Deck 7: Production
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/112
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Production
1
A carpenter hammers nails each day at work.During the first hour she can hammer 120 nails,the second hour 100 nails,the third hour 90 nails,the fourth hour 60 nails,and the fifth hour 10 nails.Her marginal product in the third hour is _____ nails.
A)10
B)-10
C)90
D)-60
A)10
B)-10
C)90
D)-60
C
2
Table 7-2 shows the combinations of labor and capital that are used to produce various levels of output.
Table 7-2
-Refer to Table 7-2.A rational producer would never operate with _____ units of labor and 2 units of capital.
A)2
B)1
C)5
D)4
Table 7-2
-Refer to Table 7-2.A rational producer would never operate with _____ units of labor and 2 units of capital.
A)2
B)1
C)5
D)4
5
3
A carpenter hammers nails each day at work.The average number of nails hammered over the first three hours is 50,and the marginal product of the fourth and fifth hours of work is 40 and 20 nails,respectively.The total output after five hours work is _____ nails.
A)150
B)110
C)210
D)60
A)150
B)110
C)210
D)60
C
4
The ratio of total product to the total quantity of the input being used is _____.
A)equal to marginal product
B)constant as the levels of the input vary
C)equal to average product
D)equal to the marginal rate of technical substitution
A)equal to marginal product
B)constant as the levels of the input vary
C)equal to average product
D)equal to the marginal rate of technical substitution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If the average product of labor is 150 bushels of wheat when three workers farm an acre of land and the marginal product of the fourth worker is 75 bushels,then the total output with four workers is _____ bushels.
A)225
B)50
C)525
D)675
A)225
B)50
C)525
D)675

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The ratio of the change in total product to the change in total quantity of the input being used is _____.
A)equal to marginal product
B)constant as employment levels of the input vary
C)equal to average product
D)equal to the marginal rate of technical substitution
A)equal to marginal product
B)constant as employment levels of the input vary
C)equal to average product
D)equal to the marginal rate of technical substitution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is true of fixed costs?
A)Fixed costs can be changed,but it is extremely costly to do so in a short period of time.
B)Fixed costs cannot be changed in the long-run.
C)Fixed costs can be changed,but only in the short run.
D)Fixed costs cannot be changed in the short-run,because most firms experience constant returns to scale in the short run.
A)Fixed costs can be changed,but it is extremely costly to do so in a short period of time.
B)Fixed costs cannot be changed in the long-run.
C)Fixed costs can be changed,but only in the short run.
D)Fixed costs cannot be changed in the short-run,because most firms experience constant returns to scale in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is meant by technological efficiency in production?
A)Using the latest available technology in production
B)Producing the maximum possible output from given inputs
C)Using the least number of inputs in production
D)Minimizing the cost of production
A)Using the latest available technology in production
B)Producing the maximum possible output from given inputs
C)Using the least number of inputs in production
D)Minimizing the cost of production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Table 7.1 shows the quantities of labor and capital required to produce various levels of output.
Table 7-1
-Refer to Table 7-1.What is the average product of labor when four units of labor are used?
A)10
B)14
C)42
D)33
Table 7-1
-Refer to Table 7-1.What is the average product of labor when four units of labor are used?
A)10
B)14
C)42
D)33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A carpenter hammers nails each day at work.In each of the first three hours 50 nails were hammered and the marginal product of the fourth and fifth hours of work is 40 and 20 nails,respectively.Diminishing returns will be experienced in the _____ hour.
A)second
B)third
C)fourth
D)first
A)second
B)third
C)fourth
D)first

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A production function for widgets will _____.
A)show the relationship between the inputs used in the production of widgets and the cost of acquiring these inputs
B)identify the least quantity of inputs that can be used to produce a given level of widgets
C)identify the maximum quantity of widgets that can be produced given the budget of the firm
D)identify the maximum quantity of widgets that can be produced by each specific combination of inputs
A)show the relationship between the inputs used in the production of widgets and the cost of acquiring these inputs
B)identify the least quantity of inputs that can be used to produce a given level of widgets
C)identify the maximum quantity of widgets that can be produced given the budget of the firm
D)identify the maximum quantity of widgets that can be produced by each specific combination of inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A production function identifies the _____.
A)minimum output that a specific combination of inputs can produce
B)maximum number of inputs that can be used to produce output
C)highest possible output for a given combination of inputs
D)least-cost method of producing a given level of output
A)minimum output that a specific combination of inputs can produce
B)maximum number of inputs that can be used to produce output
C)highest possible output for a given combination of inputs
D)least-cost method of producing a given level of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A carpenter hammers nails each day at work.During the first hour she can hammer 120 nails,the second hour 100 nails,the third hour 90 nails,the fourth hour 60 nails,and the fifth hour 10 nails.The average product of five hours work is _____ nails.
A)80
B)380
C)320
D)76
A)80
B)380
C)320
D)76

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Economists use production functions to _____.
A)define what is technically efficient for different combinations of inputs
B)explain the tradeoff between the use of different inputs in production
C)maximize profits for a firm
D)define the marginal utilities associated with the goods produced
A)define what is technically efficient for different combinations of inputs
B)explain the tradeoff between the use of different inputs in production
C)maximize profits for a firm
D)define the marginal utilities associated with the goods produced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following correctly describes a production function?
A)A production function shows the minimum output that can be produced with given inputs.
B)A production function relates employment of inputs to output.
C)A production function identifies output-cost relationships.
D)A production function identifies the profit maximizing level of output.
A)A production function shows the minimum output that can be produced with given inputs.
B)A production function relates employment of inputs to output.
C)A production function identifies output-cost relationships.
D)A production function identifies the profit maximizing level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A firm that is operating in a technologically inefficient way:
A)is getting the maximum output from its inputs.
B)is making zero economic profits.
C)is not making as much money as it potentially can.
D)should shut down immediately to reduce its losses.
A)is getting the maximum output from its inputs.
B)is making zero economic profits.
C)is not making as much money as it potentially can.
D)should shut down immediately to reduce its losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Table 7-3 shows the combinations of labor and capital required to produce various level of output.
Table 7-3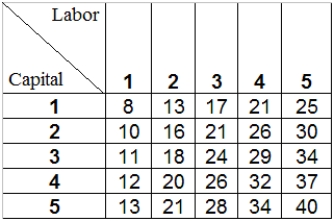
Refer to Table 7-3.Assume that capital remains fixed while labor is the only variable input used in production.If the firm is currently producing 26 units of output using three units of labor,what is the marginal product of labor at this point?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
Table 7-3

Refer to Table 7-3.Assume that capital remains fixed while labor is the only variable input used in production.If the firm is currently producing 26 units of output using three units of labor,what is the marginal product of labor at this point?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A farmer is growing corn on an acre of land.Output will be 200 bushels if one worker is hired,500 if two,700 if three,850 if four,and 900 if five.The marginal product of the fourth worker is _____ bushels of corn.
A)850
B)150
C)212.5
D)50
A)850
B)150
C)212.5
D)50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A carpenter hammers nails each day at work.During the first hour she can hammer 120 nails,the second hour 100 nails,the third hour 90 nails,the fourth hour 60 nails,and the fifth hour 10 nails.The total product of five hours of work is _____ nails.
A)10
B)380
C)320
D)60
A)10
B)380
C)320
D)60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A technologically efficient level of output is the _____.
A)maximum output possible from the least amount of inputs
B)level of output produced using the latest technology available
C)cost-minimizing level of output
D)maximum output available from a given set of inputs
A)maximum output possible from the least amount of inputs
B)level of output produced using the latest technology available
C)cost-minimizing level of output
D)maximum output available from a given set of inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Table 7-3 shows the combinations of labor and capital required to produce various level of output.
Table 7-3
Refer to Table 7-3.Assume that labor remains fixed while capital is the only variable input used in production.If the firm is currently producing 26 units of output using three units of labor,what is the marginal product of capital at this point?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8
Table 7-3

Refer to Table 7-3.Assume that labor remains fixed while capital is the only variable input used in production.If the firm is currently producing 26 units of output using three units of labor,what is the marginal product of capital at this point?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 7-1 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-1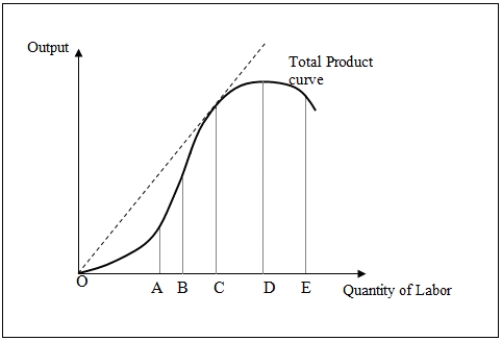
Refer to Figure 7-1.A firm would choose to operate between points C and D because:
A)marginal product has already reached a maximum.
B)average product is rising over that range.
C)marginal product and average product are positive,but falling.
D)marginal product and average product are rising.
Figure 7-1

Refer to Figure 7-1.A firm would choose to operate between points C and D because:
A)marginal product has already reached a maximum.
B)average product is rising over that range.
C)marginal product and average product are positive,but falling.
D)marginal product and average product are rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When the total product curve with only one variable input is increasing at a decreasing rate:
A)marginal product is positive but declining.
B)marginal product curve is negative and decreasing.
C)the slope of the marginal product curve is zero.
D)marginal product is positive and increasing.
A)marginal product is positive but declining.
B)marginal product curve is negative and decreasing.
C)the slope of the marginal product curve is zero.
D)marginal product is positive and increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If total product is increasing at a decreasing rate,then marginal product is _____.
A)below average product at all levels of output
B)above average product at all levels of output
C)declining faster than average product
D)increasing at a decreasing rate
A)below average product at all levels of output
B)above average product at all levels of output
C)declining faster than average product
D)increasing at a decreasing rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The average product of labor at a particular point can be determined:
A)by the slope of the total product curve at that point.
B)by multiplying the total product by the quantity of labor at that point.
C)by the slope of a line from the origin to the particular point on the total product curve.
D)by the vertical distance of the average product curve from the marginal product curve.
A)by the slope of the total product curve at that point.
B)by multiplying the total product by the quantity of labor at that point.
C)by the slope of a line from the origin to the particular point on the total product curve.
D)by the vertical distance of the average product curve from the marginal product curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2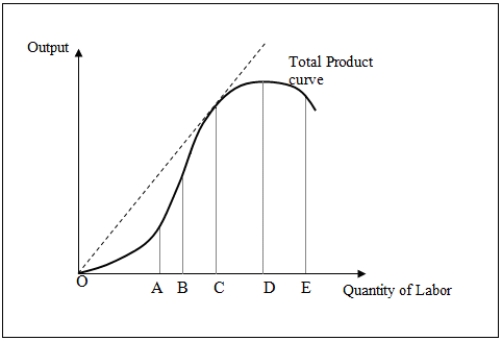
When the labor input employed in production is between points O and C in Figure 7-2:
A)average product reaches a minimum.
B)marginal product reaches a maximum.
C)marginal product is below average product.
D)total product first increases at a decreasing rate and then increases at an increasing rate.
Figure 7-2

When the labor input employed in production is between points O and C in Figure 7-2:
A)average product reaches a minimum.
B)marginal product reaches a maximum.
C)marginal product is below average product.
D)total product first increases at a decreasing rate and then increases at an increasing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 7-1 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-1
In Figure 7-1,marginal product of labor is positive but lesser than the average product of labor after point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
Figure 7-1

In Figure 7-1,marginal product of labor is positive but lesser than the average product of labor after point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the marginal product of a variable input is declining,then:
A)average product is also declining.
B)total product is also declining.
C)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.
D)average product is constant.
A)average product is also declining.
B)total product is also declining.
C)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.
D)average product is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When marginal product is decreasing:
A)average product must also be decreasing.
B)total product is decreasing.
C)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.
D)marginal product must be greater than average product.
A)average product must also be decreasing.
B)total product is decreasing.
C)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.
D)marginal product must be greater than average product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2
Refer to Figure 7-2.Which of the following is true when the labor input is between points C and D?
A)marginal product reaches a maximum and then declines.
B)marginal product reaches a maximum and then becomes negative.
C)average product is equal at point B and C.
D)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.
Figure 7-2

Refer to Figure 7-2.Which of the following is true when the labor input is between points C and D?
A)marginal product reaches a maximum and then declines.
B)marginal product reaches a maximum and then becomes negative.
C)average product is equal at point B and C.
D)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Table 7-4 shows the quantities of labor and capital required to produce various levels of output.
Table 7-4
-Refer to Table 7-4.What is the marginal product of the fourth worker?
A)10
B)14
C)42
D)56
Table 7-4
-Refer to Table 7-4.What is the marginal product of the fourth worker?
A)10
B)14
C)42
D)56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The slope of the total product curve measures the _____ of the input.
A)marginal product
B)average product
C)total product
D)cost
A)marginal product
B)average product
C)total product
D)cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 7-1 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-1
In Figure 7-1,marginal product of labor becomes negative beyond point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
Figure 7-1

In Figure 7-1,marginal product of labor becomes negative beyond point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2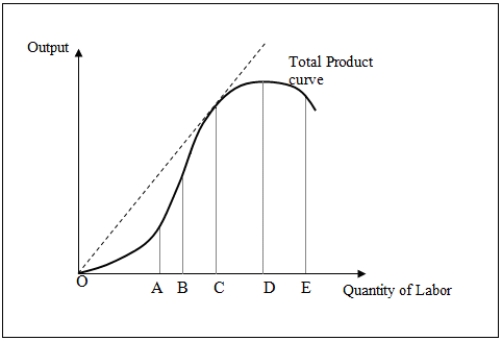
In Figure 7-2,a firm would choose to operate _____ on the total product curve.
A)between O and A
B)at point E
C)between B and D
D)between D and E
Figure 7-2

In Figure 7-2,a firm would choose to operate _____ on the total product curve.
A)between O and A
B)at point E
C)between B and D
D)between D and E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The slope of a ray from the origin to the total product curve measures _____.
A)the marginal rate of technical substitution
B)the marginal product of the variable factor
C)the average product of the variable factor
D)the maximum output
A)the marginal rate of technical substitution
B)the marginal product of the variable factor
C)the average product of the variable factor
D)the maximum output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2
Let point A be the inflection point.When the quantity of labor employed is between A and D in Figure 7-2:
A)marginal product is negative.
B)marginal product is decreasing.
C)average product is increasing.
D)marginal product is increasing at a decreasing rate.
Figure 7-2

Let point A be the inflection point.When the quantity of labor employed is between A and D in Figure 7-2:
A)marginal product is negative.
B)marginal product is decreasing.
C)average product is increasing.
D)marginal product is increasing at a decreasing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2
Between points O and C in Figure 7-2:
A)the marginal product of labor is falling.
B)the average product of labor is rising.
C)total product rises and then falls.
D)marginal product reaches its minimum.
Figure 7-2

Between points O and C in Figure 7-2:
A)the marginal product of labor is falling.
B)the average product of labor is rising.
C)total product rises and then falls.
D)marginal product reaches its minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements is true of the relationship between marginal product and average product of labor?
A)When the marginal product of labor is decreasing,the average product of labor must also be decreasing.
B)When the average product of labor is increasing,the marginal product of labor must also be increasing.
C)When the marginal and average products of labor are equal,the marginal product is at its minimum.
D)When the average product of labor is decreasing,average product must be greater than marginal product.
A)When the marginal product of labor is decreasing,the average product of labor must also be decreasing.
B)When the average product of labor is increasing,the marginal product of labor must also be increasing.
C)When the marginal and average products of labor are equal,the marginal product is at its minimum.
D)When the average product of labor is decreasing,average product must be greater than marginal product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 7-1 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-1
Refer to Figure 7-1.To the left of point B:
A)marginal product is rising but average product is falling.
B)marginal product is rising and is above the average product.
C)marginal product is falling but average product is rising.
D)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.
Figure 7-1

Refer to Figure 7-1.To the left of point B:
A)marginal product is rising but average product is falling.
B)marginal product is rising and is above the average product.
C)marginal product is falling but average product is rising.
D)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2
When the quantity of labor employed lies between points C and D in Figure 7-2:
A)marginal product reaches a maximum.
B)average product is rising and reaches a maximum at D.
C)total product declines.
D)marginal product is falling.
Figure 7-2

When the quantity of labor employed lies between points C and D in Figure 7-2:
A)marginal product reaches a maximum.
B)average product is rising and reaches a maximum at D.
C)total product declines.
D)marginal product is falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The law of diminishing marginal returns _____.
A)is relevant in the short run.
B)assumes all the inputs are fixed
C)is applicable to fixed and variable inputs
D)applies when all inputs are increased
A)is relevant in the short run.
B)assumes all the inputs are fixed
C)is applicable to fixed and variable inputs
D)applies when all inputs are increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2
When the quantity of labor employed lies between points D and E in Figure 7-2:
A)marginal product reaches a maximum and then declines.
B)marginal product reaches a maximum and then becomes negative.
C)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.
D)total product is decreasing.
Figure 7-2

When the quantity of labor employed lies between points D and E in Figure 7-2:
A)marginal product reaches a maximum and then declines.
B)marginal product reaches a maximum and then becomes negative.
C)total product is increasing at a decreasing rate.
D)total product is decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the long run,_____.
A)the marginal cost of each input differs by the ratio of their prices
B)all inputs to production are fixed
C)the marginal cost of each input equals the ratio of their prices
D)all inputs to production are variable
A)the marginal cost of each input differs by the ratio of their prices
B)all inputs to production are fixed
C)the marginal cost of each input equals the ratio of their prices
D)all inputs to production are variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An isoquant shows _____.
A)the different quantities of output that can be produced with different quantities of inputs
B)the combination of inputs that can be used to produce a fixed quantity of output
C)the different quantities of output that can be produce with fixed quantities of inputs
D)the combination of inputs than can be used to produce different quantities of output
A)the different quantities of output that can be produced with different quantities of inputs
B)the combination of inputs that can be used to produce a fixed quantity of output
C)the different quantities of output that can be produce with fixed quantities of inputs
D)the combination of inputs than can be used to produce different quantities of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2
In Figure 7-2,at point D _____.
A)total product is zero
B)marginal product is zero
C)average product is negative
D)average product reaches a maximum
Figure 7-2

In Figure 7-2,at point D _____.
A)total product is zero
B)marginal product is zero
C)average product is negative
D)average product reaches a maximum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The duration of the short run varies by industry because _____.
A)the total labor demand varies by industry
B)some inputs cost more in some industries
C)the technology used in production is not the same in all industries
D)the time required to change a variable input differs by industry
A)the total labor demand varies by industry
B)some inputs cost more in some industries
C)the technology used in production is not the same in all industries
D)the time required to change a variable input differs by industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2
In Figure 7-2,average product reaches a maximum at point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
Figure 7-2

In Figure 7-2,average product reaches a maximum at point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2
In Figure 7-2,marginal product reaches a maximum at point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
Figure 7-2

In Figure 7-2,marginal product reaches a maximum at point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The law of diminishing returns holds only:
A)for goods with inelastic demand.
B)when one input is fixed.
C)in the long run.
D)in a competitive market.
A)for goods with inelastic demand.
B)when one input is fixed.
C)in the long run.
D)in a competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A production isoquant identifies _____.
A)the maximum output possible,given a fixed budget
B)the different combinations of goods that can be produced,given fixed amounts of inputs
C)the different combinations of inputs that can be used to produce a fixed rate of output
D)the cost of producing a given output
A)the maximum output possible,given a fixed budget
B)the different combinations of goods that can be produced,given fixed amounts of inputs
C)the different combinations of inputs that can be used to produce a fixed rate of output
D)the cost of producing a given output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The fact that limited use of caffeine can improve mental alertness and help performance,while excessive use of caffeine can cause anxiety and trembling shows _____.
A)that coffee is an inferior good
B)the law of diminishing marginal returns with respect to test performance
C)the law of returns to scale with respect to test performance
D)decreasing returns to scale in coffee production
A)that coffee is an inferior good
B)the law of diminishing marginal returns with respect to test performance
C)the law of returns to scale with respect to test performance
D)decreasing returns to scale in coffee production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Diminishing marginal returns refers to the:
A)decline in the rate at which extra inputs are employed in production.
B)fall in average product associated with a unit increase in the fixed input.
C)decline in total product which is less than proportionate to a change in the fixed input.
D)fall in output per unit with an incremental increase in the variable input.
A)decline in the rate at which extra inputs are employed in production.
B)fall in average product associated with a unit increase in the fixed input.
C)decline in total product which is less than proportionate to a change in the fixed input.
D)fall in output per unit with an incremental increase in the variable input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2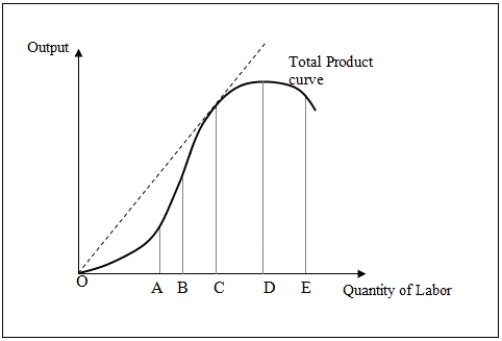
In Figure 7.3,the law of diminishing marginal returns comes into play beyond point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
Figure 7-2

In Figure 7.3,the law of diminishing marginal returns comes into play beyond point _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is constant along an isoquant?
A)Productivity of the variable input
B)Output
C)Cost
D)Utility
A)Productivity of the variable input
B)Output
C)Cost
D)Utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When the marginal and average products of labor are equal:
A)marginal product must be at its maximum.
B)marginal product must be at a minimum.
C)average product must be at its maximum.
D)average product must be increasing.
A)marginal product must be at its maximum.
B)marginal product must be at a minimum.
C)average product must be at its maximum.
D)average product must be increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Isoquants that are farther away from the origin indicate:
A)lower cost combinations of inputs.
B)technologically inefficient levels of output.
C)higher levels of output.
D)combinations of inputs that are less preferred.
A)lower cost combinations of inputs.
B)technologically inefficient levels of output.
C)higher levels of output.
D)combinations of inputs that are less preferred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the level of technical know-how increases,how would this change the total product curve?
A)It would extend horizontally.
B)It would become more bowed.
C)It would shift upwards.
D)It would become flatter.
A)It would extend horizontally.
B)It would become more bowed.
C)It would shift upwards.
D)It would become flatter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Figure 7-2 shows the total product curve for different levels of a variable input,labor.
Figure 7-2
In Figure 7-2,at point C _____.
A)average product equals marginal product
B)marginal product is at a maximum
C)total product is increasing at an increasing rate
D)average product is declining but positive
Figure 7-2

In Figure 7-2,at point C _____.
A)average product equals marginal product
B)marginal product is at a maximum
C)total product is increasing at an increasing rate
D)average product is declining but positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
According to the law of diminishing marginal returns:
A)when the amount of some input is increased by equal increments,holding other inputs constant,the resulting increments in output will be negative.
B)when all inputs are increased proportionately,output eventually will decrease at a smaller rate.
C)when the amount of some input is increased at equal increments,holding other inputs constant,the resulting increments in output will eventually decrease.
D)firms will not operate on the portion of the total product curve where marginal product is declining.
A)when the amount of some input is increased by equal increments,holding other inputs constant,the resulting increments in output will be negative.
B)when all inputs are increased proportionately,output eventually will decrease at a smaller rate.
C)when the amount of some input is increased at equal increments,holding other inputs constant,the resulting increments in output will eventually decrease.
D)firms will not operate on the portion of the total product curve where marginal product is declining.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Table 7-2 shows the combinations of labor and capital that are used to produce various levels of output
Table 7-2
-Refer to Table 7-2.Based on the input-usage ratio,we can say that the firm is operating _____.
A)at an economic loss
B)in the short-run
C)in a constant-cost industry
D)in the long-run
Table 7-2
-Refer to Table 7-2.Based on the input-usage ratio,we can say that the firm is operating _____.
A)at an economic loss
B)in the short-run
C)in a constant-cost industry
D)in the long-run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The marginal rate of technical substitution:
A)equals the marginal product of capital times the marginal product of labor.
B)measures the rate at which marginal product declines as inputs are increased.
C)measures the degree to which one input can be substituted for another,output held constant.
D)is the horizontal distance between two isoquants.
A)equals the marginal product of capital times the marginal product of labor.
B)measures the rate at which marginal product declines as inputs are increased.
C)measures the degree to which one input can be substituted for another,output held constant.
D)is the horizontal distance between two isoquants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements about the marginal rate of technical substitution is correct?
A)The MRTS is equal to the ratio of the marginal productivities of the inputs.
B)The MRTS is equal to the slope of the total product curve.
C)The MRTS is zero in the long run.
D)The MRTS is the rate at which one input can be substituted for the other in production while varying the level of output.
A)The MRTS is equal to the ratio of the marginal productivities of the inputs.
B)The MRTS is equal to the slope of the total product curve.
C)The MRTS is zero in the long run.
D)The MRTS is the rate at which one input can be substituted for the other in production while varying the level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the marginal product of labor is 25 and the marginal product of capital 10,what is the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital?
A)0.6
B)1
C)1.5
D)2.5
A)0.6
B)1
C)1.5
D)2.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The long-run refers to:
A)a time period of one year or more.
B)the time period in which all inputs are variable.
C)the time period in which it is too costly to change the usage of at least one input.
D)a time period when marginal returns are diminishing.
A)a time period of one year or more.
B)the time period in which all inputs are variable.
C)the time period in which it is too costly to change the usage of at least one input.
D)a time period when marginal returns are diminishing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Table 7-4 shows the shows the quantities of labor and capital required to produce various levels of output.
Table 7-4
-Refer to Table 7-4.When the firm increases production from 48 units of capital and 16 units of labor to 96 units of capital and 32 units of labor,the production function exhibits:
A)increasing returns to scale.
B)constant returns to scale.
C)diminishing marginal returns.
D)decreasing returns to scale.
Table 7-4
-Refer to Table 7-4.When the firm increases production from 48 units of capital and 16 units of labor to 96 units of capital and 32 units of labor,the production function exhibits:
A)increasing returns to scale.
B)constant returns to scale.
C)diminishing marginal returns.
D)decreasing returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is a feature of an isoquant?
A)Isoquants are concave to the origin.
B)Isoquants are nonintersecting.
C)Isoquants lying farther to the northeast identify lower levels of output.
D)Producers prefer higher points on an isoquant.
A)Isoquants are concave to the origin.
B)Isoquants are nonintersecting.
C)Isoquants lying farther to the northeast identify lower levels of output.
D)Producers prefer higher points on an isoquant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
One important difference between indifference curves and isoquants is that:
A)indifference curves are convex while isoquants are concave to the origin.
B)indifference curves can never intersect while isoquants can intersect.
C)output shown on isoquants is measurable while well-being shown on indifference curves is not.
D)indifference curves are likely to be positively sloped while isoquants are mostly negatively sloped.
A)indifference curves are convex while isoquants are concave to the origin.
B)indifference curves can never intersect while isoquants can intersect.
C)output shown on isoquants is measurable while well-being shown on indifference curves is not.
D)indifference curves are likely to be positively sloped while isoquants are mostly negatively sloped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Convexity of a curve implies that the slope of the curve:
A)is zero.
B)is constant.
C)diminishes along the curve.
D)approaches infinity.
A)is zero.
B)is constant.
C)diminishes along the curve.
D)approaches infinity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Table 7-4 shows the shows the quantities of labor and capital required to produce various levels of output.
Table 7-4
-Refer to Table 7-4.When the firm increases production from 24 units of capital and 8 units of labor to 48 units of capital and 16 units of labor,the production function exhibits:
A)decreasing marginal rate of technical substitution.
B)constant returns to scale.
C)increasing returns to scale.
D)diminishing marginal returns
Table 7-4
-Refer to Table 7-4.When the firm increases production from 24 units of capital and 8 units of labor to 48 units of capital and 16 units of labor,the production function exhibits:
A)decreasing marginal rate of technical substitution.
B)constant returns to scale.
C)increasing returns to scale.
D)diminishing marginal returns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An isoquant map,with labor on the horizontal axis and capital on the vertical axis,has horizontal isoquants.This implies that the:
A)marginal product of capital is zero.
B)marginal rate of substitution of capital for labor approaches infinity.
C)marginal product of labor is zero.
D)marginal rate of substitution of capital for labor is positive.
A)marginal product of capital is zero.
B)marginal rate of substitution of capital for labor approaches infinity.
C)marginal product of labor is zero.
D)marginal rate of substitution of capital for labor is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Suppose you have capital on the vertical axis and labor on the horizontal axis.The slope of the isoquant measures:
A)the marginal rate of substitution.
B)the marginal product of labor.
C)the marginal product of capital.
D)the marginal rate of technical substitution of capital for labor.
A)the marginal rate of substitution.
B)the marginal product of labor.
C)the marginal product of capital.
D)the marginal rate of technical substitution of capital for labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The short-run refers to:
A)a time period of two years or less.
B)the time period in which the usage of all inputs are held constant.
C)the time period in which it is too costly to change the usage of at least one input.
D)the time period in which the usage of all inputs can be changed.
A)a time period of two years or less.
B)the time period in which the usage of all inputs are held constant.
C)the time period in which it is too costly to change the usage of at least one input.
D)the time period in which the usage of all inputs can be changed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
With energy [E] on the horizontal axis and land [L] on the vertical axis,the marginal rate of technical substitution of energy for land (MRTSEL)equals:
A)MPL/MPE
B)- E/ L
C)- Q/ L
D)(MPL/ E)( L/MPE)
A)MPL/MPE
B)- E/ L
C)- Q/ L
D)(MPL/ E)( L/MPE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Table 7-3 shows the combinations of labor and capital required to produce various level of output.
Table 7-3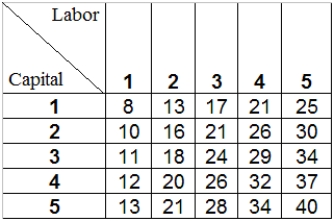
Refer to Table 7-3.If the firm is currently producing 26 units of output using three units of labor,what is the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital at this point?
A)-1
B)-2
C)-3
D)-4
Table 7-3

Refer to Table 7-3.If the firm is currently producing 26 units of output using three units of labor,what is the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital at this point?
A)-1
B)-2
C)-3
D)-4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What can you conclude about an isoquant that is concave to the origin?
A)The level of output shown on the isoquant increases along the curve.
B)The isoquant represents production in the short run as one input is kept fixed.
C)The marginal rate of technical substitution increases along the curve.
D)The slope of the isoquant is infinite.
A)The level of output shown on the isoquant increases along the curve.
B)The isoquant represents production in the short run as one input is kept fixed.
C)The marginal rate of technical substitution increases along the curve.
D)The slope of the isoquant is infinite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Suppose that at a point on an isoquant,the following information is true: L increases by 5;K falls by 3;MPL = 4,then MPK must be:
A)3.33.
B)0.67.
C)1.67.
D)6.67.
A)3.33.
B)0.67.
C)1.67.
D)6.67.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If isoquants are drawn as right angles,it implies:
A)that the two inputs are perfect substitutes for each other.
B)that the MRTS is constant.
C)that the inputs must be used in fixed proportions.
D)the isoquants can be intersecting.
A)that the two inputs are perfect substitutes for each other.
B)that the MRTS is constant.
C)that the inputs must be used in fixed proportions.
D)the isoquants can be intersecting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If isoquants are drawn as straight lines,it implies that:
A)the two inputs are perfect substitutes for each other.
B)the MRTS is decreasing.
C)that the inputs must be used in fixed proportions.
D)the MRTS is zero.
A)the two inputs are perfect substitutes for each other.
B)the MRTS is decreasing.
C)that the inputs must be used in fixed proportions.
D)the MRTS is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose that at a point on an isoquant,the following information is true: MPL = 3 and MPK = 2.Then if K falls by 5,L must increase by:
A)0.30.
B)0.67.
C)3.33.
D)1.50.
A)0.30.
B)0.67.
C)3.33.
D)1.50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The marginal rate of technical substitution equals the ratio of the _____.
A)total product of capital and labor
B)marginal products of the inputs
C)marginal cost of both inputs
D)amount of capital employed to the amount of labor employed
A)total product of capital and labor
B)marginal products of the inputs
C)marginal cost of both inputs
D)amount of capital employed to the amount of labor employed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



