Deck 16: Simulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/62
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Simulation
1
The word uniform in the term uniform random numbers means
A)all the numbers have the same number of digits.
B)if one number is, say, 10 units above the mean, the next number will be 10 units below the mean.
C)all the numbers are odd or all are even.
D)each number has an equal probability of being drawn.
A)all the numbers have the same number of digits.
B)if one number is, say, 10 units above the mean, the next number will be 10 units below the mean.
C)all the numbers are odd or all are even.
D)each number has an equal probability of being drawn.
D
2
The process of determining that the computer procedure that performs the simulation calculations is logically correct is called
A)implementation.
B)validation.
C)verification.
D)repetition.
A)implementation.
B)validation.
C)verification.
D)repetition.
C
3
A simulation model used in situations where the state of the system at one point in time does not affect the state of the system at future points in time is called a
A)dynamic simulation model.
B)static simulation model.
C)steady-state simulation model.
D)discrete-event simulation model.
A)dynamic simulation model.
B)static simulation model.
C)steady-state simulation model.
D)discrete-event simulation model.
B
4
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the disadvantages of simulation?
A)Each simulation run only provides a sample of how the real system will operate.
B)The summary of the simulation data only provides estimates about the real system.
C)The process of developing a simulation model of a complex system can be time-consuming.
D)The larger the number of probabilistic inputs a system has, the less likely a simulation will provide the best approach for studying the system.
A)Each simulation run only provides a sample of how the real system will operate.
B)The summary of the simulation data only provides estimates about the real system.
C)The process of developing a simulation model of a complex system can be time-consuming.
D)The larger the number of probabilistic inputs a system has, the less likely a simulation will provide the best approach for studying the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the advantages of simulation?
A)Simulation is relatively easy to explain and understand.
B)Simulation guarantees an optimal solution.
C)Simulation models are flexible.
D)A simulation model provides a convenient experimental laboratory for the real system.
A)Simulation is relatively easy to explain and understand.
B)Simulation guarantees an optimal solution.
C)Simulation models are flexible.
D)A simulation model provides a convenient experimental laboratory for the real system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A graphical tool that helps describe the logic of the simulation model is a
A)Gantt chart
B)histogram
C)flowchart
D)stem-and-leaf display
A)Gantt chart
B)histogram
C)flowchart
D)stem-and-leaf display

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Simulation
A)does not guarantee optimality.
B)is flexible and does not require the assumptions of theoretical models.
C)allows testing of the system without affecting the real system.
D)All of the alternatives are correct.
A)does not guarantee optimality.
B)is flexible and does not require the assumptions of theoretical models.
C)allows testing of the system without affecting the real system.
D)All of the alternatives are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Numerical values that appear in the mathematical relationships of a model and are considered known and remain constant over all trials of a simulation are
A)parameters.
B)probabilistic input.
C)controllable input.
D)events.
A)parameters.
B)probabilistic input.
C)controllable input.
D)events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If customer 2 has a service time of 1.6,and if customer 3 has an interarrival time of 1.1 and a service time of 2.3,when will customer 3's service be completed?
A)5.0
B)3.9
C)3.4
D)There is not enough information to answer.
A)5.0
B)3.9
C)3.4
D)There is not enough information to answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A simulation model uses the mathematical expressions and logical relationships of the
A)real system.
B)computer model.
C)performance measures.
D)estimated inferences.
A)real system.
B)computer model.
C)performance measures.
D)estimated inferences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A value for probabilistic input from a discrete probability distribution
A)is the value given by the RAND() function.
B)is given by matching the probabilistic input with an interval of random numbers.
C)is between 0 and 1.
D)must be non-negative.
A)is the value given by the RAND() function.
B)is given by matching the probabilistic input with an interval of random numbers.
C)is between 0 and 1.
D)must be non-negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Values for the probabilistic inputs to a simulation
A)are selected by the decision maker.
B)are controlled by the decision maker.
C)are randomly generated based on historical information.
D)are calculated by fixed mathematical formulas.
A)are selected by the decision maker.
B)are controlled by the decision maker.
C)are randomly generated based on historical information.
D)are calculated by fixed mathematical formulas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The number of units expected to be sold is uniformly distributed between 300 and 500.If r is a random number between 0 and 1,then the proper expression for sales is
A)200(r)
B)r + 300
C)300 + 500(r)
D)300 + r(200)
A)200(r)
B)r + 300
C)300 + 500(r)
D)300 + r(200)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Common features of simulations--generating values from probability distributions,maintaining records,recording data and summarizing results--led to the development of
A)Excel and Lotus.
B)BASIC, FORTRAN, PASCAL, and C.
C)GPSS, SIMSCRIPT, SLAM, and Arena
D)LINGO and The Management Scientist
A)Excel and Lotus.
B)BASIC, FORTRAN, PASCAL, and C.
C)GPSS, SIMSCRIPT, SLAM, and Arena
D)LINGO and The Management Scientist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In order to verify a simulation model
A)compare results from several simulation languages.
B)be sure that the procedures for calculations are logically correct.
C)confirm that the model accurately represents the real system.
D)run the model long enough to overcome initial start-up results.
A)compare results from several simulation languages.
B)be sure that the procedures for calculations are logically correct.
C)confirm that the model accurately represents the real system.
D)run the model long enough to overcome initial start-up results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When events occur at discrete points in time
A)a simulation clock is required.
B)the simulation advances to the next event.
C)the model is a discrete-event simulation.
D)All of the alternatives are correct.
A)a simulation clock is required.
B)the simulation advances to the next event.
C)the model is a discrete-event simulation.
D)All of the alternatives are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The process of generating probabilistic inputs and computing the value of the output is called
A)simulation.
B)verification.
C)validation.
D)implementation.
A)simulation.
B)verification.
C)validation.
D)implementation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A quantity that is difficult to measure with certainty is called a
A)risk analysis.
B)project determinant.
C)probabilistic input.
D)profit/loss process.
A)risk analysis.
B)project determinant.
C)probabilistic input.
D)profit/loss process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Simulation is an excellent technique to use when a situation is too complicated to use standard analytical procedures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A table of uniformly distributed random numbers should be read
A)from left to right.
B)from top to bottom.
C)diagonally, starting from the top left corner and moving to the bottom right.
D)in any consistent sequence.
A)from left to right.
B)from top to bottom.
C)diagonally, starting from the top left corner and moving to the bottom right.
D)in any consistent sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Simulation is a trial-and-error approach to problem solving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Computer-generated random numbers are not technically random.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A discrete-event simulation reviews the status of the system periodically,whether or not an event occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Each simulation run provides only a sample of how the real system will operate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The parameters of a simulation model are the controllable inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In comparing different policies using simulation,one should use the same set of random numbers whenever possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
One disadvantage of simulation is that it is limited in the variety of probability distributions that can be used in modeling a system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For any waiting line system,(Average number of units in waiting line)= (Total waiting time)divided by (Total time of simulation).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Using simulation to perform risk analysis is like playing out many what-if scenarios by randomly generating values for the probabilistic inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Verification is the process of ensuring that the simulation model provides an accurate representation of the real system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The degree of risk is associated with the probability or magnitude of loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Simulation models that must take into account how the system changes or evolves over time are referred to as dynamic simulation models.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Validation determines that the computer procedure is operating as it is intended to operate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Computer-generated random numbers are normally distributed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Trials of a simulation show what would happen when values of the probabilistic input change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In a Monte Carlo simulation,each simulation trial is dependent upon the result of a previous trial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Simulation is an optimization technique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Computer-generated random numbers are normally distributed over the interval from 0 to 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A static simulation model is used in situations where the state of the system affects how the system changes or evolves over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
To use Excel to generate a normally distributed random variable,you must know the mean and standard deviation of the distribution and have a random number between 0 and 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Simulation is to be used to study customer waiting patterns at several branches of an organization.Acknowledging that arrivals and service times follow different distributions over the branches,of what use is the development of a general simulation model?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Why is a flowchart useful in simulation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How can historical information be used to create discrete probability distributions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
On a visit to an amusement park you pass someone who has just ridden a roller coaster and asks you for directions to the First Aid Station.Realizing that traffic at the First Aid Station would be something to study with simulation,you gather some information.Two EMTs staff the station,and patients wait and go to the first one available.People coming there can be divided into two groups: those who need something minor (e.g.Tylenol,a band-aid)or those who need more help.Assume those in the first group constitute 25% of the patients and take 5 minutes to have their problem solved.Those in the second group need an uncertain amount of time,as given by a probability distribution.Develop a flowchart for this simulation problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The time required to set up lighting for a portrait studio is uniformly distributed between 12 and 20 minutes.Use the following random numbers to generate the setup time for 10 customers.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Seventy-five percent of calls arriving at a help line can be handled by the person who answers the phone,but the remaining 25% of them will need to be referred to someone else.Assume that every call requires one minute of attention by the person who answers the phone (either to answer the question or to figure out how the referral should be handled).Calls that are referred need an additional amount of time,as given in the table below. 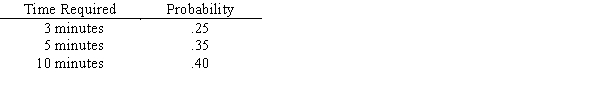 Callers are served on a first come,first served basis,and are put on hold until the line is free.Use the random numbers to simulate what happens to 10 callers.(Use the random numbers in order - from left to right,first row first - as you need them.)What percentage of your callers needs to be referred? Of those who had to be referred,what is the average referral time?
Callers are served on a first come,first served basis,and are put on hold until the line is free.Use the random numbers to simulate what happens to 10 callers.(Use the random numbers in order - from left to right,first row first - as you need them.)What percentage of your callers needs to be referred? Of those who had to be referred,what is the average referral time? 
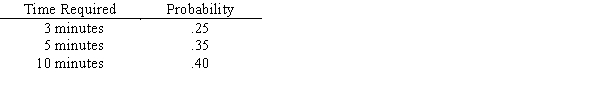 Callers are served on a first come,first served basis,and are put on hold until the line is free.Use the random numbers to simulate what happens to 10 callers.(Use the random numbers in order - from left to right,first row first - as you need them.)What percentage of your callers needs to be referred? Of those who had to be referred,what is the average referral time?
Callers are served on a first come,first served basis,and are put on hold until the line is free.Use the random numbers to simulate what happens to 10 callers.(Use the random numbers in order - from left to right,first row first - as you need them.)What percentage of your callers needs to be referred? Of those who had to be referred,what is the average referral time? 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A simulation model provides a convenient experimental laboratory for the real system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Using the spreadsheet below,give the cell address which would have the formula shown. 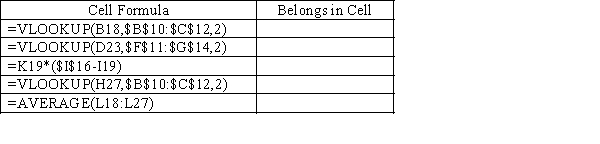
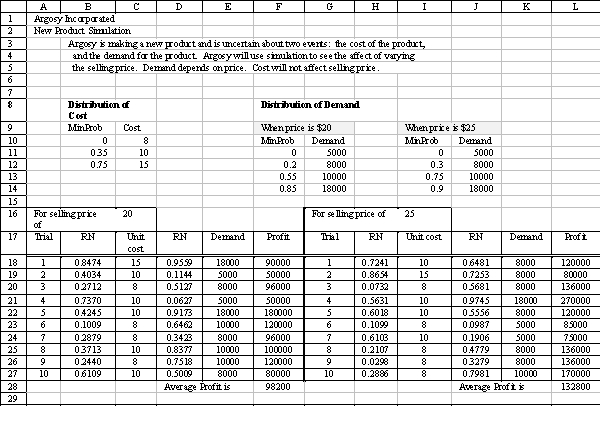



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Explain the difference between verification and validation as they relate to a simulation model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Greenfields is a mail order seed and plant business.The size of orders is uniformly distributed over the interval from $25 to $80.Use the following random numbers to generate the size of 10 orders.
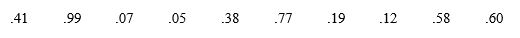
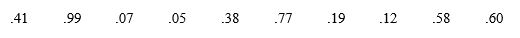

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For the past 50 days,daily sales of laundry detergent in a large grocery store have been recorded (to the nearest 10). 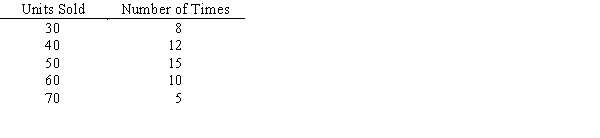
a.Determine the relative frequency for each number of units sold.
b.Suppose that the following random numbers were obtained using Excel:.12.96.53.80.95.10.40.45.77.29Use these random numbers to simulate 10 days of sales.
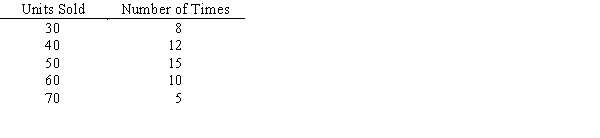
a.Determine the relative frequency for each number of units sold.
b.Suppose that the following random numbers were obtained using Excel:.12.96.53.80.95.10.40.45.77.29Use these random numbers to simulate 10 days of sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Simulation allows the user to specify certain desired results (for example,profit or service level values),and then the necessary model parameters and operating policies are determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Why would one want to use a general purpose programming language rather than a spreadsheet to develop a simulation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Susan Winslow has two alternative routes to travel from her home in Olport to her office in Lewisburg.She can travel on Freeway 5 to Freeway 57 or on Freeway 55 to Freeway 91.The time distributions are as follows: 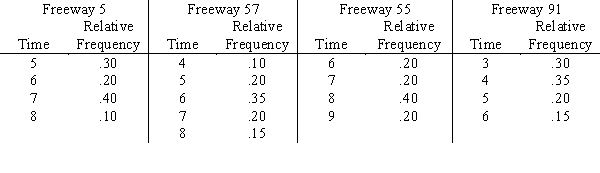 Do a five-day simulation of each of the two combinations of routes using the random numbers below.Based on this simulation,which routes should Susan take if her objective is to minimize her total travel time?
Do a five-day simulation of each of the two combinations of routes using the random numbers below.Based on this simulation,which routes should Susan take if her objective is to minimize her total travel time? 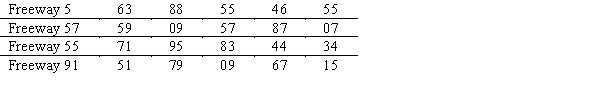
 Do a five-day simulation of each of the two combinations of routes using the random numbers below.Based on this simulation,which routes should Susan take if her objective is to minimize her total travel time?
Do a five-day simulation of each of the two combinations of routes using the random numbers below.Based on this simulation,which routes should Susan take if her objective is to minimize her total travel time? 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Arrivals to a truck repair facility have an interarrival time that is uniformly distributed between 20 and 50 minutes.Service times are normally distributed with mean 30 minutes and standard deviation 10 minutes.Develop a spreadsheet model to simulate the arrival of 100 trucks.Collect information on the time the repair facility is idle and on the average waiting time for trucks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Estimates of the financial information for a new product show the following information: 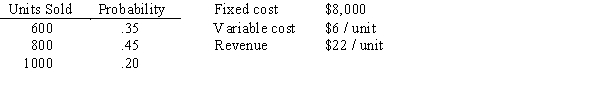 Use the random numbers .51,.97,.58,.22,and .16 to simulate five trials.What is the net profit for each trial?
Use the random numbers .51,.97,.58,.22,and .16 to simulate five trials.What is the net profit for each trial?
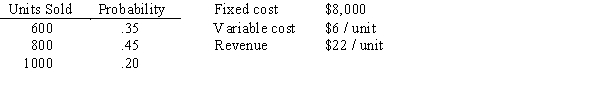 Use the random numbers .51,.97,.58,.22,and .16 to simulate five trials.What is the net profit for each trial?
Use the random numbers .51,.97,.58,.22,and .16 to simulate five trials.What is the net profit for each trial?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
As the owner of a rent-a-car agency you have determined the following statistics: 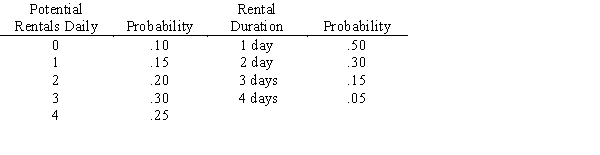 The gross profit is $40 per car per day rented.When there is demand for a car when none is available there is a goodwill loss of $80 and the rental is lost.Each day a car is unused costs you $5 per car.Your firm initially has 4 cars.
The gross profit is $40 per car per day rented.When there is demand for a car when none is available there is a goodwill loss of $80 and the rental is lost.Each day a car is unused costs you $5 per car.Your firm initially has 4 cars.
a.Conduct a 10-day simulation of this business using Row #1 below for demand and Row #2 below for rental length.
b.If your firm can obtain another car for $200 for 10 days, should you take the extra car?
 The gross profit is $40 per car per day rented.When there is demand for a car when none is available there is a goodwill loss of $80 and the rental is lost.Each day a car is unused costs you $5 per car.Your firm initially has 4 cars.
The gross profit is $40 per car per day rented.When there is demand for a car when none is available there is a goodwill loss of $80 and the rental is lost.Each day a car is unused costs you $5 per car.Your firm initially has 4 cars. a.Conduct a 10-day simulation of this business using Row #1 below for demand and Row #2 below for rental length.

b.If your firm can obtain another car for $200 for 10 days, should you take the extra car?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An airline reservation system first asks customers whether they want to schedule a domestic or an international flight.Sixty-five percent of the reservations are for domestic flights.The time distribution of advance sales is also important,and it is given below. 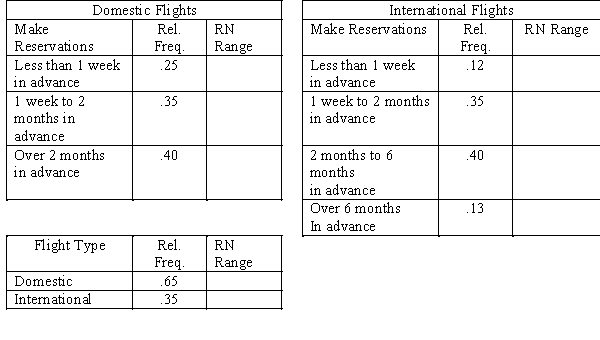
a.Place the appropriate random number ranges in the tables above.
b.Set up and perform a simulation for three customers. Determine whether they want a domestic or international flight, and how far in advance the reservation is being made. Use random numbers from this list: .632 .715 .998 .671 .744 .021

a.Place the appropriate random number ranges in the tables above.
b.Set up and perform a simulation for three customers. Determine whether they want a domestic or international flight, and how far in advance the reservation is being made. Use random numbers from this list: .632 .715 .998 .671 .744 .021

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The drying rate in an industrial process is dependent on many factors and varies according to the following distribution. 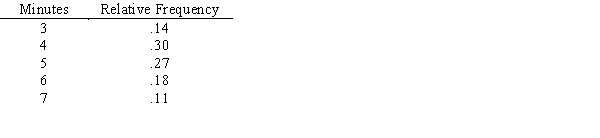
a.Compute the mean drying time.
b.Using these random numbers, simulate the drying time for 12 processes..33.09.19.81.12.88.53.95.77.61.91.47
c.What is the average drying time for the 10 processes you simulated?
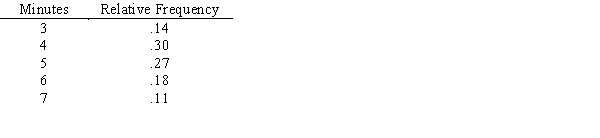
a.Compute the mean drying time.
b.Using these random numbers, simulate the drying time for 12 processes..33.09.19.81.12.88.53.95.77.61.91.47
c.What is the average drying time for the 10 processes you simulated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How are both analysts and managers involved in the validation process?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Three airlines compete on the route between New York and Los Angeles.Stanton Marketing has performed an analysis of first class business travelers to determine their airline choice.Stanton has modeled this choice as a Markov process and has determined the following transition probabilities. 
a.Show the random number assignments that can be used to simulate the first class business traveler's next airline when her last airline is A, B, and C.
b.Assume the traveler used airline C last. Simulate which airline the traveler will be using over her next 25 flights. What percent of her flights are on each of the three airlines? Use the following random numbers, going from left to right, top to bottom.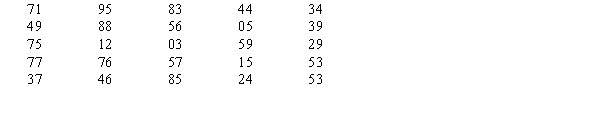

a.Show the random number assignments that can be used to simulate the first class business traveler's next airline when her last airline is A, B, and C.
b.Assume the traveler used airline C last. Simulate which airline the traveler will be using over her next 25 flights. What percent of her flights are on each of the three airlines? Use the following random numbers, going from left to right, top to bottom.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Attendees at the National Management Science Society (NMSS)Conference register by first standing in line to pay their fees.They then proceed to a designated line based on the first letter of their last name to collect their conference materials.
At the conference,it is planned to have three different parallel lines for the collection of materials: one each for people whose last names begin with A-H,I-Q,and R-Z respectively.
During each minute of the morning registration period it is anticipated that attendees will arrive to pay their fees according to the following distribution: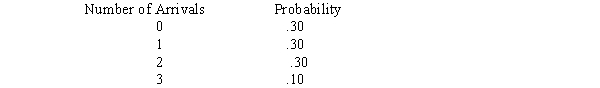 The time to pay one's fees is either one minute or two minutes depending upon whether one uses a check or credit card.The probability of a one-minute time is .60.
The time to pay one's fees is either one minute or two minutes depending upon whether one uses a check or credit card.The probability of a one-minute time is .60.
After paying his fees,an attendee then goes to the correct line for the conference materials.At this year's conference 35% of the attendees have last names beginning with A-H,36% with last names beginning with I-Q,and 29% with last names beginning with R-Z.The time required to pick up conference materials is fixed at 2 minutes.
a. Simulate the waiting line for the first 10 minutes of the morning registration that begins at 8:00 AM. Use the following random numbers to generate:Number of arrivals in any given minute: 71, 95, 83, 44, 34, 49, 88, 56, 05, 39Registration fee service time: 51, 79, 09, 67, 15, 58, 04, 78, 30, 56First letter of the last name: 15, 08, 19, 45, 76, 42, 38, 47, 82, 37
b. What is the average size of the waiting line to pay fees (not including the person being served), and the average customer waiting time to pay fees based on this simulation?
At the conference,it is planned to have three different parallel lines for the collection of materials: one each for people whose last names begin with A-H,I-Q,and R-Z respectively.
During each minute of the morning registration period it is anticipated that attendees will arrive to pay their fees according to the following distribution:
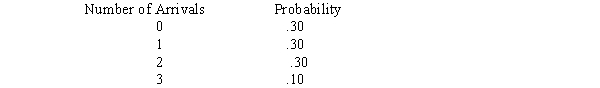 The time to pay one's fees is either one minute or two minutes depending upon whether one uses a check or credit card.The probability of a one-minute time is .60.
The time to pay one's fees is either one minute or two minutes depending upon whether one uses a check or credit card.The probability of a one-minute time is .60.After paying his fees,an attendee then goes to the correct line for the conference materials.At this year's conference 35% of the attendees have last names beginning with A-H,36% with last names beginning with I-Q,and 29% with last names beginning with R-Z.The time required to pick up conference materials is fixed at 2 minutes.
a. Simulate the waiting line for the first 10 minutes of the morning registration that begins at 8:00 AM. Use the following random numbers to generate:Number of arrivals in any given minute: 71, 95, 83, 44, 34, 49, 88, 56, 05, 39Registration fee service time: 51, 79, 09, 67, 15, 58, 04, 78, 30, 56First letter of the last name: 15, 08, 19, 45, 76, 42, 38, 47, 82, 37
b. What is the average size of the waiting line to pay fees (not including the person being served), and the average customer waiting time to pay fees based on this simulation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



