Deck 12: Product Pricing With Monopoly Power
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/89
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Product Pricing With Monopoly Power
1
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P1.
Figure 12-1![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,deadweight loss will be equal to:</strong> A)the area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)the area P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub>. C)the area ABC. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,deadweight loss will be equal to:
A)the area P3AP2.
B)the area P3CP1.
C)the area ABC.
D)zero.
Figure 12-1
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,deadweight loss will be equal to:</strong> A)the area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)the area P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub>. C)the area ABC. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,deadweight loss will be equal to:
A)the area P3AP2.
B)the area P3CP1.
C)the area ABC.
D)zero.
C
2
Which of the following is an example of price discrimination?
A)Both Andy and Beth pay $7 for a ticket to the same movie,although the show timings are different.
B)Ann purchases a coach ticket on an airline for $250 while Bill purchases a first class ticket on the same flight for $900.
C)Aaron purchases a hardback copy of Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows for $25 while Barbara waits and purchases a copy of the same book six months later for $8.
D)Audrey buys a front-row seat at a concert with back-stage access for $1,200,while Ben pays $500 for seats further away from the stage.
A)Both Andy and Beth pay $7 for a ticket to the same movie,although the show timings are different.
B)Ann purchases a coach ticket on an airline for $250 while Bill purchases a first class ticket on the same flight for $900.
C)Aaron purchases a hardback copy of Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows for $25 while Barbara waits and purchases a copy of the same book six months later for $8.
D)Audrey buys a front-row seat at a concert with back-stage access for $1,200,while Ben pays $500 for seats further away from the stage.
C
3
The strategy of charging different prices to different customers,for the same product,based on the differences in their demand elasticities is referred to as:
A)predatory pricing.
B)price skimming.
C)arbitrage.
D)price discrimination.
A)predatory pricing.
B)price skimming.
C)arbitrage.
D)price discrimination.
D
4
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist.
Figure 12-2![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.Comparing the result of perfect competition with that of a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist,there is an efficiency loss equal to:</strong> A)area VWE. B)area HEF. C)area JHFK. D)zero.There will be no efficiency loss in either case.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d742_1d86_91bf_d5b103dd63bb_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.Comparing the result of perfect competition with that of a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist,there is an efficiency loss equal to:
A)area VWE.
B)area HEF.
C)area JHFK.
D)zero.There will be no efficiency loss in either case.
Figure 12-2
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.Comparing the result of perfect competition with that of a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist,there is an efficiency loss equal to:</strong> A)area VWE. B)area HEF. C)area JHFK. D)zero.There will be no efficiency loss in either case.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d742_1d86_91bf_d5b103dd63bb_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.Comparing the result of perfect competition with that of a perfectly price-discriminating monopolist,there is an efficiency loss equal to:
A)area VWE.
B)area HEF.
C)area JHFK.
D)zero.There will be no efficiency loss in either case.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist.
Figure 12-2![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.Compared to perfect competition,monopoly pricing introduces efficiency loss equal to the area:</strong> A)VWE. B)ZVN. C)HEF. D)JHFK.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_cf64_91bf_b5d54ed71a89_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.Compared to perfect competition,monopoly pricing introduces efficiency loss equal to the area:
A)VWE.
B)ZVN.
C)HEF.
D)JHFK.
Figure 12-2
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.Compared to perfect competition,monopoly pricing introduces efficiency loss equal to the area:</strong> A)VWE. B)ZVN. C)HEF. D)JHFK.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_cf64_91bf_b5d54ed71a89_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.Compared to perfect competition,monopoly pricing introduces efficiency loss equal to the area:
A)VWE.
B)ZVN.
C)HEF.
D)JHFK.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Economists generally view the practice of perfect price discrimination favorably because it:
A)maximizes consumer surplus.
B)forces rich people to pay higher prices.
C)deters monopoly pricing.
D)eliminates deadweight loss.
A)maximizes consumer surplus.
B)forces rich people to pay higher prices.
C)deters monopoly pricing.
D)eliminates deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P1.
Figure 12-1![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist perfectly price discriminates,profit will be equal to:</strong> A)the area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)the area P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub>. C)the area ABC. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist perfectly price discriminates,profit will be equal to:
A)the area P3AP2.
B)the area P3CP1.
C)the area ABC.
D)zero.
Figure 12-1
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist perfectly price discriminates,profit will be equal to:</strong> A)the area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)the area P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub>. C)the area ABC. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist perfectly price discriminates,profit will be equal to:
A)the area P3AP2.
B)the area P3CP1.
C)the area ABC.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P1.
Figure 12-1![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist practices perfect price discrimination,consumer surplus will be equal to:</strong> A)the area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)the area P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub>. C)the area ABC. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist practices perfect price discrimination,consumer surplus will be equal to:
A)the area P3AP2.
B)the area P3CP1.
C)the area ABC.
D)zero.
Figure 12-1
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist practices perfect price discrimination,consumer surplus will be equal to:</strong> A)the area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)the area P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub>. C)the area ABC. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist practices perfect price discrimination,consumer surplus will be equal to:
A)the area P3AP2.
B)the area P3CP1.
C)the area ABC.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist.
Figure 12-2![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.What will be the consumer surplus when the monopolist practices first-degree price discrimination?</strong> A)WVE B)CVF C)ZVN D)Zero](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d742_1d86_91bf_d5b103dd63bb_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.What will be the consumer surplus when the monopolist practices first-degree price discrimination?
A)WVE
B)CVF
C)ZVN
D)Zero
Figure 12-2
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.What will be the consumer surplus when the monopolist practices first-degree price discrimination?</strong> A)WVE B)CVF C)ZVN D)Zero](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d742_1d86_91bf_d5b103dd63bb_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.What will be the consumer surplus when the monopolist practices first-degree price discrimination?
A)WVE
B)CVF
C)ZVN
D)Zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is the closest example of perfect price discrimination?
A)An airline providing discounts to its frequent-flyers as they fly more
B)At an auction of antique furniture,each piece of furniture is sold to the highest bidder
C)A golf-club imposing a very high entry fee to reduce membership requests
D)An electric utility charging higher rates to the customers in the summer season than in the winter season
A)An airline providing discounts to its frequent-flyers as they fly more
B)At an auction of antique furniture,each piece of furniture is sold to the highest bidder
C)A golf-club imposing a very high entry fee to reduce membership requests
D)An electric utility charging higher rates to the customers in the summer season than in the winter season

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
First-degree price discrimination is _____.
A)perfect because it benefits consumers the most
B)called first-degree because it does not apply to resale of products
C)also known as perfect price discrimination
D)the easiest form of price discrimination to implement
A)perfect because it benefits consumers the most
B)called first-degree because it does not apply to resale of products
C)also known as perfect price discrimination
D)the easiest form of price discrimination to implement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P1.
Figure 12-1![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,consumer surplus will be _____.</strong> A)P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub> B)P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub> C)P<sub>2</sub>ABP<sub>1</sub> D)ABC](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,consumer surplus will be _____.
A)P3AP2
B)P3CP1
C)P2ABP1
D)ABC
Figure 12-1
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,consumer surplus will be _____.</strong> A)P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub> B)P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub> C)P<sub>2</sub>ABP<sub>1</sub> D)ABC](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,consumer surplus will be _____.
A)P3AP2
B)P3CP1
C)P2ABP1
D)ABC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is not an example of price discrimination?
A)A restaurant sets a fixed cover charge in addition to menu charges.
B)A phone company charges different rates to residential and business users.
C)An electric company charges different rates to senior citizens and younger adults.
D)An airline sets different fares for adults and children.
A)A restaurant sets a fixed cover charge in addition to menu charges.
B)A phone company charges different rates to residential and business users.
C)An electric company charges different rates to senior citizens and younger adults.
D)An airline sets different fares for adults and children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist.
Figure 12-2![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.A monopolist practicing first-degree price discrimination will sell _____ quantity of output.</strong> A)OL B)OK C)OJ D)KL](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_cf64_91bf_b5d54ed71a89_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.A monopolist practicing first-degree price discrimination will sell _____ quantity of output.
A)OL
B)OK
C)OJ
D)KL
Figure 12-2
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.A monopolist practicing first-degree price discrimination will sell _____ quantity of output.</strong> A)OL B)OK C)OJ D)KL](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_cf64_91bf_b5d54ed71a89_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.A monopolist practicing first-degree price discrimination will sell _____ quantity of output.
A)OL
B)OK
C)OJ
D)KL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P1.
Figure 12-1![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 In Figure 12-1,if the monopolist cannot price discriminate it will produce:</strong> A)Q<sub>2</sub> and sell at price P<sub>1</sub>. B)Q<sub>2</sub> and sell at price P<sub>2</sub>. C)Q<sub>1</sub> and sell at price P<sub>1</sub>. D)Q<sub>1</sub> and sell at price P<sub>2</sub>.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_cf63_91bf_d5c52a3cd000_TB1825_00.jpg)
In Figure 12-1,if the monopolist cannot price discriminate it will produce:
A)Q2 and sell at price P1.
B)Q2 and sell at price P2.
C)Q1 and sell at price P1.
D)Q1 and sell at price P2.
Figure 12-1
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 In Figure 12-1,if the monopolist cannot price discriminate it will produce:</strong> A)Q<sub>2</sub> and sell at price P<sub>1</sub>. B)Q<sub>2</sub> and sell at price P<sub>2</sub>. C)Q<sub>1</sub> and sell at price P<sub>1</sub>. D)Q<sub>1</sub> and sell at price P<sub>2</sub>.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_cf63_91bf_d5c52a3cd000_TB1825_00.jpg)
In Figure 12-1,if the monopolist cannot price discriminate it will produce:
A)Q2 and sell at price P1.
B)Q2 and sell at price P2.
C)Q1 and sell at price P1.
D)Q1 and sell at price P2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist.
Figure 12-2![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.Compared to the situation when there is no price discrimination,first-degree price discrimination causes the consumer surplus to decline by the area:</strong> A)ZVN. B)CVF. C)VWE. D)EIF.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d742_1d86_91bf_d5b103dd63bb_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.Compared to the situation when there is no price discrimination,first-degree price discrimination causes the consumer surplus to decline by the area:
A)ZVN.
B)CVF.
C)VWE.
D)EIF.
Figure 12-2
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.Compared to the situation when there is no price discrimination,first-degree price discrimination causes the consumer surplus to decline by the area:</strong> A)ZVN. B)CVF. C)VWE. D)EIF.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d742_1d86_91bf_d5b103dd63bb_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.Compared to the situation when there is no price discrimination,first-degree price discrimination causes the consumer surplus to decline by the area:
A)ZVN.
B)CVF.
C)VWE.
D)EIF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose Amazon.com were to charge each consumer a different price,according to his or her willingness to pay for the latest novel in the Twilight series.The firm would be engaging in:
A)peak-load pricing.
B)first-degree price discrimination.
C)second-degree price discrimination.
D)third-degree price discrimination.
A)peak-load pricing.
B)first-degree price discrimination.
C)second-degree price discrimination.
D)third-degree price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P1.
Figure 12-1![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,profit will be equal to:</strong> A)the area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)the area P<sub>2</sub>AQ<sub>1</sub>O. C)the area P<sub>2</sub>ABP<sub>1</sub>. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,profit will be equal to:
A)the area P3AP2.
B)the area P2AQ1O.
C)the area P2ABP1.
D)zero.
Figure 12-1
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,profit will be equal to:</strong> A)the area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)the area P<sub>2</sub>AQ<sub>1</sub>O. C)the area P<sub>2</sub>ABP<sub>1</sub>. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist cannot price discriminate,profit will be equal to:
A)the area P3AP2.
B)the area P2AQ1O.
C)the area P2ABP1.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P1.
Figure 12-1![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist perfectly price discriminates,deadweight loss will be equal to:</strong> A)area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)area P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub>. C)area ABC. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist perfectly price discriminates,deadweight loss will be equal to:
A)area P3AP2.
B)area P3CP1.
C)area ABC.
D)zero.
Figure 12-1
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves of a monopolist.The MR curve intersects the marginal cost [MC] curve at point B.MC is constant at the price level P<sub>1</sub>. Figure 12-1 Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist perfectly price discriminates,deadweight loss will be equal to:</strong> A)area P<sub>3</sub>AP<sub>2</sub>. B)area P<sub>3</sub>CP<sub>1</sub>. C)area ABC. D)zero.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d741_f675_91bf_dbb7ecc0f0f7_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-1.If the monopolist perfectly price discriminates,deadweight loss will be equal to:
A)area P3AP2.
B)area P3CP1.
C)area ABC.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is true of price discrimination?
A)It refers to the illegal movement of commodities from one country to another.
B)It refers to the practice of charging different prices to different consumers for the same product.
C)It is practiced by competitive firms to enjoy long run profits.
D)It refers to the practice of buying a good at a low price and selling it at a higher price.
A)It refers to the illegal movement of commodities from one country to another.
B)It refers to the practice of charging different prices to different consumers for the same product.
C)It is practiced by competitive firms to enjoy long run profits.
D)It refers to the practice of buying a good at a low price and selling it at a higher price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A monopolist practicing second-degree price discrimination and facing a constant marginal cost:
A)should charge a higher price to the market segment that has the more elastic demand.
B)sets the price schedule according to the number of units purchased by the consumers.
C)need not worry about preventing resale of the product.
D)will supply more output than a perfectly price discriminating monopolist.
A)should charge a higher price to the market segment that has the more elastic demand.
B)sets the price schedule according to the number of units purchased by the consumers.
C)need not worry about preventing resale of the product.
D)will supply more output than a perfectly price discriminating monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Under perfect price discrimination,_____.
A)each customer pays the same price but receives a different quantity
B)each customer pays a different price based on their willingness to pay
C)efficiency loss is maximized
D)price is always above marginal revenue
A)each customer pays the same price but receives a different quantity
B)each customer pays a different price based on their willingness to pay
C)efficiency loss is maximized
D)price is always above marginal revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A popular restaurant chain,Grill n' Chill,offers its customers a 0.5% discount on a bill of $100-$200,a 1% discount on a bill of $201-$300,a 1.5% discount on a bill of $301-$400,and so on.Thus,customers enjoy a higher discount when they order more food.Which of the following forms of price discrimination is being practiced by this restaurant chain?
A)Third-degree price discrimination
B)Intertemporal price discrimination
C)First-degree price discrimination
D)Second-degree price discrimination
A)Third-degree price discrimination
B)Intertemporal price discrimination
C)First-degree price discrimination
D)Second-degree price discrimination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A perfectly price-discriminating monopolist:
A)restricts output more than an ordinary monopolist does.
B)sells the last unit of output where price equals marginal cost.
C)charges all consumers the same price but sells different quantities to each.
D)obtains less producer surplus than does an non-price discriminating monopolist.
A)restricts output more than an ordinary monopolist does.
B)sells the last unit of output where price equals marginal cost.
C)charges all consumers the same price but sells different quantities to each.
D)obtains less producer surplus than does an non-price discriminating monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
With block pricing,firms differentiate price according to _____.
A)each consumer's ability to pay
B)the average cost of producing the output
C)the quantity of output purchased
D)the marginal cost of producing a particular unit of output
A)each consumer's ability to pay
B)the average cost of producing the output
C)the quantity of output purchased
D)the marginal cost of producing a particular unit of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following situations allows monopolists to capture the entire consumer surplus as their profit?
A)When they can charge a single price for their product
B)When they are subject to a per unit excise tax
C)When they are subject to an excess profit tax
D)When they can practice perfect price discrimination
A)When they can charge a single price for their product
B)When they are subject to a per unit excise tax
C)When they are subject to an excess profit tax
D)When they can practice perfect price discrimination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is true of the comparison between a non-price discriminating monopoly and a perfectly price discriminating monopoly?
A)The non-price discriminating monopolist will produce a higher amount of output.
B)The non-price discriminating monopolist will have more producer surplus.
C)The non-price discriminating monopolist will impose a greater efficiency loss.
D)The non-price discriminating monopolist will capture more consumer surplus.
A)The non-price discriminating monopolist will produce a higher amount of output.
B)The non-price discriminating monopolist will have more producer surplus.
C)The non-price discriminating monopolist will impose a greater efficiency loss.
D)The non-price discriminating monopolist will capture more consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
With block pricing,consumers typically pay a price that:
A)reduces for additional quantities of output being purchased.
B)remains the same regardless of the quantity purchased.
C)is equal to the average cost of producing the output.
D)increases for additional quantities of output being purchased.
A)reduces for additional quantities of output being purchased.
B)remains the same regardless of the quantity purchased.
C)is equal to the average cost of producing the output.
D)increases for additional quantities of output being purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Identify the correct statement about price discrimination.
A)Price discrimination is costless.
B)Price discrimination is effective only if demand for the product is perfectly inelastic.
C)Price discrimination is effective when producers face a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)Price discrimination increases consumer surplus.
A)Price discrimination is costless.
B)Price discrimination is effective only if demand for the product is perfectly inelastic.
C)Price discrimination is effective when producers face a downward-sloping demand curve.
D)Price discrimination increases consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Under first-degree price discrimination,the marginal revenue curve:
A)is a horizontal straight line.
B)slopes upward.
C)coincides with the monopoly firm's demand curve.
D)is identical to the marginal revenue curve facing a non-price discriminating monopolist.
A)is a horizontal straight line.
B)slopes upward.
C)coincides with the monopoly firm's demand curve.
D)is identical to the marginal revenue curve facing a non-price discriminating monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consumer surplus is completely transferred to the price discriminating monopoly firm as profit under _____.
A)first-degree price discrimination
B)predatory pricing
C)third-degree price discrimination
D)block pricing
A)first-degree price discrimination
B)predatory pricing
C)third-degree price discrimination
D)block pricing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is the closest example of block pricing?
A)An airline providing discounts to its frequent-flyers as they fly more
B)At an auction of antique furniture,each piece of furniture is sold to the highest bidder
C)A golf-club imposing a very high entry fee to reduce membership requests
D)An electric utility charging higher rates to the customers in the summer season than in the winter season
A)An airline providing discounts to its frequent-flyers as they fly more
B)At an auction of antique furniture,each piece of furniture is sold to the highest bidder
C)A golf-club imposing a very high entry fee to reduce membership requests
D)An electric utility charging higher rates to the customers in the summer season than in the winter season

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The local zoo has a pricing policy in which senior citizens pay a lower price than younger adults.This policy is:
A)a form of perfect price discrimination.
B)a form of third-degree price discrimination.
C)certain to reduce total revenues for the zoo.
D)certain to reduce the number of visitors to the zoo.
A)a form of perfect price discrimination.
B)a form of third-degree price discrimination.
C)certain to reduce total revenues for the zoo.
D)certain to reduce the number of visitors to the zoo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Lewis owns an exclusive fashion accessories store and charges all consumers a uniform price for a particular product.Recently,however,he has realized that some of his customers are actually willing to pay a higher price for the items he sells,while some others feel that his prices are a little too high.Given this information,which of the following will not affect his ability to discriminate prices between these two consumer segments?
A)His level of monopoly power in this market
B)His total investment in this business
C)His ability to segment the market into high demand and low demand users
D)His ability to prevent arbitrage
A)His level of monopoly power in this market
B)His total investment in this business
C)His ability to segment the market into high demand and low demand users
D)His ability to prevent arbitrage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
With perfect price discrimination,a monopolist:
A)must lower the price on all units to increase sales.
B)will charge each consumer the maximum price they are willing to pay.
C)does not have a definite profit-maximizing level of output.
D)has a marginal revenue curve that lies below the demand curve.
A)must lower the price on all units to increase sales.
B)will charge each consumer the maximum price they are willing to pay.
C)does not have a definite profit-maximizing level of output.
D)has a marginal revenue curve that lies below the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is needed for successful price discrimination?
A)The firm must have a high market share.
B)The firm must have more than one product line.
C)The firm must be able to engage in arbitrage.
D)The firm must have some consumers whose demand is relatively price inelastic.
A)The firm must have a high market share.
B)The firm must have more than one product line.
C)The firm must be able to engage in arbitrage.
D)The firm must have some consumers whose demand is relatively price inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Block pricing by electric utilities is an example of:
A)predatory pricing.
B)second-degree price discrimination.
C)third-degree price discrimination.
D)perfect price discrimination.
A)predatory pricing.
B)second-degree price discrimination.
C)third-degree price discrimination.
D)perfect price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Park and Fly,a chain that operates off-terminal parking lots near major airports in several U.S.cities,has a "frequent-parker" program that offers customers a week's free parking after they have paid for 35 days.Which of the following types of price discrimination is the company practicing?
A)Perfect price discrimination
B)Predatory pricing
C)Third-degree price discrimination
D)Block pricing
A)Perfect price discrimination
B)Predatory pricing
C)Third-degree price discrimination
D)Block pricing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist.
Figure 12-2![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.With perfect price discrimination,the monopolist will receive producer surplus equal to the area:</strong> A)ACFH. B)BCFH. C)AVFH. D)AWEH.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d742_1d86_91bf_d5b103dd63bb_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.With perfect price discrimination,the monopolist will receive producer surplus equal to the area:
A)ACFH.
B)BCFH.
C)AVFH.
D)AWEH.
Figure 12-2
![<strong>The following figure shows the downward sloping demand and marginal revenue [MR] curves and the upward sloping marginal cost [MC] curve of a monopolist. Figure 12-2 Refer to Figure 12-2.With perfect price discrimination,the monopolist will receive producer surplus equal to the area:</strong> A)ACFH. B)BCFH. C)AVFH. D)AWEH.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1825/11ea77e2_d742_1d86_91bf_d5b103dd63bb_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00_TB1825_00.jpg)
Refer to Figure 12-2.With perfect price discrimination,the monopolist will receive producer surplus equal to the area:
A)ACFH.
B)BCFH.
C)AVFH.
D)AWEH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Under third-degree price discrimination,a producer makes profit by:
A)reducing the price of the good for every additional unit being purchased.
B)charging a higher price to the market segment with the more inelastic demand.
C)rationing the good to be sold to consumers in different markets.
D)keeping the price level steady in all markets.
A)reducing the price of the good for every additional unit being purchased.
B)charging a higher price to the market segment with the more inelastic demand.
C)rationing the good to be sold to consumers in different markets.
D)keeping the price level steady in all markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider a monopolist selling her output in two markets,A and B.The price elasticity of demand in market A is 1.5,while the same in market B is 2.5.Calculate the marginal revenue [MR] from each market,if the monopolist charges $300 for the product in both the markets.
A)MRA = 13.3;MRB = 24.8
B)MRA = 6.11;MRB = 35.8
C)MRA = 11.11;MRB = 64.8
D)MRA = 15.3;MRB = 74.8
A)MRA = 13.3;MRB = 24.8
B)MRA = 6.11;MRB = 35.8
C)MRA = 11.11;MRB = 64.8
D)MRA = 15.3;MRB = 74.8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following products/services provides the least scope for arbitrage?
A)Sports shoes
B)Live concerts
C)Jewelry
D)Books
A)Sports shoes
B)Live concerts
C)Jewelry
D)Books

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is the best example of intertemporal price discrimination?
A)Awarding financial aid to offset college tuition fees
B)Releasing movies on DVD six months after they are released in a theater
C)Charging less for a second pizza after the consumer has paid the full price for the first pizza
D)Charging people with health care insurance more for medical care relative to those without insurance
A)Awarding financial aid to offset college tuition fees
B)Releasing movies on DVD six months after they are released in a theater
C)Charging less for a second pizza after the consumer has paid the full price for the first pizza
D)Charging people with health care insurance more for medical care relative to those without insurance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is true of a price-discriminating monopolist who is selling output in two distinct markets?
A)Price will be higher in the market in which demand is unit-elastic.
B)Price will be lower in the market in which demand is more elastic.
C)Price will be equal in each market,as long as there is a constant marginal cost.
D)Price will be lower in the market for which there are fewer substitute goods.
A)Price will be higher in the market in which demand is unit-elastic.
B)Price will be lower in the market in which demand is more elastic.
C)Price will be equal in each market,as long as there is a constant marginal cost.
D)Price will be lower in the market for which there are fewer substitute goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A profit-maximizing monopoly firm that sells output in two distinct markets,A and B,will be in equilibrium when:
A)the price in each market is equal to its marginal cost of production.
B)the marginal revenue in each market is equal to the price in that particular market.
C)the marginal revenue in each market is equal to its marginal cost of production.
D)the gap between price and marginal cost is maximized in each market.
A)the price in each market is equal to its marginal cost of production.
B)the marginal revenue in each market is equal to the price in that particular market.
C)the marginal revenue in each market is equal to its marginal cost of production.
D)the gap between price and marginal cost is maximized in each market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A firm charges a higher price for its product in the domestic market than it charges abroad.Which of the following pricing strategies is the firm using?
A)Targeting
B)Block pricing
C)Dumping
D)Price skimming
A)Targeting
B)Block pricing
C)Dumping
D)Price skimming

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When a monopolist practices third-degree price discrimination,price will be:
A)the same in each market if resale is not possible.
B)higher in the market with the less elastic demand.
C)higher in the market with the higher average cost.
D)higher in the market will less number of consumers.
A)the same in each market if resale is not possible.
B)higher in the market with the less elastic demand.
C)higher in the market with the higher average cost.
D)higher in the market will less number of consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Intertemporal price discrimination is a form of:
A)first-degree price discrimination.
B)block pricing.
C)third-degree price discrimination.
D)dumping.
A)first-degree price discrimination.
B)block pricing.
C)third-degree price discrimination.
D)dumping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following conditions will allow a monopolist to charge different prices in different markets?
A)Having the ability to prevent resale of its product
B)Incurring a constant marginal cost of producing output
C)Catering to a different number of consumers in each market
D)Facing a positively sloped marginal revenue curve
A)Having the ability to prevent resale of its product
B)Incurring a constant marginal cost of producing output
C)Catering to a different number of consumers in each market
D)Facing a positively sloped marginal revenue curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider two markets segments,X and Y,for product A.The price elasticity of demand for product A in market X is 1.5,while the same in market Y is 3.The monopolist is selling product A in both the markets at a price of $300.Which of the following statements is true about the marginal revenue earned by the non-price discriminating monopolist from the two markets?
A)The monopolist earns $77.78 more from market Y.
B)The monopolist earns $99.9 more from market X.
C)The monopolist earns $88.89 more from market Y.
D)The monopolist earns $11.11 more from market X.
A)The monopolist earns $77.78 more from market Y.
B)The monopolist earns $99.9 more from market X.
C)The monopolist earns $88.89 more from market Y.
D)The monopolist earns $11.11 more from market X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Comparing a price-discriminating monopoly firm with a single-price monopoly,one tends to find that price discrimination:
A)increases the inefficiency of the market.
B)reduces economic profits.
C)typically increases total output.
D)results in lower input prices.
A)increases the inefficiency of the market.
B)reduces economic profits.
C)typically increases total output.
D)results in lower input prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
When airlines charge different fares for seats on the same flight depending on how far in advance an airline ticket has been purchased,it is using a(n)_____ strategy.
A)dumping
B)block pricing
C)first-degree price discrimination
D)intertemporal price discrimination
A)dumping
B)block pricing
C)first-degree price discrimination
D)intertemporal price discrimination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In case of third-degree price discrimination in two markets with differing demand elasticities,price will:
A)converge in the two markets if resale is possible.
B)be higher in the market with the more elastic demand.
C)be higher in the market with the higher average cost.
D)differ between the two markets only if the number of consumers varies.
A)converge in the two markets if resale is possible.
B)be higher in the market with the more elastic demand.
C)be higher in the market with the higher average cost.
D)differ between the two markets only if the number of consumers varies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
We would expect price discrimination to be most successful in the market for:
A)haircuts.
B)DVD's.
C)cars.
D)jeans.
A)haircuts.
B)DVD's.
C)cars.
D)jeans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider a monopolist selling her output in two markets,A and B.The price elasticity of demand in market A is 1.5,while the same in market B is 2.5.Calculate the price charged in each market,if the marginal revenue [MR] from market A is 15 while the same from market B is 30.
A)PA = 200;PB = 169.89
B)PA = 500;PB = 208.29
C)PA = 105;PB = 108.39
D)PA = 405;PB = 138.89
A)PA = 200;PB = 169.89
B)PA = 500;PB = 208.29
C)PA = 105;PB = 108.39
D)PA = 405;PB = 138.89

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Price discrimination is more common for firms selling services than for manufacturing firms because:
A)it is easier to prevent arbitrage of a service than of a manufactured product.
B)monopoly is more common in the production of services than in production of manufactured goods.
C)price elasticities of demand differ more among consumers of services than customers of manufactured goods.
D)firms selling services are more likely to have constant marginal cost curves.
A)it is easier to prevent arbitrage of a service than of a manufactured product.
B)monopoly is more common in the production of services than in production of manufactured goods.
C)price elasticities of demand differ more among consumers of services than customers of manufactured goods.
D)firms selling services are more likely to have constant marginal cost curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following consumer segments are benefited by price discrimination?
A)Consumers with high income
B)Consumers with perfectly inelastic demand
C)Consumers with highly elastic demand
D)Consumers with more than one source of income
A)Consumers with high income
B)Consumers with perfectly inelastic demand
C)Consumers with highly elastic demand
D)Consumers with more than one source of income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is true of intertemporal price discrimination?
A)In this form of price discrimination each consumer is charged his/her full willingness to pay.
B)In this form of price discrimination groups are charged different prices according to the time of purchase.
C)In this form of price discrimination monopolists capture the entire consumer surplus.
D)In this form of price discrimination a consumer is charged a fixed fee in each time period.
A)In this form of price discrimination each consumer is charged his/her full willingness to pay.
B)In this form of price discrimination groups are charged different prices according to the time of purchase.
C)In this form of price discrimination monopolists capture the entire consumer surplus.
D)In this form of price discrimination a consumer is charged a fixed fee in each time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is true of arbitrage?
A)It is the revenue from the sale of a used product.
B)It is the resale of a product among market segments.
C)It is the profit from initial sales of a product.
D)It is the ability of a firm to discriminate prices among customers.
A)It is the revenue from the sale of a used product.
B)It is the resale of a product among market segments.
C)It is the profit from initial sales of a product.
D)It is the ability of a firm to discriminate prices among customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is not a prerequisite for practicing third-degree price discrimination?
A)Some degree of monopoly power
B)Ability to separate customers into two or more identifiable groups
C)Some mechanism to prevent resale of the product among groups
D)A perfectly competitive market for inputs
A)Some degree of monopoly power
B)Ability to separate customers into two or more identifiable groups
C)Some mechanism to prevent resale of the product among groups
D)A perfectly competitive market for inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The following figure shows the indifference curves U1 and U2 of a consumer choosing between hours devoted at a tennis club and other goods.All consumers in this market have identical demand curves.IZ is the original budget line of a representative consumer,which shifts to AB when the club begins to charge an entry fee.
Figure 12-3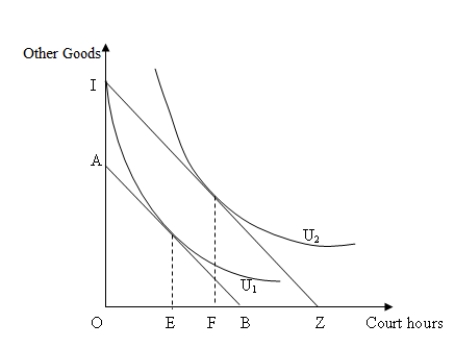
Refer to Figure 12-3.The price of a court hour to the consumer,in terms of other goods,is:
A)OI/OZ.
B)OI/BZ.
C)OI/OB.
D)AI/BZ.
Figure 12-3

Refer to Figure 12-3.The price of a court hour to the consumer,in terms of other goods,is:
A)OI/OZ.
B)OI/BZ.
C)OI/OB.
D)AI/BZ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following best describes a two-part tariff?
A)A discount provided to frequent shoppers
B)A price that varies with the quantity of output consumed
C)A price that varies with each individual consumer's ability to pay
D)An entry fee followed by a constant per-unit price
A)A discount provided to frequent shoppers
B)A price that varies with the quantity of output consumed
C)A price that varies with each individual consumer's ability to pay
D)An entry fee followed by a constant per-unit price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Consider a profit-maximizing monopolist whose consumers have identical demand curves.Which of the following will be true if the firm employs a two-part tariff pricing strategy for these consumers?
A)The firm will produce less output compared to a firm that is not using this pricing strategy.
B)The firm will capture the entire consumer surplus.
C)The firm will charge a tariff that also maximizes revenues.
D)The firm will charge consumers a different entry fee,but a constant per-unit price.
A)The firm will produce less output compared to a firm that is not using this pricing strategy.
B)The firm will capture the entire consumer surplus.
C)The firm will charge a tariff that also maximizes revenues.
D)The firm will charge consumers a different entry fee,but a constant per-unit price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The following figure shows the indifference curves U1 and U2 of a consumer choosing between hours devoted at a tennis club and other goods.All consumers in this market have identical demand curves.IZ is the original budget line of a representative consumer,which shifts to AB when the club begins to charge an entry fee.
Figure 12-3
In Figure 12-3,the consumer is indifferent between purchasing:
A)OF court hours and OE court hours.
B)OZ court hours and OB court hours.
C)zero court hours and OF court hours.
D)zero court hours and OE court hours.
Figure 12-3

In Figure 12-3,the consumer is indifferent between purchasing:
A)OF court hours and OE court hours.
B)OZ court hours and OB court hours.
C)zero court hours and OF court hours.
D)zero court hours and OE court hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
With a two-part tariff,consumers pay:
A)a constant "average" price per unit of output.
B)higher prices for purchasing greater quantities of output.
C)an "average" price per unit of output that declines with the quantity purchased.
D)a flat fee followed by an increasing per unit price.
A)a constant "average" price per unit of output.
B)higher prices for purchasing greater quantities of output.
C)an "average" price per unit of output that declines with the quantity purchased.
D)a flat fee followed by an increasing per unit price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is an advantage of peak-load pricing?
A)It allows a firm to reduce its total cost by reallocating its production.
B)It allows a firm to capture the entire consumer surplus.
C)It allows a firm to clearly identify each consumer's willingness to pay.
D)It reduces monopoly profits and increases consumer surplus.
A)It allows a firm to reduce its total cost by reallocating its production.
B)It allows a firm to capture the entire consumer surplus.
C)It allows a firm to clearly identify each consumer's willingness to pay.
D)It reduces monopoly profits and increases consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following strategies will allow a monopolist to earn higher profits by employing a two-part tariff on consumers with different demands?
A)Setting price equal to the marginal cost
B)Setting price above the marginal cost
C)Setting an entry fee equal to the consumer surplus
D)Setting an entry fee higher than the consumer surplus
A)Setting price equal to the marginal cost
B)Setting price above the marginal cost
C)Setting an entry fee equal to the consumer surplus
D)Setting an entry fee higher than the consumer surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Traffic congestion can be controlled by charging fees for the use of roadways.The fees vary with the demand for roadways at different hours of the day.It is usually very high during the business hours and low at other times of the day.This form of pricing strategy is referred to as:
A)price gouging.
B)peak-load pricing.
C)marginal use pricing.
D)second-degree price discrimination.
A)price gouging.
B)peak-load pricing.
C)marginal use pricing.
D)second-degree price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When a two-part tariff is employed on consumers with identical demand curves,the maximum entry fee the firm can charge:
A)is represented by the total area below the demand curve.
B)is equal to the total consumer surplus.
C)is equal to the total cost.
D)is equal to the average total cost.
A)is represented by the total area below the demand curve.
B)is equal to the total consumer surplus.
C)is equal to the total cost.
D)is equal to the average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Peak-load pricing is typically introduced when:
A)there are several competing firms.
B)resale of the product is relatively easy.
C)production costs vary in different time periods.
D)consumer demands are highly stable.
A)there are several competing firms.
B)resale of the product is relatively easy.
C)production costs vary in different time periods.
D)consumer demands are highly stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following price discrimination strategies allows a monopolist to distribute a product/service most efficiently between two periods of time?
A)Predatory pricing
B)Peak-load pricing
C)Block pricing
D)Two-part tariff
A)Predatory pricing
B)Peak-load pricing
C)Block pricing
D)Two-part tariff

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A two-part tariff involves:
A)a fixed entry fee plus a variable per-unit price.
B)a variable entry fee plus a variable per-unit price.
C)a fixed entry fee plus a fixed per-unit price.
D)a variable entry fee plus a fixed per-unit price.
A)a fixed entry fee plus a variable per-unit price.
B)a variable entry fee plus a variable per-unit price.
C)a fixed entry fee plus a fixed per-unit price.
D)a variable entry fee plus a fixed per-unit price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is true of a price discriminating monopolist employing a two-part tariff on consumers having different demands?
A)They earn less profit than the non-price discriminating monopolists.
B)They supply an output which is higher than the non-price discriminating monopoly output.
C)They set a price that is higher than the non- price discriminating monopoly price.
D)They set an entry fee which is more than the total consumer surplus.
A)They earn less profit than the non-price discriminating monopolists.
B)They supply an output which is higher than the non-price discriminating monopoly output.
C)They set a price that is higher than the non- price discriminating monopoly price.
D)They set an entry fee which is more than the total consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The efficiency gains from peak-load pricing depend largely upon:
A)the amount of regulation in the market.
B)the ability of users to cut back on consumption during peak periods.
C)the pricing strategy followed by the firm in the past.
D)the productivity of the inputs used in producing the output.
A)the amount of regulation in the market.
B)the ability of users to cut back on consumption during peak periods.
C)the pricing strategy followed by the firm in the past.
D)the productivity of the inputs used in producing the output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
With peak-load pricing,a firm charges a different price in each period,because:
A)its supply is perfectly inelastic.
B)its marginal cost of production varies in each period.
C)the number of consumers change every period.
D)the demand for the good is perfectly price elastic.
A)its supply is perfectly inelastic.
B)its marginal cost of production varies in each period.
C)the number of consumers change every period.
D)the demand for the good is perfectly price elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Under peak-load pricing,the price in each period is set:
A)equal to the average cost of production in that period.
B)above the marginal cost of production in that period.
C)where the marginal cost intersects the demand for that period.
D)where the average cost intersects the demand for that period.
A)equal to the average cost of production in that period.
B)above the marginal cost of production in that period.
C)where the marginal cost intersects the demand for that period.
D)where the average cost intersects the demand for that period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The following figure shows the indifference curves U1 and U2 of a consumer choosing between hours devoted at a tennis club and other goods.All consumers in this market have identical demand curves.IZ is the original budget line of a representative consumer,which shifts to AB when the club begins to charge an entry fee.
Figure 12-3
In Figure 12-3,if the fee goes above _____,the consumer will purchase no court hours.
A)OZ
B)IA
C)EF
D)OE
Figure 12-3

In Figure 12-3,if the fee goes above _____,the consumer will purchase no court hours.
A)OZ
B)IA
C)EF
D)OE

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A profit-maximizing monopolist employing a two-part tariff on consumers having different demands,_____.
A)should simply set price to maximize total revenue
B)should charge a single price,with no entry fee,like a regular monopolist
C)should set price equal to average cost plus a constant profit margin
D)does not have a clearly defined profit-maximizing pricing scheme
A)should simply set price to maximize total revenue
B)should charge a single price,with no entry fee,like a regular monopolist
C)should set price equal to average cost plus a constant profit margin
D)does not have a clearly defined profit-maximizing pricing scheme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A two-part tariff is a form of:
A)first-degree price discrimination because average cost falls with quantity purchased.
B)second-degree price discrimination because average price paid by the consumer falls with higher quantity purchased.
C)block pricing because marginal cost rises with quantity sold.
D)third-degree price discrimination because different customers pay different prices.
A)first-degree price discrimination because average cost falls with quantity purchased.
B)second-degree price discrimination because average price paid by the consumer falls with higher quantity purchased.
C)block pricing because marginal cost rises with quantity sold.
D)third-degree price discrimination because different customers pay different prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The following figure shows the indifference curves U1 and U2 of a consumer choosing between hours devoted at a tennis club and other goods.All consumers in this market have identical demand curves.IZ is the original budget line of a representative consumer,which shifts to AB when the club begins to charge an entry fee.
Figure 12-3
Refer to Figure 12-3.What is the amount of entry fee the club is charging the consumer?
A)OZ
B)IA
C)OI
D)OA
Figure 12-3

Refer to Figure 12-3.What is the amount of entry fee the club is charging the consumer?
A)OZ
B)IA
C)OI
D)OA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



