Deck 25: Synthetic and Natural Organic Polymers
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Synthetic and Natural Organic Polymers
1
Which of the following polymers has an isotactic structure
A)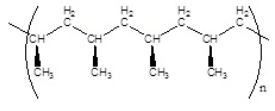
B)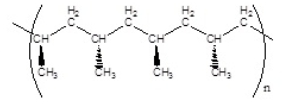
C)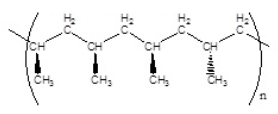
D)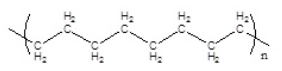
A)

B)

C)

D)


2
Polypropene results from the polymerization of
A)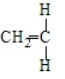
B)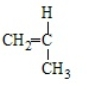
C)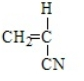
D)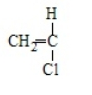
E)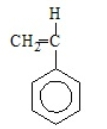
A)
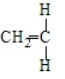
B)

C)
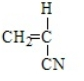
D)
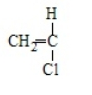
E)


3
The only true hydrocarbon polymer found in nature is
A) rubber.
B) nylon.
C) Tyvek.
D) polystyrene.
E) neoprene.
A) rubber.
B) nylon.
C) Tyvek.
D) polystyrene.
E) neoprene.
rubber.
4
The segment 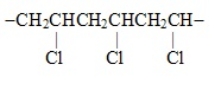 represents the polymer named
represents the polymer named
A) polybutylene..
B) polyvinyl chloride.
C) polypropylene.
D) polystyrene
E) polyethylene
 represents the polymer named
represents the polymer namedA) polybutylene..
B) polyvinyl chloride.
C) polypropylene.
D) polystyrene
E) polyethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which polymerization shown takes place by a condensation
I.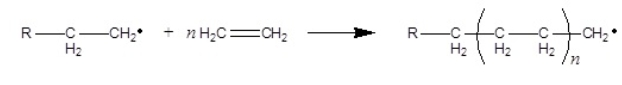
II.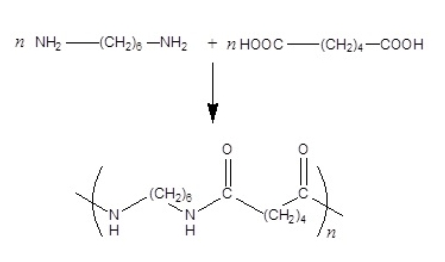
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) None of the above
I.

II.

A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What type of polymer is represented by the following repeating segment 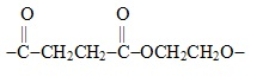
A) polyamide
B) polyester
C) polyether
D) polyolefin
E) polyethylene

A) polyamide
B) polyester
C) polyether
D) polyolefin
E) polyethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A protein is
A) a polysaccharide.
B) a saturated ester of glycerol.
C) one of the units making up a nucleic acid.
D) a polymer of amino acids.
E) an aromatic hydrocarbon.
A) a polysaccharide.
B) a saturated ester of glycerol.
C) one of the units making up a nucleic acid.
D) a polymer of amino acids.
E) an aromatic hydrocarbon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following polymers is formed by a condensation process
A) PVC
B) nylon
C) Teflon
D) Plexiglas
E) neoprene
A) PVC
B) nylon
C) Teflon
D) Plexiglas
E) neoprene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The segment 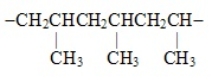 represents the polymer named
represents the polymer named
A) polybutylene.
B) polyvinyl chloride..
C) polypropylene.
D) polystyrene.
E) polyethylene
 represents the polymer named
represents the polymer namedA) polybutylene.
B) polyvinyl chloride..
C) polypropylene.
D) polystyrene.
E) polyethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following polymers has an atactic structure
A)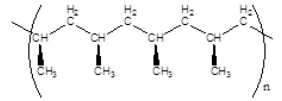
B)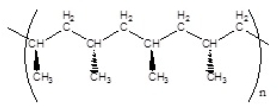
C)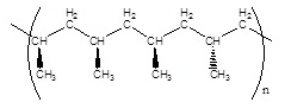
D)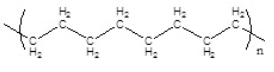
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which polymerization shown takes place by a radical mechanism
i.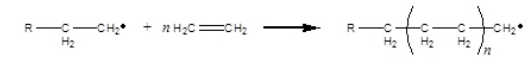
ii.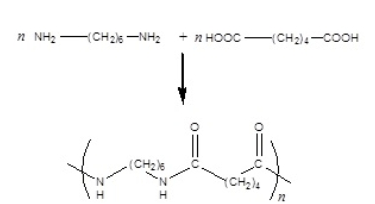
A) i only
B) ii only
C) i and ii
D) None of the above
i.

ii.

A) i only
B) ii only
C) i and ii
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following polymers has a syndiotactic structure
A)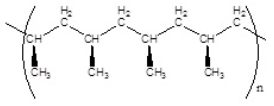
B)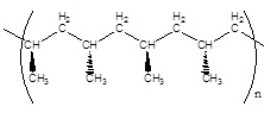
C)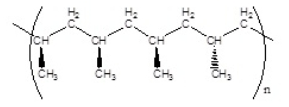
D)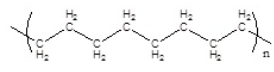
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What structural feature is required to have an isotactic or syndiotactic carbon-based polymer
A) A repeating unit that contains an asymmetric carbon
B) A repeating unit that contains a double bond
C) A repeating unit that contains a triple bond
D) A repeating unit that contains an aromatic hydrocarbon
E) A repeating unit that contains an atom other than carbon
A) A repeating unit that contains an asymmetric carbon
B) A repeating unit that contains a double bond
C) A repeating unit that contains a triple bond
D) A repeating unit that contains an aromatic hydrocarbon
E) A repeating unit that contains an atom other than carbon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Poly(vinyl chloride) results from the polymerization of
A)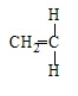
B)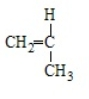
C)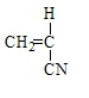
D)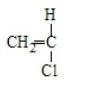
E)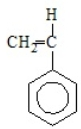
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which one of these molecules could not serve as a monomer for an addition polymer
A) ClCH=CH2
B) H2C=CH-CN
C) H2C=CH-C6H5
D)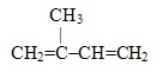
E)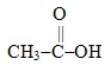
A) ClCH=CH2
B) H2C=CH-CN
C) H2C=CH-C6H5
D)
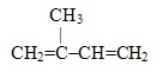
E)
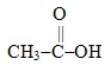

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Acrylonitrile results from the polymerization of
A)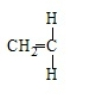
B)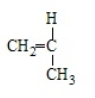
C)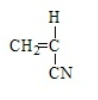
D)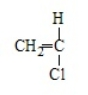
E)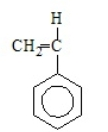
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which statement is false concerning a Natta-Ziegler catalyst
A) A Natta-Ziegler catalyst can be used to promote a polymerization that is selective for isotactic or syndiotactic polymer.
B) A Natta-Ziegler catalyst containing [Al(C2H5)3] and TiCl3 can be used to promote the formation of specific isomers in a polymerization.
C) A Natta-Ziegler catalyst is used to make a polymerization thermodynamically favorable.
D)A Natta-Ziegler catalyst has been used by chemists to design polymers with different properties.
A) A Natta-Ziegler catalyst can be used to promote a polymerization that is selective for isotactic or syndiotactic polymer.
B) A Natta-Ziegler catalyst containing [Al(C2H5)3] and TiCl3 can be used to promote the formation of specific isomers in a polymerization.
C) A Natta-Ziegler catalyst is used to make a polymerization thermodynamically favorable.
D)A Natta-Ziegler catalyst has been used by chemists to design polymers with different properties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The polymer formed from the monomer CH2=CH-CN is
A)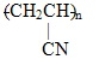
B) (CH2=CHCN)n
C) (CH2=CH=CN)n
D)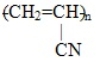
A)

B) (CH2=CHCN)n
C) (CH2=CH=CN)n
D)
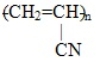

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Polystyrene results from the polymerization of
A)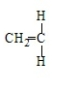
B)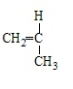
C)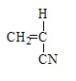
D)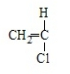
E)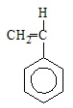
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which one of these materials is a copolymer
A) Styrene-butadiene
B) polyvinyl chloride
C) polypropylene
D) poly-cis-isoprene
E) polyethylene
A) Styrene-butadiene
B) polyvinyl chloride
C) polypropylene
D) poly-cis-isoprene
E) polyethylene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Phosphorus is an essential mineral element. It is an important atom in which one of the following
A) amino acids
B) proteins
C) polyethylene
D) nylon
E) DNA
A) amino acids
B) proteins
C) polyethylene
D) nylon
E) DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An amino acid is a compound that contains at least
A) one amino group and one amide group.
B) two amino groups and one carboxylic acid group.
C) one hydroxyl group and one methyl group.
D) one carboxylic acid group and one amino group.
E) one methyl group and one amide group.
A) one amino group and one amide group.
B) two amino groups and one carboxylic acid group.
C) one hydroxyl group and one methyl group.
D) one carboxylic acid group and one amino group.
E) one methyl group and one amide group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The backbone of a strand of nucleic acid consists of
A) phosphate units only.
B) phosphate and sugar units.
C) polyester.
D) phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base units.
E) sugar units only.
A) phosphate units only.
B) phosphate and sugar units.
C) polyester.
D) phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base units.
E) sugar units only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Cysteine and methionine are unique among the twenty essential amino acids in that they
A) are chiral.
B) contain an aromatic ring.
C) do not form dipolar ions.
D) contain sulfur.
E) cannot join with other amino acids to form peptides.
A) are chiral.
B) contain an aromatic ring.
C) do not form dipolar ions.
D) contain sulfur.
E) cannot join with other amino acids to form peptides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements about the binding of oxygen to deoxyhemoglobin is correct
A) The binding of oxygen to Fe2+ in the first heme pulls the iron ion into the porphyrin ring, decreasing the affinity for the second oxygen.
B) The binding of oxygen to Fe2+ in the first heme pushes the iron ion out of the porphyrin ring, decreasing the affinity for the second oxygen.
C) The binding of oxygen to Fe2+ in the first heme pulls the iron ion into the porphyrin ring, increasing the affinity for the second oxygen.
D) The binding of oxygen to Fe2+ in the first heme pushes the iron ion out of the porphyrin ring, increasing the affinity for the second oxygen.
E) Oxygen does not bind to deoxyhemoglobin.
A) The binding of oxygen to Fe2+ in the first heme pulls the iron ion into the porphyrin ring, decreasing the affinity for the second oxygen.
B) The binding of oxygen to Fe2+ in the first heme pushes the iron ion out of the porphyrin ring, decreasing the affinity for the second oxygen.
C) The binding of oxygen to Fe2+ in the first heme pulls the iron ion into the porphyrin ring, increasing the affinity for the second oxygen.
D) The binding of oxygen to Fe2+ in the first heme pushes the iron ion out of the porphyrin ring, increasing the affinity for the second oxygen.
E) Oxygen does not bind to deoxyhemoglobin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Proteins occurring in the b-pleated sheet structure
A) are relatively inelastic.
B) never occur in nature.
C) produce structurally weak materials.
D) contain no peptide bonds.
E) are not involved in hydrogen bonds.
A) are relatively inelastic.
B) never occur in nature.
C) produce structurally weak materials.
D) contain no peptide bonds.
E) are not involved in hydrogen bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
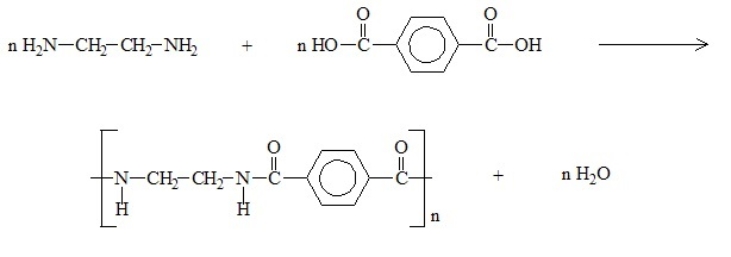
27
The reaction of the diamine and di-carboxylic acid shown below produces nylon polymer. The correct structure for the repeating unit of the nylon polymer follows the arrow. 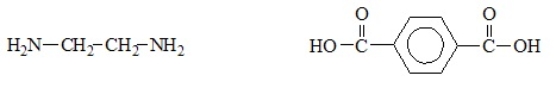
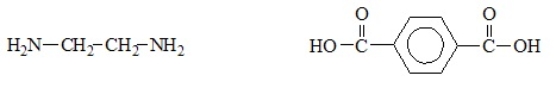


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The secondary structure of a protein is the
A) configuration of those parts of the chain stabilized by a regular pattern of covalent bonds between C and O groups of the backbone of the chain.
B) configuration of those parts of the chain stabilized by a regular pattern of hydrogen bonds between CO and NH groups of the backbone of the chain.
C) specific order of amino acids in the chain.
D) overall three-dimensional structure of the molecule.
E) overall arrangement of several polypeptide chains into one functional unit.
A) configuration of those parts of the chain stabilized by a regular pattern of covalent bonds between C and O groups of the backbone of the chain.
B) configuration of those parts of the chain stabilized by a regular pattern of hydrogen bonds between CO and NH groups of the backbone of the chain.
C) specific order of amino acids in the chain.
D) overall three-dimensional structure of the molecule.
E) overall arrangement of several polypeptide chains into one functional unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which choice lists both the sugar and the nitrogen base that are a part of RNA but are not part of DNA
A) deoxyribose and thymine
B) ribose and deoxyribose
C) ribose and uracil
D) uracil and thymine
E) ribose and thymine
A) deoxyribose and thymine
B) ribose and deoxyribose
C) ribose and uracil
D) uracil and thymine
E) ribose and thymine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A peptide bond (also called an amide bond) joins two amino acids together. What atoms are linked by this bond
A) C - O
B) C - H
C) C - N
D) N - S
E) S - C
A) C - O
B) C - H
C) C - N
D) N - S
E) S - C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The functional group 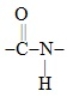 found in proteins is called a (an)
found in proteins is called a (an)
A) amide.
B) carboxylic acid.
C) amine.
D) amino acid.
E) dipeptide.
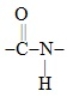 found in proteins is called a (an)
found in proteins is called a (an)A) amide.
B) carboxylic acid.
C) amine.
D) amino acid.
E) dipeptide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The intermolecular force between bases on the opposite strands of DNA responsible for its double-helical structure is
A) hydrogen bonding..
B) dispersion force..
C) covalent bonding.
D) ionic force
E) dipole-dipole force
A) hydrogen bonding..
B) dispersion force..
C) covalent bonding.
D) ionic force
E) dipole-dipole force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which choice contains all three molecular units found in nucleotides
A) phosphate, sugar, amino acid
B) amino acid, nitrogen-containing base, sugar
C) carboxylic acid, sugar, protein
D) phosphate, nitrogen-containing base, sugar
E) sugar, amino acid, protein
A) phosphate, sugar, amino acid
B) amino acid, nitrogen-containing base, sugar
C) carboxylic acid, sugar, protein
D) phosphate, nitrogen-containing base, sugar
E) sugar, amino acid, protein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An essential amino acid is one that
A) must be included in the diet.
B) contains no sulfur.
C) occurs in all types of proteins.
D) is necessary for vitamin production.
E) the body can synthesize.
A) must be included in the diet.
B) contains no sulfur.
C) occurs in all types of proteins.
D) is necessary for vitamin production.
E) the body can synthesize.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which one of these choices is the general structural formula of an amino acid
A)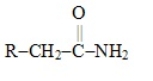
B) R-CH2-NH2
C)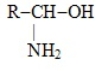
D)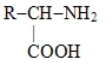
A)
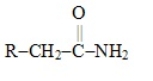
B) R-CH2-NH2
C)
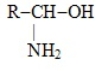
D)
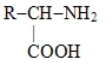

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which one of these molecules is part of the make-up of both DNA and RNA
A) deoxyribose
B) ribose
C) phosphate
D) thymine
E) uracil
A) deoxyribose
B) ribose
C) phosphate
D) thymine
E) uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of these molecules is a product of the hydrolysis of DNA
A) acetic acid
B) glucose
C) adenine
D) ribose
E) water
A) acetic acid
B) glucose
C) adenine
D) ribose
E) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which nitrogen base is found in RNA but not in DNA
A) adenine
B) cytosine
C) guanine
D) thymine
E) uracil
A) adenine
B) cytosine
C) guanine
D) thymine
E) uracil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Amides are synthesized from two classes of organic compounds. Those two types of compounds are
A) carboxylic acids and alkenes.
B) amines and alcohols.
C) alcohols and carboxylic acids.
D) amines and carboxylic acids..
E) alkenes and amines.
A) carboxylic acids and alkenes.
B) amines and alcohols.
C) alcohols and carboxylic acids.
D) amines and carboxylic acids..
E) alkenes and amines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A protein that has been reversibly denatured has
A) temporarily lost part or all of its secondary or tertiary structure.
B) temporarily lost part or all of its primary structure.
C) been genetically modified due to errors in the nucleotides in the parent DNA.
D) temporarily lost its amino acid residues.
E) temporarily lost the hydrogen bonding between nitrogenous bases.
A) temporarily lost part or all of its secondary or tertiary structure.
B) temporarily lost part or all of its primary structure.
C) been genetically modified due to errors in the nucleotides in the parent DNA.
D) temporarily lost its amino acid residues.
E) temporarily lost the hydrogen bonding between nitrogenous bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Both DNA and RNA have double-helical structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A portion of the polymer Teflon is shown here. The monomer that would be used to produce this polymer would consist of one carbon and two fluorine atoms.polymer (Teflon): 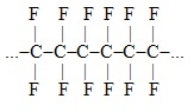


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The primary structure of a protein refers to the unique amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The monomer used to prepare polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is CHCl=CHCl.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The following amino acids all have nonpolar side chains. 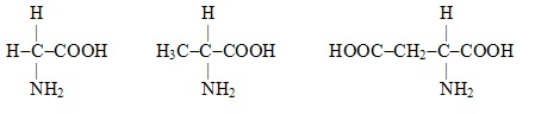
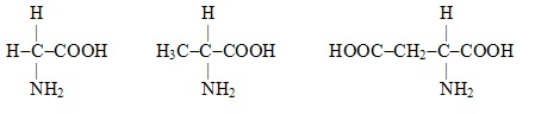

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Hydrogen bonding, dispersion forces, ionic forces, and dipole-dipole forces all affect the structure of a protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



