Deck 35: Animal Behavior
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 35: Animal Behavior
1
Animal behaviors that become more frequent when rewarded are:
A)Taxis
B)Imprinting
C)Reflex
D)Observational
E)Innate
A)Taxis
B)Imprinting
C)Reflex
D)Observational
E)Innate
D
2
If scientists ask "how" questions about the behavior of living organisms,they are studying the ___________________ causes of a behavior.
A)Dominant
B)Recessive
C)Proximate
D)Ultimate
E)Anatomical
A)Dominant
B)Recessive
C)Proximate
D)Ultimate
E)Anatomical
C
3
Ethology is the scientific study of:
A)Inheritance
B)How organisms interact with the living and nonliving components of their environment
C)Animal behavior
D)Plants
E)None of the above are correct
A)Inheritance
B)How organisms interact with the living and nonliving components of their environment
C)Animal behavior
D)Plants
E)None of the above are correct
C
4
A sequence of innate behaviors that is performed to completion when triggered by an environmental stimulus is termed a:
A)Substantive blueprint
B)Methodology template
C)Fixed action pattern
D)Minimum survival pattern
E)Maximum survival pattern
A)Substantive blueprint
B)Methodology template
C)Fixed action pattern
D)Minimum survival pattern
E)Maximum survival pattern

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A movement toward or away from a stimulus is a(an):
A)Reflex
B)Fixed action pattern
C)Taxis
D)Aneurysm
E)Methodology
A)Reflex
B)Fixed action pattern
C)Taxis
D)Aneurysm
E)Methodology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The odd bouncing of a Thompson's gazelle to warn others of a nearby predator is termed:
A)Stotting
B)Dribbling
C)Mobbing
D)Bobbing
E)Cavorting
A)Stotting
B)Dribbling
C)Mobbing
D)Bobbing
E)Cavorting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A flock of crows attacking a great horned owl is an example of:
A)Stotting
B)Mobbing
C)Dribbling
D)Bobbing
E)Cavorting
A)Stotting
B)Mobbing
C)Dribbling
D)Bobbing
E)Cavorting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If scientists ask "why" questions about the behavior of living organisms,they are studying the ___________________ causes of behavior.
A)Dominant
B)Recessive
C)Proximate
D)Ultimate
E)Anatomical
A)Dominant
B)Recessive
C)Proximate
D)Ultimate
E)Anatomical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is not a type of learned behavior?
A)Observational learning
B)Imprinting
C)Habituation
D)Taxis
E)All are learned behaviors
A)Observational learning
B)Imprinting
C)Habituation
D)Taxis
E)All are learned behaviors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a proximate question in regards to animal behavior?
A)Why do parents risk their lives for those of their offspring?
B)When does a human male develop a deep voice?
C)Why does a gazelle leap to warn others in the herd when a predator is present?
D)How does a male songbird learn the songs that attract females of his species?
E)Why do crows work together to attack great horned owls?
A)Why do parents risk their lives for those of their offspring?
B)When does a human male develop a deep voice?
C)Why does a gazelle leap to warn others in the herd when a predator is present?
D)How does a male songbird learn the songs that attract females of his species?
E)Why do crows work together to attack great horned owls?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An instantaneous automatic response to a stimulus is a(an):
A)Learned behavior
B)Imprinting
C)Taxis
D)Fixed action pattern
E)Reflex
A)Learned behavior
B)Imprinting
C)Taxis
D)Fixed action pattern
E)Reflex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The type of behavior that does not require learning or experience to be performed correctly is:
A)Innate behavior
B)Dominant behavior
C)Recessive behavior
D)Imprinting
E)Habituation
A)Innate behavior
B)Dominant behavior
C)Recessive behavior
D)Imprinting
E)Habituation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Scientists have no way to measure objectively of:
A)The love that humans feel for a pet
B)The level of insulin in the blood stream
C)The force of a muscular contraction
D)The volume of blood flow through an artery
E)The effect of a neurotransmitter on a muscle
A)The love that humans feel for a pet
B)The level of insulin in the blood stream
C)The force of a muscular contraction
D)The volume of blood flow through an artery
E)The effect of a neurotransmitter on a muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Observational behavior:
A)Is a learned behavior that becomes less frequent when punished
B)Is an innate behavior that becomes less frequent when punished
C)Is a learned behavior that becomes more frequent when punished
D)Is an innate behavior that becomes more frequent when punished
A)Is a learned behavior that becomes less frequent when punished
B)Is an innate behavior that becomes less frequent when punished
C)Is a learned behavior that becomes more frequent when punished
D)Is an innate behavior that becomes more frequent when punished

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Biologists traditionally classify ______________________ based on the way they are acquired and how changeable they are.
A)Animal phyla
B)Animal behaviors
C)Animal size
D)Animal territories
E)Animal offspring
A)Animal phyla
B)Animal behaviors
C)Animal size
D)Animal territories
E)Animal offspring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A behavior in which an animal learns not to respond to a stimulus is:
A)Imprinting
B)Observational
C)Habituation
D)Taxis
E)Reflex
A)Imprinting
B)Observational
C)Habituation
D)Taxis
E)Reflex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A type of behavior that cause babies of many animals to back away from a visual cliff is a(an):
A)Learned behavior
B)Innate behavior
C)Observational learning
D)Habituation
E)Both A and D are correct
A)Learned behavior
B)Innate behavior
C)Observational learning
D)Habituation
E)Both A and D are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A kind of rapid learning that occurs only during a restricted time early in the life of an animal is:
A)Observational
B)Taxis
C)Imprinting
D)Habituation
E)Reflex
A)Observational
B)Taxis
C)Imprinting
D)Habituation
E)Reflex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Behaviors that result from an animal's experiences are:
A)Learned behaviors
B)Imprinting and learned behaviors
C)Innate behaviors
D)Imprinting and innate behaviors
E)Imprinting
A)Learned behaviors
B)Imprinting and learned behaviors
C)Innate behaviors
D)Imprinting and innate behaviors
E)Imprinting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is an ultimate question in regards to animal behavior?
A)How does a male songbird learn the songs that attract females of his species?
B)When does a human male develop a deep voice?
C)How does the nervous system translate instinct into action?
D)How do crows know to work together to attack a great horned owl?
E)Why do parents risk their lives for those of their offspring?
A)How does a male songbird learn the songs that attract females of his species?
B)When does a human male develop a deep voice?
C)How does the nervous system translate instinct into action?
D)How do crows know to work together to attack a great horned owl?
E)Why do parents risk their lives for those of their offspring?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In optimizing foraging,birds must always balance which two variables?
A)Energy taken in per unit time versus the chance of finding a mate
B)Chance of finding a mate versus risk of being eaten by a predator
C)Risk of being eaten by a predator versus the energy density of food
D)Energy taken in per unit time versus risk of being eaten by a predator
E)Chance of finding a mate versus the energy density of food
A)Energy taken in per unit time versus the chance of finding a mate
B)Chance of finding a mate versus risk of being eaten by a predator
C)Risk of being eaten by a predator versus the energy density of food
D)Energy taken in per unit time versus risk of being eaten by a predator
E)Chance of finding a mate versus the energy density of food

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the wild,an animal avoiding a food that they gotten sick from when eating it in the past is an example of which of the following?
A)Operant conditioning
B)Imprinting
C)Observational learning
D)Classical conditioning
E)Habituation
A)Operant conditioning
B)Imprinting
C)Observational learning
D)Classical conditioning
E)Habituation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Mutation of the fru (fruitless)gene in fruit flies results in males attempting to mate with other males.This is an example of which of the following?
A)Reflex
B)Fixed action pattern
C)Learned behavior
D)Imprinting
E)Taxis
A)Reflex
B)Fixed action pattern
C)Learned behavior
D)Imprinting
E)Taxis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In optimizing foraging,birds often stop feeding in an area and move on even though there are still some seeds left.What is the best explanation for this observation?
A)They are safer from predators when moving
B)They are more likely to find a mate if they move around
C)Other areas may have food at a lower density
D)The density of the food becomes low, so it will take too much energy to find
E)They will leave some seeds to create the next generation of plants
A)They are safer from predators when moving
B)They are more likely to find a mate if they move around
C)Other areas may have food at a lower density
D)The density of the food becomes low, so it will take too much energy to find
E)They will leave some seeds to create the next generation of plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Sexual dimorphism in humans is most likely due to which of the following?
A)Uncertainty of paternity by males
B)Competition between males
C)Desire for monogamy by females
D)Higher discrimination in mates by males
E)Female preference for physically attractive males
A)Uncertainty of paternity by males
B)Competition between males
C)Desire for monogamy by females
D)Higher discrimination in mates by males
E)Female preference for physically attractive males

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the evidence that genes are involved in a white-crowned sparrow learning to sing?
A)If they do not hear singing from other white-crowned sparrows they will not sing at all
B)If they hear singing from both white-crowned and other species of sparrows, they will sing abnormally
C)If they do not hear singing from other white-crowned sparrows they will eventually learn to sing normally
D)If the sparrows are deafened after learning to sing they will sing abnormally as adults
E)If they do not hear singing from other white-crowned sparrows they will sing, but abnormally
A)If they do not hear singing from other white-crowned sparrows they will not sing at all
B)If they hear singing from both white-crowned and other species of sparrows, they will sing abnormally
C)If they do not hear singing from other white-crowned sparrows they will eventually learn to sing normally
D)If the sparrows are deafened after learning to sing they will sing abnormally as adults
E)If they do not hear singing from other white-crowned sparrows they will sing, but abnormally

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The behavior in which an animal mates for life,lives with its mate,helps care for the young and defends the family is:
A)Polygamy which is rare in mammals
B)Monogamy which is common in mammals
C)Monogamy which is rare in mammals
D)Polygamy which is common in mammals
A)Polygamy which is rare in mammals
B)Monogamy which is common in mammals
C)Monogamy which is rare in mammals
D)Polygamy which is common in mammals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is an advantage for birds living in a group?
A)Increased resistance to diseases
B)Increased availability of seeds to feed on
C)Protection against predators
D)Decreased aggression among members of the same species
E)Increased availability of nesting sites
A)Increased resistance to diseases
B)Increased availability of seeds to feed on
C)Protection against predators
D)Decreased aggression among members of the same species
E)Increased availability of nesting sites

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Using a hand puppet to feed a baby condor is done to promote ____ on condors and prevent ____ to humans.
A)Imprinting, habituation
B)Habituation, imprinting
C)Imprinting, operant conditioning
D)Operant conditioning, imprinting
E)Habituation, operant conditioning
A)Imprinting, habituation
B)Habituation, imprinting
C)Imprinting, operant conditioning
D)Operant conditioning, imprinting
E)Habituation, operant conditioning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Crows feeding on whelks drop the whelks from the air until their shell breaks,allowing the crow to eat the mussel inside.What would the crow need to optimize in this foraging strategy?
A)The number of drops needed to break the shell and the height per drop
B)The number of drops needed to break the shell
C)The height per drop
D)The force of gravity in each drop
E)The force of gravity in each drop and the height per drop
A)The number of drops needed to break the shell and the height per drop
B)The number of drops needed to break the shell
C)The height per drop
D)The force of gravity in each drop
E)The force of gravity in each drop and the height per drop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Given that female cats produce relatively few eggs relative to the number of sperm produced by males,which behavior would you predict?
A)Males would be more choosy about their mate
B)Both males and females would not be choosy about their mate, and would mate with multiple partners
C)Females would be more choosy about their mate
D)Both males and females would be equally choosy about their mates
A)Males would be more choosy about their mate
B)Both males and females would not be choosy about their mate, and would mate with multiple partners
C)Females would be more choosy about their mate
D)Both males and females would be equally choosy about their mates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Animals that mark and defend a home range against other animals are exhibiting:
A)Imprinting
B)Taxis behavior
C)Habituation
D)Symbiotic behavior
E)Territorial behavior
A)Imprinting
B)Taxis behavior
C)Habituation
D)Symbiotic behavior
E)Territorial behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is an advantage of birds traveling in flocks?
A)An individual bird will have more food available
B)An individual bird's chance of being eaten by a predator is diminished
C)An individual bird will need to spend less time finding food
D)An individual bird's chance of finding a mate will increase
E)A flock of birds is like a warning signal to predators not to feed on them
A)An individual bird will have more food available
B)An individual bird's chance of being eaten by a predator is diminished
C)An individual bird will need to spend less time finding food
D)An individual bird's chance of finding a mate will increase
E)A flock of birds is like a warning signal to predators not to feed on them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A squirrel visits your bird feeder every day,and has learned that if it jumps onto the feeder,seeds will fall on the ground that it can then eat.The squirrel has gone through which of the following?
A)Operant conditioning
B)Classical conditioning
C)Imprinting
D)Observational learning
E)Habituation
A)Operant conditioning
B)Classical conditioning
C)Imprinting
D)Observational learning
E)Habituation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following hormones has been experimentally shown to stimulate ovulation in the ring dove?
A)Follicle stimulating hormone
B)Growth hormone
C)Antidiuretic hormone
D)Estrogen
E)Insulin
A)Follicle stimulating hormone
B)Growth hormone
C)Antidiuretic hormone
D)Estrogen
E)Insulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A homing pigeon that uses landmarks to find its way back to its nest is engaging in:
A)Magnetic orientation
B)True navigation
C)Solar navigation
D)Piloting
E)Stellar navigation
A)Magnetic orientation
B)True navigation
C)Solar navigation
D)Piloting
E)Stellar navigation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Fish eggs are fertilized externally while a dogs' eggs are fertilized internally.In which case is a male more likely to be involved in protecting his offspring?
A)A male dog will help rear his young to adulthood
B)A male dog will guard a female that he fertilized
C)A male fish will help rear his young to adulthood
D)A male fish will guard eggs that he fertilized
A)A male dog will help rear his young to adulthood
B)A male dog will guard a female that he fertilized
C)A male fish will help rear his young to adulthood
D)A male fish will guard eggs that he fertilized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Antlers on a male deer and the lack of antlers on a female deer are examples of:
A)Sexual dimorphism
B)Polygamy
C)Monogamy
D)Optimal foraging
E)Sexual behavior
A)Sexual dimorphism
B)Polygamy
C)Monogamy
D)Optimal foraging
E)Sexual behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Male sticklebacks shown a model of a fish with a red belly will attack thinking it is a breeding male.Model fish without a red belly are not attacked.This is an example of which of the following?
A)Reflex
B)Fixed action pattern
C)Learned behavior
D)Imprinting
E)Taxis
A)Reflex
B)Fixed action pattern
C)Learned behavior
D)Imprinting
E)Taxis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Evidence experience is important in white-crowned sparrows learning to sing includes:
A)They need to hear songs from any sparrow from 10-50 days after hatching to sing properly.
B)They need to hear songs from other male white-crowned sparrows from 10-50 days after hatching.
C)They will not produce any song at all if they do not hear other birds sing.
D)They must imprint on their father to learn how to sing their song properly.
E)White-crowned sparrows raised in a laboratory cannot learn how to sing properly.
A)They need to hear songs from any sparrow from 10-50 days after hatching to sing properly.
B)They need to hear songs from other male white-crowned sparrows from 10-50 days after hatching.
C)They will not produce any song at all if they do not hear other birds sing.
D)They must imprint on their father to learn how to sing their song properly.
E)White-crowned sparrows raised in a laboratory cannot learn how to sing properly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Ethologists asking "why" type questions in their studies are studying proximate causes of animal behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
figure 35.26 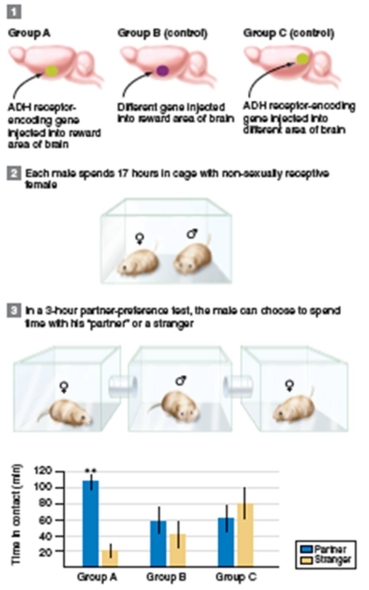
What was the purpose of the Group B control in figure 35.26?
A)To determine if injection of the ADH receptor in other areas of the brain caused a change in bonding.
B)To determine if injection of any gene into other areas of the brain caused a change in bonding.
C)To determine if injection of any gene into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.
D)To determine if injection of the ADH receptor into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.
E)To determine if injection of ADH into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.

What was the purpose of the Group B control in figure 35.26?
A)To determine if injection of the ADH receptor in other areas of the brain caused a change in bonding.
B)To determine if injection of any gene into other areas of the brain caused a change in bonding.
C)To determine if injection of any gene into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.
D)To determine if injection of the ADH receptor into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.
E)To determine if injection of ADH into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Previous work in the 1990s had shown that when prairie voles were given antidiuretic hormone (ADH or vasopressin),what happened?
A)They became promiscuous
B)They formed monogamous bonds
C)They became solitary
D)They became violent
E)They retained water
A)They became promiscuous
B)They formed monogamous bonds
C)They became solitary
D)They became violent
E)They retained water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
figure 35.26 
What is the independent variable in figure 35.26?
A)The time spent in contact with a partner
B)The time spent in contact with a stranger
C)The location where the ADH receptor was injected into the brain
D)The species of vole
E)The amount of ADH injected into the bloodstream of the vole

What is the independent variable in figure 35.26?
A)The time spent in contact with a partner
B)The time spent in contact with a stranger
C)The location where the ADH receptor was injected into the brain
D)The species of vole
E)The amount of ADH injected into the bloodstream of the vole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In addition to affecting behavior,what does ADH regulate?
A)Heart rate
B)Respiratory rate
C)Muscle contractions
D)Blood pressure
E)Release of testosterone
A)Heart rate
B)Respiratory rate
C)Muscle contractions
D)Blood pressure
E)Release of testosterone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When ADH binds to an ADH receptor in the brain,which of the following would occur?
A)Neurons containing the ADH receptor would depolarize
B)ADH would enter neurons containing the ADH receptor
C)ADH would be released from neurons into the synapse
D)ADH would be enzymatically broken down by the receptor
A)Neurons containing the ADH receptor would depolarize
B)ADH would enter neurons containing the ADH receptor
C)ADH would be released from neurons into the synapse
D)ADH would be enzymatically broken down by the receptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the study the scientists compared the levels of ADH in the two species of voles.What hypothesis were they testing?
A)That montane voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus monogamous
B)That pug-nosed voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus promiscuous
C)That prairie voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus promiscuous
D)That montane voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus promiscuous
E)That prairie voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus monogamous
A)That montane voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus monogamous
B)That pug-nosed voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus promiscuous
C)That prairie voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus promiscuous
D)That montane voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus promiscuous
E)That prairie voles have higher levels of ADH and are thus monogamous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
figure 35.26 
What did the scientists conclude from figure 35.26?
A)Increased ADH receptor in the reward area of the brain led to more bonding with a partner
B)Increased ADH receptor in the reward area of the brain led to more bonding with a stranger
C)Increased ADH receptor in the brain had no effect on bonding
D)Increased ADH receptor anywhere in the brain led to more bonding with a partner
E)Increased ADH receptor anywhere in the brain led to more bonding with a stranger

What did the scientists conclude from figure 35.26?
A)Increased ADH receptor in the reward area of the brain led to more bonding with a partner
B)Increased ADH receptor in the reward area of the brain led to more bonding with a stranger
C)Increased ADH receptor in the brain had no effect on bonding
D)Increased ADH receptor anywhere in the brain led to more bonding with a partner
E)Increased ADH receptor anywhere in the brain led to more bonding with a stranger

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the study,______ voles were monogamous and social,while _____ voles were promiscuous and solitary.
A)Prairie, Montane
B)Montane, Prairie
C)Pug-nosed, Prairie
D)Montane, Pug-nosed
E)Prairie, Pug-nosed
A)Prairie, Montane
B)Montane, Prairie
C)Pug-nosed, Prairie
D)Montane, Pug-nosed
E)Prairie, Pug-nosed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Stotting and mobbing are altruistic behaviors used by certain animals to warn others of danger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In eusocial animals like ants the queen is diploid and the male is haploid.Why would female worker ants be more likely than other animals to engage in altruism,feeding the queen's offspring?
A)They are more related to the queen's offspring than they would be to their own offspring
B)The queen establishes a dominance hierarchy over the colony
C)It is a reflex for the worker ants to be altruistic
D)The worker ants are monogamous and remain faithful to the queen ant
E)The worker ants hope for reciprocal altruism and may become the queen ant
A)They are more related to the queen's offspring than they would be to their own offspring
B)The queen establishes a dominance hierarchy over the colony
C)It is a reflex for the worker ants to be altruistic
D)The worker ants are monogamous and remain faithful to the queen ant
E)The worker ants hope for reciprocal altruism and may become the queen ant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Chimpanzees given food will readily share with other chimpanzees,even if not related.Which of the following is an explanation for this observation?
A)It is a reflex
B)They are engaging in kin selection
C)Sexual dimorphism is occurring
D)Dominance hierarchy is occurring
E)They anticipate reciprocal altruism
A)It is a reflex
B)They are engaging in kin selection
C)Sexual dimorphism is occurring
D)Dominance hierarchy is occurring
E)They anticipate reciprocal altruism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The scientists next examined where ADH receptors were found in the brain.They observed that in prairie voles receptors were found in parts of the brain associated with ____,while in montane voles receptors were found in parts of the brain associated with ____.
A)Aggression, addiction
B)Aggression, depression
C)Depression, addiction
D)Addiction, aggression
E)Depression, aggression
A)Aggression, addiction
B)Aggression, depression
C)Depression, addiction
D)Addiction, aggression
E)Depression, aggression

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Ethologists asking "how" type questions in their studies are studying proximate causes of animal behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The type of animal behavior that is inborn and does not require experience or learning to be performed correctly is innate behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Imprinting is a kind of rapid learning that occurs only during a restricted time,early in the life of an animal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The scientific study of animal behavior is ethology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In almost all cases innate and learned behaviors are determined by both genetics and environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A meerkat sentry is not an example of altruistic behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
figure 35.26 
What was the purpose of the Group C control in figure 35.26?
A)To determine if injection of any gene into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.
B)To determine if injection of the ADH receptor in other areas of the brain caused a change in bonding.
C)To determine if injection of any gene into other areas of the brain caused a change in bonding.
D)To determine if injection of the ADH receptor into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.
E)To determine if injection of ADH into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.

What was the purpose of the Group C control in figure 35.26?
A)To determine if injection of any gene into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.
B)To determine if injection of the ADH receptor in other areas of the brain caused a change in bonding.
C)To determine if injection of any gene into other areas of the brain caused a change in bonding.
D)To determine if injection of the ADH receptor into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.
E)To determine if injection of ADH into the reward area of the brain caused a change in bonding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Monogamous animals mate for life,live with their mate,and help take care of the young.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Chemicals released into the environment by animals that usually influence behavior in other members of the same species are pheromones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Imprinting is a type of innate behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Reproducing is a type of innate behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Response to a predator is a type of innate behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A chimp using a stick to probe for termites from a nest is evidence of cognition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Chemicals released into the environment by animals that usually influence behavior in other members of the same species are hormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An evolutionary mechanism in animals that sacrifices an individual's genes for the sake of the genes it shares with related animals is termed kin selection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



