Deck 6: Markets, Maximizers, and Efficiency
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/239
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Markets, Maximizers, and Efficiency
1
According to the marginal decision rule, if marginal benefit:
A) exceeds marginal cost, an activity should be reduced.
B) is less than marginal cost, an activity should be reduced.
C) is equal to marginal cost, an activity should be reduced.
D) exceeds marginal cost, net benefit is maximized.
A) exceeds marginal cost, an activity should be reduced.
B) is less than marginal cost, an activity should be reduced.
C) is equal to marginal cost, an activity should be reduced.
D) exceeds marginal cost, net benefit is maximized.
is less than marginal cost, an activity should be reduced.
2
Economists assume that consumers seek to maximize:
A) usefulness.
B) profit.
C) utility.
D) time.
A) usefulness.
B) profit.
C) utility.
D) time.
utility.
3
The amount by which an additional unit of an activity increases total cost is:
A) net benefit.
B) marginal benefit.
C) negative benefit.
D) marginal cost.
A) net benefit.
B) marginal benefit.
C) negative benefit.
D) marginal cost.
marginal cost.
4
To say that individuals maximize is illustrated by saying:
A) they pick some objective and then seek to make the value of that objective as great as they can.
B) a sprinter wants to be as fast as possible.
C) a businessperson wants to earn the highest level of profit attainable.
D) all of the above.
A) they pick some objective and then seek to make the value of that objective as great as they can.
B) a sprinter wants to be as fast as possible.
C) a businessperson wants to earn the highest level of profit attainable.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Profit is the difference between _______ and _______ .
A) total sales; total revenues
B) total profits; total costs
C) total revenues; total costs
D) marginal costs; marginal revenues
A) total sales; total revenues
B) total profits; total costs
C) total revenues; total costs
D) marginal costs; marginal revenues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
According to the marginal decision rule, if marginal benefit:
A) exceeds marginal cost, an activity should be reduced.
B) is less than marginal cost, an activity should be increased.
C) is equal to marginal cost, net benefit is maximized.
D) exceeds marginal cost, net benefit is maximized.
A) exceeds marginal cost, an activity should be reduced.
B) is less than marginal cost, an activity should be increased.
C) is equal to marginal cost, net benefit is maximized.
D) exceeds marginal cost, net benefit is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A boundary that limits the range of choices an individual or a firm can make is:
A) a constraint.
B) utility.
C) a maximum.
D) a minimum.
A) a constraint.
B) utility.
C) a maximum.
D) a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Profit is the:
A) difference between a firm's total revenue and its total economic cost.
B) satisfaction consumers derive from their consumption of goods and services.
C) highest price that buyers are willing to pay for a given quantity of a good.
D) lowest price that sellers are willing to accept for a given quantity of a good.
A) difference between a firm's total revenue and its total economic cost.
B) satisfaction consumers derive from their consumption of goods and services.
C) highest price that buyers are willing to pay for a given quantity of a good.
D) lowest price that sellers are willing to accept for a given quantity of a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the price of popcorn is $0.50 per box and the price of peanuts is $0.25 per bag, and you have $5 to spend on both goods, the maximum quantity of peanuts that you can purchase is _______ bags.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The difference between a firm's total revenue and its total economic cost is:
A) production.
B) utility.
C) efficiency.
D) profit.
A) production.
B) utility.
C) efficiency.
D) profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the price of popcorn is $0.50 per box and the price of peanuts is $0.25 per bag, and you have $5 to spend on both goods, the maximum quantity of popcorn that you can purchase is _______ boxes.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The amount by which an additional unit of an activity increases total benefit is:
A) net benefit.
B) marginal benefit.
C) marginal cost.
D) utility.
A) net benefit.
B) marginal benefit.
C) marginal cost.
D) utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The total benefit of an activity minus its total cost is:
A) net benefit.
B) marginal benefit.
C) marginal cost.
D) utility.
A) net benefit.
B) marginal benefit.
C) marginal cost.
D) utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Economists assume that firms seek to maximize:
A) sales.
B) profits.
C) costs.
D) all of the above.
A) sales.
B) profits.
C) costs.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If the price of popcorn is $0.50 per box and the price of peanuts is $0.25 per bag, and you have $10 to spend on both goods, the maximum quantity of peanuts that you can purchase is _______ bags.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The satisfaction consumers derive from their consumption of goods and services is:
A) utility.
B) production.
C) efficiency.
D) profit.
A) utility.
B) production.
C) efficiency.
D) profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Utility is the:
A) difference between a firm's total revenue and its total economic cost.
B) good not adequately provided by a free market and usually provided by the government.
C) satisfaction consumers derive from their consumption of goods and services.
D) lowest price that buyers are willing to pay for a given quantity of a good.
A) difference between a firm's total revenue and its total economic cost.
B) good not adequately provided by a free market and usually provided by the government.
C) satisfaction consumers derive from their consumption of goods and services.
D) lowest price that buyers are willing to pay for a given quantity of a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the price of popcorn is $0.50 per box and the price of peanuts is $0.25 per bag, and you have $10 to spend on both goods, the maximum quantity of popcorn that you can purchase is _______ boxes.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the marginal decision rule, if marginal benefit:
A) exceeds marginal cost, an activity should be increased.
B) is less than marginal cost, an activity should be increased.
C) is equal to marginal cost, an activity should be increased.
D) exceeds marginal cost, net benefit is maximized.
A) exceeds marginal cost, an activity should be increased.
B) is less than marginal cost, an activity should be increased.
C) is equal to marginal cost, an activity should be increased.
D) exceeds marginal cost, net benefit is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the price of popcorn is $0.50 per box and the price of peanuts is $0.25 per bag, and you have $10 to spend and decide to purchase 8 bags of peanuts, the maximum quantity of popcorn that you can purchase is _______ boxes.
A) 4
B) 8
C) 10
D) 16
A) 4
B) 8
C) 10
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the price of popcorn is $0.50 per box and the price of peanuts is $0.25 per bag, and you have $5 to spend and decide to purchase 8 boxes of popcorn, the maximum quantity of peanuts that you can purchase is _______ bags.
A) 4
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12
A) 4
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Use the following to answer question(s): Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs
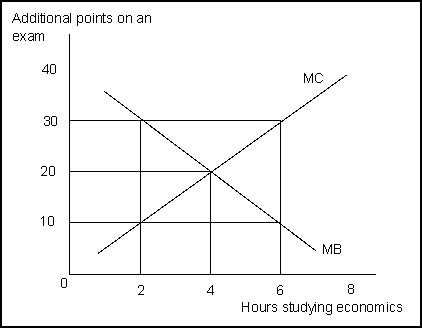
(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) In the exhibit, more time spent studying economics adds points to economics scores but subtracts points from accounting scores.When the student studies economics for 4 hours, the marginal benefit is _______ ; when the student studies for 6 hours, the marginal benefit is _______.
A) 20; 10
B) 30; 10
C) 20; 0
D) 20; 30

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) In the exhibit, more time spent studying economics adds points to economics scores but subtracts points from accounting scores.When the student studies economics for 4 hours, the marginal benefit is _______ ; when the student studies for 6 hours, the marginal benefit is _______.
A) 20; 10
B) 30; 10
C) 20; 0
D) 20; 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The costs economists use in the concept of economic profit are:
A) accounting costs.
B) strictly dollar costs, not opportunity costs.
C) opportunity costs, or the value of the best opportunity forgone.
D) both A and C.
A) accounting costs.
B) strictly dollar costs, not opportunity costs.
C) opportunity costs, or the value of the best opportunity forgone.
D) both A and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Activities of consumers and firms:
A) have benefits but not costs.
B) have costs but not benefits.
C) have both costs and benefits.
D) are too complex to be analyzed with economic theory.
A) have benefits but not costs.
B) have costs but not benefits.
C) have both costs and benefits.
D) are too complex to be analyzed with economic theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Use the following to answer question(s): Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) The marginal benefit of studying economics when the student is at 4 hours is _______ points and the marginal cost is ________ points.
A) 30; 30
B) 20; 10
C) 20; 20
D) 30; 10

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) The marginal benefit of studying economics when the student is at 4 hours is _______ points and the marginal cost is ________ points.
A) 30; 30
B) 20; 10
C) 20; 20
D) 30; 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose that the expected exam scores from studying economics for 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours are 65, 80, 90, and 95 points, respectively, while the expected exam scores for studying 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours of accounting are 50, 65, 70, and 70 points, respectively.With 3 total hours of study time, your combined scores can be maximized by spending _______ hours studying accounting.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The _______ is the amount by which an additional unit of an activity increases its total benefit.
A) average benefit
B) net benefit
C) marginal benefit
D) top benefit
A) average benefit
B) net benefit
C) marginal benefit
D) top benefit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following to answer question(s): Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) In the exhibit, more time spent studying economics adds points to economics scores but subtracts points from accounting scores.The student in this example would maximize net benefits by studying economics for _______ hours.
A) 0
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) In the exhibit, more time spent studying economics adds points to economics scores but subtracts points from accounting scores.The student in this example would maximize net benefits by studying economics for _______ hours.
A) 0
B) 2
C) 4
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Use the following to answer question(s): Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) In the exhibit, more time spent studying economics adds points to economics scores but subtracts points from accounting scores.At 4 hours of study the student will "maximize" because:
A) MB = MC.
B) MB = 20 and MC = 20.
C) the difference between total benefits and total costs is maximized.
D) of all of the above.

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) In the exhibit, more time spent studying economics adds points to economics scores but subtracts points from accounting scores.At 4 hours of study the student will "maximize" because:
A) MB = MC.
B) MB = 20 and MC = 20.
C) the difference between total benefits and total costs is maximized.
D) of all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Use the following to answer question(s): Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) In the exhibit, more time spent studying economics adds points to economics scores but subtracts points from accounting scores.The marginal benefit of studying economics when the student is at 2 hours is _______ points and the marginal cost is _______ points.
A) 40; 0
B) 30; 10
C) 20; 20
D) 10; 30

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefits and Marginal Costs) In the exhibit, more time spent studying economics adds points to economics scores but subtracts points from accounting scores.The marginal benefit of studying economics when the student is at 2 hours is _______ points and the marginal cost is _______ points.
A) 40; 0
B) 30; 10
C) 20; 20
D) 10; 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In economics the assumption is made that consumers and firms will make choices that maximize(s) the _______ of each activity.
A) net benefit
B) total benefit
C) sum of total benefit and total cost
D) product of total benefit and total cost
A) net benefit
B) total benefit
C) sum of total benefit and total cost
D) product of total benefit and total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In order to maximize net benefit, consumers and firms evaluate each activity at the:
A) average.
B) top.
C) margin.
D) end.
A) average.
B) top.
C) margin.
D) end.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
To determine the quantity of any activity that will maximize net benefit, economists employ the ________ rule.
A) average decision
B) total decision
C) net decision
D) marginal decision
A) average decision
B) total decision
C) net decision
D) marginal decision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Maximization of the net benefit of an activity occurs when:
A) MB = MC.
B) MB > MC.
C) MB < MC.
D) MB approaches MC.
A) MB = MC.
B) MB > MC.
C) MB < MC.
D) MB approaches MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the price of popcorn is $0.50 per box and the price of peanuts is $0.25 per bag, and you have $5 to spend and decide to purchase 6 boxes of popcorn, the maximum quantity of peanuts that you can purchase is _______ bags.
A) 4
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12
A) 4
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Net benefit is maximized when marginal benefit _______ marginal cost.
A) exceeds
B) is less than
C) is equal to
D) approaches
A) exceeds
B) is less than
C) is equal to
D) approaches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Suppose that the expected exam scores from studying economics for 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours are 65, 80, 90, and 95 points, respectively, while the expected exam scores for studying 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours of accounting are 50, 65, 70, and 70 points, respectively.With 3 total hours of study time, your combined scores can be maximized by spending _______ hours studying economics.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the price of popcorn is $0.50 per box and the price of peanuts is $0.25 per bag, and you have $10 to spend and decide to purchase 20 bags of peanuts, the maximum quantity of popcorn that you can purchase is _______ boxes.
A) 8
B) 10
C) 12
D) 16
A) 8
B) 10
C) 12
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The _______ is the amount by which an additional unit of activity increases its cost.
A) marginal cost
B) average cost
C) average profit
D) marginal benefit
A) marginal cost
B) average cost
C) average profit
D) marginal benefit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Maximizing choices must be made within parameters imposed by:
A) a constraint.
B) a boundary.
C) a limit.
D) all of the above.
A) a constraint.
B) a boundary.
C) a limit.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the marginal benefit received from a good is less than the marginal cost of production, then:
A) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
B) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
C) the market is producing too much of the good.
D) the market is producing too little of the good.
A) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
B) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
C) the market is producing too much of the good.
D) the market is producing too little of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following for questions 55-59.
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit
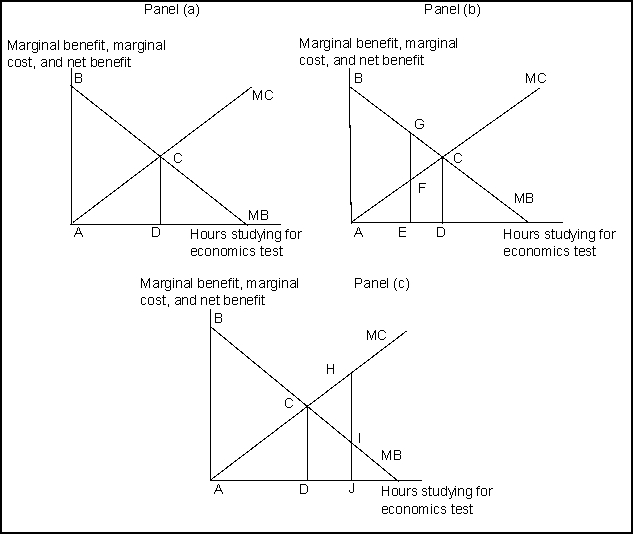
(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (b) at activity level E, _______ , and in Panel (c) at activity level J, _______ .
A) MB < MC; MB < MC
B) MB > MC; MB < MC
C) net benefit is ABGF; net benefit is ABC.
D) there is no deadweight loss; deadweight loss is CHI
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (b) at activity level E, _______ , and in Panel (c) at activity level J, _______ .
A) MB < MC; MB < MC
B) MB > MC; MB < MC
C) net benefit is ABGF; net benefit is ABC.
D) there is no deadweight loss; deadweight loss is CHI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the marginal benefit received from a good is greater than the marginal cost of production, then:
A) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
B) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
C) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
D) the market is producing too much of the good.
A) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
B) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
C) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
D) the market is producing too much of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Whenever MB = MC, the decisionmaker should do _______ of the activity.
A) less
B) the same amount
C) more
D) none
A) less
B) the same amount
C) more
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose that the expected exam scores from studying economics for 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours are 65, 80, 90, and 95 points, respectively, while the expected exam scores for studying 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours of accounting are 50, 65, 70, and 70 points, respectively.With 3 total hours of study time, the marginal benefit in terms of your economics score of spending the first hour studying economics is _______ points.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20
A) 5
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the marginal benefit received from a good is equal to the marginal cost of production, then:
A) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
B) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
C) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
D) the market is producing too much of the good.
A) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
B) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
C) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
D) the market is producing too much of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the following for questions 55-59.
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (a), the maximum net benefit is shown:
A) where the level of activity is at D.
B) by the intersection of MB and MC.
C) by the area of triangle ABC.
D) in all of the above cases.
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (a), the maximum net benefit is shown:
A) where the level of activity is at D.
B) by the intersection of MB and MC.
C) by the area of triangle ABC.
D) in all of the above cases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the marginal benefit received from a good is greater than the marginal cost of production, then:
A) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
B) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
C) the market is producing too much of the good.
D) the market is producing too little of the good.
A) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
B) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
C) the market is producing too much of the good.
D) the market is producing too little of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the following for questions 55-59.
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (b), if the activity level is at E, then there will be a deadweight loss shown by the area:
A) EGC.
B) FGC.
C) ABC.
D) AFE.
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (b), if the activity level is at E, then there will be a deadweight loss shown by the area:
A) EGC.
B) FGC.
C) ABC.
D) AFE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the marginal benefit received from a good is less than the marginal cost of production, then:
A) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
B) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
C) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
D) the market is producing too little of the good.
A) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
B) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
C) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
D) the market is producing too little of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An economist might say that the United States doesn't have enough oil spills in its rivers if it were determined that:
A) fewer than 1 million fish were being killed by oil spills each year.
B) the marginal benefits of more oil pollution in the river outweighed the marginal cost of preventing or cleaning up the oil spill pollution.
C) the marginal benefits of less oil pollution in the river were less than the marginal cost of reducing the amount of oil spilled at that level.
D) both B and C would lead an economist to that conclusion.
A) fewer than 1 million fish were being killed by oil spills each year.
B) the marginal benefits of more oil pollution in the river outweighed the marginal cost of preventing or cleaning up the oil spill pollution.
C) the marginal benefits of less oil pollution in the river were less than the marginal cost of reducing the amount of oil spilled at that level.
D) both B and C would lead an economist to that conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the marginal benefit received from a good is equal to the marginal cost of production, then:
A) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
B) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
C) the market is producing too much of the good.
D) the market is producing an efficient quantity.
A) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
B) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
C) the market is producing too much of the good.
D) the market is producing an efficient quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Use the following for questions 55-59.
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (b), if activity is restricted to activity level E, the net benefit will be shown by the area:
A) ABGF.
B) ABCD.
C) AEFG.
D) ABC.
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (b), if activity is restricted to activity level E, the net benefit will be shown by the area:
A) ABGF.
B) ABCD.
C) AEFG.
D) ABC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the following for questions 55-59.
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (c), if activity level is at J, then there will be a deadweight loss of _______ and a net benefit of _______ .
A) CHI; ABC
B) ABC; CHI.
C) CHI; ABC minus CHI.
D) ABC minus CHI; CHI.
Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit

(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (c), if activity level is at J, then there will be a deadweight loss of _______ and a net benefit of _______ .
A) CHI; ABC
B) ABC; CHI.
C) CHI; ABC minus CHI.
D) ABC minus CHI; CHI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Whenever MB < MC, the decisionmaker should do _______ of the activity.
A) less
B) the same amount
C) more
D) none
A) less
B) the same amount
C) more
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Suppose that the expected exam scores from studying economics for 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours are 65, 80, 90, and 95 points, respectively, while the expected exam scores for studying 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours of accounting are 50, 65, 70, and 70 points, respectively.With 3 total hours of study time, your combined scores can reach a maximum of _______ points.
A) 145
B) 150
C) 155
D) 165
A) 145
B) 150
C) 155
D) 165

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Net benefit can be maximized by equating:
A) total benefit to total cost.
B) marginal benefit to marginal cost.
C) marginal benefit to total cost.
D) total benefit to marginal cost.
A) total benefit to total cost.
B) marginal benefit to marginal cost.
C) marginal benefit to total cost.
D) total benefit to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Whenever MB > MC, the decisionmaker should do _______ of the activity.
A) less
B) the same amount
C) more
D) none
A) less
B) the same amount
C) more
D) none

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose that the expected exam scores from studying economics for 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours are 65, 80, 90, and 95 points, respectively, while the expected exam scores for studying 0, 1, 2, or 3 hours of accounting are 50, 65, 70, and 70 points, respectively.With 3 total hours of study time, the opportunity (or marginal) cost in terms of your accounting score of spending the first hour studying economics is ________ points.
A) 0
B) 5
C) 10
D) 15
A) 0
B) 5
C) 10
D) 15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Net benefit can be maximized by finding the greatest difference between:
A) total benefit and total cost.
B) marginal benefit and marginal cost.
C) marginal benefit and total cost.
D) total benefit and marginal cost.
A) total benefit and total cost.
B) marginal benefit and marginal cost.
C) marginal benefit and total cost.
D) total benefit and marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following to answer question(s): Markets and Efficiency
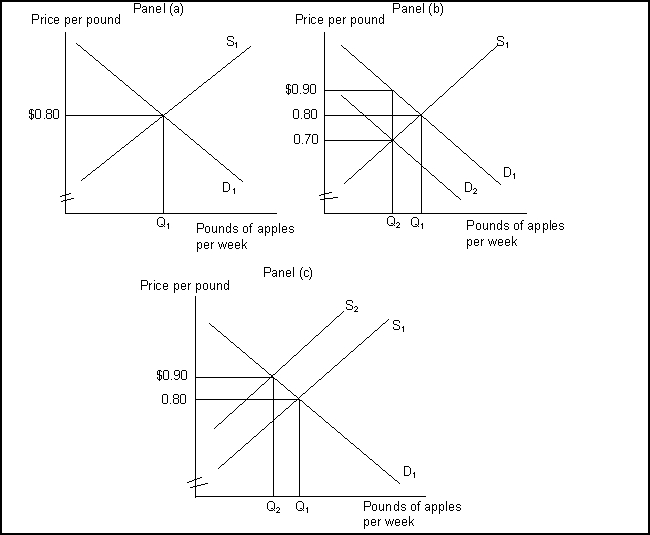
(Exhibit: Markets and Efficiency) The equilibrium price in Panel (a) tells us that the marginal cost of a pound of apples is:
A) less than $0.80.
B) equal to $0.80.
C) greater than $0.80.
D) equal to the average cost of producing apples.

(Exhibit: Markets and Efficiency) The equilibrium price in Panel (a) tells us that the marginal cost of a pound of apples is:
A) less than $0.80.
B) equal to $0.80.
C) greater than $0.80.
D) equal to the average cost of producing apples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The Case in Point on Preventing Oil Spills stated that an economist who studied the costs and benefits of preventing oil spills in coastal waters and rivers concluded that:
A) the marginal cost of preventing oil spills was greater than the marginal benefit and the U.S.Coast Guard could not justify its excessive prevention efforts.
B) The marginal cost of preventing oil spills was less than the marginal benefit and that the U.S.Cost Guard could justify even greater efforts at preventing them.
C) that oil spills are so terrible and have such a pervasively destructive impact on the coastal waters and rivers that they should be prevented entirely-no oil spills should be tolerated.
D) both B and C were conclusions reached by the economist.
A) the marginal cost of preventing oil spills was greater than the marginal benefit and the U.S.Coast Guard could not justify its excessive prevention efforts.
B) The marginal cost of preventing oil spills was less than the marginal benefit and that the U.S.Cost Guard could justify even greater efforts at preventing them.
C) that oil spills are so terrible and have such a pervasively destructive impact on the coastal waters and rivers that they should be prevented entirely-no oil spills should be tolerated.
D) both B and C were conclusions reached by the economist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When the net benefits of all economic activities are not maximized, economists say the allocation of resources is _______ .
A) inefficient
B) incorrect
C) efficient
D) poorly done
A) inefficient
B) incorrect
C) efficient
D) poorly done

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The Case in Point on gift giving suggests that gifts from _____ generated the most satisfaction per dollar spent.
A) friends
B) significant others
C) grandparents
D) parents
A) friends
B) significant others
C) grandparents
D) parents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A set of rules that specify the ways in which the resource for which they are defined may be used are:
A) public goods.
B) quasi-public goods.
C) property rights.
D) free-rider rights.
A) public goods.
B) quasi-public goods.
C) property rights.
D) free-rider rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Property rights are defined as a set of rules that:
A) specify how consumers buy a product.
B) allows owners to use their property any way they choose.
C) determine the value of property.
D) specify the ways in which an owner can use a resource.
A) specify how consumers buy a product.
B) allows owners to use their property any way they choose.
C) determine the value of property.
D) specify the ways in which an owner can use a resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer question(s): Markets and Efficiency

(Exhibit: Markets and Efficiency) In panel (a):
A) the price of apples is $0.80 and the quantity demanded is Q₁.
B) the equilibrium price ensures that quantity demanded will match quantity supplied.
C) the equilibrium price ensures that there will be neither surpluses nor shortages.
D) all of the above are true.

(Exhibit: Markets and Efficiency) In panel (a):
A) the price of apples is $0.80 and the quantity demanded is Q₁.
B) the equilibrium price ensures that quantity demanded will match quantity supplied.
C) the equilibrium price ensures that there will be neither surpluses nor shortages.
D) all of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
To be effective, property rights must be:
A) exclusive and transferable.
B) free and quasi-public.
C) constrained and marginal.
D) all of the above.
A) exclusive and transferable.
B) free and quasi-public.
C) constrained and marginal.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Based on the type of analysis described in the Case in Point on Preventing Oil Spills, an economist might reasonably argue that too few people die in airplane crashes if:
A) the marginal cost of preventing airplane crashes was less than the marginal benefit of preventing them.
B) the marginal benefit of preventing airplane crashes was less than the marginal cost of preventing them.
C) he or she were nuts; no reasonable economist would make such a statement because even though zero airplane crashes are an unlikely outcome, the efforts to prevent them to the greatest extent possible are justified because human lives are at stake.
D) both A and B are true.
A) the marginal cost of preventing airplane crashes was less than the marginal benefit of preventing them.
B) the marginal benefit of preventing airplane crashes was less than the marginal cost of preventing them.
C) he or she were nuts; no reasonable economist would make such a statement because even though zero airplane crashes are an unlikely outcome, the efforts to prevent them to the greatest extent possible are justified because human lives are at stake.
D) both A and B are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The efficiency condition requires:
A) marginal costs be generally less than marginal benefits.
B) prices in the marketplace confront decision makers with the marginal benefits and marginal costs of their decisions.
C) more goods be produced than exchanged.
D) more goods be exchanged than produced.
A) marginal costs be generally less than marginal benefits.
B) prices in the marketplace confront decision makers with the marginal benefits and marginal costs of their decisions.
C) more goods be produced than exchanged.
D) more goods be exchanged than produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer question(s): Markets and Efficiency

(Exhibit: Markets and Efficiency) The price and marginal cost in Panel(a) are equal because of:
A) the marginal decision rule.
B) the law of demand.
C) the law of supply.
D) the law of increasing cost.

(Exhibit: Markets and Efficiency) The price and marginal cost in Panel(a) are equal because of:
A) the marginal decision rule.
B) the law of demand.
C) the law of supply.
D) the law of increasing cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
An allocation of resources that achieves the maximum net benefit from all activities is:
A) inefficient.
B) external.
C) internal.
D) efficient.
A) inefficient.
B) external.
C) internal.
D) efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements is (are) true?
A) A system of property rights forms the basis for all market exchange.
B) A system of property rights is essential to an efficient allocation of resources.
C) Property rights must exist if market exchange is to occur.
D) All of the above are true.
A) A system of property rights forms the basis for all market exchange.
B) A system of property rights is essential to an efficient allocation of resources.
C) Property rights must exist if market exchange is to occur.
D) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When we judge the performance of the economy, we must consider:
A) efficiency.
B) external costs and external benefits.
C) equity and value judgments.
D) all of the above.
A) efficiency.
B) external costs and external benefits.
C) equity and value judgments.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The market for apples achieves an efficient allocation of resources when prices respond and send signals to producers and consumers.That set of interactions requires that producers possess:
A) lobby access to government.
B) monopoly power.
C) property rights to the apples they grow.
D) the ability to set any price they choose for their apples.
A) lobby access to government.
B) monopoly power.
C) property rights to the apples they grow.
D) the ability to set any price they choose for their apples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The Case in Point on gift giving suggests that:
A) when you buy something for yourself, the price you pay is at least equal to the value of the satisfaction you derive from the item.
B) gift giving creates a significant deadweight loss.
C) the frequency of contact between giver and receiver increases the yield of the gift.
D) all of the above are true.
A) when you buy something for yourself, the price you pay is at least equal to the value of the satisfaction you derive from the item.
B) gift giving creates a significant deadweight loss.
C) the frequency of contact between giver and receiver increases the yield of the gift.
D) all of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
An allocation of resources that does not achieve the maximum net benefit from one or more activities is:
A) inefficient.
B) external.
C) internal.
D) efficient.
A) inefficient.
B) external.
C) internal.
D) efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An exclusive property right is one that:
A) lets anyone use a resource without cost to society.
B) allows its owners to prevent others from using a resource.
C) equates marginal benefits to marginal costs.
D) can be sold or leased to someone else.
A) lets anyone use a resource without cost to society.
B) allows its owners to prevent others from using a resource.
C) equates marginal benefits to marginal costs.
D) can be sold or leased to someone else.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When the net benefits of all economic activities are maximized, economists say the allocation of resources is _______ .
A) inefficient
B) correct
C) efficient
D) well done
A) inefficient
B) correct
C) efficient
D) well done

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A transferable property right is one that:
A) can be sold or leased to someone else.
B) allows its owners to prevent others from using a resource.
C) equates marginal benefits to marginal costs.
D) lets anyone use a resource without cost to society.
A) can be sold or leased to someone else.
B) allows its owners to prevent others from using a resource.
C) equates marginal benefits to marginal costs.
D) lets anyone use a resource without cost to society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 239 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



