Deck 11: Inheritance and Composition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Inheritance and Composition
1
Inheritance is an example of a(n) ____ relationship.
A) is-a
B) has-a
C) handshaking
D) had-a
A) is-a
B) has-a
C) handshaking
D) had-a
A
2
A derived class can directly access the protected members of the base class.
True
3
The private members of a base class can be directly accessed by a derived class.
False
4
The constructors of a derived class can (directly) initialize only the (public data) members inherited from the base class of the derived class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Existing classes, from which you create new classes, are called ____ classes.
A) child
B) base
C) sibling
D) derived
A) child
B) base
C) sibling
D) derived

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following class definitions makes the public members of the class aClass become the public members of the class bClass?
A) class aClass: public bClass
{
//)..
};
B) class bClass: public aClass
{
//)..
};
C) class bClass: aClass
{
//)..
};
D) class aClass: bClass
{
//)..
};
A) class aClass: public bClass
{
//)..
};
B) class bClass: public aClass
{
//)..
};
C) class bClass: aClass
{
//)..
};
D) class aClass: bClass
{
//)..
};

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The class io is the base class of the C++ stream classes istream and ostream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is true about inheritance?
A) All public member functions of the base class become the public member functions of the derived class.
B) All public member variables of the base class become the public member variables of the derived class.
C) All public members of the base class become the public members of the derived class.
D) The public member variables of the base class become the public or private member variables of the derived class.
A) All public member functions of the base class become the public member functions of the derived class.
B) All public member variables of the base class become the public member variables of the derived class.
C) All public members of the base class become the public members of the derived class.
D) The public member variables of the base class become the public or private member variables of the derived class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is a valid definition of the derived class bClass?
A) class aClass: public bClass
{
//)..
};
B) class bClass: public aClass
{
//)..
};
C) class aClass::bClass
{
//)..
};
D) class bClass::aClass
{
//)..
}
A) class aClass: public bClass
{
//)..
};
B) class bClass: public aClass
{
//)..
};
C) class aClass::bClass
{
//)..
};
D) class bClass::aClass
{
//)..
}

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
____ is a "has-a" relationship.
A) Inheritance
B) Encapsulation
C) Composition
D) Polymorphism
A) Inheritance
B) Encapsulation
C) Composition
D) Polymorphism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In multiple inheritance, the derived class has more than one base class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If inheritance is private, all members of the base class, including private members, become private members of the derived class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A call to the base class's constructor is specified in the heading of the definition of a derived class constructor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In protected inheritance, public and protected members of the base class become the protected members of the derived class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The new classes that we create from existing classes are called ____ classes.
A) sibling
B) base
C) derived
D) parent
A) sibling
B) base
C) derived
D) parent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Classes can create new classes from existing classes. This important feature ____.
A) encourages code reuse
B) aids the separation of data and operations
C) provides public access to the internal state of an object
D) results in more software complexity
A) encourages code reuse
B) aids the separation of data and operations
C) provides public access to the internal state of an object
D) results in more software complexity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the derived class does not override a public member function of the base class, you may specify a call to that public member function by using the name of the function and the appropriate parameter list.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the following class definition: The class dClass is derived from the class bClass using the ____ type of inheritance.

A) public
B) private
C) protected
D) static

A) public
B) private
C) protected
D) static

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose that bClass is a class. Which of the following statements correctly derives the class dClass from bClass?
A) class dClass:: public bClass
{
//classMembersList
};
B) class dClass: private bClass
{
//classMembersList
};
C) class dClass:: protected bClass
{
//classMembersList
};
D) class bClass: public dClass
{
//classMembersList
};
A) class dClass:: public bClass
{
//classMembersList
};
B) class dClass: private bClass
{
//classMembersList
};
C) class dClass:: protected bClass
{
//classMembersList
};
D) class bClass: public dClass
{
//classMembersList
};

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A derived class cannot directly access public members of a base class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The ____ members of an object form its internal state.
A) private
B) protected
C) public
D) static
A) private
B) protected
C) public
D) static

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The constructor of a derived class cannot directly access the ____________________ member variables of the base class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In ____________________ (aggregation), one or more members of a class are objects of another class type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the corresponding functions in the base class and the derived class have the same name but different sets of parameters, then this function is ____ in the derived class.
A) reused
B) redefined
C) overloaded
D) overridden
A) reused
B) redefined
C) overloaded
D) overridden

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
C++ provides ____ functions as a means to implement polymorphism in an inheritance hierarchy, which allows the run-time selection of appropriate member functions.
A) redefined
B) overridden
C) virtual
D) overloaded
A) redefined
B) overridden
C) virtual
D) overloaded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
OOP implements ____.
A) UML
B) IPE
C) EIP
D) OOD
A) UML
B) IPE
C) EIP
D) OOD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider the following class definitions: Which of the following correctly sets the values of x and y?

A) void dClass::setXY(int a, int b)
{
BClass::setX(a);
Y = b;
}
B) void dClass::setXY(int a, int b)
{
X = a;
Y = b;
}
C) void dClass::setXY(int a, int b)
{
X = bClass::setX(a);
Y = bClass::setY(b);
}
D) void dClass::setXY(int a, int b)
{
X = bClass.setX(a);
B = y;
}

A) void dClass::setXY(int a, int b)
{
BClass::setX(a);
Y = b;
}
B) void dClass::setXY(int a, int b)
{
X = a;
Y = b;
}
C) void dClass::setXY(int a, int b)
{
X = bClass::setX(a);
Y = bClass::setY(b);
}
D) void dClass::setXY(int a, int b)
{
X = bClass.setX(a);
B = y;
}

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is true about a derived class?
A) A derived class can directly access any member variable of the base class.
B) A derived class can redefine any public member function of the base class.
C) A derived class can have at most one base class.
D) A derived class can redefine any member function of the base class.
A) A derived class can directly access any member variable of the base class.
B) A derived class can redefine any public member function of the base class.
C) A derived class can have at most one base class.
D) A derived class can redefine any member function of the base class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements about inheritance is true if memberAccessSpecifier is protected?
A) The private members of the base class become protected members of the derived class.
B) The derived class can directly access any member of the base class.
C) The public members of the base class become protected members of the derived class.
D) The protected members of the base class become private members of the derived class.
A) The private members of the base class become protected members of the derived class.
B) The derived class can directly access any member of the base class.
C) The public members of the base class become protected members of the derived class.
D) The protected members of the base class become private members of the derived class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The preprocessor directive ____________________ is used to prevent multiple inclusions of a header file in a program.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
To ____ a public member function of a base class in the derived class, the corresponding function in the derived class must have the same name, number, and types of parameters.
A) redefine
B) overload
C) rename
D) reuse
A) redefine
B) overload
C) rename
D) reuse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If inheritance is public, all protected members of the base class are ____________________ members of the derived class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the following class definitions:  Which of the following statements correctly redefines the member function print of bClass?
Which of the following statements correctly redefines the member function print of bClass?
A) void dClass::print() const
{
DClass:print();
Cout << " " << y << endl;
}
B) void dClass::print() const
{
Cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
C) void bClass::print() const
{
Cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
D) void dClass::print() const
{
BClass::print();
Cout << "y = " << y << endl;
}
 Which of the following statements correctly redefines the member function print of bClass?
Which of the following statements correctly redefines the member function print of bClass?A) void dClass::print() const
{
DClass:print();
Cout << " " << y << endl;
}
B) void dClass::print() const
{
Cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
C) void bClass::print() const
{
Cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
D) void dClass::print() const
{
BClass::print();
Cout << "y = " << y << endl;
}

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the following class definitions: Which of the following dClass constructor definitions is valid in C++?

A) dClass::dClass(double a, double b, double c)
: bClass()
{
X = a;
Y = b;
Z = c;
}
B) dClass::dClass(double a, double c)
{
X = a;
Z = c;
}
C) dClass::dClass(double a, double b)
: bClass()
{
X = a;
Y = b;
}
D) dClass::dClass(double a, double b, double c)
: bClass(a, b)
{
Z = c;
}

A) dClass::dClass(double a, double b, double c)
: bClass()
{
X = a;
Y = b;
Z = c;
}
B) dClass::dClass(double a, double c)
{
X = a;
Z = c;
}
C) dClass::dClass(double a, double b)
: bClass()
{
X = a;
Y = b;
}
D) dClass::dClass(double a, double b, double c)
: bClass(a, b)
{
Z = c;
}

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the derived class classD overrides a public member function functionName of the base class classB, then to specify a call to that public member function of the base class, you use the statement ____.
A) classD::functionName();
B) classB::functionName();
C) classD.functionName();
D) classB.functionName();
A) classD::functionName();
B) classB::functionName();
C) classD.functionName();
D) classB.functionName();

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
____ is the ability to combine data, and operations on that data, in a single unit.
A) Inheritance
B) Encapsulation
C) Polymorphism
D) Composition
A) Inheritance
B) Encapsulation
C) Polymorphism
D) Composition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In OOD, a program is a collection of interacting ____________________; in structured programming, a program is a collection of interacting functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
____ is the ability to use the same expression to denote different operations.
A) Inheritance
B) Encapsulation
C) Polymorphism
D) Composition
A) Inheritance
B) Encapsulation
C) Polymorphism
D) Composition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The ____ members of an object form its external state.
A) private
B) public
C) protected
D) static
A) private
B) public
C) protected
D) static

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the output of the following program? 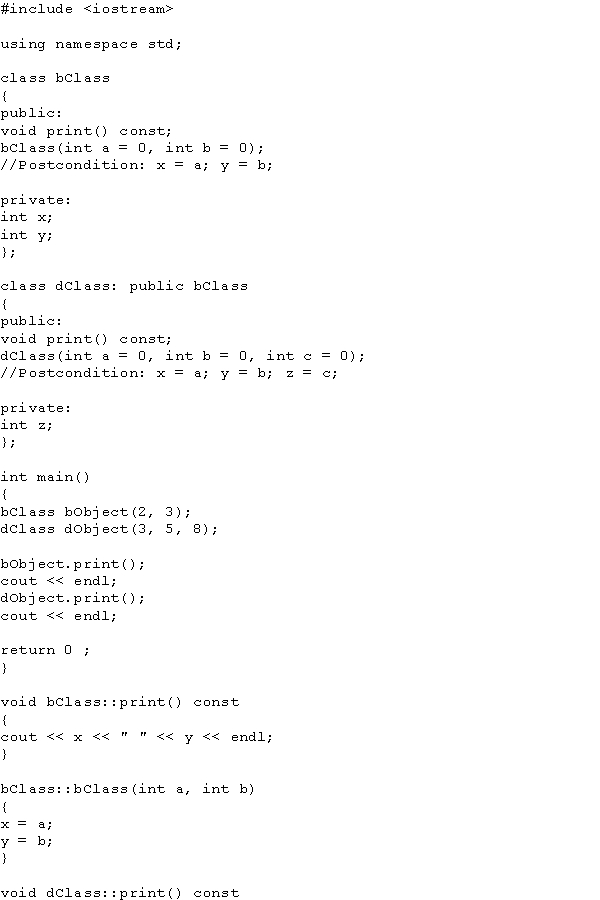
A) 2 3
2 3
B) 2 3
3 5 8
C) 3 5 8
3 5 8
D) 5 8
3 5 8

A) 2 3
2 3
B) 2 3
3 5 8
C) 3 5 8
3 5 8
D) 5 8
3 5 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
C++ provides ____________________ functions as a means to implement polymorphism in an inheritance hierarchy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



