Deck 13: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/98
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
1
Product differentiation in monopolistically competitive markets:
A)can reflect real or perceived differences in the product.
B)cannot be done on the basis of a simple difference in packaging.
C)is not easily identifiable.
D)reduces each firm's ability to control prices.
A)can reflect real or perceived differences in the product.
B)cannot be done on the basis of a simple difference in packaging.
C)is not easily identifiable.
D)reduces each firm's ability to control prices.
A
2
Which of the following conditions holds for a monopolistically competitive firm that is in equilibrium in the long run?
A)Price equal to marginal cost
B)Marginal cost equal to average cost
C)Price equal to average cost
D)Marginal cost equal to average revenue
A)Price equal to marginal cost
B)Marginal cost equal to average cost
C)Price equal to average cost
D)Marginal cost equal to average revenue
C
3
Which of the following is not true of a monopolistically competitive firm in long run equilibrium?
A)Price exceeds marginal cost
B)The average total cost curve lies above the demand curve
C)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
D)The price elasticity of demand is zero
A)Price exceeds marginal cost
B)The average total cost curve lies above the demand curve
C)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
D)The price elasticity of demand is zero
D
4
Which of the following is true of product differentiation?
A)Product differentiation ensures that firms face a horizontal market demand curve.
B)Product differentiation allows monopolistically competitive firms to make positive economic profits in the long run.
C)Prices of differentiated products have to vary substantially for product differentiation to be successful.
D)Successful product differentiation can be based on differences that are perceived by consumers.
A)Product differentiation ensures that firms face a horizontal market demand curve.
B)Product differentiation allows monopolistically competitive firms to make positive economic profits in the long run.
C)Prices of differentiated products have to vary substantially for product differentiation to be successful.
D)Successful product differentiation can be based on differences that are perceived by consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
ABC Inc. ,is a leading consumer goods conglomerate.ABC launched a new variant of their existing brand of toothpaste that claimed not only to whiten teeth within 4 weeks but also fight cavities.In other words,ABC was practicing _____.
A)market segmentation
B)product differentiation
C)product customization
D)price skimming
A)market segmentation
B)product differentiation
C)product customization
D)price skimming

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
A)Inelastic demand
B)Free entry and exit
C)Homogeneous products
D)A small number of buyers
A)Inelastic demand
B)Free entry and exit
C)Homogeneous products
D)A small number of buyers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The markup of price over marginal cost of a profit-maximizing firm in the long run is _____.
A)higher in a perfectly competitive market than in a monopoly market
B)higher in a monopoly market than in a monopolistically competitive market
C)higher in a perfectly competitive market than in an oligopoly
D)higher in a monopolistically competitive market than in a competitive market
A)higher in a perfectly competitive market than in a monopoly market
B)higher in a monopoly market than in a monopolistically competitive market
C)higher in a perfectly competitive market than in an oligopoly
D)higher in a monopolistically competitive market than in a competitive market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When a monopolistically competitive firm is maximizing its profit: A)marginal revenue is also maximized.
B)average revenue exceeds marginal revenue.
C)total revenue declines to zero.
D)marginal revenue equals average revenue.
B)average revenue exceeds marginal revenue.
C)total revenue declines to zero.
D)marginal revenue equals average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Unlike a perfectly competitive firm,a monopolistically competitive firm:
A)makes zero economic profits in the short run.
B)caters to a large portion of the market.
C)does not face barriers to entry and exit.
D)sells a differentiated product.
A)makes zero economic profits in the short run.
B)caters to a large portion of the market.
C)does not face barriers to entry and exit.
D)sells a differentiated product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Unlike a monopolistically competitive market,firms in a perfectly competitive market:
A)equate marginal cost and marginal revenue.
B)set price at a level that is greater than marginal cost.
C)do not have any entry or exit barriers.
D)produce homogeneous goods.
A)equate marginal cost and marginal revenue.
B)set price at a level that is greater than marginal cost.
C)do not have any entry or exit barriers.
D)produce homogeneous goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A monopolistically competitive firm differs from a perfectly competitive firm in that:
A)the monopolistically competitive firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
B)the demand for the monopolistically competitive firm's product is fairly inelastic.
C)entry into a monopolistic market is restricted while entry is free in a perfectly competitive market.
D)a monopolistically competitive firm is a price taker in the market.
A)the monopolistically competitive firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
B)the demand for the monopolistically competitive firm's product is fairly inelastic.
C)entry into a monopolistic market is restricted while entry is free in a perfectly competitive market.
D)a monopolistically competitive firm is a price taker in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The demand curve that a monopolistically competitive firm faces is _____.
A)relatively elastic compared to a monopoly
B)perfectly elastic at the equilibrium price
C)relatively elastic compared to a perfectly competitive firm
D)perfectly inelastic at the equilibrium output
A)relatively elastic compared to a monopoly
B)perfectly elastic at the equilibrium price
C)relatively elastic compared to a perfectly competitive firm
D)perfectly inelastic at the equilibrium output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A monopolistically competitive firm that is maximizing profit will choose to produce at the level where:
A)total revenue is maximized.
B)average total cost exceeds average revenue.
C)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue exceeds average revenue.
A)total revenue is maximized.
B)average total cost exceeds average revenue.
C)marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue exceeds average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
From the shape of the monopolistically competitive firm's demand curve,you can imply that:
A)the firm has some degree of market power.
B)the firm sells a homogeneous good.
C)the firm's product has no substitutes.
D)the firm's level of output is efficient.
A)the firm has some degree of market power.
B)the firm sells a homogeneous good.
C)the firm's product has no substitutes.
D)the firm's level of output is efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The demand curve facing a monopolistically competitive firm is downward-sloping because:
A)substitutes for the good are easily available.
B)the firm produces homogeneous products.
C)there is only one seller in the market.
D)the price/marginal-cost markup is zero.
A)substitutes for the good are easily available.
B)the firm produces homogeneous products.
C)there is only one seller in the market.
D)the price/marginal-cost markup is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A monopolistically competitive firm is similar to a monopoly in that the firm:
A)has no rivals that produce close substitutes.
B)is very large relative to the market.
C)produces on the inelastic portion of its demand curve.
D)faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
A)has no rivals that produce close substitutes.
B)is very large relative to the market.
C)produces on the inelastic portion of its demand curve.
D)faces a downward-sloping demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A monopolistically competitive industry is similar to a perfectly competitive industry in that:
A)there is free entry and exit in both markets.
B)products are differentiated in both markets.
C)firms in both markets decide output and prices on the basis of strategic interaction.
D)the demand curves in both markets are downward-sloping.
A)there is free entry and exit in both markets.
B)products are differentiated in both markets.
C)firms in both markets decide output and prices on the basis of strategic interaction.
D)the demand curves in both markets are downward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The demand curve that a monopolistically competitive firm faces is _____.
A)downward-sloping but fairly elastic
B)upward-sloping but fairly inelastic
C)horizontal
D)vertical
A)downward-sloping but fairly elastic
B)upward-sloping but fairly inelastic
C)horizontal
D)vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market satisfies all of the following conditions,except:
A)zero economic profit.
B)excess capacity.
C)price equal to marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue equal to marginal cost.
A)zero economic profit.
B)excess capacity.
C)price equal to marginal cost.
D)marginal revenue equal to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Product differentiation and a certain degree of monopoly power are characteristics of:
A)perfectly competitive firms.
B)monopolistically competitive firms.
C)monopoly markets.
D)monopsony markets.
A)perfectly competitive firms.
B)monopolistically competitive firms.
C)monopoly markets.
D)monopsony markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Unlike monopolistically competitive firms,oligopolistic firms:
A)face a downward-sloping demand curve.
B)exhibit a strong mutual interdependence.
C)produce at the point where price is equal to marginal cost.
D)do not have a supply curve.
A)face a downward-sloping demand curve.
B)exhibit a strong mutual interdependence.
C)produce at the point where price is equal to marginal cost.
D)do not have a supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition is characterized by:
A)a positive deadweight loss.
B)a positive but small economic profit.
C)an equilibrium price that is equal to marginal cost.
D)an equilibrium price that is greater than average cost.
A)a positive deadweight loss.
B)a positive but small economic profit.
C)an equilibrium price that is equal to marginal cost.
D)an equilibrium price that is greater than average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In Cournot's duopoly model,a firm's profit-maximizing level of output:
A)depends on the market price of the good.
B)is based on the assumption that the other firm produces zero output.
C)based on the other firm's expected level of output,which is assumed to remain unchanged.
D)is equal to the other firm's expected level of output,which is assumed to remain unchanged.
A)depends on the market price of the good.
B)is based on the assumption that the other firm produces zero output.
C)based on the other firm's expected level of output,which is assumed to remain unchanged.
D)is equal to the other firm's expected level of output,which is assumed to remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Assume that there are only three sellers in the aluminium industry each producing identical aluminium sheets.Given that these three firms own all the known sources of aluminium,the _____ model of the market is most applicable to the aluminium industry.
A)oligopoly
B)monopoly
C)dominant firm model
D)monopolistic competition
A)oligopoly
B)monopoly
C)dominant firm model
D)monopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Monopolistically competitive firms _____.
A)earn positive economic profit both in the short run and the long run
B)suffer an economic loss in the long run
C)earn positive economic profit in the long run
D)earn zero economic profit in the long run
A)earn positive economic profit both in the short run and the long run
B)suffer an economic loss in the long run
C)earn positive economic profit in the long run
D)earn zero economic profit in the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is true of monopolistically competitive markets?
A)The economic profits of firms in a monopolistically competitive market are positive in the long run.
B)The cost of government regulation is small relative to the social losses from monopolistic competition.
C)Since the price and output combination in a monopolistically competitive market is efficient,there is no need for government regulation.
D)It is possible that the value created through product differentiation outweighs the efficiency loss from monopolistic competition.
A)The economic profits of firms in a monopolistically competitive market are positive in the long run.
B)The cost of government regulation is small relative to the social losses from monopolistic competition.
C)Since the price and output combination in a monopolistically competitive market is efficient,there is no need for government regulation.
D)It is possible that the value created through product differentiation outweighs the efficiency loss from monopolistic competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A monopolistically competitive industry is characterized by:
A)excess capacity.
B)an efficient level of output.
C)inelastic demand for its products.
D)positive economic profits in the long run.
A)excess capacity.
B)an efficient level of output.
C)inelastic demand for its products.
D)positive economic profits in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Government intervention in monopolistically competitive industries is probably not warranted because:
A)monopolistic firms produce the efficient level of output.
B)deadweight losses from monopolistic competition are hard to quantify.
C)the cost of regulation may be higher than the deadweight loss.
D)price regulation usually leads to a decline in total surplus .
A)monopolistic firms produce the efficient level of output.
B)deadweight losses from monopolistic competition are hard to quantify.
C)the cost of regulation may be higher than the deadweight loss.
D)price regulation usually leads to a decline in total surplus .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is true of the Cournot duopoly model?
A)It shows how the interaction of uncoordinated output decisions of rival firms leads to equilibrium in the oligopoly market.
B)It explains how prices are determined in a market that has a large number of firms and a homogeneous product.
C)It shows how equilibrium is attained in a market where two firms collude to set output and price equal to the monopoly output and price.
D)It explains how prices are determined in a market with a single dominant firm and a large number of competitive fringe firms.
A)It shows how the interaction of uncoordinated output decisions of rival firms leads to equilibrium in the oligopoly market.
B)It explains how prices are determined in a market that has a large number of firms and a homogeneous product.
C)It shows how equilibrium is attained in a market where two firms collude to set output and price equal to the monopoly output and price.
D)It explains how prices are determined in a market with a single dominant firm and a large number of competitive fringe firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A duopoly is defined as an industry with _____.
A)two distinct types of buyers
B)two sellers
C)multiple product lines
D)a homogeneous product
A)two distinct types of buyers
B)two sellers
C)multiple product lines
D)a homogeneous product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Oligopoly cannot be explained using a single theoretical model because:
A)oligopolistic markets are not really found in the real world.
B)the assumptions of the oligopoly model are not realistic.
C)product differentiation makes the model too complex.
D)mutual interdependence makes it difficult to analyze strategic behavior.
A)oligopolistic markets are not really found in the real world.
B)the assumptions of the oligopoly model are not realistic.
C)product differentiation makes the model too complex.
D)mutual interdependence makes it difficult to analyze strategic behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a defining characteristic of an oligopoly?
A)A large number of sellers
B)Mutual interdependence between firms
C)Economies of scale in production
D)A large number of buyers
A)A large number of sellers
B)Mutual interdependence between firms
C)Economies of scale in production
D)A large number of buyers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The output of a monopolistically competitive industry is inefficient because firms:
A)produce at the highest point on the average cost curve.
B)do not produce at the minimum point on their average cost curve.
C)produce at the highest point on the marginal cost curve.
D)do not produce at the minimum point on the marginal cost curve.
A)produce at the highest point on the average cost curve.
B)do not produce at the minimum point on their average cost curve.
C)produce at the highest point on the marginal cost curve.
D)do not produce at the minimum point on the marginal cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is a key element of the Cournot model?
A)The price in an oligopoly market increases proportionally for both firms.
B)The output of one firm is determined keeping the output of other firms fixed.
C)The output of both firms in an oligopoly market is kept fixed.
D)The price in an oligopoly market will not increase above a certain level.
A)The price in an oligopoly market increases proportionally for both firms.
B)The output of one firm is determined keeping the output of other firms fixed.
C)The output of both firms in an oligopoly market is kept fixed.
D)The price in an oligopoly market will not increase above a certain level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For a monopolistically competitive firm,excess capacity is the difference between the equilibrium level of output and the level of output where:
A)marginal cost is minimum.
B)average total cost is minimum.
C)marginal revenue is maximum.
D)total revenue is maximum.
A)marginal cost is minimum.
B)average total cost is minimum.
C)marginal revenue is maximum.
D)total revenue is maximum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following would weaken the argument that monopolistically competitive firms should be regulated by the government?
A)Monopolistically competitive firms and perfectly competitive firms are similar in that their equilibrium prices and quantities are efficient.
B)Monopolistically competitive firms earn zero economic profits in the short run just as perfectly competitive firms do.
C)The benefits of increased product variety produced by monopolistic competition offsets the relatively small welfare costs.
D)The cost of regulating a monopolistically competitive firm could possibly be lower than the deadweight loss from monopolistic competition.
A)Monopolistically competitive firms and perfectly competitive firms are similar in that their equilibrium prices and quantities are efficient.
B)Monopolistically competitive firms earn zero economic profits in the short run just as perfectly competitive firms do.
C)The benefits of increased product variety produced by monopolistic competition offsets the relatively small welfare costs.
D)The cost of regulating a monopolistically competitive firm could possibly be lower than the deadweight loss from monopolistic competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When a firm in a monopolistically competitive market is operating at excess capacity it implies that:
A)it is producing the efficient level of output.
B)it is producing more than the competitive level of output
C)it can produce output at a lower cost
D)it is facing an upward-sloping average cost curve
A)it is producing the efficient level of output.
B)it is producing more than the competitive level of output
C)it can produce output at a lower cost
D)it is facing an upward-sloping average cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following,if true,will be the best example of an oligopoly market?
A)The cigarette industry where a similar product is produced by a small number of sellers
B)Dine-in pizza outlets where a differentiated product is produced by a large number of sellers
C)The milk industry where a homogeneous product is provided by a large number of sellers
D)The market for electricity where a single firm can produce electricity at the lowest possible cost
A)The cigarette industry where a similar product is produced by a small number of sellers
B)Dine-in pizza outlets where a differentiated product is produced by a large number of sellers
C)The milk industry where a homogeneous product is provided by a large number of sellers
D)The market for electricity where a single firm can produce electricity at the lowest possible cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is true of a firm in an oligopoly market?
A)Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve with a kink at the current price.
B)Firms in oligopoly markets are very small relative to the market.
C)Products in oligopoly markets could either be differentiated or homogeneous.
D)The profit-maximizing output is determined by equating price and marginal cost.
A)Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve with a kink at the current price.
B)Firms in oligopoly markets are very small relative to the market.
C)Products in oligopoly markets could either be differentiated or homogeneous.
D)The profit-maximizing output is determined by equating price and marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A monopolistically competitive firm is considered to have excess capacity because it:
A)does not operate at the minimum point on its long-run average cost curve.
B)does not operate at the minimum point on its marginal cost curve.
C)operates at the point where average cost is greater than average revenue.
D)operates at the point where marginal cost is above average revenue.
A)does not operate at the minimum point on its long-run average cost curve.
B)does not operate at the minimum point on its marginal cost curve.
C)operates at the point where average cost is greater than average revenue.
D)operates at the point where marginal cost is above average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the Stackelberg model,the leader firm's residual demand curve _____.
A)has a slope that is twice that of the market demand curve
B)has a slope that is half the slope of the market demand curve
C)is the same as the market demand curve
D)is more inelastic than the market demand curve
A)has a slope that is twice that of the market demand curve
B)has a slope that is half the slope of the market demand curve
C)is the same as the market demand curve
D)is more inelastic than the market demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 13-1 shows the Stackelberg model of a duopoly.Both firms face constant marginal costs equal to OJ and the market demand curve is AD.The Stackelberg firm produces an output of OF and OF is equal to FL. 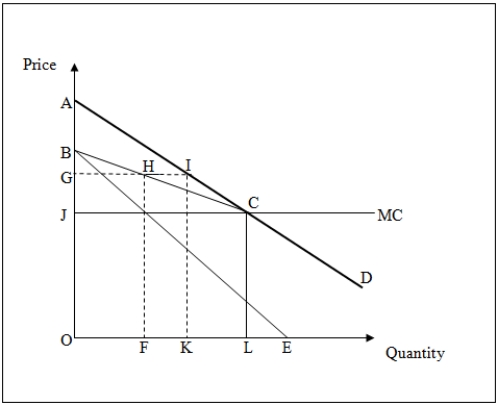
Refer to Figure 13-1.The output of the follower firm is represented by the distance _____.
A)OF
B)OK
C)KL
D)FK

Refer to Figure 13-1.The output of the follower firm is represented by the distance _____.
A)OF
B)OK
C)KL
D)FK

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 13-1 shows the Stackelberg model of a duopoly.Both firms face constant marginal costs equal to OJ and the market demand curve is AD.The Stackelberg firm produces an output of OF and OF is equal to FL. 
Refer to Figure 13-1.In the Stackelberg equilibrium,the total industry output is _____.
A)OF
B)OK
C)OE
D)OL

Refer to Figure 13-1.In the Stackelberg equilibrium,the total industry output is _____.
A)OF
B)OK
C)OE
D)OL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Compared to a Cournot equilibrium,the _____ in a Stackelberg equilibrium.
A)price paid by the consumers is higher
B)total industry output is higher
C)profit made by the leader firm is lower
D)output is closer to monopoly output
A)price paid by the consumers is higher
B)total industry output is higher
C)profit made by the leader firm is lower
D)output is closer to monopoly output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 13-1 shows the Stackelberg model of a duopoly.Both firms face constant marginal costs equal to OJ and the market demand curve is AD.The Stackelberg firm produces an output of OF and OF is equal to FL. 
Refer to Figure 13-1.The Stackelberg firm's residual demand curve is given by:
A)AC
B)BCD
C)BE
D)JCD

Refer to Figure 13-1.The Stackelberg firm's residual demand curve is given by:
A)AC
B)BCD
C)BE
D)JCD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In _____,one firm uses its knowledge of the other firms' reaction functions to enhance its own profits.
A)the Cournot duopoly
B)a monopolistically competitive market
C)a perfectly competitive market
D)the Stackelberg model
A)the Cournot duopoly
B)a monopolistically competitive market
C)a perfectly competitive market
D)the Stackelberg model

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The Stackelberg model is different from the Cournot model because:
A)the Stackelberg model assumes that firms compete by varying their prices while the Cournot model assumes that firms compete by varying their output.
B)the Stackelberg model assumes that one firm selects its output on the basis of the other firm's reaction curve while the Cournot model assumes that both firms take each other's output as given.
C)the Stackelberg model assumes that both firms try to predict each other's reaction curves while the Cournot model assumes that the level of output of both firms is fixed.
D)the Stackelberg model assumes that one firm dominates the market through its market share while the Cournot model assumes that all firms are small relative to the market.
A)the Stackelberg model assumes that firms compete by varying their prices while the Cournot model assumes that firms compete by varying their output.
B)the Stackelberg model assumes that one firm selects its output on the basis of the other firm's reaction curve while the Cournot model assumes that both firms take each other's output as given.
C)the Stackelberg model assumes that both firms try to predict each other's reaction curves while the Cournot model assumes that the level of output of both firms is fixed.
D)the Stackelberg model assumes that one firm dominates the market through its market share while the Cournot model assumes that all firms are small relative to the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A _____ shows the relationship between one firm's profit-maximizing output as a function of the output of a rival firm in a duopoly market.
A)demand curve
B)supply curve
C)joint output curve
D)reaction curve
A)demand curve
B)supply curve
C)joint output curve
D)reaction curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The main assumption of the Cournot model:
A)is more plausible the larger the number of firms in the industry.
B)is that each firm takes the other firm's price as given.
C)is not valid once equilibrium is established in the market.
D)takes into account the reactions of other firms.
A)is more plausible the larger the number of firms in the industry.
B)is that each firm takes the other firm's price as given.
C)is not valid once equilibrium is established in the market.
D)takes into account the reactions of other firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For firms with constant and equal long-run marginal cost curves,the Cournot equilibrium occurs at:
A)the point of intersection of the firms' reaction curves.
B)the point where price equals marginal cost.
C)the point where the demand curve is tangent to the marginal cost curve.
D)the point of intersection of one firm's reaction curve and the demand curve.
A)the point of intersection of the firms' reaction curves.
B)the point where price equals marginal cost.
C)the point where the demand curve is tangent to the marginal cost curve.
D)the point of intersection of one firm's reaction curve and the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure 13-1 shows the Stackelberg model of a duopoly.Both firms face constant marginal costs equal to OJ and the market demand curve is AD.The Stackelberg firm produces an output of OF and OF is equal to FL. 
Refer to Figure 13-1.The difference between the total industry output produced under a perfect competition model and a Stackelberg model is represented by the distance _____.
A)KF
B)KL
C)LE
D)FL

Refer to Figure 13-1.The difference between the total industry output produced under a perfect competition model and a Stackelberg model is represented by the distance _____.
A)KF
B)KL
C)LE
D)FL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the Stackelberg model of oligopoly:
A)each firm takes the other firm's output as constant in deciding its own output level.
B)the leader firm's output is determined at the point where demand equals price.
C)the leader firm selects its output first,taking the reactions of follower firms into account.
D)each firm decides its output based on the interaction of demand and supply.
A)each firm takes the other firm's output as constant in deciding its own output level.
B)the leader firm's output is determined at the point where demand equals price.
C)the leader firm selects its output first,taking the reactions of follower firms into account.
D)each firm decides its output based on the interaction of demand and supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The residual demand curve shows:
A)the quantity that the dominant firm sells at each price after accounting for the fringe firms' output.
B)the quantity that fringe firms sell at each price based on the output of the dominant firm.
C)the quantity that the dominant firm supplies at each price irrespective of the market output.
D)the combined quantity that is sold at each price in the market by the dominant and fringe firms.
A)the quantity that the dominant firm sells at each price after accounting for the fringe firms' output.
B)the quantity that fringe firms sell at each price based on the output of the dominant firm.
C)the quantity that the dominant firm supplies at each price irrespective of the market output.
D)the combined quantity that is sold at each price in the market by the dominant and fringe firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the Cournot duopoly model,the reaction curve shows:
A)one firm's best possible price as a function of the profit of the other firm.
B)one firm's most possible profit as a function of the costs of the other firm.
C)one firm's best possible revenue as a function of the profit of the other firm.
D)one firm's most profitable output as a function of the output of the other firm.
A)one firm's best possible price as a function of the profit of the other firm.
B)one firm's most possible profit as a function of the costs of the other firm.
C)one firm's best possible revenue as a function of the profit of the other firm.
D)one firm's most profitable output as a function of the output of the other firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Given the same demand and cost conditions,_____ for a Stackelberg model as compared to a Cournot duopoly model.
A)total output is lower and price is higher
B)total output is higher and price is lower
C)total output and price are both lower
D)total output and price are both higher
A)total output is lower and price is higher
B)total output is higher and price is lower
C)total output and price are both lower
D)total output and price are both higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If,in the Cournot model of a duopoly,the firms colluded instead of behaving independently:
A)the outcome would be closer to the competitive equilibrium.
B)the outcome would be indeterminate.
C)firms could increase their combined profit.
D)the price will be below average cost.
A)the outcome would be closer to the competitive equilibrium.
B)the outcome would be indeterminate.
C)firms could increase their combined profit.
D)the price will be below average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the Stackelberg model of oligopoly,the dominant firm:
A)will equate marginal cost with the residual demand curve to maximize profits.
B)faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
C)can maximize profits ignoring the actions of other firms in the industry.
D)faces a marginal revenue curve that lies under the residual demand curve.
A)will equate marginal cost with the residual demand curve to maximize profits.
B)faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
C)can maximize profits ignoring the actions of other firms in the industry.
D)faces a marginal revenue curve that lies under the residual demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A significant criticism of the Cournot model is that:
A)markets do not operate according to the Cournot model in the real world.
B)its key assumption does not hold if the market is still adjusting toward equilibrium.
C)firms cannot estimate reaction curves of other firms.
D)the Cournot model cannot be applied to industries with more than two firms.
A)markets do not operate according to the Cournot model in the real world.
B)its key assumption does not hold if the market is still adjusting toward equilibrium.
C)firms cannot estimate reaction curves of other firms.
D)the Cournot model cannot be applied to industries with more than two firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Assume that there are only two full-service airline firms in a country.The service provided to the consumers by each of them is marginally different.Given that the full-service airline industry has high entry costs,the _____ model of the market is most applicable to this industry.
A)oligopoly
B)monopoly
C)dominant firm model
D)perfectly competitive
A)oligopoly
B)monopoly
C)dominant firm model
D)perfectly competitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the Stackelberg model of oligopoly,the leader firm:
A)sets the price in the market which the follower firms take as given.
B)produces a larger quantity than follower firms and enhances its profits.
C)chooses output and prices irrespective of the other firms in the market.
D)produces a level of output which is equal to that of the follower firms.
A)sets the price in the market which the follower firms take as given.
B)produces a larger quantity than follower firms and enhances its profits.
C)chooses output and prices irrespective of the other firms in the market.
D)produces a level of output which is equal to that of the follower firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the dominant firm model,if the elasticity of market demand is 0.75,the dominant firm's market share is 0.25,and the elasticity of supply of the competitive fringe is 2,then the dominant firm's elasticity of demand is _____.
A)3
B)5
C)7
D)9
A)3
B)5
C)7
D)9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A single firm serves a large part of the market.The rest of the market is served by a large number of competitive firms.Which market model is best applicable to this type of industry?
A)Monopoly
B)Monopolistic competition
C)Dominant firm model
D)Cournot duopoly
A)Monopoly
B)Monopolistic competition
C)Dominant firm model
D)Cournot duopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the dominant firm model of oligopoly,the dominant firm assumes that the other firms in the market:
A)will charge a higher price than it does.
B)will together produce a lower quantity of output than it does.
C)behave like competitive firms.
D)behave like monopolistic firms.
A)will charge a higher price than it does.
B)will together produce a lower quantity of output than it does.
C)behave like competitive firms.
D)behave like monopolistic firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following will determine the elasticity of a dominant firm's demand curve?
A)The dominant firm's marginal cost of production
B)The demand elasticity of the fringe firms
C)The total output in the market
D)The supply elasticity of the fringe firms
A)The dominant firm's marginal cost of production
B)The demand elasticity of the fringe firms
C)The total output in the market
D)The supply elasticity of the fringe firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How does the Cournot model of oligopoly differ from the Stackelberg model?
A)The Cournot model cannot be extended to include more than two firms unlike the Stackelberg model.
B)The Cournot model explains the mutual interdependence of firms in an oligopoly market unlike the Stackelberg model.
C)The equilibrium output in the Stackelberg model is relatively higher than the Cournot model.
D)The Cournot model assumes that a single firm is the market leader while the Stackelberg model assumes no single firm has a large market share.
A)The Cournot model cannot be extended to include more than two firms unlike the Stackelberg model.
B)The Cournot model explains the mutual interdependence of firms in an oligopoly market unlike the Stackelberg model.
C)The equilibrium output in the Stackelberg model is relatively higher than the Cournot model.
D)The Cournot model assumes that a single firm is the market leader while the Stackelberg model assumes no single firm has a large market share.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following the best example of a cartel?
A)An association of tobacco companies that attempts to influence anti-tobacco legislation
B)A labor union that raises wages above competitive level by restricting the supply of labor
C)A group of countries that sign an agreement to lower trade barriers and exchange goods and services
D)Firms that register their headquarters in the Cayman Islands in order to evade corporate taxes
A)An association of tobacco companies that attempts to influence anti-tobacco legislation
B)A labor union that raises wages above competitive level by restricting the supply of labor
C)A group of countries that sign an agreement to lower trade barriers and exchange goods and services
D)Firms that register their headquarters in the Cayman Islands in order to evade corporate taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the dominant firm model of oligopoly,the rival firms will:
A)equate marginal cost with marginal revenue.
B)produce at the point where marginal cost is equal to residual demand.
C)produce on the inelastic portion of the demand curve.
D)equate marginal cost with the dominant firm's price.
A)equate marginal cost with marginal revenue.
B)produce at the point where marginal cost is equal to residual demand.
C)produce on the inelastic portion of the demand curve.
D)equate marginal cost with the dominant firm's price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Consider a dominant firm model where the elasticity of market demand is 2,the elasticity of supply of the competitive fringe is 4,and the elasticity of the dominant firm's demand is 10.Calculate the dominant firm's market share.
A)2/3
B)2/5
C)3/5
D)3/7
A)2/3
B)2/5
C)3/5
D)3/7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In an industry where one firm with a high market share uses the reaction curves of other firms to set output,the _____ model is most applicable.
A)Cournot duopoly
B)perfectly competitive
C)Stackelberg
D)dominant firm
A)Cournot duopoly
B)perfectly competitive
C)Stackelberg
D)dominant firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How is total output determined in the dominant firm model?
A)The dominant firm produces the highest level of output given its production function.
B)All firms in the market produce at the level where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
C)The dominant firm produces at the level where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
D)The fringe firms produce at the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A)The dominant firm produces the highest level of output given its production function.
B)All firms in the market produce at the level where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
C)The dominant firm produces at the level where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
D)The fringe firms produce at the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How does the Stackelberg model of oligopoly differ from the dominant firm model?
A)The Stackelberg model assumes a single leader firm unlike the dominant firm model where all firms share output equally.
B)In the dominant firm model,the fringe firms are competitive while in the Stackelberg model,the follower firms display Cournot behavior.
C)The dominant firm model is only applicable to a duopoly while the Stackelberg model can be applied to all oligopolistic markets.
D)The Stackelberg leader produces along the market demand curve while the dominant firm produces along the residual demand curve.
A)The Stackelberg model assumes a single leader firm unlike the dominant firm model where all firms share output equally.
B)In the dominant firm model,the fringe firms are competitive while in the Stackelberg model,the follower firms display Cournot behavior.
C)The dominant firm model is only applicable to a duopoly while the Stackelberg model can be applied to all oligopolistic markets.
D)The Stackelberg leader produces along the market demand curve while the dominant firm produces along the residual demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose ABC Concrete is the dominant firm in a market consisting of five firms.ABC's market share is 40% of the market.The elasticity of market demand is 0.8 and the elasticity of supply for the remaining firms is 6.What is the elasticity of demand for ABC's product?
A)6
B)8
C)11
D)13
A)6
B)8
C)11
D)13

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Consider a dominant firm model in which the elasticity of market demand is 1,the dominant firm's market share is 0.5,and the elasticity of supply of the competitive fringe firms is 4.What would be the dominant firm's elasticity of demand?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The output of a cartel that maximizes profits is closest to the equilibrium output of:
A)a perfectly competitive firm.
B)a monopoly.
C)a monopolistically competitive firm.
D)an oligopoly.
A)a perfectly competitive firm.
B)a monopoly.
C)a monopolistically competitive firm.
D)an oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries [OPEC] serves the global oil market.Suppose Saudi Arabia,an OPEC member country,produces 50% of the oil supplied to this market.The elasticity of market demand is 0.4 and the elasticity of supply for the other eleven OPEC countries is 1.What is the elasticity of demand for oil produced by Saudi Arabia?
A)0.4
B)2.4
C)1.8
D)3.4
A)0.4
B)2.4
C)1.8
D)3.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In an industry with a small number of equal-sized firms where none of the firms have superior knowledge,the _____ is most likely to apply.
A)Cournot model of oligopoly
B)perfectly competitive model
C)dominant firm model of oligopoly
D)Stackelberg model of oligopoly
A)Cournot model of oligopoly
B)perfectly competitive model
C)dominant firm model of oligopoly
D)Stackelberg model of oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In the dominant firm model of oligopoly,the dominant firm maximizes profits by producing at the point where:
A)its marginal revenue is equal to its marginal cost.
B)the market demand equals the supply by the competitive fringe firms.
C)its marginal cost curve intersects the market demand curve.
D)its demand curve coincides with the market demand curve.
A)its marginal revenue is equal to its marginal cost.
B)the market demand equals the supply by the competitive fringe firms.
C)its marginal cost curve intersects the market demand curve.
D)its demand curve coincides with the market demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the dominant firm model,if the dominant firm's market share is 3/7,its elasticity of demand is 10 and the elasticity of supply of the competitive fringe firms is 4,then the elasticity of market demand must be _____.
A)4
B)3
C)2
D)1
A)4
B)3
C)2
D)1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If the member of a cartel violates the cartel agreement and sells at a price below the cartel price:
A)the violator will not be able to sell the additional output at a price above his marginal cost.
B)the violator will make a smaller profit per unit that he sells.
C)the violator will face a more elastic demand curve for the additional output.
D)the violator's demand curve will be downward sloping for the additional output.
A)the violator will not be able to sell the additional output at a price above his marginal cost.
B)the violator will make a smaller profit per unit that he sells.
C)the violator will face a more elastic demand curve for the additional output.
D)the violator's demand curve will be downward sloping for the additional output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The price that is set by a cartel is most likely to be:
A)lower than the marginal cost.
B)lower than the competitive price.
C)higher than average revenue.
D)equal to the monopoly price.
A)lower than the marginal cost.
B)lower than the competitive price.
C)higher than average revenue.
D)equal to the monopoly price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



