Deck 2: The Market System and the Circular Flow
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/252
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Market System and the Circular Flow
1
Which of the following is a fundamental characteristic of the market system?
A) property rights
B) central planning by government
C) unselfish behavior
D) government-set wages and prices
A) property rights
B) central planning by government
C) unselfish behavior
D) government-set wages and prices
property rights
2
The main mechanism that regulates the market system is
A) self-interest.
B) private property.
C) competition.
D) freedom of enterprise and choice.
A) self-interest.
B) private property.
C) competition.
D) freedom of enterprise and choice.
competition.
3
Competition means that
A) sellers can manipulate market price by causing product scarcities.
B) there are independently acting buyers and sellers in each market.
C) a product can be purchased at a number of different prices.
D) there is more than one seller in a market.
A) sellers can manipulate market price by causing product scarcities.
B) there are independently acting buyers and sellers in each market.
C) a product can be purchased at a number of different prices.
D) there is more than one seller in a market.
there are independently acting buyers and sellers in each market.
4
Economic systems differ according to which two main characteristics?
A) who owns the factors of production and the methods used to coordinate economic activity
B) the technology used in production and the quantity and quality of natural resources
C) how goods are produced and who gets them
D) the political system in place and the degree of scarcity facing the economy
A) who owns the factors of production and the methods used to coordinate economic activity
B) the technology used in production and the quantity and quality of natural resources
C) how goods are produced and who gets them
D) the political system in place and the degree of scarcity facing the economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A fundamental difference between the command system and laissez-faire capitalism is that, in command systems,
A) the division of output is decided by central planning rather than by individuals operating freely through markets.
B) all economic decisions are made by the government, whereas there is no government in laissez-faire capitalism.
C) scarcity does not exist, whereas it does in laissez-faire capitalism.
D) money is not used, whereas it is in laissez-faire capitalism.
A) the division of output is decided by central planning rather than by individuals operating freely through markets.
B) all economic decisions are made by the government, whereas there is no government in laissez-faire capitalism.
C) scarcity does not exist, whereas it does in laissez-faire capitalism.
D) money is not used, whereas it is in laissez-faire capitalism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is a distinguishing feature of a command system?
A) private ownership of all capital
B) central planning
C) heavy reliance on markets
D) widespread dispersion of economic power
A) private ownership of all capital
B) central planning
C) heavy reliance on markets
D) widespread dispersion of economic power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The division of labor means that
A) labor markets are geographically segmented.
B) unskilled workers outnumber skilled workers.
C) workers specialize in various production tasks.
D) each worker performs a large number of tasks.
A) labor markets are geographically segmented.
B) unskilled workers outnumber skilled workers.
C) workers specialize in various production tasks.
D) each worker performs a large number of tasks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Copyrights and trademarks are examples of
A) capital goods.
B) human capital.
C) property rights.
D) public goods.
A) capital goods.
B) human capital.
C) property rights.
D) public goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The term "laissez-faire" suggests that
A) land and other natural resources should be privately owned, but capital should be publicly owned.
B) land and other natural resources should be publicly owned, but capital should be privately owned.
C) government should not interfere with the operation of the economy.
D) government action is absolutely necessary if the economy is to achieve full employment and full production.
A) land and other natural resources should be privately owned, but capital should be publicly owned.
B) land and other natural resources should be publicly owned, but capital should be privately owned.
C) government should not interfere with the operation of the economy.
D) government action is absolutely necessary if the economy is to achieve full employment and full production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Private property
A) discourages cooperation because people don't want to part with what they own.
B) discourages innovation, as people are often afraid to risk losing their own property.
C) encourages owners to maintain or improve their property so as to preserve or enhance value.
D) does everything indicated by the other answers.
A) discourages cooperation because people don't want to part with what they own.
B) discourages innovation, as people are often afraid to risk losing their own property.
C) encourages owners to maintain or improve their property so as to preserve or enhance value.
D) does everything indicated by the other answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Of the following countries, which one best exhibits the characteristics of a market economy?
A) Canada
B) Cuba
C) North Korea
D) Belarus
A) Canada
B) Cuba
C) North Korea
D) Belarus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Examples of command economies are
A) the United States and Japan.
B) Sweden and Norway.
C) Mexico and Brazil.
D) Cuba and North Korea.
A) the United States and Japan.
B) Sweden and Norway.
C) Mexico and Brazil.
D) Cuba and North Korea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The French term "laissez-faire" means
A) "there is no free lunch."
B) "let it be."
C) "circular flow."
D) "public ownership."
A) "there is no free lunch."
B) "let it be."
C) "circular flow."
D) "public ownership."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Broadly defined, competition involves
A) private property and freedom of expression.
B) independently acting buyers and sellers and freedom to enter or leave markets.
C) increasing opportunity costs and diminishing marginal utility.
D) capital goods and division of labor.
A) private property and freedom of expression.
B) independently acting buyers and sellers and freedom to enter or leave markets.
C) increasing opportunity costs and diminishing marginal utility.
D) capital goods and division of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is not a typical characteristic of a market system?
A) private property
B) freedom of enterprise
C) government ownership of most property resources
D) competition in product and resource markets
A) private property
B) freedom of enterprise
C) government ownership of most property resources
D) competition in product and resource markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is a distinguishing feature of laissez-faire capitalism?
A) public ownership of all capital
B) central planning
C) minimal government intervention
D) a circular flow of goods, resources, and money
A) public ownership of all capital
B) central planning
C) minimal government intervention
D) a circular flow of goods, resources, and money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Freedom of enterprise
A) is a characteristic that is common to most economic systems.
B) in a market system means that entrepreneurs can obtain and use economic resources without any legal restraint.
C) allows businesses, within broad limits, to choose what goods to produce.
D) refers primarily to the right of consumers to purchase what they want.
A) is a characteristic that is common to most economic systems.
B) in a market system means that entrepreneurs can obtain and use economic resources without any legal restraint.
C) allows businesses, within broad limits, to choose what goods to produce.
D) refers primarily to the right of consumers to purchase what they want.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An economic system
A) requires a grouping of private markets linked to one another.
B) is a particular set of institutional arrangements and a coordinating mechanism used to respond to the economizing problem.
C) requires some sort of centralized authority (such as government) to coordinate economic activity.
D) is a plan or scheme that allows a firm to make money at some other firm's expense.
A) requires a grouping of private markets linked to one another.
B) is a particular set of institutional arrangements and a coordinating mechanism used to respond to the economizing problem.
C) requires some sort of centralized authority (such as government) to coordinate economic activity.
D) is a plan or scheme that allows a firm to make money at some other firm's expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Command systems are also known as
A) market systems.
B) pure capitalism.
C) laissez-faire capitalism.
D) communism.
A) market systems.
B) pure capitalism.
C) laissez-faire capitalism.
D) communism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Property rights are important because they
A) ensure an equal distribution of income.
B) encourage cooperation by improving the chances of mutually agreeable transactions.
C) guarantee that any exchange will make all parties better off than prior to the exchange.
D) allow the government to control how resources are allocated.
A) ensure an equal distribution of income.
B) encourage cooperation by improving the chances of mutually agreeable transactions.
C) guarantee that any exchange will make all parties better off than prior to the exchange.
D) allow the government to control how resources are allocated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The "coincidence of wants" problem associated with barter refers to the fact that
A) for exchange to occur, each seller must have a product that some buyer wants.
B) money must be used as a medium of exchange or trade will never occur.
C) specialization is restricted by the size or scope of a market.
D) buyers in resource markets and sellers in product markets can never engage in exchange.
A) for exchange to occur, each seller must have a product that some buyer wants.
B) money must be used as a medium of exchange or trade will never occur.
C) specialization is restricted by the size or scope of a market.
D) buyers in resource markets and sellers in product markets can never engage in exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The presence of market failures implies that
A) money is not an effective tool for exchange in a market system.
B) there is an active role for government, even in a market system.
C) individuals and firms should strive to be self-sufficient rather than specialize.
D) command systems are superior to market systems in the allocation of resources.
A) money is not an effective tool for exchange in a market system.
B) there is an active role for government, even in a market system.
C) individuals and firms should strive to be self-sufficient rather than specialize.
D) command systems are superior to market systems in the allocation of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If competitive industry Z is making substantial economic profit, output will
A) fall in industry Z and firms will likely leave the market.
B) fall in all industries except industry Z.
C) expand in industry Z, as more resources will move to that industry.
D) expand in industry Z, but no new firms will enter the market.
A) fall in industry Z and firms will likely leave the market.
B) fall in all industries except industry Z.
C) expand in industry Z, as more resources will move to that industry.
D) expand in industry Z, but no new firms will enter the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Specialization-the division of labor-enhances productivity and efficiency by
A) allowing workers to take advantage of existing differences in their abilities and skills.
B) avoiding the time loss involved in shifting from one production task to another.
C) allowing workers to develop skills by working on one, or a limited number, of tasks.
D) all of the means identified in the other answers.
A) allowing workers to take advantage of existing differences in their abilities and skills.
B) avoiding the time loss involved in shifting from one production task to another.
C) allowing workers to develop skills by working on one, or a limited number, of tasks.
D) all of the means identified in the other answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
From society's point of view, the economic function of profits and losses is to
A) promote the equal distribution of real assets and wealth.
B) achieve full employment and price level stability.
C) contribute to a more equal distribution of income.
D) reallocate resources from less-desired to more-desired uses.
A) promote the equal distribution of real assets and wealth.
B) achieve full employment and price level stability.
C) contribute to a more equal distribution of income.
D) reallocate resources from less-desired to more-desired uses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If competitive industry Y is incurring substantial losses, output will
A) expand as resources move toward industry Y.
B) contract as resources move toward industry Y.
C) contract as resources move away from industry Y.
D) expand as resources move away from industry Y.
A) expand as resources move toward industry Y.
B) contract as resources move toward industry Y.
C) contract as resources move away from industry Y.
D) expand as resources move away from industry Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The use of money contributes to economic efficiency because
A) governmental direction of the production and distribution of output can be avoided by using money.
B) roundabout production could not occur without the availability of money.
C) it is necessary for the creation of capital goods.
D) it promotes specialization by overcoming the problems with barter.
A) governmental direction of the production and distribution of output can be avoided by using money.
B) roundabout production could not occur without the availability of money.
C) it is necessary for the creation of capital goods.
D) it promotes specialization by overcoming the problems with barter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is one of the Five Fundamental Questions?
A) Which products will be in scarce supply and which in excess supply?
B) Who should appoint the head of the central bank?
C) How much should society save?
D) What goods and services will be produced?
A) Which products will be in scarce supply and which in excess supply?
B) Who should appoint the head of the central bank?
C) How much should society save?
D) What goods and services will be produced?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a market economy, a significant change in consumers' desire for product X will
A) alter the profits or losses received by suppliers of product X.
B) cause a reallocation of scarce resources.
C) cause some industries to expand and others to contract.
D) do all of the things mentioned in the other answers.
A) alter the profits or losses received by suppliers of product X.
B) cause a reallocation of scarce resources.
C) cause some industries to expand and others to contract.
D) do all of the things mentioned in the other answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An increase in consumer desire for strawberries is most likely to
A) increase the number of strawberry pickers needed by farmers.
B) reduce the supply of strawberries.
C) reduce the number of people willing to pick strawberries.
D) reduce the need for strawberry pickers.
A) increase the number of strawberry pickers needed by farmers.
B) reduce the supply of strawberries.
C) reduce the number of people willing to pick strawberries.
D) reduce the need for strawberry pickers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Barter
A) is the major means of exchange in centrally planned economies.
B) accounts for over 30 percent of the dollar volume of all exchange in the U.S. economy.
C) entails the exchange of goods for goods.
D) is used to circumvent the problem of a lack of coincidence of wants among potential buyers and sellers.
A) is the major means of exchange in centrally planned economies.
B) accounts for over 30 percent of the dollar volume of all exchange in the U.S. economy.
C) entails the exchange of goods for goods.
D) is used to circumvent the problem of a lack of coincidence of wants among potential buyers and sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The competitive market system
A) encourages innovation because government provides tax breaks and subsidies to those who develop new products or new productive techniques.
B) discourages innovation because it is difficult to acquire additional capital in the form of new machinery and equipment.
C) discourages innovation because firms want to get all the profits possible from existing machinery and equipment.
D) encourages innovation because successful innovators are rewarded with economic profits.
A) encourages innovation because government provides tax breaks and subsidies to those who develop new products or new productive techniques.
B) discourages innovation because it is difficult to acquire additional capital in the form of new machinery and equipment.
C) discourages innovation because firms want to get all the profits possible from existing machinery and equipment.
D) encourages innovation because successful innovators are rewarded with economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The economic function of profits and losses is to
A) bring about a more equal distribution of income.
B) signal that resources should be reallocated.
C) eliminate small firms and reduce competition.
D) tell government which industries need to be subsidized.
A) bring about a more equal distribution of income.
B) signal that resources should be reallocated.
C) eliminate small firms and reduce competition.
D) tell government which industries need to be subsidized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Economic profits and losses
A) are both considered by economists to be a part of production costs.
B) are essential to the reallocation of resources from less desired to more desired goods.
C) have no influence on the composition of domestic output.
D) equalize the distribution of income in the long run.
A) are both considered by economists to be a part of production costs.
B) are essential to the reallocation of resources from less desired to more desired goods.
C) have no influence on the composition of domestic output.
D) equalize the distribution of income in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following characteristics is least unique to a market system?
A) private ownership of property resources
B) competition among buyers and sellers pursuing monetary returns
C) the widespread use of money
D) freedom of enterprise and choice
A) private ownership of property resources
B) competition among buyers and sellers pursuing monetary returns
C) the widespread use of money
D) freedom of enterprise and choice

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Specialization in production is economically beneficial primarily because it
A) allows everyone to have a job that he or she likes.
B) permits the production of a larger output with fixed amounts of resources.
C) facilitates trade by bartering.
D) guarantees full employment.
A) allows everyone to have a job that he or she likes.
B) permits the production of a larger output with fixed amounts of resources.
C) facilitates trade by bartering.
D) guarantees full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Economic profits in an industry suggest the industry
A) can earn more profits by increasing product price.
B) should be larger to better satisfy consumers' desire for the product.
C) has excess production capacity.
D) is the size that consumers want it to be.
A) can earn more profits by increasing product price.
B) should be larger to better satisfy consumers' desire for the product.
C) has excess production capacity.
D) is the size that consumers want it to be.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Specialization in production is important primarily because it
A) results in greater total output.
B) allows society to avoid the coincidence-of-wants problem.
C) allows society to trade by barter.
D) allows society to have fewer capital goods.
A) results in greater total output.
B) allows society to avoid the coincidence-of-wants problem.
C) allows society to trade by barter.
D) allows society to have fewer capital goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If consumer desire for product X increases, all of the following will occur except
A) an increase in the profits of industry X.
B) an increase in the quantity of resources employed by industry X.
C) an increase in the output of industry X.
D) a decrease in the quantity of resources employed in industry X.
A) an increase in the profits of industry X.
B) an increase in the quantity of resources employed by industry X.
C) an increase in the output of industry X.
D) a decrease in the quantity of resources employed in industry X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a competitive industry is neither expanding nor contracting, we would expect
A) total revenue to be zero.
B) economic profits to be zero.
C) total opportunity cost to be zero.
D) more resources to flow to that industry.
A) total revenue to be zero.
B) economic profits to be zero.
C) total opportunity cost to be zero.
D) more resources to flow to that industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a competitive market economy, firms select the least-cost production technique because
A) such choices will result in full employment of available resources.
B) to do so will maximize the firms' profits.
C) this will prevent new firms from entering the industry.
D) "dollar voting" by consumers mandates such a choice.
A) such choices will result in full employment of available resources.
B) to do so will maximize the firms' profits.
C) this will prevent new firms from entering the industry.
D) "dollar voting" by consumers mandates such a choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The market system's answer to the fundamental question "How will the system accommodate change?" is essentially
A) "Through government leadership and direction."
B) "Through the guiding function of prices and the incentive function of profits."
C) "Through training and retraining programs."
D) "Through trial and error."
A) "Through government leadership and direction."
B) "Through the guiding function of prices and the incentive function of profits."
C) "Through training and retraining programs."
D) "Through trial and error."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In a market economy, the distribution of output will be determined primarily by
A) consumer needs and preferences.
B) the quantities and prices of the resources that households supply.
C) government regulations that provide a minimum income for all.
D) a social consensus as to which distribution of income is most equitable.
A) consumer needs and preferences.
B) the quantities and prices of the resources that households supply.
C) government regulations that provide a minimum income for all.
D) a social consensus as to which distribution of income is most equitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The market system's answer to the fundamental question "How will the system promote progress?" is essentially
A) "Through government-funded research programs."
B) "Through redistribution of income to promote greater equality."
C) "Through training and retraining programs."
D) "Through the profit potential that encourages development of new technology."
A) "Through government-funded research programs."
B) "Through redistribution of income to promote greater equality."
C) "Through training and retraining programs."
D) "Through the profit potential that encourages development of new technology."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Answer the question on the basis of the following information: Suppose 30 units of product A can be produced by employing just labor and capital in the four ways shown below. Assume the prices of labor and capital are $2 and $3, respectively.  Which technique is economically most efficient in producing A?
Which technique is economically most efficient in producing A?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
 Which technique is economically most efficient in producing A?
Which technique is economically most efficient in producing A?A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The dollar votes of consumers ultimately determine the composition of output and the allocation of resources in a market economy. This statement best describes the concept of
A) derived demand.
B) consumer sovereignty.
C) the invisible hand.
D) market failure.
A) derived demand.
B) consumer sovereignty.
C) the invisible hand.
D) market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The market system's answer to the fundamental question "What will be produced?" is essentially
A) "Goods and services that are profitable."
B) "Low-cost goods and services."
C) "Goods and services that can be produced using large amounts of capital."
D) "Goods and services that possess lasting value."
A) "Goods and services that are profitable."
B) "Low-cost goods and services."
C) "Goods and services that can be produced using large amounts of capital."
D) "Goods and services that possess lasting value."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following best describes the invisible-hand concept?
A) The desires of resource suppliers and producers to further their own self-interest will automatically further the public interest.
B) The inability to substitute resources creates a conflict between private and public interests and calls for government intervention.
C) The market system is the best system for overcoming the scarce resources-unlimited wants problem.
D) Central direction by the government will improve resource allocation in a capitalistic economy.
A) The desires of resource suppliers and producers to further their own self-interest will automatically further the public interest.
B) The inability to substitute resources creates a conflict between private and public interests and calls for government intervention.
C) The market system is the best system for overcoming the scarce resources-unlimited wants problem.
D) Central direction by the government will improve resource allocation in a capitalistic economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
"Consumer sovereignty" refers to the
A) fact that resource prices are higher than product prices in capitalistic economies.
B) idea that the pursuit of self-interest is in the public interest.
C) idea that the decisions of producers must ultimately conform to consumer demands.
D) fact that a federal agency exists to protect consumers from harmful and defective products.
A) fact that resource prices are higher than product prices in capitalistic economies.
B) idea that the pursuit of self-interest is in the public interest.
C) idea that the decisions of producers must ultimately conform to consumer demands.
D) fact that a federal agency exists to protect consumers from harmful and defective products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Answer the question using the following data, which show all available techniques for producing 20 units of a particular commodity 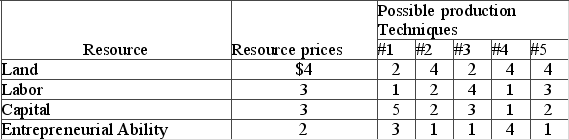 In view of the indicated resource prices, the economically most efficient production technique(s) is (are) technique(s)
In view of the indicated resource prices, the economically most efficient production technique(s) is (are) technique(s)
A) 1.
B) 2 and 4.
C) 3.
D) 1 and 3.
 In view of the indicated resource prices, the economically most efficient production technique(s) is (are) technique(s)
In view of the indicated resource prices, the economically most efficient production technique(s) is (are) technique(s)A) 1.
B) 2 and 4.
C) 3.
D) 1 and 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The market system's answer to the fundamental question "How will the goods and services be produced?" is essentially
A) "With as much machinery as possible."
B) "Using the latest technology."
C) "By exploiting labor."
D) "In ways that minimize the cost per unit of output."
A) "With as much machinery as possible."
B) "Using the latest technology."
C) "By exploiting labor."
D) "In ways that minimize the cost per unit of output."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
"Consumer sovereignty" means that
A) buyers can dictate the prices at which goods and services will be offered.
B) advertising is ineffective because consumers already know what they want.
C) buyers control the quality of goods and services through regulatory agencies.
D) buyers determine what will be produced based on their "dollar votes" for the goods and services offered by sellers.
A) buyers can dictate the prices at which goods and services will be offered.
B) advertising is ineffective because consumers already know what they want.
C) buyers control the quality of goods and services through regulatory agencies.
D) buyers determine what will be produced based on their "dollar votes" for the goods and services offered by sellers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Answer the question using the following data, which show all available techniques for producing 20 units of a particular commodity 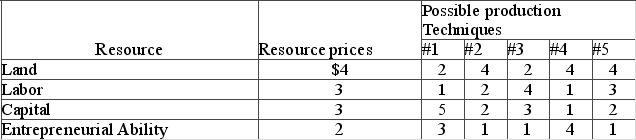 If a new production technique is developed that enables a firm to produce 20 units of output with 3 units of land, 3 of labor, 1 of capital, and 2 of entrepreneurial ability, this technique would
If a new production technique is developed that enables a firm to produce 20 units of output with 3 units of land, 3 of labor, 1 of capital, and 2 of entrepreneurial ability, this technique would
A) not be adopted because, although it reduces production costs, it does not increase profit.
B) be adopted because it would lower production costs and increase economic profit.
C) not be adopted because it entails higher production costs than other available techniques.
D) be adopted, even though economic profits would be reduced slightly.
 If a new production technique is developed that enables a firm to produce 20 units of output with 3 units of land, 3 of labor, 1 of capital, and 2 of entrepreneurial ability, this technique would
If a new production technique is developed that enables a firm to produce 20 units of output with 3 units of land, 3 of labor, 1 of capital, and 2 of entrepreneurial ability, this technique wouldA) not be adopted because, although it reduces production costs, it does not increase profit.
B) be adopted because it would lower production costs and increase economic profit.
C) not be adopted because it entails higher production costs than other available techniques.
D) be adopted, even though economic profits would be reduced slightly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The advent of Netflix movie streaming and Redbox kiosks renting DVD and Blu-ray movies have virtually demolished the market for video rentals from brick and mortar stores such as Blockbuster. This is an example of
A) creative destruction.
B) derived demand.
C) capital accumulation.
D) the difference between normal and economic profits.
A) creative destruction.
B) derived demand.
C) capital accumulation.
D) the difference between normal and economic profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The market system's answer to the fundamental question "Who will get the goods and services?" is essentially
A. "Those most willing and able to pay for them."
B. "Those who physically produced them."
C. "Those who most need them."
D. "Those who get utility from them."
A. "Those most willing and able to pay for them."
B. "Those who physically produced them."
C. "Those who most need them."
D. "Those who get utility from them."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Answer the question on the basis of the following information: Suppose 30 units of product A can be produced by employing just labor and capital in the four ways shown below. Assume the prices of labor and capital are $2 and $3, respectively.  If the price of product A is $0.50, the firm will realize
If the price of product A is $0.50, the firm will realize
A) an economic profit of $4.
B) an economic profit of $2.
C) an economic profit of $6.
D) a loss of $3.
 If the price of product A is $0.50, the firm will realize
If the price of product A is $0.50, the firm will realizeA) an economic profit of $4.
B) an economic profit of $2.
C) an economic profit of $6.
D) a loss of $3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Answer the question using the following data, which show all available techniques for producing 20 units of a particular commodity  Assuming that the firm is motivated by self-interest and that the 20 units that can be produced with each technique can be sold for $2 per unit, the firm will
Assuming that the firm is motivated by self-interest and that the 20 units that can be produced with each technique can be sold for $2 per unit, the firm will
A) realize an economic profit of $10.
B) realize an economic profit of $4.
C) not earn any economic profit.
D) shut down rather than incur a loss by producing.
 Assuming that the firm is motivated by self-interest and that the 20 units that can be produced with each technique can be sold for $2 per unit, the firm will
Assuming that the firm is motivated by self-interest and that the 20 units that can be produced with each technique can be sold for $2 per unit, the firm willA) realize an economic profit of $10.
B) realize an economic profit of $4.
C) not earn any economic profit.
D) shut down rather than incur a loss by producing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Firms are motivated to minimize production costs because
A) it is the most environmentally friendly way to produce goods.
B) least-cost production techniques use the smallest total quantity of resources.
C) competitive pressures in the market will drive out higher-cost producers.
D) the government provides tax credits and subsidies to low-cost producers.
A) it is the most environmentally friendly way to produce goods.
B) least-cost production techniques use the smallest total quantity of resources.
C) competitive pressures in the market will drive out higher-cost producers.
D) the government provides tax credits and subsidies to low-cost producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The most efficient combination of resources in producing a given output is the combination that
A) comes closest to using the same quantities of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability.
B) minimizes the cost per unit of output.
C) uses the smallest total quantity of all resources.
D) conserves most on the use of labor.
A) comes closest to using the same quantities of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability.
B) minimizes the cost per unit of output.
C) uses the smallest total quantity of all resources.
D) conserves most on the use of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is not one of the five fundamental questions?
A) What prices will be charged for goods and services?
B) Who will get the goods and services?
C) What goods and services will be produced?
D) How will the system promote progress?
A) What prices will be charged for goods and services?
B) Who will get the goods and services?
C) What goods and services will be produced?
D) How will the system promote progress?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The invisible hand concept suggests that
A) market failures imply the need for a national economic plan.
B) big businesses are inherently more efficient than small businesses.
C) the competitiveness of a capitalistic market economy invariably diminishes over time.
D) assuming competition, private and public interests will coincide.
A) market failures imply the need for a national economic plan.
B) big businesses are inherently more efficient than small businesses.
C) the competitiveness of a capitalistic market economy invariably diminishes over time.
D) assuming competition, private and public interests will coincide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The fact that the major indicator of enterprise success in the Soviet Union and pre-reform China was the quantity of output implied that
A) product quality was neglected.
B) production costs were minimized.
C) product mix met consumer needs.
D) technological advance was too rapid.
A) product quality was neglected.
B) production costs were minimized.
C) product mix met consumer needs.
D) technological advance was too rapid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The market system
A) produces considerable inefficiency in the use of scarce resources.
B) effectively harnesses the incentives of workers and entrepreneurs.
C) is not consistent with freedom of choice in the long run.
D) has slowly lost ground to emerging command systems.
A) produces considerable inefficiency in the use of scarce resources.
B) effectively harnesses the incentives of workers and entrepreneurs.
C) is not consistent with freedom of choice in the long run.
D) has slowly lost ground to emerging command systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the concept of the "invisible hand," if Susie opens and operates a profitable childcare center, then
A) government should regulate the business to ensure quality.
B) the profit Susie earns indicates that she is overcharging for her services.
C) she has served society's interests by providing a desired good or service.
D) this demonstrates that consumer sovereignty is not present in this market.
A) government should regulate the business to ensure quality.
B) the profit Susie earns indicates that she is overcharging for her services.
C) she has served society's interests by providing a desired good or service.
D) this demonstrates that consumer sovereignty is not present in this market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Two major virtues of the market system are that it
A) allocates resources efficiently and allows economic freedom.
B) results in an equitable personal distribution of income and always maintains full employment.
C) results in price-level stability and a fair personal distribution of income.
D) eliminates discrimination and minimizes environmental pollution.
A) allocates resources efficiently and allows economic freedom.
B) results in an equitable personal distribution of income and always maintains full employment.
C) results in price-level stability and a fair personal distribution of income.
D) eliminates discrimination and minimizes environmental pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The invisible hand promotes society's interests because
A) individuals pursuing their self-interest will try to produce goods and services that people in society want and are willing to purchase.
B) individuals will produce goods for others out of concern for their fellow human beings.
C) it makes sure that everyone wins from competition in the market.
D) government regulation pushes business into producing the right mix of goods and services.
A) individuals pursuing their self-interest will try to produce goods and services that people in society want and are willing to purchase.
B) individuals will produce goods for others out of concern for their fellow human beings.
C) it makes sure that everyone wins from competition in the market.
D) government regulation pushes business into producing the right mix of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In what type of business do the owners bear no personal financial responsibility for the company's debts and obligations?
A) partnerships
B) corporations
C) sole proprietorships
D) in all of the businesses listed in the other answers
A) partnerships
B) corporations
C) sole proprietorships
D) in all of the businesses listed in the other answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose that an individual sees a tremendous opportunity to produce and sell a new product but dismisses the idea because there is no way to exploit this opportunity for personal gain. This situation best identifies the
A) coordination problem under communist central planning.
B) self-sufficiency dilemma under communism.
C) asymmetric information problem under communism.
D) incentive problem under communist central planning.
A) coordination problem under communist central planning.
B) self-sufficiency dilemma under communism.
C) asymmetric information problem under communism.
D) incentive problem under communist central planning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
"Under central planning, some group has to decide how to get the necessary inputs produced in the right amounts and delivered to the right places at the right time. This is a nearly impossible task without markets and profits." This quotation best identifies the
A) incentive problem under central planning.
B) coordination problem under central planning.
C) self-sufficiency dilemma under communism.
D) resource overcommitment problem under communism.
A) incentive problem under central planning.
B) coordination problem under central planning.
C) self-sufficiency dilemma under communism.
D) resource overcommitment problem under communism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the resource market,
A) businesses borrow financial capital from households.
B) businesses sell services to households.
C) households sell resources to businesses.
D) firms sell raw materials to households.
A) businesses borrow financial capital from households.
B) businesses sell services to households.
C) households sell resources to businesses.
D) firms sell raw materials to households.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The incentive problem under communist central planning refers to the idea that
A) planners had to direct required inputs to each enterprise.
B) workers, managers, and entrepreneurs could not personally gain by responding to shortages or surpluses or by introducing new and improved products.
C) the immediate effect of more investment was less consumption.
D) exports had to be equal to imports for a central plan to work.
A) planners had to direct required inputs to each enterprise.
B) workers, managers, and entrepreneurs could not personally gain by responding to shortages or surpluses or by introducing new and improved products.
C) the immediate effect of more investment was less consumption.
D) exports had to be equal to imports for a central plan to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The coordination problem in the centrally planned economies refers to the idea that
A) planners had to direct required inputs to each enterprise.
B) the price level and the level of employment were inversely related.
C) the immediate effect of more investment was less consumption.
D) exports had to be equal to imports for a central plan to work.
A) planners had to direct required inputs to each enterprise.
B) the price level and the level of employment were inversely related.
C) the immediate effect of more investment was less consumption.
D) exports had to be equal to imports for a central plan to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Innovation lagged in the centrally planned economies because
A) there was too much domestic business competition.
B) there was too much competition from foreign firms.
C) enterprises resisted innovation in fear that their production targets would be raised.
D) exports had to equal imports for the plan to work.
A) there was too much domestic business competition.
B) there was too much competition from foreign firms.
C) enterprises resisted innovation in fear that their production targets would be raised.
D) exports had to equal imports for the plan to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
"Because the outputs of many industries are the inputs to other industries, the failure of any single industry to fulfil the output quantities specified in the central plan caused a chain reaction of adverse repercussions on production." This quotation best identifies the
A) incentive problem under central planning.
B) self-sufficiency dilemma under communism.
C) resource overcommitment problem under communism.
D) coordination problem under central planning.
A) incentive problem under central planning.
B) self-sufficiency dilemma under communism.
C) resource overcommitment problem under communism.
D) coordination problem under central planning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The invisible hand refers to the
A) fact that the U.S. tax system redistributes income from rich to poor.
B) notion that, under competition, decisions motivated by self-interest promote the social interest.
C) tendency of monopolistic sellers to raise prices above competitive levels.
D) fact that government controls the functioning of the market system.
A) fact that the U.S. tax system redistributes income from rich to poor.
B) notion that, under competition, decisions motivated by self-interest promote the social interest.
C) tendency of monopolistic sellers to raise prices above competitive levels.
D) fact that government controls the functioning of the market system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The two basic markets shown by the simple circular flow model are
A) capital goods and consumer goods.
B) competitive and regulated.
C) product and resource.
D) household and business.
A) capital goods and consumer goods.
B) competitive and regulated.
C) product and resource.
D) household and business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If products were in short or surplus supply in the Soviet Union,
A) price and profit signals eliminated those shortages and surpluses.
B) price and profit signals intensified those shortages and surpluses.
C) producers would not react because no price or profit signals occurred.
D) the planners would immediately adjust production to achieve equilibrium.
A) price and profit signals eliminated those shortages and surpluses.
B) price and profit signals intensified those shortages and surpluses.
C) producers would not react because no price or profit signals occurred.
D) the planners would immediately adjust production to achieve equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Enterprise managers and workers in the Soviet Union often resisted innovations in production methods because
A. production targets were often increased when innovation occurred.
B. there was a chronic shortage of computers.
C. workers could not be reallocated geographically.
D. innovations ordinarily increased dependence on world markets.
A. production targets were often increased when innovation occurred.
B. there was a chronic shortage of computers.
C. workers could not be reallocated geographically.
D. innovations ordinarily increased dependence on world markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The simple circular flow model shows that
A) households are on the buying side of both product and resource markets.
B) businesses are on the selling side of both product and resource markets.
C) households are on the selling side of the resource market and on the buying side of the product market.
D) businesses are on the buying side of the product market and on the selling side of the resource market.
A) households are on the buying side of both product and resource markets.
B) businesses are on the selling side of both product and resource markets.
C) households are on the selling side of the resource market and on the buying side of the product market.
D) businesses are on the buying side of the product market and on the selling side of the resource market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In the simple circular flow model,
A) households are buyers of resources.
B) businesses are sellers of final products.
C) households are sellers of final products.
D) there are real flows of goods, services, and resources, but not money flows.
A) households are buyers of resources.
B) businesses are sellers of final products.
C) households are sellers of final products.
D) there are real flows of goods, services, and resources, but not money flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 252 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



