulation now requires them to incur pollution-control costs that they were previously getting for free (at society's expense),society will be better off to have the polluter exit the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When evaluating proposals for building a new sewage treatment plant,a cost-benefit analysis does not have to include the cost of the land if it is to be donated.
The analysis should include the opportunity cost related to the value the land would have in its next best use.
The analysis should include the opportunity cost related to the value the land would have in its next best use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A city is evaluating a proposal to build a recycling depot.If a generous citizen is willing to donate land for the project with a current market value of $800,000,the ________ of the land is ________.
A)social opportunity cost;$0
B)social opportunity cost;unknown
C)private cost to the city;$800,000
D)social opportunity cost;$800,000
A)social opportunity cost;$0
B)social opportunity cost;unknown
C)private cost to the city;$800,000
D)social opportunity cost;$800,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



