Deck 17: Linked Lists
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Linked Lists
1
Linked lists allow you to overcome the size limitations of an array data type.
True
2
Every node (except of the last node) in a singly linked list contains ____.
A) the next node
B) no address information
C) the address of the next node
D) the address of the previous node
A) the next node
B) no address information
C) the address of the next node
D) the address of the previous node
C
3
When you build a linked list in the backward manner, a new node is always inserted at the end of the linked list.
False
4
The link field of the last node of a linked list is ____.
A) nullptr
B) 1
C) n-1
D) n
A) nullptr
B) 1
C) n-1
D) n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Because each node of a linked list has two components, we need to declare each node as a(n) ____.
A) reference and string
B) int and object
C) index and element
D) class or struct
A) reference and string
B) int and object
C) index and element
D) class or struct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A doubly linked list can be traversed in either direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the purpose of the following code? 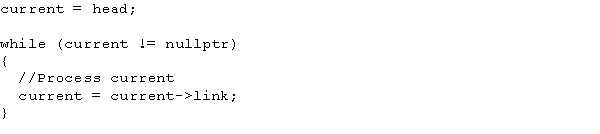
A) Insertion of a node
B) Selection of a node
C) Traversal of a linked list
D) Creation of a new list
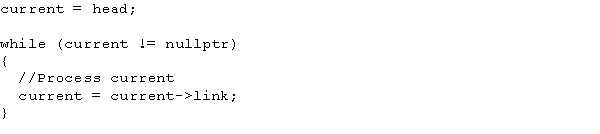
A) Insertion of a node
B) Selection of a node
C) Traversal of a linked list
D) Creation of a new list

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Data can be organized and processed sequentially using an array, called a(n) ____ list.
A) linked
B) ordered
C) sequential
D) ascending
A) linked
B) ordered
C) sequential
D) ascending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a linked list, if a new item is always inserted at the beginning or at the end of the list and the data we read is unsorted, the linked list will be unsorted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A linked list is a collection of components, called ____.
A) elements
B) nodes
C) members
D) pointers
A) elements
B) nodes
C) members
D) pointers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
We deallocate the memory for a linked list by calling the operator clear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
It is not possible to create an ordered linked list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The length of a linked list is the number of nodes in the list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Each node of a singly linked list has two components: ____ and ____.
A) info, head
B) link, back
C) back, head
D) info, link
A) info, head
B) link, back
C) back, head
D) info, link

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In a linked list, the address of the first node in the list is stored in a separate location, called the ____ or first.
A) head
B) pointer
C) front
D) top
A) head
B) pointer
C) front
D) top

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Memory for the components of an array does not need to be contiguous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
You can use the pointer head of a linked list to traverse the list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A linked list is a random access data structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose that the pointer head points to the first node in the list, and the link of the last node is nullptr. The first node of the linked list contains the address of the ____ node.
A) head
B) first
C) second
D) tail
A) head
B) first
C) second
D) tail

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In a linked list, the order of the nodes is determined by the address, called the ____, stored in each node.
A) head
B) tail
C) link
D) first
A) head
B) tail
C) link
D) first

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following correctly initializes a doubly linked list in the default constructor?
A) head = nullptr;
Back = nullptr;
B) head = 0;
Back = 0;
Count = 0;
C) first = 0;
Last = 0;
D) first = nullptr;
Last = nullptr;
Count = 0;
A) head = nullptr;
Back = nullptr;
B) head = 0;
Back = 0;
Count = 0;
C) first = 0;
Last = 0;
D) first = nullptr;
Last = nullptr;
Count = 0;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The ____ deallocates the memory occupied by the nodes of a list when the class object goes out of scope.
A) constructor
B) destructor
C) head pointer
D) tail pointer
A) constructor
B) destructor
C) head pointer
D) tail pointer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Create a new node.
2. Insert the node before first.
3. Increment the counter by 1.
b.
2. Insert the node before first.
3. Increment the counter by 1.
b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consider the following code: The statement that provides the length of the linked list is ____.

A) cout <<< count;
B) destroy();
C) return count;
D) return next;

A) cout <<< count;
B) destroy();
C) return count;
D) return next;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The steps involved in inserting a new item at the beginning of an unordered linked list are ____.
a.
a.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider the accompanying statements. The operation returns true if the list is empty; otherwise, it returns false. The missing code is ____.
A) protected
B) int
C) void
D) bool
A) protected
B) int
C) void
D) bool

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Each node of a linked list must store the data as well as the ____________________ of the next node in the list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In C++, the dereferencing operator is ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider the following code which deletes all the nodes in a linked list.  Which of the following is the missing statement?
Which of the following is the missing statement?
A) delete first;
B) delete temp;
C) destroy temp;
D) clear temp;
 Which of the following is the missing statement?
Which of the following is the missing statement?A) delete first;
B) delete temp;
C) destroy temp;
D) clear temp;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a linked list, the link component of each node is a(n) ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Create a new node.
2. Store the new item in the new node.
3. Insert the node before first.
4. Increment the counter by 1.
c.
2. Store the new item in the new node.
3. Insert the node before first.
4. Increment the counter by 1.
c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consider the statements above. The list is empty if the pointer first is ____.
A) nullptr
B) 0
C) last
D) next
A) nullptr
B) 0
C) last
D) next

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many pointers are needed to build a linked list in a backward manner?
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Create a new node. 2. Store the new item in the new node.
3) Insert the node before first.
4) Decrement the counter by 1.
3) Insert the node before first.
4) Decrement the counter by 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Every node in a doubly linked list has two pointers: ____ and ____.
A) top; bottom
B) back; next
C) current; forward
D) previous; forward
A) top; bottom
B) back; next
C) current; forward
D) previous; forward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the accompanying code. What is the effect of the following statement? newNode->info = 50;
A) Stores 50 in the info field of the newNode
B) Creates a new node
C) Places the node at location 50
D) Cannot be determined from this code
A) Stores 50 in the info field of the newNode
B) Creates a new node
C) Places the node at location 50
D) Cannot be determined from this code

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Create a new node.
2. Store the new item in the new node.
3. Insert the node before first.
d.
2. Store the new item in the new node.
3. Insert the node before first.
d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements appears in the insert function of a doubly linked list?
A) current++;
B) trailCurrent++;
C) newNode++;
D) count++;
A) current++;
B) trailCurrent++;
C) newNode++;
D) count++;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When building a linked list in the ____ manner, a new node is always inserted at the end of the linked list.
A) backward
B) forward
C) traversal
D) random
A) backward
B) forward
C) traversal
D) random

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is a basic operation on singly linked lists?
A) Retrieve the data of an arbitrary node.
B) Swap the head and the last nodes.
C) Determine whether the list is nearly full.
D) Make a copy of the linked list.
A) Retrieve the data of an arbitrary node.
B) Swap the head and the last nodes.
C) Determine whether the list is nearly full.
D) Make a copy of the linked list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A(n) ____________________ is an object that produces each element of a container, such as a linked list, one element at a time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A(n) ____________________ linked list is a linked list in which every node has a next pointer and a back pointer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The ____________________ operator advances the iterator to the next node in the linked list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For classes that include pointer data members, the assignment operator must be explicitly ____________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The ____________________ constructor executes when an object is declared and initialized using another object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



