Deck 37: Extending the Analysis of Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 37: Extending the Analysis of Aggregate Supply
1
In the extended aggregate demand-aggregate supply model:
A) long-run equilibrium occurs wherever the aggregate demand curve intersects the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
C) the level of real output is the same in the long run regardless of the location of the aggregate demand curve.
D) the short-run aggregate supply curve is downsloping.
A) long-run equilibrium occurs wherever the aggregate demand curve intersects the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
C) the level of real output is the same in the long run regardless of the location of the aggregate demand curve.
D) the short-run aggregate supply curve is downsloping.
C
2
Suppose the full employment level of real output (Q)for a hypothetical economy is $500,the price level (P)initially is 100,and prices and wages are flexible both upward and downward.Use the following short-run aggregate supply schedules to answer the question. 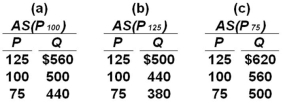 Refer to the information given.If the price level unexpectedly declines from 100 to 75,the level of real output in the short run will:
Refer to the information given.If the price level unexpectedly declines from 100 to 75,the level of real output in the short run will:
A) rise from $500 to $560.
B) fall from $500 to $440.
C) fall from $560 to $500.
D) rise from $440 to $500.
 Refer to the information given.If the price level unexpectedly declines from 100 to 75,the level of real output in the short run will:
Refer to the information given.If the price level unexpectedly declines from 100 to 75,the level of real output in the short run will:A) rise from $500 to $560.
B) fall from $500 to $440.
C) fall from $560 to $500.
D) rise from $440 to $500.
B
3
In the extended analysis of aggregate supply,the short-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) vertical and the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
B) horizontal and the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
C) upsloping and the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) horizontal and the long-run aggregate supply curve is upsloping.
A) vertical and the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
B) horizontal and the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
C) upsloping and the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) horizontal and the long-run aggregate supply curve is upsloping.
C
4
One policy dilemma posed by cost-push inflation is that:
A) an increase in aggregate demand will increase inflation and the unemployment rate simultaneously.
B) tax rates can be reduced without lowering tax revenues.
C) the reduction of aggregate demand to restrain inflation will cause a further reduction in the real GDP.
D) the adjustment of aggregate demand can neither increase real GDP nor reduce inflation.
A) an increase in aggregate demand will increase inflation and the unemployment rate simultaneously.
B) tax rates can be reduced without lowering tax revenues.
C) the reduction of aggregate demand to restrain inflation will cause a further reduction in the real GDP.
D) the adjustment of aggregate demand can neither increase real GDP nor reduce inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In terms of aggregate supply,the difference between the long run and the short run is that in the long run:
A) the price level is variable.
B) employment is variable.
C) real output is variable.
D) nominal wages and other input prices are fully responsive to price-level changes.
A) the price level is variable.
B) employment is variable.
C) real output is variable.
D) nominal wages and other input prices are fully responsive to price-level changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The short-run aggregate supply curve is downsloping.
B) The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
C) The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) The long-run aggregate supply curve is upsloping.
A) The short-run aggregate supply curve is downsloping.
B) The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
C) The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) The long-run aggregate supply curve is upsloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In terms of aggregate supply,a period in which nominal wages and other resource prices are fully responsive to price-level changes is called the:
A) long run.
B) short run.
C) immediate market period.
D) very long run.
A) long run.
B) short run.
C) immediate market period.
D) very long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The natural rate of unemployment:
A) can vary over time and defines the location of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B) is constant over time and defines the location of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) varies over time in response to changes in aggregate demand.
D) is inversely related to the price level.
A) can vary over time and defines the location of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
B) is constant over time and defines the location of the long-run aggregate supply curve.
C) varies over time in response to changes in aggregate demand.
D) is inversely related to the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the extended aggregate demand-aggregate supply model:
A) long-run equilibrium occurs wherever the aggregate demand curve intersects the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
C) the price level is the same regardless of the location of the aggregate demand curve.
D) long-run equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve,the short-run aggregate supply curve,and the long-run aggregate supply curve.
A) long-run equilibrium occurs wherever the aggregate demand curve intersects the short-run aggregate supply curve.
B) the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
C) the price level is the same regardless of the location of the aggregate demand curve.
D) long-run equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve,the short-run aggregate supply curve,and the long-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If government uses fiscal policy to restrain cost-push inflation,we can expect:
A) the unemployment rate to rise.
B) the unemployment rate to fall.
C) the aggregate demand curve to shift rightward.
D) tax-rate declines and increases in government spending.
A) the unemployment rate to rise.
B) the unemployment rate to fall.
C) the aggregate demand curve to shift rightward.
D) tax-rate declines and increases in government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Other things equal,the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts positions when:
A) the price level changes.
B) the rate of inflation changes.
C) nominal wages and other input prices change.
D) aggregate demand changes.
A) the price level changes.
B) the rate of inflation changes.
C) nominal wages and other input prices change.
D) aggregate demand changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical:
A) because the rate of inflation is steady in the long run.
B) because resource prices eventually rise and fall with product prices.
C) because product prices tend to increase at a faster rate than resource prices.
D) only when the money supply increases at the same rate as real GDP.
A) because the rate of inflation is steady in the long run.
B) because resource prices eventually rise and fall with product prices.
C) because product prices tend to increase at a faster rate than resource prices.
D) only when the money supply increases at the same rate as real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The short-run aggregate supply curve is upsloping because higher price levels:
A) lower interest rates and encourage firms to invest and produce more.
B) create incentives to expand output when resource prices are unresponsive to price-level changes.
C) encourage importation of foreign goods.
D) create an expectation among producers of still higher price levels.
A) lower interest rates and encourage firms to invest and produce more.
B) create incentives to expand output when resource prices are unresponsive to price-level changes.
C) encourage importation of foreign goods.
D) create an expectation among producers of still higher price levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In terms of aggregate supply,a period in which nominal wages and other resource prices are unresponsive to price-level changes is called the:
A) long run.
B) short run.
C) immediate market period.
D) very long run.
A) long run.
B) short run.
C) immediate market period.
D) very long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose the full employment level of real output (Q)for a hypothetical economy is $500,the price level (P)initially is 100,and prices and wages are flexible both upward and downward.Use the following short-run aggregate supply schedules to answer the question. 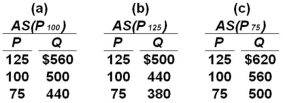 Refer to the information given.If the price level unexpectedly increases from 100 to 125,the level of real output in the short run will:
Refer to the information given.If the price level unexpectedly increases from 100 to 125,the level of real output in the short run will:
A) rise from $500 to $560.
B) fall from $500 to $440.
C) fall from $560 to $500.
D) rise from $440 to $500.
 Refer to the information given.If the price level unexpectedly increases from 100 to 125,the level of real output in the short run will:
Refer to the information given.If the price level unexpectedly increases from 100 to 125,the level of real output in the short run will:A) rise from $500 to $560.
B) fall from $500 to $440.
C) fall from $560 to $500.
D) rise from $440 to $500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose the full employment level of real output (Q)for a hypothetical economy is $500,the price level (P)initially is 100,and prices and wages are flexible both upward and downward.Use the following short-run aggregate supply schedules to answer the question. 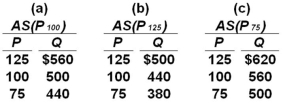 Refer to the information given.In the long run,an increase in the price level from 100 to 125 will:
Refer to the information given.In the long run,an increase in the price level from 100 to 125 will:
A) increase real output from $500 to $560.
B) decrease real output from $500 to $440.
C) change the aggregate supply schedule from (a)to (c)and result in an equilibrium level of real output of $560.
D) change the aggregate supply schedule from (a)to (b)and result in an equilibrium level of real output of $500.
 Refer to the information given.In the long run,an increase in the price level from 100 to 125 will:
Refer to the information given.In the long run,an increase in the price level from 100 to 125 will:A) increase real output from $500 to $560.
B) decrease real output from $500 to $440.
C) change the aggregate supply schedule from (a)to (c)and result in an equilibrium level of real output of $560.
D) change the aggregate supply schedule from (a)to (b)and result in an equilibrium level of real output of $500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose the full employment level of real output (Q)for a hypothetical economy is $500,the price level (P)initially is 100,and prices and wages are flexible both upward and downward.Use the following short-run aggregate supply schedules to answer the question. 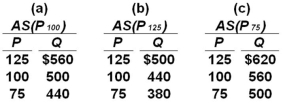 Refer to the information given.In the long run,a fall in the price level from 100 to 75 will:
Refer to the information given.In the long run,a fall in the price level from 100 to 75 will:
A) decrease real output from $500 to $440.
B) increase real output from $500 to $620.
C) change the aggregate supply schedule from (a)to (c)and produce an equilibrium level of real output of $500.
D) change the aggregate supply schedule from (a)to (b)and produce an equilibrium level of real output of $500.
 Refer to the information given.In the long run,a fall in the price level from 100 to 75 will:
Refer to the information given.In the long run,a fall in the price level from 100 to 75 will:A) decrease real output from $500 to $440.
B) increase real output from $500 to $620.
C) change the aggregate supply schedule from (a)to (c)and produce an equilibrium level of real output of $500.
D) change the aggregate supply schedule from (a)to (b)and produce an equilibrium level of real output of $500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In terms of aggregate supply,the short run is a period in which:
A) the price level is constant.
B) employment is constant.
C) real output is constant.
D) nominal wages and other resource prices are unresponsive to price-level changes.
A) the price level is constant.
B) employment is constant.
C) real output is constant.
D) nominal wages and other resource prices are unresponsive to price-level changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The level of potential output and location of the long-run aggregate supply curve are determined by:
A) Federal Reserve policy.
B) the price level.
C) the intersection of aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply.
D) the natural rate of unemployment.
A) Federal Reserve policy.
B) the price level.
C) the intersection of aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply.
D) the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Other things equal,a decrease in the price level will:
A) shift the aggregate supply curve to the left.
B) shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C) cause a movement up a short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) cause a movement down an aggregate supply curve.
A) shift the aggregate supply curve to the left.
B) shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C) cause a movement up a short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) cause a movement down an aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Inflation in the U.S.economy tends to be:
A) a finite,one-time event resulting from a shock.
B) ongoing,as increases in aggregate demand generally exceed the increases in aggregate supply.
C) a finite,one-time event as the Fed actively works to eliminate all inflation.
D) ongoing,as aggregate supply is continually shifting to the left.
A) a finite,one-time event resulting from a shock.
B) ongoing,as increases in aggregate demand generally exceed the increases in aggregate supply.
C) a finite,one-time event as the Fed actively works to eliminate all inflation.
D) ongoing,as aggregate supply is continually shifting to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Stagflation refers to:
A) an increase in inflation accompanied by decreases in real output and employment.
B) a decline in the price level accompanied by increases in real output and employment.
C) a simultaneous increase in real output and the price level.
D) a simultaneous reduction in real output and the price level.
A) an increase in inflation accompanied by decreases in real output and employment.
B) a decline in the price level accompanied by increases in real output and employment.
C) a simultaneous increase in real output and the price level.
D) a simultaneous reduction in real output and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The traditional Phillips Curve suggests a trade-off between:
A) price stability and income equality.
B) the level of unemployment and inflation.
C) unemployment and income equality.
D) economic growth and full employment.
A) price stability and income equality.
B) the level of unemployment and inflation.
C) unemployment and income equality.
D) economic growth and full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the last half of the 1990s,the usual short-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment did not arise because:
A) the Fed held interest rates constant.
B) the federal government balanced its budget.
C) the U.S.personal savings rate rose.
D) productivity (and thus aggregate supply)grew faster than previously.
A) the Fed held interest rates constant.
B) the federal government balanced its budget.
C) the U.S.personal savings rate rose.
D) productivity (and thus aggregate supply)grew faster than previously.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following allegedly contributed to the stagflation in the mid-1970s?
A) Appreciation of the dollar.
B) A sharp drop in the prices of farm products.
C) A dramatic increase in oil prices.
D) Rising productivity in manufacturing.
A) Appreciation of the dollar.
B) A sharp drop in the prices of farm products.
C) A dramatic increase in oil prices.
D) Rising productivity in manufacturing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An adverse aggregate supply shock could result from:
A) a sharp rise in productivity.
B) a rapid rise in oil prices.
C) a decline in wages.
D) an appreciation of the dollar.
A) a sharp rise in productivity.
B) a rapid rise in oil prices.
C) a decline in wages.
D) an appreciation of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The basic problem portrayed by the traditional Phillips Curve is:
A) that a level of aggregate demand sufficiently high to result in full employment may also cause inflation.
B) that changes in the composition of total labor demand tend to be deflationary.
C) that unemployment rises at the same time the general price level is rising.
D) the possibility that automation will increase the level of noncyclical unemployment.
A) that a level of aggregate demand sufficiently high to result in full employment may also cause inflation.
B) that changes in the composition of total labor demand tend to be deflationary.
C) that unemployment rises at the same time the general price level is rising.
D) the possibility that automation will increase the level of noncyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Rightward and upward shifts of the Phillips Curve in the 1970s and early 1980s were caused by:
A) adverse shocks to aggregate supply.
B) adverse shocks to aggregate demand.
C) an increase in the misery index.
D) the Vietnam War.
A) adverse shocks to aggregate supply.
B) adverse shocks to aggregate demand.
C) an increase in the misery index.
D) the Vietnam War.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose that the Consumer Price Index for a particular economy rose from 110 to 120 in year 1,120 to 130 in year 2,and 130 to 140 in year 3.We could conclude that this economy is experiencing:
A) accelerating inflation.
B) deflation.
C) disinflation.
D) a constant rate of inflation.
A) accelerating inflation.
B) deflation.
C) disinflation.
D) a constant rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Statistical data for the 1970s and 1980s suggest that:
A) the Phillips Curve was stable.
B) the Phillips Curve was unstable.
C) low levels of unemployment were consistently associated with high rates of inflation.
D) the inflation rate was highly stable.
A) the Phillips Curve was stable.
B) the Phillips Curve was unstable.
C) low levels of unemployment were consistently associated with high rates of inflation.
D) the inflation rate was highly stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The traditional Phillips Curve suggests that,if government uses an expansionary fiscal policy to stimulate output and employment:
A) unemployment may actually increase because of the crowding-out effect.
B) tax revenues may increase even though tax rates have been reduced.
C) deflation may result.
D) the natural rate of unemployment may fall.
A) unemployment may actually increase because of the crowding-out effect.
B) tax revenues may increase even though tax rates have been reduced.
C) deflation may result.
D) the natural rate of unemployment may fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If government uses its stabilization policies to maintain full employment under conditions of cost-push inflation:
A) a deflationary spiral is likely to occur.
B) an inflationary spiral is likely to occur.
C) stagflation is likely to occur.
D) the Phillips Curve is likely to shift inward.
A) a deflationary spiral is likely to occur.
B) an inflationary spiral is likely to occur.
C) stagflation is likely to occur.
D) the Phillips Curve is likely to shift inward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An adverse aggregate supply shock:
A) automatically shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward.
B) causes the Phillips Curve to shift leftward and downward.
C) can be caused by a boost in the rate of growth of productivity.
D) can cause stagflation.
A) automatically shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward.
B) causes the Phillips Curve to shift leftward and downward.
C) can be caused by a boost in the rate of growth of productivity.
D) can cause stagflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the absence of unexpected shocks,the economy will tend to experience:
A) positive,noninflationary growth.
B) no changes in output or prices.
C) positive growth with mild amounts of deflation.
D) positive growth with mild amounts of inflation.
A) positive,noninflationary growth.
B) no changes in output or prices.
C) positive growth with mild amounts of deflation.
D) positive growth with mild amounts of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The last few years of the 1990s in the United States were characterized by:
A) low inflation and high unemployment.
B) stagflation.
C) low inflation and low unemployment.
D) a high misery index.
A) low inflation and high unemployment.
B) stagflation.
C) low inflation and low unemployment.
D) a high misery index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a true statement?
A) Under normal conditions,there is a short-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) There is a long-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
C) The short-run Phillips Curve is vertical.
D) The long-run Phillips Curve is horizontal.
A) Under normal conditions,there is a short-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) There is a long-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
C) The short-run Phillips Curve is vertical.
D) The long-run Phillips Curve is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is a true statement?
A) There is a long-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) There is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the long run.
C) The short-run Phillips Curve is horizontal.
D) The long-run Phillips Curve is horizontal.
A) There is a long-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) There is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the long run.
C) The short-run Phillips Curve is horizontal.
D) The long-run Phillips Curve is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Inflation accompanied by falling real output and employment is known as:
A) Laffer's law.
B) Okun's law.
C) stagflation.
D) the Phillips Curve.
A) Laffer's law.
B) Okun's law.
C) stagflation.
D) the Phillips Curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A rightward shift of the traditional Phillips Curve would suggest that:
A) the productivity of labor increased.
B) the rate of inflation is now higher at each rate of unemployment.
C) cost-push inflation decreased.
D) the rate of inflation is now lower at each rate of unemployment.
A) the productivity of labor increased.
B) the rate of inflation is now higher at each rate of unemployment.
C) cost-push inflation decreased.
D) the rate of inflation is now lower at each rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is a true statement?
A) There is a long-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) There is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the short-run.
C) The short-run Phillips Curve is horizontal.
D) The long-run Phillips Curve is vertical.
A) There is a long-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) There is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the short-run.
C) The short-run Phillips Curve is horizontal.
D) The long-run Phillips Curve is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Disinflation occurs when:
A) the price level is falling.
B) investment plans exceed saving.
C) a speculative investment "bubble" is bursting.
D) the inflation rate is declining.
A) the price level is falling.
B) investment plans exceed saving.
C) a speculative investment "bubble" is bursting.
D) the inflation rate is declining.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left when nominal wages rise in response to price level increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Laffer Curve is a central concept in:
A) monetarism.
B) Keynesianism.
C) welfare economics.
D) supply-side economics.
A) monetarism.
B) Keynesianism.
C) welfare economics.
D) supply-side economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the extended AD-AS model,the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When the actual rate of inflation exceeds the expected rate:
A) the unemployment rate will temporarily rise.
B) firms will experience rising profits and thus increase their employment.
C) the actual rate of inflation will fall.
D) nominal wages will decline.
A) the unemployment rate will temporarily rise.
B) firms will experience rising profits and thus increase their employment.
C) the actual rate of inflation will fall.
D) nominal wages will decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A basic criticism of supply-side economics is that:
A) empirical research clearly shows that incentives to work and invest vary directly with marginal tax rates.
B) lower taxes will increase aggregate supply much more than they will increase aggregate demand.
C) lower taxes will increase aggregate demand much more than they will increase aggregate supply.
D) higher taxes will reduce incentives to work,invest,and innovate.
A) empirical research clearly shows that incentives to work and invest vary directly with marginal tax rates.
B) lower taxes will increase aggregate supply much more than they will increase aggregate demand.
C) lower taxes will increase aggregate demand much more than they will increase aggregate supply.
D) higher taxes will reduce incentives to work,invest,and innovate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
(Last Word)According to the research of Christina Romer and David Romer,tax increases implemented to reduce an inherited budget deficit:
A) reduce real output by the same amount as any other tax increase.
B) reduce real output by more than other tax increases.
C) reduce real output by less than other tax increases.
D) increase real output,contrary to what occurs with other tax increases.
A) reduce real output by the same amount as any other tax increase.
B) reduce real output by more than other tax increases.
C) reduce real output by less than other tax increases.
D) increase real output,contrary to what occurs with other tax increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When the actual rate of inflation is less than the expected rate:
A) the unemployment rate will temporarily rise.
B) firms will increase their output to recoup their falling profits.
C) the unemployment rate will temporarily fall.
D) firms will experience rising profits and thus increase their employment.
A) the unemployment rate will temporarily rise.
B) firms will increase their output to recoup their falling profits.
C) the unemployment rate will temporarily fall.
D) firms will experience rising profits and thus increase their employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
As distinct from reductions in the price level,reductions in the rate of inflation are referred to as:
A) dollar depreciation.
B) stagflation.
C) deflation.
D) disinflation.
A) dollar depreciation.
B) stagflation.
C) deflation.
D) disinflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
(Consider This)Economist Arthur Laffer equated Robin Hood to:
A) government and equated the people passing through Sherwood Forest to taxpayers.
B) charitable organizations and equated the people passing through Sherwood Forest to poor people.
C) businesses and equated the people passing through Sherwood Forest to consumers.
D) government and equated the people passing through Sherwood Forest to importers of goods and services.
A) government and equated the people passing through Sherwood Forest to taxpayers.
B) charitable organizations and equated the people passing through Sherwood Forest to poor people.
C) businesses and equated the people passing through Sherwood Forest to consumers.
D) government and equated the people passing through Sherwood Forest to importers of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In 1993 the federal government boosted income tax rates.The change in tax revenue that occurred in the seven years that followed:
A) supported the claims of supply-side economists and the Laffer Curve.
B) contradicted the claims of supply-side economists and the Laffer Curve.
C) caused productivity growth to slow.
D) significantly increased the size of the government's budget deficit.
A) supported the claims of supply-side economists and the Laffer Curve.
B) contradicted the claims of supply-side economists and the Laffer Curve.
C) caused productivity growth to slow.
D) significantly increased the size of the government's budget deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
(Consider This)The ideas of economist Arthur Laffer became the centerpiece for tax policy during the:
A) Ford administration.
B) Clinton administration.
C) Nixon administration.
D) Reagan administration.
A) Ford administration.
B) Clinton administration.
C) Nixon administration.
D) Reagan administration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Supply-side economist Arthur Laffer has argued that:
A) there is no empirically proven relationship between tax rates and incentives.
B) large reductions in personal and corporate income taxes will increase aggregate supply much more than aggregate demand.
C) the only way to eliminate inflation is to increase taxes to induce a recession severe enough to eliminate inflationary expectations.
D) large cuts in income taxes will increase aggregate demand more than aggregate supply.
A) there is no empirically proven relationship between tax rates and incentives.
B) large reductions in personal and corporate income taxes will increase aggregate supply much more than aggregate demand.
C) the only way to eliminate inflation is to increase taxes to induce a recession severe enough to eliminate inflationary expectations.
D) large cuts in income taxes will increase aggregate demand more than aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In 1993 the federal government boosted income tax rates.In the seven years that followed:
A) tax revenues fell slightly.
B) productivity growth slowed.
C) the unemployment rate increased.
D) tax revenues expanded rapidly.
A) tax revenues fell slightly.
B) productivity growth slowed.
C) the unemployment rate increased.
D) tax revenues expanded rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical and the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Government can push the unemployment rate below the natural rate only by:
A) instituting supply-side economic policies.
B) producing a higher rate of inflation than people expect.
C) balancing the federal budget.
D) achieving zero inflation.
A) instituting supply-side economic policies.
B) producing a higher rate of inflation than people expect.
C) balancing the federal budget.
D) achieving zero inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Critics of supply-side economics:
A) argue that a tax cut will increase aggregate supply by more than it increases aggregate demand.
B) contend that the relationship between tax rates and economic incentives is small and of uncertain direction.
C) believe that a decline in tax rates will increase tax revenues.
D) point out that tax cuts enable households to substitute work for leisure.
A) argue that a tax cut will increase aggregate supply by more than it increases aggregate demand.
B) contend that the relationship between tax rates and economic incentives is small and of uncertain direction.
C) believe that a decline in tax rates will increase tax revenues.
D) point out that tax cuts enable households to substitute work for leisure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the long run:
A) attempts to "fine-tune" the economy cause the rate of unemployment to accelerate.
B) there is no inflation-unemployment trade-off.
C) there is an inflation-unemployment trade-off and the terms of that trade-off have worsened in recent years.
D) there is an inflation-unemployment trade-off,but the terms of that trade-off have improved in recent years.
A) attempts to "fine-tune" the economy cause the rate of unemployment to accelerate.
B) there is no inflation-unemployment trade-off.
C) there is an inflation-unemployment trade-off and the terms of that trade-off have worsened in recent years.
D) there is an inflation-unemployment trade-off,but the terms of that trade-off have improved in recent years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
(Last Word)According to the research of Christina Romer and David Romer:
A) a tax reduction of 1 percent of GDP lowers real GDP by roughly 2 to 3 percent.
B) a tax increase of 1 percent of GDP lowers real GDP by roughly 2 to 3 percent.
C) a tax reduction of 2 to 3 percent raises real GDP by roughly 1 percent.
D) a tax increase of 2 to 3 percent lowers real GDP by roughly 1 percent.
A) a tax reduction of 1 percent of GDP lowers real GDP by roughly 2 to 3 percent.
B) a tax increase of 1 percent of GDP lowers real GDP by roughly 2 to 3 percent.
C) a tax reduction of 2 to 3 percent raises real GDP by roughly 1 percent.
D) a tax increase of 2 to 3 percent lowers real GDP by roughly 1 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is a tenet of supply-side economics?
A) High marginal tax rates severely discourage work,saving,and investment.
B) Increases in social security taxes and other business taxes shift the aggregate supply curve to the right.
C) The Federal Reserve should adhere to a monetary rule that limits increases in the money supply to a 5 percent annual rate.
D) Transfer payments increase incentives to work.
A) High marginal tax rates severely discourage work,saving,and investment.
B) Increases in social security taxes and other business taxes shift the aggregate supply curve to the right.
C) The Federal Reserve should adhere to a monetary rule that limits increases in the money supply to a 5 percent annual rate.
D) Transfer payments increase incentives to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Demand-pull inflation and cost-push inflation are identical concepts because both involve lower unemployment rates and rising prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A rightward and upward shift of the Phillips Curve is consistent with the occurrence of stagflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Answer the question on the basis of the following economic data for a hypothetical economy:
Refer to the given data.There is evidence that cost-push inflationary pressure is present in this economy.
Refer to the given data.There is evidence that cost-push inflationary pressure is present in this economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The Laffer Curve shows the trade-off between the price level and tax rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The Phillips Curve suggests an inverse relationship between increases in the price level and the level of employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
There is no trade-off between unemployment and inflation in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Answer the question on the basis of the following economic data for a hypothetical economy:
The given data indicate that the economy has entered a period of demand-pull inflation.
The given data indicate that the economy has entered a period of demand-pull inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Answer the question on the basis of the following economic data for a hypothetical economy:
Refer to the given data.It would be the appropriate stabilization policy to raise interest rates,raise taxes,and reduce government expenditures.
Refer to the given data.It would be the appropriate stabilization policy to raise interest rates,raise taxes,and reduce government expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Answer the question on the basis of the following economic data for a hypothetical economy:
Refer to the given data.This economy has encountered stagflation.
Refer to the given data.This economy has encountered stagflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A shift in the Phillips Curve to the left will improve the short-run inflation-unemployment choices available to society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The Laffer Curve underlies the contention that lower tax rates need not reduce tax revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



