Deck 16: Investment and Personal Financial Planning
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/104
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Investment and Personal Financial Planning
1
An owner of a life insurance policy that includes an investment element must recognize income equal to the annual increase in the policy's cash surrender value.
False
2
The tax consequences of a business activity are generally the same as the tax consequences of an investment activity.
False
3
If an investor sells some of the securities in a block but can't identify which ones were sold, she is presumed to have sold the securities with the latest acquisition date.
False
4
Electing to reinvest dividends in additional shares of stock does not defer income recognition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The interest earned on a state or local government bond is exempt from federal taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Unrecaptured Section 1250 gain is taxed at a maximum rate of 28%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Two years ago, James loaned $60,000 to his friend. The debt is now uncollectible. If the loan created a bona fide debt, James recognizes a short-term capital loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Individual taxpayers may carry nondeductible capital losses forward indefinitely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Ms. Martin received $80,000 from a $100,000 life insurance policy as an accelerated death benefit. None of the $80,000 is taxable to her.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An individual with a 15% rate marginal tax rate on ordinary income will pay no tax on long-term capital gains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The interest earned on investments in U.S. debt obligations is subject to state taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The cash surrender value of a life insurance policy is taxable to the policy beneficiary upon the death of the insured individual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
On April 19 of this year, Sandy learned that her stock investment had become worthless. The stock is deemed to be worthless on December 31 of this year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Cash basis individuals must accrue market discount on a bond as annual interest income over the life of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Qualified dividend income earned by an individual taxpayer is taxed at a maximum rate of 15%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The tax rate on capital gains is determined solely by reference to the capital asset's holding period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The income generated from an investment activity is primarily attributable to invested capital rather than the owner's personal involvement in the activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Mr. Adams paid $53,500 in premiums on a whole life insurance policy. When he canceled the policy, he received its cash surrender value of $61,600. He must recognize $61,600 of income as a result of the cancellation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Brokerage fees paid when stock is purchased are added to the basis of the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Only accrual basis individuals are required to accrue original issue discount on a bond as annual interest income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Mr. Moyer owns residential rental property. This year, he received $7,000 revenue from the tenants and incurred $14,900 rental expenses. Mr. Moyer must include $7,000 in gross income and is allowed only $7,000 of above-the-line deductions for the expenses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Investment expenses are a miscellaneous itemized deduction subject to the 2% AGI limitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Ruth Darma is a shareholder who is not involved in the day-to-day activities of an S corporation. Her interest in the business is a passive activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An inter vivos transfer is a gratuitous transfer of property by an individual that occurs at death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The kiddie tax limits the tax savings from a transfer of income-producing property to a minor child by taxing a portion of such income at the parent's marginal tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A beneficiary's basis of inherited property equals the decedent's adjusted basis immediately prior to death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Up to $100,000 of loss recognized on the sale of Section 1244 stock by a married individual filing a joint return is characterized as ordinary loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Investment interest expense is a miscellaneous itemized deduction subject to the 2% AGI limitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Lana owns 50 shares of stock qualifying as Section 1244 stock. If she sells the stock to George, he can also treat the stock as Section 1244 stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Mr. Gray recognized a $60,000 loss on sale of his entire interest in a passive activity. He had a $52,000 passive activity loss carryforward from prior years. Mr. Gray can deduct the $52,000 loss in the year of sale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Gift tax is based on the donor's adjusted tax basis in the transferred property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Gain on the sale of qualified small business stock is taxed at a maximum rate of 15%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
This year, Mr. Chester gave $50,000 to an old friend who has no legal obligation to repay the money. The entire $50,000 is a taxable gift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Investors must hold qualified small business stock for more than five years in order to exclude a percentage of the gain on sale of such stock from gross income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
All gratuitous transfers of property are subject to gift tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Individual taxpayers are not allowed to deduct capital losses in excess of capital gains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An owner of undeveloped land held for investment must capitalize the property taxes paid on the land each year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The federal taxable estate of a decedent can exceed the value of the probate estate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Material participation in a business activity means that the individual is involved in the day-to-day operations on a regular, continuous, and substantial basis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Mr. Johnson borrowed money to buy Chicago municipal bonds. This year, he paid $2,000 of interest on his loan and earned $3,500 of interest income from the bonds. None of the interest expense is deductible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Jane, a cash basis individual, purchased a publicly traded bond at a $6,000 market discount. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Jane must accrue the market discount as interest income over the life of the bond.
B) If Jane holds the bond to maturity, she will recognize a $6,000 capital gain.
C) If Jane holds the bond to maturity, she will recognize $6,000 ordinary income.
D) None of the statements is true.
A) Jane must accrue the market discount as interest income over the life of the bond.
B) If Jane holds the bond to maturity, she will recognize a $6,000 capital gain.
C) If Jane holds the bond to maturity, she will recognize $6,000 ordinary income.
D) None of the statements is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
At the beginning of the year, Calvin paid $5,000 for 60 shares of Eddington stock. In June, he received a $300 cash distribution with respect to the stock. His Form 1099-DIV reported that $170 was an ordinary dividend and $130 was nontaxable. Compute Calvin's tax basis in his 60 shares at year-end.
A) $4,870
B) $4,700
C) $4,830
D) $5,000
A) $4,870
B) $4,700
C) $4,830
D) $5,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Sixteen years ago, Ms. Herbert purchased an annuity for $96,000. Beginning in September of this year, the annuity began paying Ms. Herbert $4,000 per month for the rest of her life. Based on her age, Ms. Herbert's expected return is $300,000. How much of the $16,000 that she received this year is included in taxable income?
A) $0
B) $5,120
C) $10,880
D) None of the above
A) $0
B) $5,120
C) $10,880
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Mr. Gordon, a resident of Pennsylvania, paid $20,000 for a bond issued by Delaware. This year, he received $800 of interest on the bond. His marginal state tax rate is 7%, and under Pennsylvania law, interest on debt obligations issued by another state is taxable. Mr. Gordon can deduct state income tax on his federal return, and his marginal federal tax rate is 35%. Computer his after-tax rate of return on the bond.
A) 4%
B) 3.82%
C) 3.72%
D) 2.42%
A) 4%
B) 3.82%
C) 3.72%
D) 2.42%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Life insurance proceeds are includible in the taxable estate of the decedent if the decedent was the owner of the policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Ten years ago, Elaine paid $10 per share for 2,000 shares of Lazlo common stock. This year, Elaine learned that Lazlo is in bankruptcy and can pay only 40% of its outstanding debt. What are the tax consequences to Elaine of Lazlo's bankruptcy?
A) $20,000 long-term capital loss
B) $12,000 long-term capital loss
C) $20,000 ordinary loss
D) No gain or loss
A) $20,000 long-term capital loss
B) $12,000 long-term capital loss
C) $20,000 ordinary loss
D) No gain or loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Twenty years ago, Mr. Wallace purchased a $250,000 insurance policy on his own life and named his daughter as sole beneficiary. He has paid $14,250 total premiums to keep this policy in force. This year, he liquidates the policy for its $20,000 cash surrender value. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Mr. Wallace recognizes $5,750 ordinary income on the liquidation.
B) Mr. Wallace recognizes $20,000 ordinary income on the liquidation.
C) Mr. Wallace recognizes no gain on the liquidation.
D) Mr. Wallace recognizes $5,750 capital gain on the liquidation.
A) Mr. Wallace recognizes $5,750 ordinary income on the liquidation.
B) Mr. Wallace recognizes $20,000 ordinary income on the liquidation.
C) Mr. Wallace recognizes no gain on the liquidation.
D) Mr. Wallace recognizes $5,750 capital gain on the liquidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Twenty years ago, Mrs. Cole purchased an insurance policy on her own life. Mrs. Cole died this year, and the policy paid the $300,000 death benefit to her son Jeffrey. During her life, Mrs. Cole paid total premiums of $71,200 on the policy. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Jeffrey must recognize the $300,000 payment as ordinary income.
B) Jeffrey must recognize $228,800 of the $300,000 payment as capital gain.
C) Jeffrey can exclude the $300,000 payment from gross income.
D) Jeffrey must recognize $228,800 of the $300,000 payment as ordinary income.
A) Jeffrey must recognize the $300,000 payment as ordinary income.
B) Jeffrey must recognize $228,800 of the $300,000 payment as capital gain.
C) Jeffrey can exclude the $300,000 payment from gross income.
D) Jeffrey must recognize $228,800 of the $300,000 payment as ordinary income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Mr. Ricardo exchanged 75 shares of Haslet common stock for 516 shares of Newland common stock pursuant to a reorganization of the two corporations. His basis in the Haslet stock was $49,200, and the fair market value of the Newland stock was $138,000. Which of the following statements about the exchange is true?
A) Mr. Ricardo recognizes no gain and takes a $138,000 basis in the Newland stock.
B) Mr. Ricardo recognizes an $88,800 gain and takes a $138,000 basis in the Newland stock.
C) Mr. Ricardo recognizes no gain and takes a zero basis in the Newland stock.
D) Mr. Ricardo recognizes no gain and takes a $49,200 basis in the Newland stock.
A) Mr. Ricardo recognizes no gain and takes a $138,000 basis in the Newland stock.
B) Mr. Ricardo recognizes an $88,800 gain and takes a $138,000 basis in the Newland stock.
C) Mr. Ricardo recognizes no gain and takes a zero basis in the Newland stock.
D) Mr. Ricardo recognizes no gain and takes a $49,200 basis in the Newland stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
At the beginning of the year, Ms. Faro paid $15,000 for 750 shares of Gravois stock. She instructed her broker to reinvest any dividends in additional Gravois shares. Her Form 1099-DIV reported that she earned $820 dividend income which purchased 39 additional shares. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Ms. Faro recognizes no dividend income and has a $15,000 basis in her 789 shares.
B) Ms. Faro recognizes no dividend income and has a $15,820 basis in her 789 shares.
C) Ms. Faro recognizes $820 dividend income and has a $15,820 basis in her 789 shares.
D) None of the above statements is true.
A) Ms. Faro recognizes no dividend income and has a $15,000 basis in her 789 shares.
B) Ms. Faro recognizes no dividend income and has a $15,820 basis in her 789 shares.
C) Ms. Faro recognizes $820 dividend income and has a $15,820 basis in her 789 shares.
D) None of the above statements is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Mrs. Lindt exchanged 212 shares of Nipher common stock for 773 shares of Newland common stock. Her basis in the Nipher stock was $49,200, and the fair market value of the Newland stock was $138,000. Which of the following statements about the exchange is true?
A) Mrs. Lindt's basis in her Newland stock is $138,000.
B) Mrs. Lindt recognizes no gain on the exchange because she did not receive any cash.
C) If the exchange is pursuant to a reorganization of Nipher and Newland, Mrs. Lindt recognizes no gain.
D) None of the above is true.
A) Mrs. Lindt's basis in her Newland stock is $138,000.
B) Mrs. Lindt recognizes no gain on the exchange because she did not receive any cash.
C) If the exchange is pursuant to a reorganization of Nipher and Newland, Mrs. Lindt recognizes no gain.
D) None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
As a general tax planning rule, an individual should sell assets that have declined in value prior to death and keep appreciated property to transfer to his heirs at his death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Fifteen years ago, Lenny purchased an insurance policy on his own life. The policy provides a $3 million death benefit. Lenny has paid $682,000 of premiums, and the cash surrender value of the policy is $725,000. He plans to liquidate the policy to generate cash for his business. If Lenny's marginal tax rate is 35%, how much after-tax cash will the liquidation generate?
A) $725,000
B) $734,950
C) $682,000
D) $471,250
A) $725,000
B) $734,950
C) $682,000
D) $471,250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements about annuity contracts is true?
A) Annuity contracts provide a fixed income stream.
B) Payments received from an annuity contract are tax-exempt.
C) Payments received from an annuity contract are fully taxable as ordinary income.
D) Payments received from an annuity contract are fully taxable as capital gain.
A) Annuity contracts provide a fixed income stream.
B) Payments received from an annuity contract are tax-exempt.
C) Payments received from an annuity contract are fully taxable as ordinary income.
D) Payments received from an annuity contract are fully taxable as capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Six years ago, Mr. Ahmed loaned $10,000 to a neighbor in exchange for an interest-bearing debt obligation. This year, the neighbor informed Mr. Ahmed that he was defaulting on the debt. What are the tax consequences to Mr. Ahmed of this bad debt?
A) $10,000 ordinary loss
B) $10,000 short-term capital loss
C) $10,000 long-term capital loss
D) No loss recognized
A) $10,000 ordinary loss
B) $10,000 short-term capital loss
C) $10,000 long-term capital loss
D) No loss recognized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Mr. and Mrs. Golding own 13,850 shares in PTJ mutual fund. This year, they received a $6,390 cash distribution from PTJ. Which of the following statements is false?
A) Some or all of the distribution may be a capital gain distribution.
B) Some or all of the distribution may be a qualifying dividend.
C) Some or all of the distribution may be ordinary income.
D) None of the above is false.
A) Some or all of the distribution may be a capital gain distribution.
B) Some or all of the distribution may be a qualifying dividend.
C) Some or all of the distribution may be ordinary income.
D) None of the above is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements about investment property is false?
A) The term securities includes corporate stock, certificates of deposit, notes, bonds, and other debt instruments.
B) Interest and dividends are taxed at the same rate as long-term capital gain.
C) Interest on private activity bonds issued by a state or local government is excluded from ordinary income.
D) A mutual fund is a diversified portfolio of securities owned and managed by a regulated investment company.
A) The term securities includes corporate stock, certificates of deposit, notes, bonds, and other debt instruments.
B) Interest and dividends are taxed at the same rate as long-term capital gain.
C) Interest on private activity bonds issued by a state or local government is excluded from ordinary income.
D) A mutual fund is a diversified portfolio of securities owned and managed by a regulated investment company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Three years ago, Mr. Lewis paid $40,000 for a newly issued corporate bond with a $50,000 stated redemption value. This year, he sold the bond for $43,900. Through date of sale, Mr. Lewis recognized $940 of the original issue discount (OID) as accrued interest income. Compute his gain or loss on sale.
A) $3,900 long-term capital gain
B) $3,900 ordinary income
C) $2,960 ordinary income
D) $2,960 long-term capital gain
A) $3,900 long-term capital gain
B) $3,900 ordinary income
C) $2,960 ordinary income
D) $2,960 long-term capital gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Two years ago, Mr. Young paid $40,000 to buy a publicly traded corporate bond through his broker. The bond's stated redemption value was $45,000. This year, Mr. Young sold the bond for $47,100. Compute his gain or loss on sale.
A) $2,100 long-term capital gain.
B) $7,100 ordinary income.
C) $5,000 ordinary income and $2,100 long-term capital gain.
D) $7,100 long-term capital gain.
A) $2,100 long-term capital gain.
B) $7,100 ordinary income.
C) $5,000 ordinary income and $2,100 long-term capital gain.
D) $7,100 long-term capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Emil Nelson paid $174,500 for an annuity that will pay him $1,300 per month for life. Based on Emil's age, his expected return is $405,813. This year, Emil received 12 payments totaling $15,600. How much of this total is taxable income?
A) $0
B) $5,300
C) $6,708
D) None of the above.
A) $0
B) $5,300
C) $6,708
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In 2001, Mrs. Qualley, contributed $100,000 in exchange for 1,000 shares of Little Corporation, which is a qualified small business. This year, Mrs. Qualley's only capital transaction was the sale of the 1,000 shares of Little qualified small business stock for $180,000. Compute Mrs. Qualley's tax on her capital gain from this sale.
A) $6,000
B) $11,200
C) $22,400
D) None of the above.
A) $6,000
B) $11,200
C) $22,400
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
This year, Ms. Kwan recognized a $16,900 net long-term capital loss. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Ms. Kwan has a $16,900 long-term capital loss carryforward into future years.
B) Ms. Kwan has a $16,900 nondeductible loss that she can carry back three years and forward five years.
C) Ms. Kwan can deduct $3,000 of the loss as an itemized deduction.
D) None of the above is true.
A) Ms. Kwan has a $16,900 long-term capital loss carryforward into future years.
B) Ms. Kwan has a $16,900 nondeductible loss that she can carry back three years and forward five years.
C) Ms. Kwan can deduct $3,000 of the loss as an itemized deduction.
D) None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Ms. Regga, a physician, earned $375,000 from her medical practice and $20,500 interest and qualified dividends from her investment portfolio. She was allocated a $67,000 loss from a passive activity. Compute Ms. Regga's AGI.
A) $328,500
B) $375,000
C) $395,500
D) None of the above
A) $328,500
B) $375,000
C) $395,500
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Ms. Lopez paid $7,260 interest on a mortgage on undeveloped land that she holds as an investment. Ms. Lopez's AGI is $112,200, which includes $4,900 interest income from a certificate of deposit. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Ms. Lopez can't deduct any of the $7,260 interest expense.
B) Ms. Lopez can deduct $7,260 interest expense as an itemized deduction.
C) Ms. Lopez can deduct $4,900 interest expense as an itemized deduction.
D) Ms. Lopez can deduct $4,900 interest expense as an above-the-line deduction.
A) Ms. Lopez can't deduct any of the $7,260 interest expense.
B) Ms. Lopez can deduct $7,260 interest expense as an itemized deduction.
C) Ms. Lopez can deduct $4,900 interest expense as an itemized deduction.
D) Ms. Lopez can deduct $4,900 interest expense as an above-the-line deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Tom Johnson, whose marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 35%, sold four investment assets resulting in the following capital gains and losses.  How much of Tom's net capital gain is taxed at 15%?
How much of Tom's net capital gain is taxed at 15%?
A) $42,800
B) $3,900
C) $2,700
D) $0
 How much of Tom's net capital gain is taxed at 15%?
How much of Tom's net capital gain is taxed at 15%?A) $42,800
B) $3,900
C) $2,700
D) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Ms. Kerry, who itemized deductions on Schedule A, paid $15,000 interest on funds borrowed to acquire taxable bonds. She also paid $660 of management fees that were fully deductible on Schedule A. Her AGI is $100,000, which includes $19,700 of interest income. How much of the interest expense can she deduct?
A) $0
B) $19,039
C) $19,699
D) $15,001
A) $0
B) $19,039
C) $19,699
D) $15,001

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Frederick Tims, a single individual, sold the following investment assets this year. 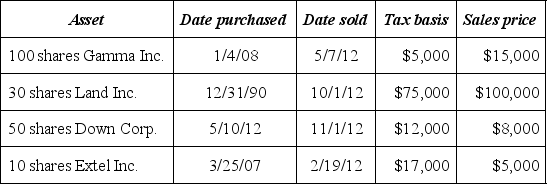 If Frederick's marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 33%, compute his tax attributable to the above sales.
If Frederick's marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 33%, compute his tax attributable to the above sales.
A) $5,250
B) $3,450
C) $2,850
D) $0
 If Frederick's marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 33%, compute his tax attributable to the above sales.
If Frederick's marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 33%, compute his tax attributable to the above sales.A) $5,250
B) $3,450
C) $2,850
D) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following statements about an investment in undeveloped land is false?
A) An investor can elect to capitalize interest expense on a mortgage incurred to purchase the undeveloped land.
B) An investor can elect to capitalize property taxes on undeveloped land.
C) An investment in undeveloped land is considered a liquid asset.
D) Gain recognized on the sale of undeveloped land held as an investment is capital gain.
A) An investor can elect to capitalize interest expense on a mortgage incurred to purchase the undeveloped land.
B) An investor can elect to capitalize property taxes on undeveloped land.
C) An investment in undeveloped land is considered a liquid asset.
D) Gain recognized on the sale of undeveloped land held as an investment is capital gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In 2010, Mrs. Owens paid $50,000 for 3,000 shares of a mutual fund and elected to reinvest dividends in additional shares. In 2010 and 2011, she received Form 1099s reporting the following. 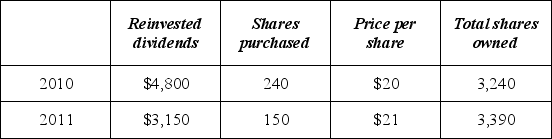 If Mrs. Owens sells 1,000 shares in 2012 for $22 per share and uses the average basis method, compute her recognized gain.
If Mrs. Owens sells 1,000 shares in 2012 for $22 per share and uses the average basis method, compute her recognized gain.
A) $4,910
B) $5,333
C) $3,883
D) $0
 If Mrs. Owens sells 1,000 shares in 2012 for $22 per share and uses the average basis method, compute her recognized gain.
If Mrs. Owens sells 1,000 shares in 2012 for $22 per share and uses the average basis method, compute her recognized gain.A) $4,910
B) $5,333
C) $3,883
D) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
This year, Mr. and Mrs. Lebold paid $3,100 investment interest expense. They earned $4,750 investment income consisting of $1,900 interest and $2,850 qualified dividends, and they incurred no investment expenses. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The Lebolds can deduct $3,100 interest expense if they elect to treat $1,200 of the qualifying dividends as ordinary income not taxed at a preferential rate.
B) The Lebolds can deduct $3,100 interest expense if they elect to treat the qualifying dividends as ordinary income not taxed at a preferential rate.
C) The Lebolds can deduct $3,100 interest expense because their investment income exceeds $3,100.
D) The Lebolds' deduction for their interest expense is limited to $1,900.
A) The Lebolds can deduct $3,100 interest expense if they elect to treat $1,200 of the qualifying dividends as ordinary income not taxed at a preferential rate.
B) The Lebolds can deduct $3,100 interest expense if they elect to treat the qualifying dividends as ordinary income not taxed at a preferential rate.
C) The Lebolds can deduct $3,100 interest expense because their investment income exceeds $3,100.
D) The Lebolds' deduction for their interest expense is limited to $1,900.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In 1996, Mr. Exton, a single taxpayer, contributed $30,000 in exchange for 100 shares of Morton stock. In 2005, he paid $43,000 to another shareholder to purchase 100 more shares of Morton stock. Morton stock qualified as Section 1244 stock when it was issued. This year, Mr. Exton sold his 200 Morton shares for $250 per share. What is the amount and character of Mr. Exton's recognized loss?
A) $23,000 ordinary loss
B) $23,000 long-term capital loss
C) $3,000 long-term capital gain and $30,000 ordinary loss
D) $5,000 long-term capital loss and $18,000 ordinary loss
A) $23,000 ordinary loss
B) $23,000 long-term capital loss
C) $3,000 long-term capital gain and $30,000 ordinary loss
D) $5,000 long-term capital loss and $18,000 ordinary loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements about investment interest expense is true?
A) The interest is allowed as an above-the-line deduction.
B) The interest is allowed as a miscellaneous itemized deduction.
C) Nondeductible interest carries forward into future years.
D) The interest is deductible to the extent of the individual's gross investment income.
A) The interest is allowed as an above-the-line deduction.
B) The interest is allowed as a miscellaneous itemized deduction.
C) Nondeductible interest carries forward into future years.
D) The interest is deductible to the extent of the individual's gross investment income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Mr. and Mrs. Philips recognized the following capital gains and losses this year. 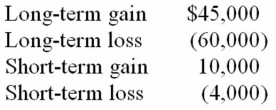 Their AGI before consideration of these gains and losses was $140,000. Compute their AGI.
Their AGI before consideration of these gains and losses was $140,000. Compute their AGI.
A) $140,000
B) $131,000
C) $137,000
D) $143,000
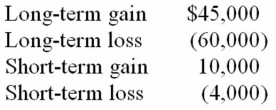 Their AGI before consideration of these gains and losses was $140,000. Compute their AGI.
Their AGI before consideration of these gains and losses was $140,000. Compute their AGI.A) $140,000
B) $131,000
C) $137,000
D) $143,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In 2010, Mrs. Owens paid $50,000 for 3,000 shares of a mutual fund and elected to reinvest dividends in additional shares. In 2010 and 2011, she received Form 1099s reporting the following. 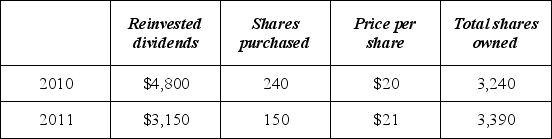 If Mrs. Owens sells her 3,390 shares in 2012 for $22 per share, compute her recognized gain.
If Mrs. Owens sells her 3,390 shares in 2012 for $22 per share, compute her recognized gain.
A) $24,580
B) $19,780
C) $16,630
D) $0
 If Mrs. Owens sells her 3,390 shares in 2012 for $22 per share, compute her recognized gain.
If Mrs. Owens sells her 3,390 shares in 2012 for $22 per share, compute her recognized gain.A) $24,580
B) $19,780
C) $16,630
D) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Mr. Forest, a single taxpayer, recognized a $252,000 loss on the sale of Section 1244 stock. What is the character of this loss?
A) $50,000 ordinary and $202,000 capital
B) $100,000 ordinary and $152,000 capital
C) $252,000 capital
D) $252,000 ordinary
A) $50,000 ordinary and $202,000 capital
B) $100,000 ordinary and $152,000 capital
C) $252,000 capital
D) $252,000 ordinary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements about the individual capital gains and losses is false?
A) Gain on sale of Section 1231 depreciable real property is taxed at a 25% maximum rate.
B) Short-term capital gains are taxed as ordinary income.
C) Capital losses are deductible only against capital gains.
D) Nondeductible capital losses are carried forward for deduction against future capital gains.
A) Gain on sale of Section 1231 depreciable real property is taxed at a 25% maximum rate.
B) Short-term capital gains are taxed as ordinary income.
C) Capital losses are deductible only against capital gains.
D) Nondeductible capital losses are carried forward for deduction against future capital gains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Ms. Beal recognized a $42,400 net long-term capital gain and a $33,000 net short-term capital loss this year. What is her current net tax cost from her capital transactions if her marginal rate on ordinary income is 35%?
A) $6,360
B) $5,910
C) $1,410
D) $0
A) $6,360
B) $5,910
C) $1,410
D) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements about Section 1244 stock is true?
A) Some portion of a loss recognized on sale of Section 1244 stock is an ordinary deduction.
B) Gain recognized on sale of Section 1244 stock is taxed at a 28% maximum rate.
C) Individuals may purchase Section 1244 stock directly from the issuing corporation or from another shareholder.
D) Corporations may issue an unlimited amount of Section 1244 stock.
A) Some portion of a loss recognized on sale of Section 1244 stock is an ordinary deduction.
B) Gain recognized on sale of Section 1244 stock is taxed at a 28% maximum rate.
C) Individuals may purchase Section 1244 stock directly from the issuing corporation or from another shareholder.
D) Corporations may issue an unlimited amount of Section 1244 stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Mr. Quinn recognized a $900 net short-term capital gain and a $1,380 long-term capital gain this year. Which of the following statements is false?
A) If Mr. Quinn's marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 15%, the tax liability on his capital gains is $135.
B) If Mr. Quinn's marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 33%, the tax liability on his capital gains is $504.
C) Only $1,380 of the capital gain is subject to a preferential tax rate.
D) None of the above is false.
A) If Mr. Quinn's marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 15%, the tax liability on his capital gains is $135.
B) If Mr. Quinn's marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 33%, the tax liability on his capital gains is $504.
C) Only $1,380 of the capital gain is subject to a preferential tax rate.
D) None of the above is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Kate recognized a $25,700 net long-term capital gain and a $33,000 net short-term capital loss this year. What is her current net tax cost or savings from her capital transactions if her marginal rate on ordinary income is 28%?
A) $0
B) $840 net tax savings
C) $2,044 net tax savings
D) $3,015 net tax cost
A) $0
B) $840 net tax savings
C) $2,044 net tax savings
D) $3,015 net tax cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 104 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



